The basics of programming for Android on the example of the game Sudoku
The article describes the main difficulties of creating applications for Android.
We consider the basic concepts of programming Android.
For example, described the creation of the game Sudoku from the book Hello, Android - Ed Burnette .
Carefully a lot of screenshots.
1. Difficulties of development
')
Android is a unique operating system. An application developer should know its features and nuances to get a good result. There are some difficulties that need to be considered when developing (a good description here ). We list them briefly:
1) The application requires to install twice (or even four) more space than the original size of the application.
2) The speed of working with files on the built-in flash drive drops tenfold when the free space decreases.
3) Each process can use up to 16 MB (sometimes 24 MB) of RAM.
2. Principles of developing productive applications for Android
There are a number of recommendations for creating productive applications for Android. They can also be expanded on the basis of the books Effective Java - Joshua Bloch and Mobile Device Programming on the .Net Compact Framework - I. Salmre.
We list the basic principles for the development of productive applications for Android.
Strategic:
1) Resources need to save.
2) It is necessary to instantly give a response to the actions and maintain feedback with the user.
3) Application performance is the main goal. It is necessary constantly in the development process to optimize performance without leaving this work for later.
4) It is necessary to measure the execution time, log and analyze the progress of the application, narrow sections of code, the occurrence of events, memory allocation, the lifetime of objects. What is not measured , it can not be optimized.
Tactical:
1) Avoid creating unnecessary objects.
2) If possible, make the methods static.
3) Use direct field access instead of intermediary methods.
4) Use static final for constants.
5) Do not use enum where a normal integer variable is sufficient.
3. Key features of Android
Android is based on Linux. Between the application and the kernel is the API layer and the library layer on the native code. The application runs on a Java virtual machine (Dalvik Virtual Machine).
In Android, you can run many applications. But one of them is the main one and occupies the screen. From the current application, you can go to the previous one or start a new one. It looks like a browser with browsing history.
Each user interface screen is represented by an Activity class in code. Various Activities are contained in processes. An activity may even live longer than the process. Activity can be paused and started again with saving all the necessary information.
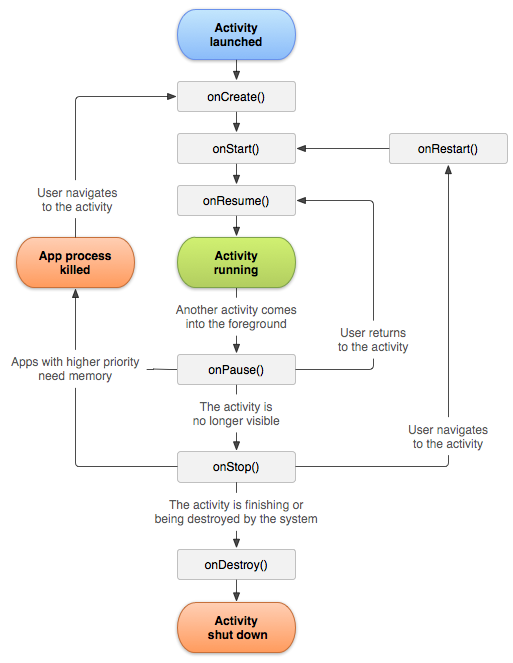
Android uses a special action description engine based on Intent. When you need to perform an action (make a call, send a letter, show a window), Intent is called.
Android also contains services similar to Linux daemons to perform the necessary actions in the background (for example, playing music).
Content providers are used to exchange data between applications.
4. Sample Application - Sudoku
We will consider the finished draft of the game Sudoku (the full code in the Sudokuv4 folder ).
To work, you need the Android SDK and Eclipse. About how to install and start everything is written here .
To load a project in Eclipse, you can do this:
1) Unzip the project to a separate folder in the Eclipse workspace.
2) Select the menu item File-> New-> Android Project.
3) In the New Android Project dialog, select the option Create project from existing source.
4) In the Location field, specify the path to the project folder. Click Next.
Program menu
The game menu is described in the file res / layout / main.xml. The interface description can be edited as XML or as a rendered interface. To switch, use the tabs at the bottom of the content display area.
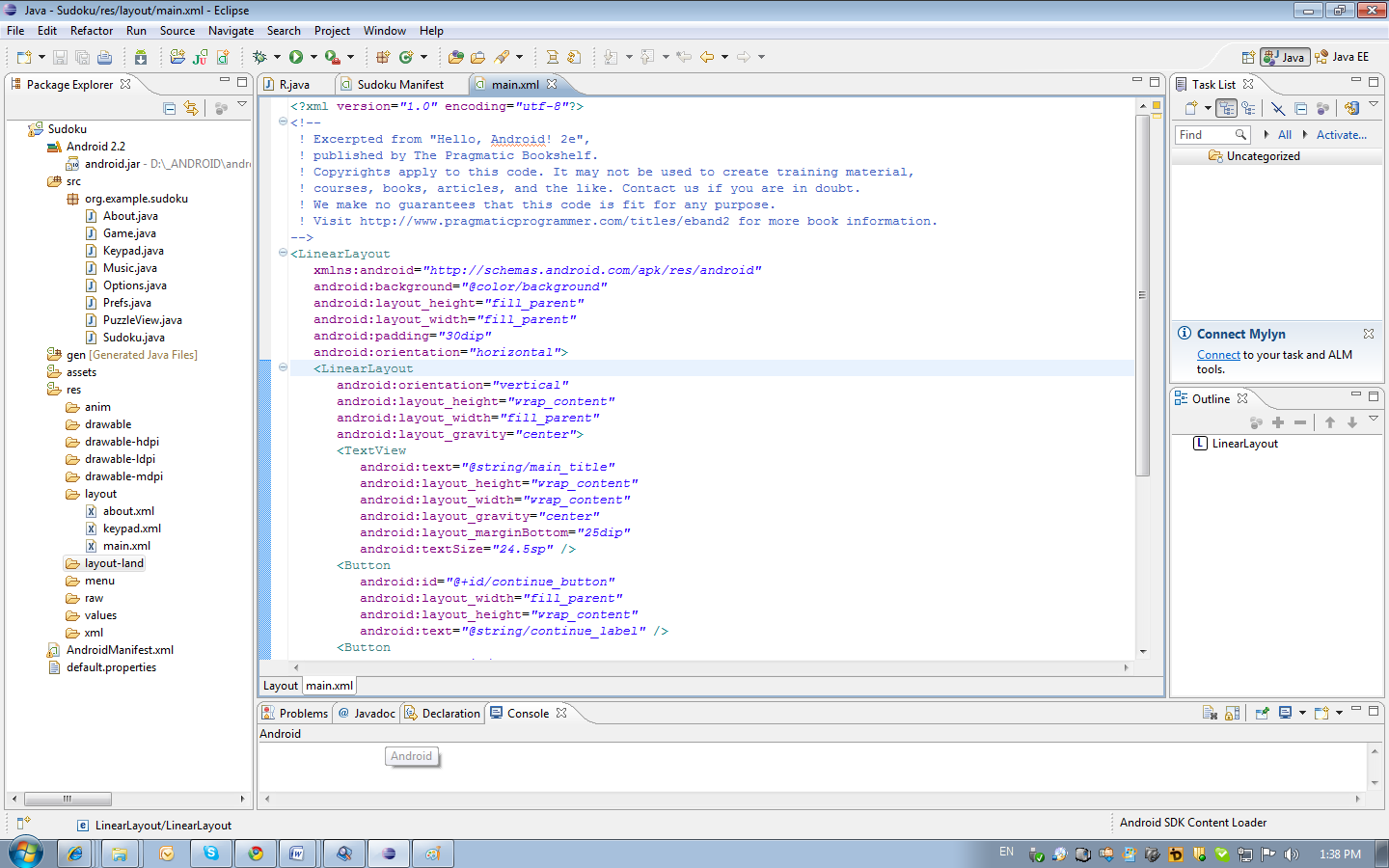

Typically, controls are contained within a container; in our case, this is a LinearLayout. It arranges all the elements as a single column.
Resources
Please note that all text labels (android: text) take data from resources. For example, the entry android: text = "@ string / main_title" indicates that the text should be searched in the res / values / string.xml file in the node named main_title (Android Sudoku). The background color is also contained in the resources (android: background = "@ color / background") but in the color.xml file (# 3500ffff). When opening resource files in the editor, an error may occur. But you can always go to the XML mapping.
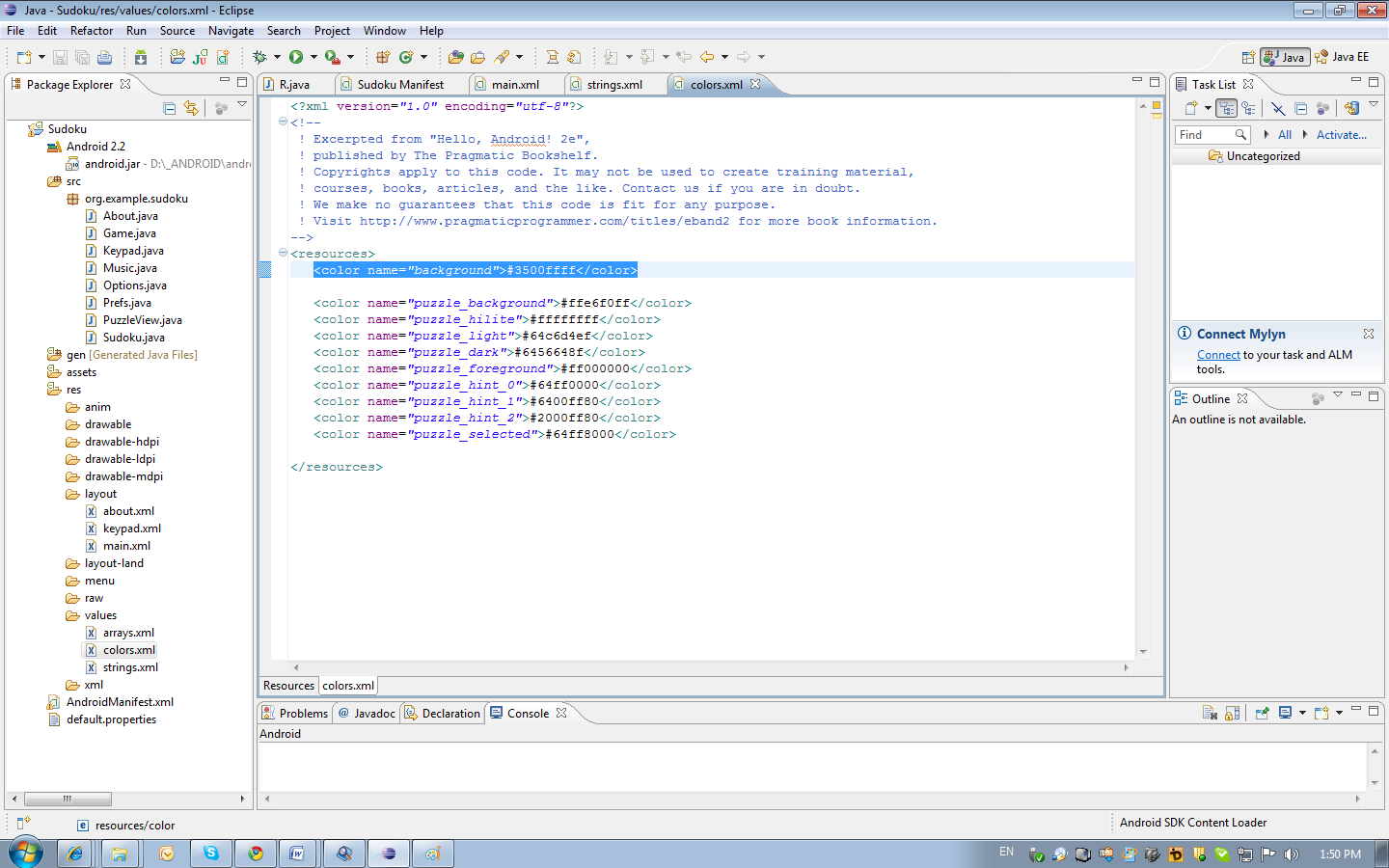
Controls that need to be accessed from the code must have an id. The buttons have an id (android: id = "@ + id / continue_button") in order to add a click handler to the button. The plus sign indicates that you need to create an identifier for the button in the /gen/org.example.sudoku/R.java file (public static final int continue_button = 0x7f0b000b;). This file is generated automatically and it is not recommended to change it. The file contains a class R through it you can access any interface element and other resources.
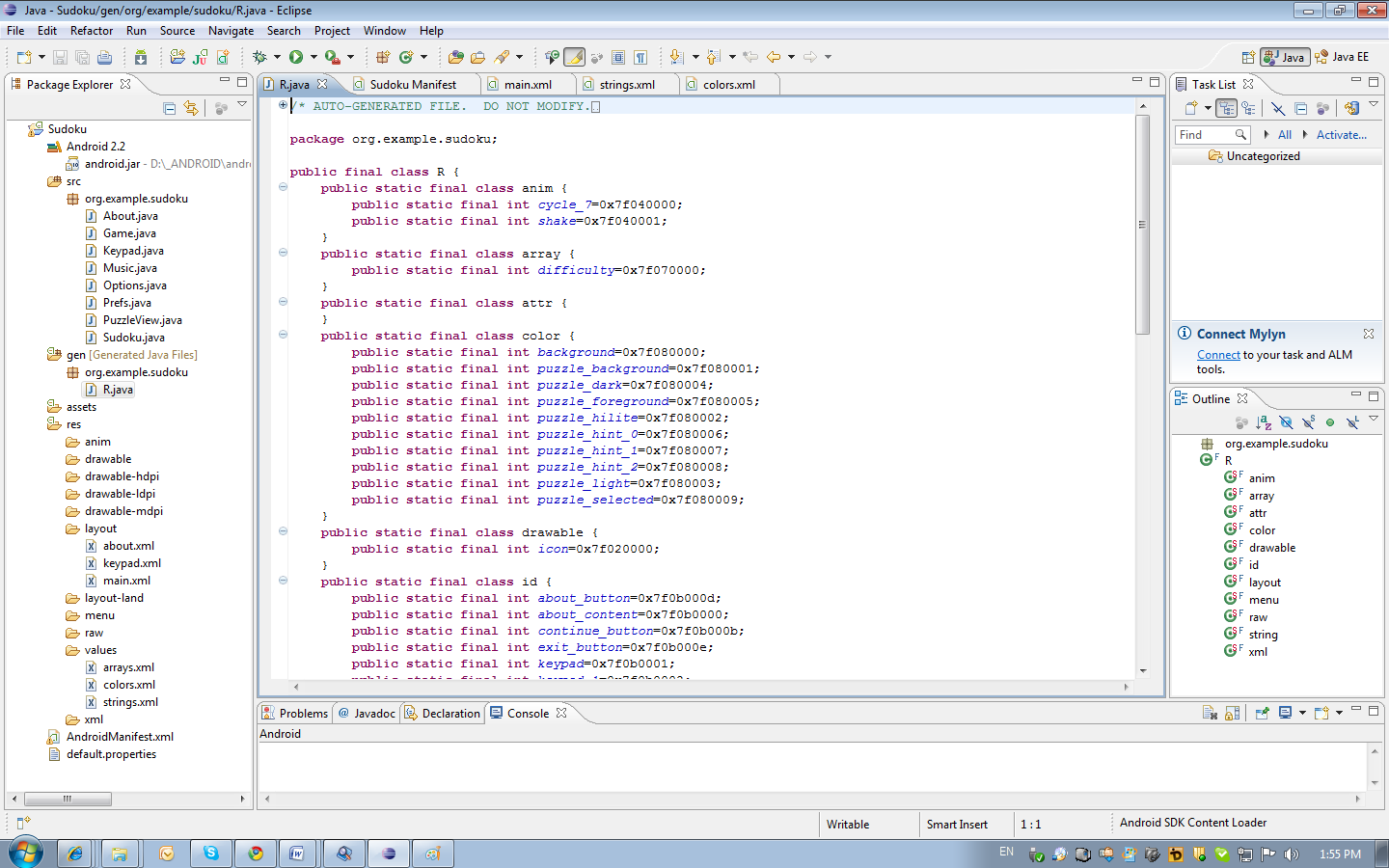
Creating windows
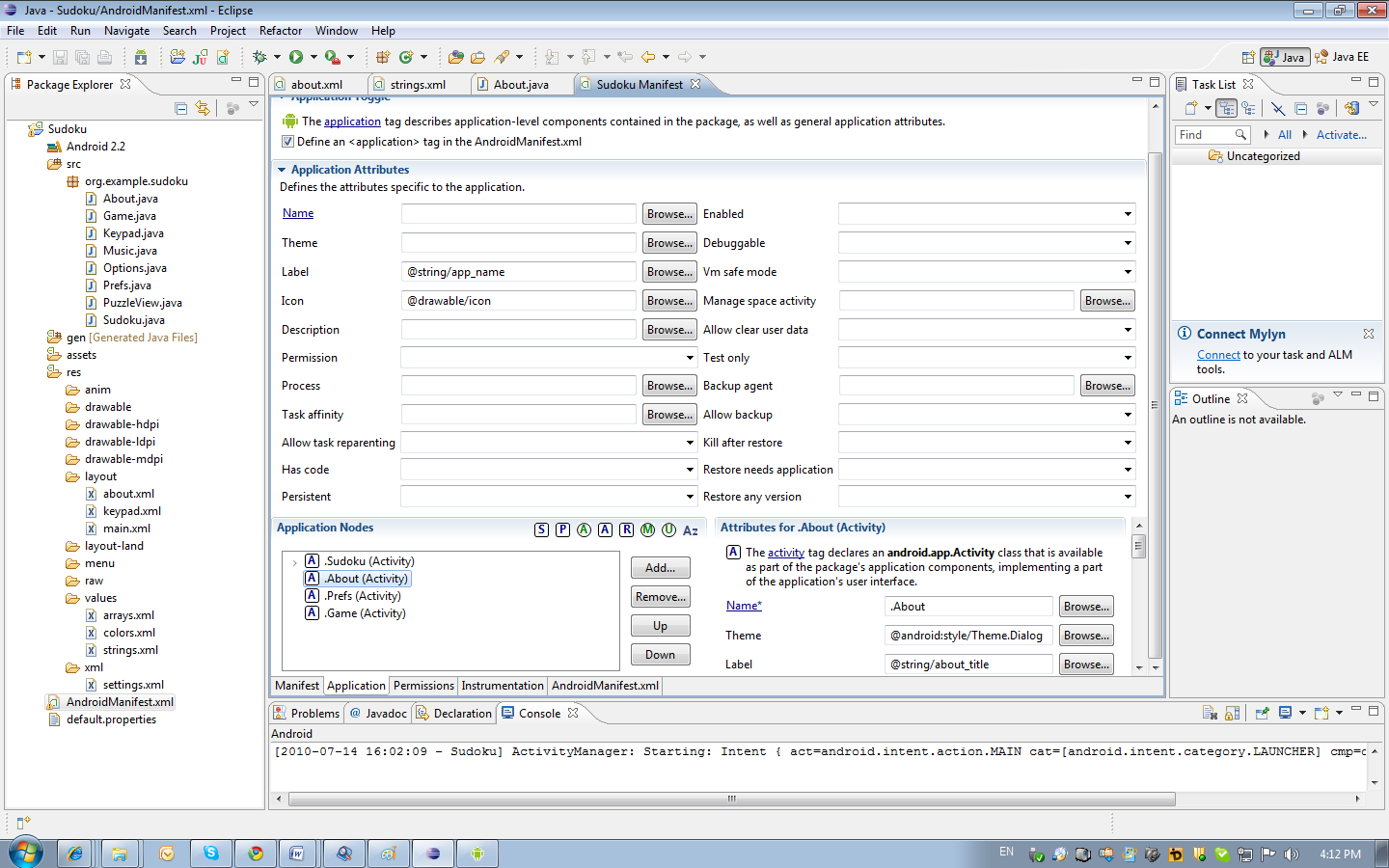
Consider creating a window with information about the program. The markup for this window is in the /res/layout/about.xml file. The activity class is described in the file /src/org.example.sudoku/About.java. Activity is associated with markup in the AndroidManifest.xml file. This file can be viewed either through the editor or as XML. On different tabs of the editor, you can select different sections of the file. The Application section contains the Activity parameters. Note that the Theme parameter is set to android : style / Theme.Dialog. Because of this, the style of the window looks more like a modal dialog.
Calling the window with information about the program is carried out from the Sudoku class by pressing the About button. The Sudoku class is written in such a way that it handles the Click event (public class Sudoku extends Activity implements OnClickListener). In the public void onClick method (View v), it is determined which button caused the event and the corresponding code is executed. To display the About window, the corresponding Intent is called.
Event handlers can also be installed on specific controls. For example, in the Keypad class, when a class is created in the setListeners () method, handlers are set for individual buttons.
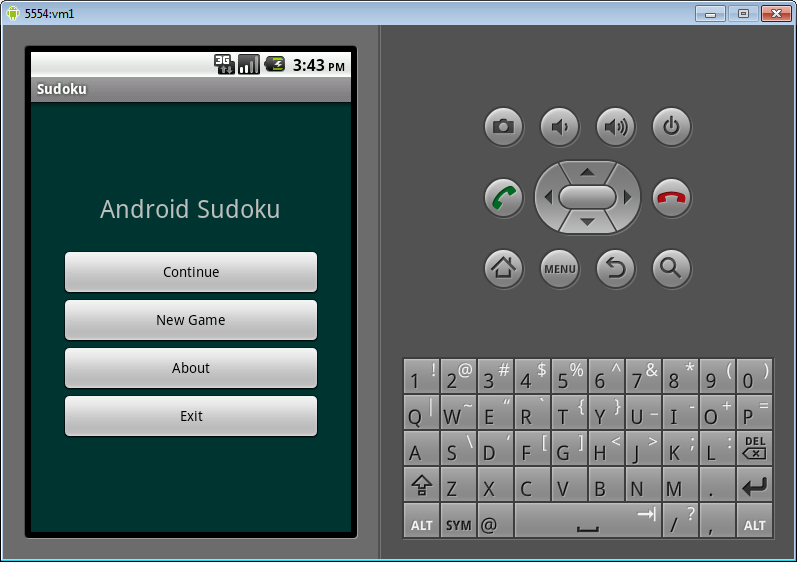
Simple dialogue
The user should be given the opportunity to choose the level of complexity. This is a small dialogue in which you need to choose one of several options. I am very pleased that for this you do not need to create a separate Intent, but it suffices to use the AlertDialog class.
Let us examine the process of starting a new game. The user clicks on the New Game button. The click handler is the Sudoku class method - onClick. Next, the openNewGameDialog method is invoked, which shows the complexity selection dialog and starts the game with the selected difficulty level. This dialog is built using the AlertDialog class.
Notice that the contents of the dialog (a set of buttons) is built from an array of R.array.difficulty strings. Immediately assigned to the handler clicking on the buttons of the dialogue, which by the number of the pressed button launches a new game with a given level of complexity, calling the startGame method.
Graphics
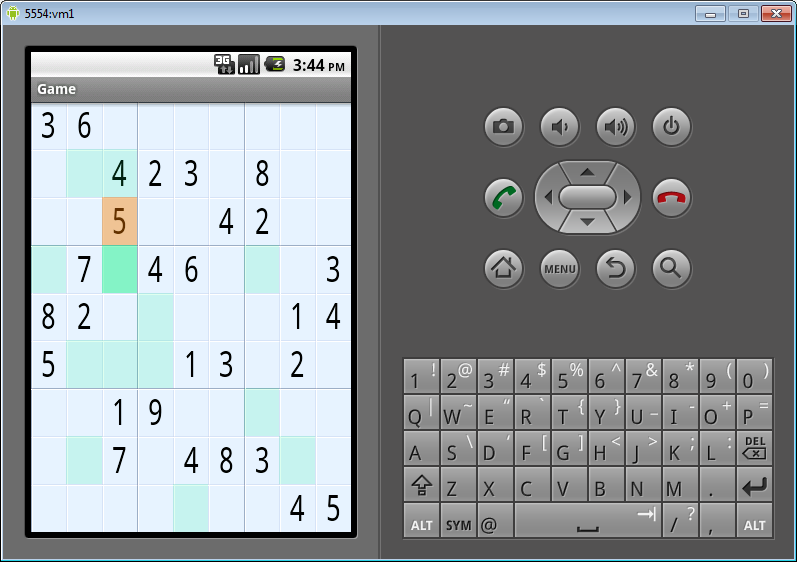
The class Game is responsible for the game logic. Jobs are loaded here, win conditions are checked. The Game class is an Activity, but the interface is not described in XML, but created by code. In the onCreate method, a View is created:
PazzleView is a class derived from View, it draws the playing field and handles screen touch events (onTouchEvent method) and keystrokes (onKeyDown method).
Let's analyze the drawing process in Android. For drawing, you need to overload the onDraw method. The method gets the Canvas object through which drawing is performed. To set the colors, objects of the Paint class are created. Color is set in ARGB format. Color is best stored as a resource (colors.xml file). Paint is not only a class for storing color information. For example, when drawing text, it contains information about the method of painting, font, and alignment of the text.
Canvas contains a set of methods for drawing graphics (drawRect, drawLine, drawPath, drawText, and others).
To optimize graphics, it is better to refrain from creating objects and unnecessary calculations inside the onDraw method (the considered example of the implementation of graphics is not optimal).
Music
To play music, the MediaPlayer class is used. Music for the game added to the resources. You just need to copy the necessary files to the / res / raw folder (formats WAV, AAC, MP3, WMA, AMR, OGG, MIDI).
First you need to create an instance of the MediaPlayer class:
mp = MediaPlayer.create (context, resource);
here context is usually the class that initiates the launch of music, resource is the identifier of the resource with the music. To control playback, use the methods start, stop and release.
In the game, music is played in the main menu (launch from the Sudoku class) and in the game process (launch from the Game class). To control playback created class Music. The class contains a static instance of MediaPlayer, which allows you not to create a separate project for each launch of a sound resource.
In the Sudoku and Game classes, the onResume and onPause methods are redefined, in which the music starts at the start of the Activity and stops when it is deactivated.
findings
The example that is considered in the article is not too complicated, which allows you to sort it out without much effort. At the same time, it touches upon various aspects of development for Android.
PS Many thanks to malkolm for comments.
We consider the basic concepts of programming Android.
For example, described the creation of the game Sudoku from the book Hello, Android - Ed Burnette .
Carefully a lot of screenshots.
1. Difficulties of development
')
Android is a unique operating system. An application developer should know its features and nuances to get a good result. There are some difficulties that need to be considered when developing (a good description here ). We list them briefly:
1) The application requires to install twice (or even four) more space than the original size of the application.
2) The speed of working with files on the built-in flash drive drops tenfold when the free space decreases.
3) Each process can use up to 16 MB (sometimes 24 MB) of RAM.
2. Principles of developing productive applications for Android
There are a number of recommendations for creating productive applications for Android. They can also be expanded on the basis of the books Effective Java - Joshua Bloch and Mobile Device Programming on the .Net Compact Framework - I. Salmre.
We list the basic principles for the development of productive applications for Android.
Strategic:
1) Resources need to save.
2) It is necessary to instantly give a response to the actions and maintain feedback with the user.
3) Application performance is the main goal. It is necessary constantly in the development process to optimize performance without leaving this work for later.
4) It is necessary to measure the execution time, log and analyze the progress of the application, narrow sections of code, the occurrence of events, memory allocation, the lifetime of objects. What is not measured , it can not be optimized.
Tactical:
1) Avoid creating unnecessary objects.
2) If possible, make the methods static.
3) Use direct field access instead of intermediary methods.
4) Use static final for constants.
5) Do not use enum where a normal integer variable is sufficient.
3. Key features of Android
Android is based on Linux. Between the application and the kernel is the API layer and the library layer on the native code. The application runs on a Java virtual machine (Dalvik Virtual Machine).
In Android, you can run many applications. But one of them is the main one and occupies the screen. From the current application, you can go to the previous one or start a new one. It looks like a browser with browsing history.
Each user interface screen is represented by an Activity class in code. Various Activities are contained in processes. An activity may even live longer than the process. Activity can be paused and started again with saving all the necessary information.

Android uses a special action description engine based on Intent. When you need to perform an action (make a call, send a letter, show a window), Intent is called.
Android also contains services similar to Linux daemons to perform the necessary actions in the background (for example, playing music).
Content providers are used to exchange data between applications.
4. Sample Application - Sudoku
We will consider the finished draft of the game Sudoku (the full code in the Sudokuv4 folder ).
To work, you need the Android SDK and Eclipse. About how to install and start everything is written here .
To load a project in Eclipse, you can do this:
1) Unzip the project to a separate folder in the Eclipse workspace.
2) Select the menu item File-> New-> Android Project.
3) In the New Android Project dialog, select the option Create project from existing source.
4) In the Location field, specify the path to the project folder. Click Next.
Program menu
The game menu is described in the file res / layout / main.xml. The interface description can be edited as XML or as a rendered interface. To switch, use the tabs at the bottom of the content display area.


Typically, controls are contained within a container; in our case, this is a LinearLayout. It arranges all the elements as a single column.
Resources
Please note that all text labels (android: text) take data from resources. For example, the entry android: text = "@ string / main_title" indicates that the text should be searched in the res / values / string.xml file in the node named main_title (Android Sudoku). The background color is also contained in the resources (android: background = "@ color / background") but in the color.xml file (# 3500ffff). When opening resource files in the editor, an error may occur. But you can always go to the XML mapping.


Controls that need to be accessed from the code must have an id. The buttons have an id (android: id = "@ + id / continue_button") in order to add a click handler to the button. The plus sign indicates that you need to create an identifier for the button in the /gen/org.example.sudoku/R.java file (public static final int continue_button = 0x7f0b000b;). This file is generated automatically and it is not recommended to change it. The file contains a class R through it you can access any interface element and other resources.

Creating windows
Consider creating a window with information about the program. The markup for this window is in the /res/layout/about.xml file. The activity class is described in the file /src/org.example.sudoku/About.java. Activity is associated with markup in the AndroidManifest.xml file. This file can be viewed either through the editor or as XML. On different tabs of the editor, you can select different sections of the file. The Application section contains the Activity parameters. Note that the Theme parameter is set to android : style / Theme.Dialog. Because of this, the style of the window looks more like a modal dialog.

Calling the window with information about the program is carried out from the Sudoku class by pressing the About button. The Sudoku class is written in such a way that it handles the Click event (public class Sudoku extends Activity implements OnClickListener). In the public void onClick method (View v), it is determined which button caused the event and the corresponding code is executed. To display the About window, the corresponding Intent is called.
case R.id.about_button:
Intent i = new Intent(this, About.class);
startActivity(i);
break;Event handlers can also be installed on specific controls. For example, in the Keypad class, when a class is created in the setListeners () method, handlers are set for individual buttons.

Simple dialogue
The user should be given the opportunity to choose the level of complexity. This is a small dialogue in which you need to choose one of several options. I am very pleased that for this you do not need to create a separate Intent, but it suffices to use the AlertDialog class.
Let us examine the process of starting a new game. The user clicks on the New Game button. The click handler is the Sudoku class method - onClick. Next, the openNewGameDialog method is invoked, which shows the complexity selection dialog and starts the game with the selected difficulty level. This dialog is built using the AlertDialog class.
private void openNewGameDialog() { new AlertDialog.Builder(this) .setTitle(R.string.new_game_title) .setItems(R.array.difficulty, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialoginterface, int i) { startGame(i); } }) .show(); } Notice that the contents of the dialog (a set of buttons) is built from an array of R.array.difficulty strings. Immediately assigned to the handler clicking on the buttons of the dialogue, which by the number of the pressed button launches a new game with a given level of complexity, calling the startGame method.
Graphics
The class Game is responsible for the game logic. Jobs are loaded here, win conditions are checked. The Game class is an Activity, but the interface is not described in XML, but created by code. In the onCreate method, a View is created:
puzzleView = new PuzzleView(this);
setContentView(puzzleView);
puzzleView.requestFocus();PazzleView is a class derived from View, it draws the playing field and handles screen touch events (onTouchEvent method) and keystrokes (onKeyDown method).
Let's analyze the drawing process in Android. For drawing, you need to overload the onDraw method. The method gets the Canvas object through which drawing is performed. To set the colors, objects of the Paint class are created. Color is set in ARGB format. Color is best stored as a resource (colors.xml file). Paint is not only a class for storing color information. For example, when drawing text, it contains information about the method of painting, font, and alignment of the text.
Canvas contains a set of methods for drawing graphics (drawRect, drawLine, drawPath, drawText, and others).
To optimize graphics, it is better to refrain from creating objects and unnecessary calculations inside the onDraw method (the considered example of the implementation of graphics is not optimal).

Music
To play music, the MediaPlayer class is used. Music for the game added to the resources. You just need to copy the necessary files to the / res / raw folder (formats WAV, AAC, MP3, WMA, AMR, OGG, MIDI).
First you need to create an instance of the MediaPlayer class:
mp = MediaPlayer.create (context, resource);
here context is usually the class that initiates the launch of music, resource is the identifier of the resource with the music. To control playback, use the methods start, stop and release.
In the game, music is played in the main menu (launch from the Sudoku class) and in the game process (launch from the Game class). To control playback created class Music. The class contains a static instance of MediaPlayer, which allows you not to create a separate project for each launch of a sound resource.
In the Sudoku and Game classes, the onResume and onPause methods are redefined, in which the music starts at the start of the Activity and stops when it is deactivated.
findings
The example that is considered in the article is not too complicated, which allows you to sort it out without much effort. At the same time, it touches upon various aspects of development for Android.
PS Many thanks to malkolm for comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/99323/
All Articles