Wireless video: external wireless video cards
So let's talk about the first, in the class of wireless video devices - these are external wireless video cards. Such devices are determined by your computer / (laptop, no) beech as an additional module for connecting a monitor or TV. So, a second video card appears on your system, which you can customize using standard system tools.
Attention, under the cut a lot of pictures!
')
Of course, the most important thing that interests us is how it all looks and what characteristics it possesses. Naturally, the video signal is transmitted without wires, but from where and where? Let's figure it out.
In order for our system to have some extra. device, to the computer, you still need to connect something. Almost never occurs imitation of an additional video card at the program level. Thus, all such devices consist of two parts: directly the wireless video card itself, to which you need to connect the monitor, and some kind of USB adapter that supports high-speed wireless connection directly to the video card. In other words, the existing USB video card is taken as the basis, except that the USB connection to the computer is replaced with a Wireless USB (WUSB) connection. Look like these kits like this:
1. Kits based on chips from the Israeli company Wisair ( wisair.com/shop ):

Black and VGA and HDMI:
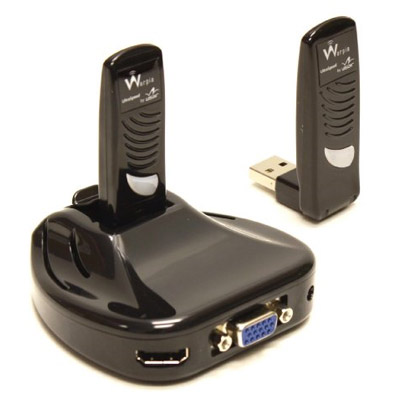

Same, only white and with, 3.5mm-jack:

Same with only one DVI port and a wireless USB hub:

2. IOGear Kit ( www.iogear.com/product/GUW2015VKIT )

3. Products based on Alereon solutions (www.alereon.com/products/reference-designs):

4. Device from Cables-To-Go ( www.cablestogo.com/categories.asp?cat_id=3800 ):
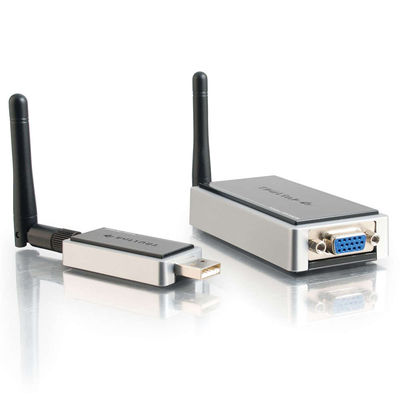

As you can see, all devices are similar to the presence of a USB transmitter and receiver with a built-in video (and in most cases audio) card. A reasonable question arises: but why do we need some kind of new Wireless USB, if there is, for example, such a familiar, beloved and tested Wi-Fi? How is it worse? Especially since the Wi-Fi module, built-in computer / laptop, now you will not surprise anyone ...
... The answer lies in the standards of the radio. Our devices use Wireless USB, which, in turn, is based on the UWB standard - Ultra-Wide band, or ultra-wideband. Unlike Wi-Fi, which operates at a fixed radio frequency (in most cases at 2.4Ghz or 5Ghz), UWB simultaneously uses a whole range of frequencies - from 3.1Ghz to 10.6Ghz, which allows you to transmit a lot of information with minimal power consumption.
However, there are no ideal standards, and there are also disadvantages to UWB - although ultra-wideband transmission is productive, it is very sensitive to distance - the more radio broadcasts are used at the same time, the more interference they cause: problems start at a distance of more than 10 meters with a connection. With obstacles, devices get worse and worse: they just don’t work through walls and that's it.
For comparison: UWB is as if you were pulling a cloth from one place to another in a strong wind. It’s hard ... In turn, Wi-Fi is the pulling of the same fabric, but with one or two or three (MIMO) threads — much slower, but the wind at long distances is not a hindrance.
Design, construction
From a hardware point of view, we can say the following: all devices are compact enough, but do not forget that video cards cannot be powered by the Holy Spirit, therefore, an additional outlet for the receiver’s power adapter must be provided next to the monitor / projector on which the image is being transmitted.
But the transmitter is powered by voltage from the USB port of a computer / laptop. It is worth noting that during operation, the transmitter heats up quite strongly, this is due to the intense, broadband transmission of the radio signal.
Ultimately, depending on the actual characteristics of the device you are using, you can get an additional, wireless VGA interface, wireless DVI, or wireless HDMI for your computer.
Almost all of the above devices have activity indicators - LEDs that signal the intensity of signal transmission.
Soft
The device software consists of two components: the Wireless Connection Manager (Wireless USB Manager), which controls only the communication between the receiver and the transmitter (by the way, the first time you connect, in addition to updating the device firmware, you must pair (pair) the receiver and the transmitter, which is very similar to bluetooth) :
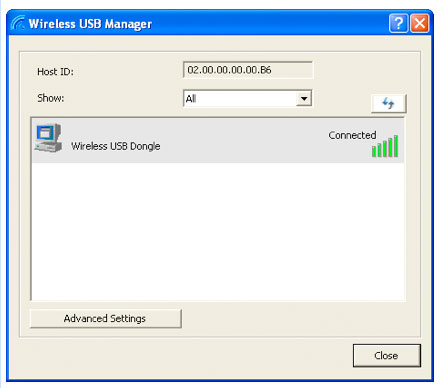
the second component of the device software is the DisplayLink program installed in the tray, from the same company

This program was originally designed to manage USB-based video cards, but since in our case this is the imitation of such a connection, it works well over Wireless USB Manager.
After the first connection, installation of drivers and programs, and the procedures for updating the firmware (firmware) and device binding, you simply connect the transmitter to the computer, and the video signal will immediately start to be transmitted to the receiver. Removing the device is as easy as connecting.
Several standard settings of the remote monitor are available to you: the copy mode of your screen or the extension of your desktop in any direction: a monitor connected without wires or a TV will complement the main one on the right, left, top or bottom.

Programs and drivers work under Windows XP, Vista, 7, and under Mac OS X
The devices have quite high minimum system requirements: you need a computer with an Intel Atom processor or equivalent, with a frequency of at least 1.6Ghz and a RAM of at least 512Mb for Windows XP and at least 1Gb for the remaining operating systems. This is due to the fact that most of the calculations related to the display of the image on a wireless screen are not performed at the hardware level, but just as a driver in conjunction with DisplayLink, which, in turn, decently loads the CPU.
findings
This class of devices is intended mainly for lectures and presentations. The performance of the device is enough to display presentations, slide shows and video clips of average quality, such as youtube, without delay. The speaker, who is usually in the same room as the projector or the screen with his presentation, will get advantageous mobility, be able to move with his laptop around the hall and place it in different lectures in different places, depending on the current need.
Home devices can also do a good job: while you are working on a laptop or computer, members of your family can watch videos from it on TV in HD up to 720progressive. Without wires.
Also, the devices bring in a certain mobility during and after repair: it is not necessary to make walls for laying a bundle of wires and putting it in a fixed place - now it’s enough to connect a small receiver box to the TV / plasma or projector, and insert a small transmitter and signal into the computer right away same goes.
In Runet, I found only two places where you can find such devices, and not very cheap:
bezprovodnik.ru and
bezprovodnoe.ru
If profitability plays a role for you, and you are ready to wait for the month, I recommend ordering such toys from eBay or Amazon.
To be continued…
Attention, under the cut a lot of pictures!
')
Of course, the most important thing that interests us is how it all looks and what characteristics it possesses. Naturally, the video signal is transmitted without wires, but from where and where? Let's figure it out.
In order for our system to have some extra. device, to the computer, you still need to connect something. Almost never occurs imitation of an additional video card at the program level. Thus, all such devices consist of two parts: directly the wireless video card itself, to which you need to connect the monitor, and some kind of USB adapter that supports high-speed wireless connection directly to the video card. In other words, the existing USB video card is taken as the basis, except that the USB connection to the computer is replaced with a Wireless USB (WUSB) connection. Look like these kits like this:
1. Kits based on chips from the Israeli company Wisair ( wisair.com/shop ):

Black and VGA and HDMI:

Same, only white and with, 3.5mm-jack:

Same with only one DVI port and a wireless USB hub:

2. IOGear Kit ( www.iogear.com/product/GUW2015VKIT )

3. Products based on Alereon solutions (www.alereon.com/products/reference-designs):

4. Device from Cables-To-Go ( www.cablestogo.com/categories.asp?cat_id=3800 ):

As you can see, all devices are similar to the presence of a USB transmitter and receiver with a built-in video (and in most cases audio) card. A reasonable question arises: but why do we need some kind of new Wireless USB, if there is, for example, such a familiar, beloved and tested Wi-Fi? How is it worse? Especially since the Wi-Fi module, built-in computer / laptop, now you will not surprise anyone ...
... The answer lies in the standards of the radio. Our devices use Wireless USB, which, in turn, is based on the UWB standard - Ultra-Wide band, or ultra-wideband. Unlike Wi-Fi, which operates at a fixed radio frequency (in most cases at 2.4Ghz or 5Ghz), UWB simultaneously uses a whole range of frequencies - from 3.1Ghz to 10.6Ghz, which allows you to transmit a lot of information with minimal power consumption.
However, there are no ideal standards, and there are also disadvantages to UWB - although ultra-wideband transmission is productive, it is very sensitive to distance - the more radio broadcasts are used at the same time, the more interference they cause: problems start at a distance of more than 10 meters with a connection. With obstacles, devices get worse and worse: they just don’t work through walls and that's it.
For comparison: UWB is as if you were pulling a cloth from one place to another in a strong wind. It’s hard ... In turn, Wi-Fi is the pulling of the same fabric, but with one or two or three (MIMO) threads — much slower, but the wind at long distances is not a hindrance.
Design, construction
From a hardware point of view, we can say the following: all devices are compact enough, but do not forget that video cards cannot be powered by the Holy Spirit, therefore, an additional outlet for the receiver’s power adapter must be provided next to the monitor / projector on which the image is being transmitted.
But the transmitter is powered by voltage from the USB port of a computer / laptop. It is worth noting that during operation, the transmitter heats up quite strongly, this is due to the intense, broadband transmission of the radio signal.
Ultimately, depending on the actual characteristics of the device you are using, you can get an additional, wireless VGA interface, wireless DVI, or wireless HDMI for your computer.
Almost all of the above devices have activity indicators - LEDs that signal the intensity of signal transmission.
Soft
The device software consists of two components: the Wireless Connection Manager (Wireless USB Manager), which controls only the communication between the receiver and the transmitter (by the way, the first time you connect, in addition to updating the device firmware, you must pair (pair) the receiver and the transmitter, which is very similar to bluetooth) :

the second component of the device software is the DisplayLink program installed in the tray, from the same company

This program was originally designed to manage USB-based video cards, but since in our case this is the imitation of such a connection, it works well over Wireless USB Manager.
After the first connection, installation of drivers and programs, and the procedures for updating the firmware (firmware) and device binding, you simply connect the transmitter to the computer, and the video signal will immediately start to be transmitted to the receiver. Removing the device is as easy as connecting.
Several standard settings of the remote monitor are available to you: the copy mode of your screen or the extension of your desktop in any direction: a monitor connected without wires or a TV will complement the main one on the right, left, top or bottom.

Programs and drivers work under Windows XP, Vista, 7, and under Mac OS X
The devices have quite high minimum system requirements: you need a computer with an Intel Atom processor or equivalent, with a frequency of at least 1.6Ghz and a RAM of at least 512Mb for Windows XP and at least 1Gb for the remaining operating systems. This is due to the fact that most of the calculations related to the display of the image on a wireless screen are not performed at the hardware level, but just as a driver in conjunction with DisplayLink, which, in turn, decently loads the CPU.
findings
This class of devices is intended mainly for lectures and presentations. The performance of the device is enough to display presentations, slide shows and video clips of average quality, such as youtube, without delay. The speaker, who is usually in the same room as the projector or the screen with his presentation, will get advantageous mobility, be able to move with his laptop around the hall and place it in different lectures in different places, depending on the current need.
Home devices can also do a good job: while you are working on a laptop or computer, members of your family can watch videos from it on TV in HD up to 720progressive. Without wires.
Also, the devices bring in a certain mobility during and after repair: it is not necessary to make walls for laying a bundle of wires and putting it in a fixed place - now it’s enough to connect a small receiver box to the TV / plasma or projector, and insert a small transmitter and signal into the computer right away same goes.
In Runet, I found only two places where you can find such devices, and not very cheap:
bezprovodnik.ru and
bezprovodnoe.ru
If profitability plays a role for you, and you are ready to wait for the month, I recommend ordering such toys from eBay or Amazon.
To be continued…
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/99928/
All Articles