Electronic signature. The history of the emergence and development
In the modern world, when in a few hours you can earn a million, lose a billion, cross two continents, while talking with a business partner on the third, in the modern world just needed a tool that would legally replace paper and a human signature with a ballpoint pen.
The Law on Electronic Signature provides a wonderful definition of an electronic signature - this is information that, when attached to other information, allows you to determine the identity of the person who signed the document.
Electronic signature can be stored on
')
You can sometimes save the digital signature on the computer as a .cer file. But it is understood that you always carry it with you or keep it out of the reach of outsiders. Like a seal.
In essence, an electronic signature is your electronic stamp that holds and verifies the document.
Electronic signatures are issued by state-accredited certification centers. By issuing an EDS, they verify the identity of the person who applied to them, as well as his powers, if the EDS is issued to a legal entity.
The electronic signature that you receive contains an electronic signature verification key certificate. This set of symbols is your identifier that everyone who reads your document can see.
If you lost a digital signature - immediately contact the police. Otherwise, all documents signed by your EDS will be considered valid!
In addition to the identifying certificate, the electronic signature contains:
They need them to encrypt your document.
Remember, signing a paper contract you sign on each page or carefully sew a thick stack of sheets so that the counterparty, no matter how trustworthy it may look, does not make changes to the text of your agreement.
In addition to identification, the electronic signature should freeze the structure of the document so that any changes are either impossible or violate the “electronic stamp”.
Information protection is the first rule of military commanders, therefore the origins of the encryption technique must be sought in the history of wars.
At all times it was necessary to send messages that are protected from enemy spies. At first they were locked chests, and then scrolls containing an incomprehensible set of letters. Humanity has long invented a huge variety of different ways encrypted. But for each secret message needed a key.
In spy films, usually a book becomes the key, the numbers of pages, lines and letters of which are contained in the message. The reliability of such a cipher is not higher than that of a locked chest - the sender still had to first pass the key.
In 1976, Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman and Ralph Merkle were the first to propose a “one-way trap function” - a theory that allowed you to transmit an encrypted message without passing on the key to solve the message.
If it is quite simple, their method is that it is easy to do a certain mathematical action only in one direction and very difficult in the opposite direction. For example, if you multiply five by ten, you get fifty. To fifty decomposed into a product of five and ten need incomparably more time. It’s as if you are given a disassembled mechanical watch, you’re hardly able to assemble it back.
Suppose you have openly agreed on a common key and exchanged secret data modified in a certain way. Thus, you will have on hand: the public key, your secret data and the encrypted message. Malicious users may have a key and both encrypted messages. But you can only decrypt the encrypted message with your unencrypted information.
This encryption system is wonderfully illustrated by the following example:
We have two spies named Alice and Bob. They really want to agree on a common secret number, but Eve intercepts their messages, so they can't just send a message to each other.
Alice and Bob agree that function 3 is modulo 17 as the public key.

Alice encrypts 15 and sends Bob the resulting value - 6.
Eve intercepts 6, which means nothing.
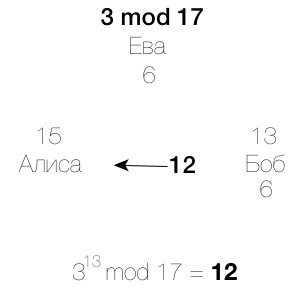
Bob encrypts the secret value 13 and sends it to Alice 12.
Eve intercepts and 12, which also does not tell her anything.
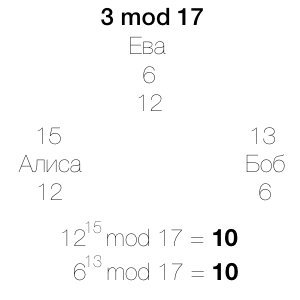
Alice and Bob use their secret values to decrypt received messages:
12 to degree 15 modulo 17 = 10
6 to the power of 13 modulo 17 = 10
Thus, 10 is a shared secret number that can be used as a decryption key for subsequent messages between Alice and Bob.
Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman and Ralph Merkle launched a new wave of encryption, but nowadays their system is no longer in use, and their patent term under number US Patent 4,200,770 has expired.
The method invented by them showed up flaws. First, it takes some time to exchange messages, and second, what is most serious, if you have many contacts, you need to store a lot of keys. Suppose Alice is a bank, in which case there are thousands of people like Bob. With each need to agree on a secret key.
The next milestone in encryption was the RSA algorithm — Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman. Invented in 1977, the method even now can be used to create primitive digital signatures.
In fact, the RSA algorithm was coined in 1973 by Clifford Cox, but his research was instantly encrypted, so the work of Rivest, Shamir and Adleman was offered to the public.
At the core of their work was the theory that Alice just sent Bob a lock, with which Bob could close the message and return it to Alice. It turns out that there should be two keys - an encryption key and a decryption key.
The encryption key can be public, because it is easier to encrypt than to decrypt, then the decryption code must be secret.
All that we talked about above concerns the enhanced qualified electronic signature. The new law of 2011 “On electronic signature” also introduced the concepts of unqualified electronic signature and simple electronic signature.
A qualified one differs from an unqualified one in that a qualified signature is issued by an accredited certifying center, and an unqualified one is not accredited.
Now it is safer and safer to use a qualified electronic signature.
An unqualified signature is now used, oddly enough in public procurement, which causes certain difficulties, since obtaining both a qualified certificate and an unqualified one is difficult and expensive.
Previously, the need for such a signature was in transition, when the law was, and there were no accredited certification authorities. Why you need to save this kind of signature now is completely unclear.
A simple electronic signature, as the name implies, is significantly easier to use than a qualified one. A simple signature does not require contacting certification centers, does not use methods of protection against document changes, and the only characteristic is the identification of the person who signed the document.
Examples of a simple electronic signature can be a username and password when logging into your email account, VKontakte or Facebook.
Your documents signed with a simple electronic signature will be legally significant only if you address them to state or municipal authorities, for example, through the website of public services.
Recall also this kind of "electronic signature", as the image of a handwritten signature. Often there are applications for mobile platforms, Gmail, and even there - even in the “Viewer” on Mac OS there is a convenient mode of “signing” a document.
Under the American law on electronic signatures in international and domestic trade relations, such a signature is more than legally significant. They say Bill Clinton even signed this law with an electronic signature.
Under Russian law, an electronic image of a signature is no more than a faxel, the use of which is permissible only between counterparties who have agreed in advance in writing about the possibility of using such a document.
Today, over three million e-signature certificates have been issued. Anyone can participate in electronic trading, submit tax reports, register a legal entity, order an extract from the USRR, register an invention or trademark, publish information about a legal entity and, of course, sign a contract and invoice - anywhere in the world ... where there is internet, of course.
Only one problem remains - to get an electronic signature, you need to come to the certification center, show yourself and the documents (employees will carry out the identification procedure) and receive a USB key for one year. Next year - all over again.
So it was before. Now you can not go anywhere - you can order and get an electronic signature without leaving the office. But this is a topic for a slightly different article ...
The Law on Electronic Signature provides a wonderful definition of an electronic signature - this is information that, when attached to other information, allows you to determine the identity of the person who signed the document.
What?
Electronic signature can be stored on
- Diskette
- Smart card
- Usb stick
- Touch Memory tablet
')
You can sometimes save the digital signature on the computer as a .cer file. But it is understood that you always carry it with you or keep it out of the reach of outsiders. Like a seal.
In essence, an electronic signature is your electronic stamp that holds and verifies the document.
Electronic signatures are issued by state-accredited certification centers. By issuing an EDS, they verify the identity of the person who applied to them, as well as his powers, if the EDS is issued to a legal entity.
The electronic signature that you receive contains an electronic signature verification key certificate. This set of symbols is your identifier that everyone who reads your document can see.
If you lost a digital signature - immediately contact the police. Otherwise, all documents signed by your EDS will be considered valid!
In addition to the identifying certificate, the electronic signature contains:
- Electronic signature key - private key
- Electronic signature verification key - public key
They need them to encrypt your document.
Remember, signing a paper contract you sign on each page or carefully sew a thick stack of sheets so that the counterparty, no matter how trustworthy it may look, does not make changes to the text of your agreement.
In addition to identification, the electronic signature should freeze the structure of the document so that any changes are either impossible or violate the “electronic stamp”.
Information protection is the first rule of military commanders, therefore the origins of the encryption technique must be sought in the history of wars.
Istria Wars
At all times it was necessary to send messages that are protected from enemy spies. At first they were locked chests, and then scrolls containing an incomprehensible set of letters. Humanity has long invented a huge variety of different ways encrypted. But for each secret message needed a key.
In spy films, usually a book becomes the key, the numbers of pages, lines and letters of which are contained in the message. The reliability of such a cipher is not higher than that of a locked chest - the sender still had to first pass the key.
In 1976, Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman and Ralph Merkle were the first to propose a “one-way trap function” - a theory that allowed you to transmit an encrypted message without passing on the key to solve the message.
If it is quite simple, their method is that it is easy to do a certain mathematical action only in one direction and very difficult in the opposite direction. For example, if you multiply five by ten, you get fifty. To fifty decomposed into a product of five and ten need incomparably more time. It’s as if you are given a disassembled mechanical watch, you’re hardly able to assemble it back.
Suppose you have openly agreed on a common key and exchanged secret data modified in a certain way. Thus, you will have on hand: the public key, your secret data and the encrypted message. Malicious users may have a key and both encrypted messages. But you can only decrypt the encrypted message with your unencrypted information.
This encryption system is wonderfully illustrated by the following example:
We have two spies named Alice and Bob. They really want to agree on a common secret number, but Eve intercepts their messages, so they can't just send a message to each other.
Alice and Bob agree that function 3 is modulo 17 as the public key.

Alice encrypts 15 and sends Bob the resulting value - 6.
Eve intercepts 6, which means nothing.

Bob encrypts the secret value 13 and sends it to Alice 12.
Eve intercepts and 12, which also does not tell her anything.

Alice and Bob use their secret values to decrypt received messages:
12 to degree 15 modulo 17 = 10
6 to the power of 13 modulo 17 = 10
Thus, 10 is a shared secret number that can be used as a decryption key for subsequent messages between Alice and Bob.
Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman and Ralph Merkle launched a new wave of encryption, but nowadays their system is no longer in use, and their patent term under number US Patent 4,200,770 has expired.
The method invented by them showed up flaws. First, it takes some time to exchange messages, and second, what is most serious, if you have many contacts, you need to store a lot of keys. Suppose Alice is a bank, in which case there are thousands of people like Bob. With each need to agree on a secret key.
The next milestone in encryption was the RSA algorithm — Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman. Invented in 1977, the method even now can be used to create primitive digital signatures.
In fact, the RSA algorithm was coined in 1973 by Clifford Cox, but his research was instantly encrypted, so the work of Rivest, Shamir and Adleman was offered to the public.
At the core of their work was the theory that Alice just sent Bob a lock, with which Bob could close the message and return it to Alice. It turns out that there should be two keys - an encryption key and a decryption key.
The encryption key can be public, because it is easier to encrypt than to decrypt, then the decryption code must be secret.
Simple and difficult signatures
All that we talked about above concerns the enhanced qualified electronic signature. The new law of 2011 “On electronic signature” also introduced the concepts of unqualified electronic signature and simple electronic signature.
A qualified one differs from an unqualified one in that a qualified signature is issued by an accredited certifying center, and an unqualified one is not accredited.
Now it is safer and safer to use a qualified electronic signature.
An unqualified signature is now used, oddly enough in public procurement, which causes certain difficulties, since obtaining both a qualified certificate and an unqualified one is difficult and expensive.
Previously, the need for such a signature was in transition, when the law was, and there were no accredited certification authorities. Why you need to save this kind of signature now is completely unclear.
A simple electronic signature, as the name implies, is significantly easier to use than a qualified one. A simple signature does not require contacting certification centers, does not use methods of protection against document changes, and the only characteristic is the identification of the person who signed the document.
Examples of a simple electronic signature can be a username and password when logging into your email account, VKontakte or Facebook.
Your documents signed with a simple electronic signature will be legally significant only if you address them to state or municipal authorities, for example, through the website of public services.
Recall also this kind of "electronic signature", as the image of a handwritten signature. Often there are applications for mobile platforms, Gmail, and even there - even in the “Viewer” on Mac OS there is a convenient mode of “signing” a document.
Under the American law on electronic signatures in international and domestic trade relations, such a signature is more than legally significant. They say Bill Clinton even signed this law with an electronic signature.
Under Russian law, an electronic image of a signature is no more than a faxel, the use of which is permissible only between counterparties who have agreed in advance in writing about the possibility of using such a document.
Development
Today, over three million e-signature certificates have been issued. Anyone can participate in electronic trading, submit tax reports, register a legal entity, order an extract from the USRR, register an invention or trademark, publish information about a legal entity and, of course, sign a contract and invoice - anywhere in the world ... where there is internet, of course.
Only one problem remains - to get an electronic signature, you need to come to the certification center, show yourself and the documents (employees will carry out the identification procedure) and receive a USB key for one year. Next year - all over again.
So it was before. Now you can not go anywhere - you can order and get an electronic signature without leaving the office. But this is a topic for a slightly different article ...
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/242675/
All Articles