Supercomputer problems in the middle lane
The third series of the program “ 5 weeks with Intel ” is dedicated to high-performance computing (HPC) - this is how supercomputers and calculations are made in professional jargon.

This picture is related to the post.
 Konstantin Zamkov , an enterprise technology specialist, deals with what is called presale at Intel, his main task is to provide technical advice to major customers on processors, platforms and technologies in both HPC and traditional IT environments. Konstantin helps the customer to integrate these solutions in their IT infrastructure. In the photo before kata Konstantin recalls his childhood :)
Konstantin Zamkov , an enterprise technology specialist, deals with what is called presale at Intel, his main task is to provide technical advice to major customers on processors, platforms and technologies in both HPC and traditional IT environments. Konstantin helps the customer to integrate these solutions in their IT infrastructure. In the photo before kata Konstantin recalls his childhood :)
')

 Andrei Semin is Intel Technical Director for High Performance Computing in the EMEA region. Engaged in HPC at Intel for over 10 years, since 1999. Until 2004, he worked in the Moscow office, and then moved to Munich to lead a group of engineers who help to use and apply HPC technologies based on Intel platforms as developers, vendors and users of software (for example, many commercial companies develop their own supercomputer software for their needs) and end users of HPC systems - from corporate customers from the automotive industry or oil and gas to government organizations such as meteorological services.
Andrei Semin is Intel Technical Director for High Performance Computing in the EMEA region. Engaged in HPC at Intel for over 10 years, since 1999. Until 2004, he worked in the Moscow office, and then moved to Munich to lead a group of engineers who help to use and apply HPC technologies based on Intel platforms as developers, vendors and users of software (for example, many commercial companies develop their own supercomputer software for their needs) and end users of HPC systems - from corporate customers from the automotive industry or oil and gas to government organizations such as meteorological services.
Andrew, since you have such a big and serious position, can you look back and try to formulate what has changed in the last 5-7 years in the field of high-performance computing in Russia?
 : The Russian market is closer to me than any other in Europe, so I rather closely follow what is happening to it. In the early 2000s, Russia was practically not represented in the supercomputer industry, there was only one large center, MSC RAS , which has been working on HPC for 20 years. There were smaller centers, for example, in the Siberian branch of the Academy of Sciences and in the Kurchatov Institute, but these were smaller initiatives. scales, not included in the Top500 supercomputer list .
: The Russian market is closer to me than any other in Europe, so I rather closely follow what is happening to it. In the early 2000s, Russia was practically not represented in the supercomputer industry, there was only one large center, MSC RAS , which has been working on HPC for 20 years. There were smaller centers, for example, in the Siberian branch of the Academy of Sciences and in the Kurchatov Institute, but these were smaller initiatives. scales, not included in the Top500 supercomputer list .
Toward the mid-2000s, a turning point for the industry took place, and Russian systems began to appear in the Top500: first there were 2-3, then 6-8, in the last June list of such supercomputers 11. In many respects, it is due to the fact that government funding supercomputer program has become more focused. In 2002, the SKIF program was created, which gradually began to finance the creation of clusters in universities: in Tomsk State, South Ural, Moscow State and so on.
In parallel with this, the industrial part began to catch up; in Russia, it is concentrated in those companies that are engaged in the development of high technology products. For example, aircraft engine developers use high-performance computing, because it is almost impossible to create modern competitive aircraft engines without modern modeling methods. In Russia, enterprises engaged in these are created on the basis of the Salyut and Saturn factories, which develop aircraft engines for Russian aircraft and sell them in Russia and abroad.
It is curious that the last edition of the Top500 list in the Russian academic sector turned out to be 5 systems, and the remaining 6 systems — more than half of the Russian ones — turned out to be in the commercial sector: in banks and in other companies that use HPC to conduct business. This suggests that, on the one hand, there were specialists who know how to exploit supercomputer systems, and on the other hand, people began to appear in the commercial sector who understand the importance of using high-performance systems. For example, in the banking sector, HPCs are commonly used to assess the risk of investment portfolios.
Summarizing - now in Russia there is a steady growth of the HPC market; Systems began to appear in the commercial sector, which suggests that high-performance computing is being democratized and there are people who know how to exploit supercomputers and understand their importance for specific, real-world applications.
Any examples of high-tech customers?
 : Yes, for example, the Russian company Rock Flow Dynamics , which creates specialized software for the oil and gas industry. We are very good friends with RFD, they always try our most recent developments, in particular the newest processors.
: Yes, for example, the Russian company Rock Flow Dynamics , which creates specialized software for the oil and gas industry. We are very good friends with RFD, they always try our most recent developments, in particular the newest processors.
Rock Flow Dynamics is a Russian team of 20 mathematicians, physicists and engineers who develop tNavigator, a specialized product for computer modeling of oil and gas fields.

RFD is a unique case in domestic and international practice; For five years working on tNavigator, former Yukos immigrants have created advanced software that easily competes with software industry leader Schlumberger (80 thousand people in the state and an annual turnover of more than $ 20 billion in 2009). tNavigator is an interactive visual application that is radically different from the command-line programs used in the oilfield services industry. However, the growing interest in tNavigator is also due to the fact that the package is well optimized for multi-core desktop systems based on Intel processors. Vasily Shelkov , RFD Director:

We got acquainted with Intel at the very beginning of our journey, in 2005, and the company's employees convinced us that the future belongs to multi-core processors and parallel programming, so we started development, already on the assumption that our package will run on multi-core hardware. The software of our competitors, such as Schlumberger , had already existed on the market for 20-30 years. It is clear that computational realities then and now differ markedly, so even with all the power and parallelism of their decisions in practice, they lose factor 2 on modern systems due to the fact that they do not use all the technologies that can be used in software development.
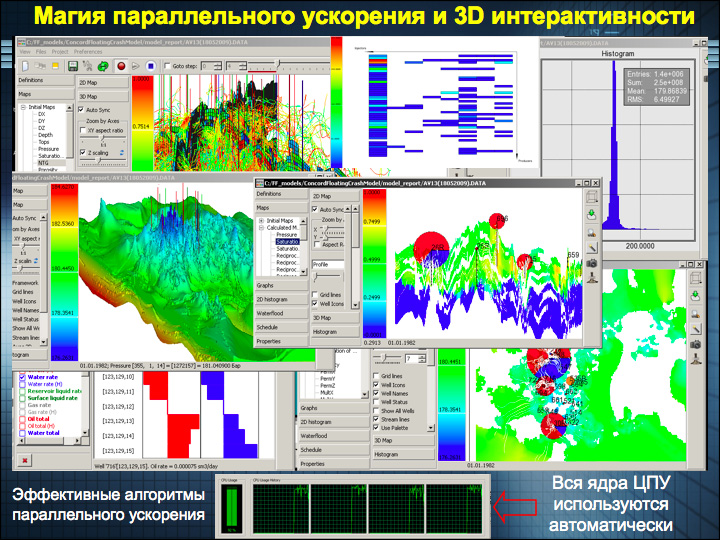
An example of tNavigator's work on the latest Intel Xeon Series 7500 could be a project for VolgoUralNIPIgaz: a field model that the previous generation of equipment and other software performed was calculated for more than 12 hours; tNavigator in conjunction with the Xeon 7500 solves the same problem in an hour and twenty minutes.
Who in Russia is developing and implementing HPC solutions?
 : In Russia, there are two main companies involved in the development of their own supercomputer design: the T-Platform company and the RSK SKIF . There are several companies that make high-performance clusters based on standard components, such as R-Style, Storus, Aquarius and Kraftway. They also have an impact on the market, although they use standard components in their decisions.
: In Russia, there are two main companies involved in the development of their own supercomputer design: the T-Platform company and the RSK SKIF . There are several companies that make high-performance clusters based on standard components, such as R-Style, Storus, Aquarius and Kraftway. They also have an impact on the market, although they use standard components in their decisions.
Recently, Intel has updated its line of server processors. One gets the impression that for high-performance solutions, Intel is trying to preserve as much as possible the processor sockets and other strapping on the motherboards. How new are compatible with old equipment?
 : The socket is indeed compatible, but with motherboards there are nuances associated, for example, with the voltage regulators of the processors. Since there are a lot of manufacturers, some of them are better, while others follow worse the recommendations or reference designs provided by Intel. For those who follow our recommendations more carefully, compatibility is better. Unfortunately, this cannot be said about all manufacturers.
: The socket is indeed compatible, but with motherboards there are nuances associated, for example, with the voltage regulators of the processors. Since there are a lot of manufacturers, some of them are better, while others follow worse the recommendations or reference designs provided by Intel. For those who follow our recommendations more carefully, compatibility is better. Unfortunately, this cannot be said about all manufacturers.
In the end, it turns out that some manufacturers manage the BIOS update, after which the new hardware works fine, while others have to release new revisions of motherboards. The question is, what will this mean for the end customer? If he has already purchased the systems and just wants to replace the processors in them, which is not such a common case in itself, everything will depend on the particular manufacturer of the solution.
Among the updated Xeon was presented a fault-tolerant processor, which in the event of a critical failure does not bring down the system.
 A: Yes, this is the Xeon Series 7500, codenamed Nehalem-EX. One of the applications of this family of processors is what is called mission critical applications.
A: Yes, this is the Xeon Series 7500, codenamed Nehalem-EX. One of the applications of this family of processors is what is called mission critical applications.
Are there examples of the use of mission critical solutions?
 : A classic example is billing systems. Suppose, for example, billing of cellular operators - as you know, the technology of data exchange between operators about the cost of roaming services is somewhat imperfect, so if the billing system of an individual operator falls, this means that such data will go nowhere and the company will lose money. I can only guess at the scale of the problem, but the idle time of such a system can mean the loss of hundreds of thousands of dollars.
: A classic example is billing systems. Suppose, for example, billing of cellular operators - as you know, the technology of data exchange between operators about the cost of roaming services is somewhat imperfect, so if the billing system of an individual operator falls, this means that such data will go nowhere and the company will lose money. I can only guess at the scale of the problem, but the idle time of such a system can mean the loss of hundreds of thousands of dollars.
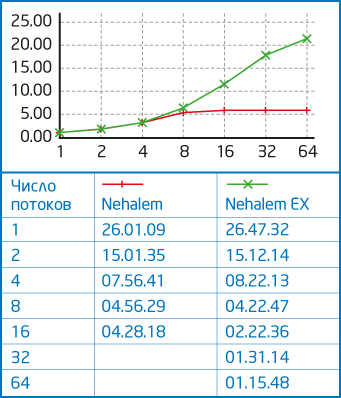
 : By the way, the Xeon 7500 platform is interesting not only for mission critical, but also for HPC applications because compared to the previous platform built on the Xeon 7400 base, the memory bandwidth of the same number of processors of the Xeon 7500 increased 8 times .
: By the way, the Xeon 7500 platform is interesting not only for mission critical, but also for HPC applications because compared to the previous platform built on the Xeon 7400 base, the memory bandwidth of the same number of processors of the Xeon 7500 increased 8 times .
But this is a bottleneck in many HPC systems?
 A: Yes, for HPC applications, memory performance is very important because the amount of data being processed is huge, so an eightfold increase in memory bandwidth has a very positive effect on application performance.
A: Yes, for HPC applications, memory performance is very important because the amount of data being processed is huge, so an eightfold increase in memory bandwidth has a very positive effect on application performance.
There are many vertical markets for applying HPC solutions: the chemical industry, bioinformatics, finance, oil and gas, and so on. Inside some verticals there are areas where there are no alternatives to using platforms like the Xeon 7500. Examples here are some tasks in the manufacturing sphere, modeling of aerodynamic or gas-dynamic properties, fluid flows, and so on. Creating grids is usually not parallelized into a cluster of several nodes. As a rule, it is most efficient to use one system with a sufficiently large amount of memory - up to terabytes of memory in one server. In this case, the creation of the grid, the very time of the bill may take several hours or even days, depending on the model. Accordingly, if in the course of this work the server fails - the disk crashes, the memory module crashes, just something happens, then you have to start all the work over. In such cases, a combination of fault tolerance properties is required along with other indicators (for example, all the same amounts of memory).
Another area where fault-tolerant systems are used is in the chemical industry, where some modeling packages have been written for a long time. These software products are 20-25 years old. They have been tested, tested over the past decades and have a large number of certificates, they are very difficult to change according to business criteria. Packages such as GAUSSIAN effectively use up to 32 cores, and after 32 cores on most models do not give a performance boost, but they require large amounts of memory (terabytes), and the counting time of models lasts several days or even tens of days.
One example that we can talk about publicly is the case of the German chemical company BASF. They had software packages that worked on the same server without ceasing for several days from the beginning of the application and until the result was obtained. Accordingly, any stop during these one and a half months led to the fact that it was necessary to start work anew. BASF and I took measures to optimize their software and reduced the counting time to about one day, but even one day for a server running under full load is quite a stressful mode of operation, so all components of such a system should be fault-tolerant, handle errors and self-repair .
The application could not adequately scale to a large number of cores?
 A: Yes, they had an application that did not scale to the cluster, because it used input and output very strongly, reading and writing dozens of terabytes of data to the file system. Parallelizing these operations between nodes was very inefficient, so practically the work was limited to one node with a very large file system. A read cycle of several hundred gigabytes from a disk, their processing, a writeback cycle. This data processing process lasted several days, until the system came to the desired result.
A: Yes, they had an application that did not scale to the cluster, because it used input and output very strongly, reading and writing dozens of terabytes of data to the file system. Parallelizing these operations between nodes was very inefficient, so practically the work was limited to one node with a very large file system. A read cycle of several hundred gigabytes from a disk, their processing, a writeback cycle. This data processing process lasted several days, until the system came to the desired result.
How are SSDs used in HPC?
 : SSD has several advantages, first of all - a high number of I / O operations, which is important because HPC has a lot of applications that actually use active I / O - the example of BASF is indicative here. In many other areas the same picture: real-world applications use large amounts of data. These data volumes are created either by some kind of physical experiment, or by a simulation method at a workstation, and then processed in a software package.
: SSD has several advantages, first of all - a high number of I / O operations, which is important because HPC has a lot of applications that actually use active I / O - the example of BASF is indicative here. In many other areas the same picture: real-world applications use large amounts of data. These data volumes are created either by some kind of physical experiment, or by a simulation method at a workstation, and then processed in a software package.
SSDs are not always an effective way to solve data storage problems, because at the price per bit, SSD information is more expensive than regular drives. But many HPC applications get quite a big performance boost due to the use of SSD. We had an example of such use for applications such as NASTRAN, such applications are concerned with structural mechanics. NASTRAN - software package for analyzing the stability of structures to various kinds of mechanical deformations. With the use of SSD on the Nehalem platform, we received about 20% of the performance gain - and all this without changing the processors, only due to the SSD.
If we talk about the broader applications of SSD, they are actively used in parallel file systems, such as Luster or GPFS, on metadata servers for storing information about files and directories. As a rule, in this case the quality of SSD is used, that they allow you to effectively make a sufficiently large number of small disk operations. Accordingly, if a certain process scans a directory in which there are a lot of files, then it causes a huge number of file attribute request operations, and these are a lot of small disk accesses, which are many times more efficiently done on SSD.
How do Intel's HPC programs connect to the academic world?
 : Intel in Russia is investing a lot of effort in support of HPC. We already have a HPC infrastructure, so Intel sees its role in a greater democratization of HPC, in that high-performance computing becomes available to a wider range of users.
: Intel in Russia is investing a lot of effort in support of HPC. We already have a HPC infrastructure, so Intel sees its role in a greater democratization of HPC, in that high-performance computing becomes available to a wider range of users.
Now the question is to expand the scope of HPC beyond the typical industries - oil and gas, weather modeling, etc. There are several such initiatives in the academic field, for example, using HPC in linguistics to analyze texts, to analyze human speech, and so on. In addition, we hold various contests to understand where HPC can be applied. In particular, the third contest called “ Impossible became possible: real applications for HPC ” is held, its main goal is to find and support the development of applications in areas of science and technology that have certain tasks that were previously considered unsolvable. This year the competition is held with the support of Rosnano and the SKIF consortium for the third time. It should be said that a half million processor hours on a supercomputer are added to a decent prize pool , so that the winners can calculate their applied tasks on leading Russian supercomputers. For the first place, the author will receive 250,000 rubles from Intel, as well as gifts from other partners.

Why do you do HPC?
 : For me, high performance computing (HPC) is a tool that allows you to solve problems that were previously considered completely unsolvable. Just imagine, you can give an example of what a large supercomputer is: a large supercomputer Jaguar, which ranks first on the Top500 list, for each second performs such a number of operations that six billion people working without stopping all day would require 47 years. This is a huge computational power that allows you to find a numerical solution for problems that cannot be found analytically using scientific methods. The result of all these calculations means improving the quality of life of people: the creation and use of new drugs, the creation of safer and faster cars, the cheapening of various kinds of materials and products.
: For me, high performance computing (HPC) is a tool that allows you to solve problems that were previously considered completely unsolvable. Just imagine, you can give an example of what a large supercomputer is: a large supercomputer Jaguar, which ranks first on the Top500 list, for each second performs such a number of operations that six billion people working without stopping all day would require 47 years. This is a huge computational power that allows you to find a numerical solution for problems that cannot be found analytically using scientific methods. The result of all these calculations means improving the quality of life of people: the creation and use of new drugs, the creation of safer and faster cars, the cheapening of various kinds of materials and products.
What kind of questions will you be interested to discuss with readers?
NB : A lot of technical issues about Xeon processors are regularly discussed in online chat rooms with Intel experts . Perhaps an exhaustive answer to your question is already there.
 : I am pleased to talk about server processors, platforms, solutions and servers from different manufacturers. But you can touch on other topics: desktops and laptops, and something related to Intel vPro processor technology.
: I am pleased to talk about server processors, platforms, solutions and servers from different manufacturers. But you can touch on other topics: desktops and laptops, and something related to Intel vPro processor technology.
 : Any ideas on the use of HPC, even the most incredible, are very important to us. When I studied at the Moscow University in the Faculty of Physics in the early nineties, we were engaged in mathematical methods for solving various problems.A very popular topic was the use of various statistical methods to predict the behavior of financial markets, forecast the status of investment portfolios, and so on. Then it was exotic, no one seriously talked about it, and supercomputers in banks were not used so widely. And now, no serious financial institution, be it an insurance company, a bank, or an investment company, can’t do without HPC for such methods, and in fact a little less than 20 years passed from the moment these ideas appeared on the market to turn them into a product. We would be very interested to discuss such ideas.
: Any ideas on the use of HPC, even the most incredible, are very important to us. When I studied at the Moscow University in the Faculty of Physics in the early nineties, we were engaged in mathematical methods for solving various problems.A very popular topic was the use of various statistical methods to predict the behavior of financial markets, forecast the status of investment portfolios, and so on. Then it was exotic, no one seriously talked about it, and supercomputers in banks were not used so widely. And now, no serious financial institution, be it an insurance company, a bank, or an investment company, can’t do without HPC for such methods, and in fact a little less than 20 years passed from the moment these ideas appeared on the market to turn them into a product. We would be very interested to discuss such ideas.
 By the way, last week, dedicated to the story about Intel Labs , the "winner" was the user of Rule , with which we congratulate him.
By the way, last week, dedicated to the story about Intel Labs , the "winner" was the user of Rule , with which we congratulate him.
Do not forget to connect to the company's blog on Habré!
Icons by Yusuke Kamiyamane
To be continued.

This picture is related to the post.
 Konstantin Zamkov , an enterprise technology specialist, deals with what is called presale at Intel, his main task is to provide technical advice to major customers on processors, platforms and technologies in both HPC and traditional IT environments. Konstantin helps the customer to integrate these solutions in their IT infrastructure. In the photo before kata Konstantin recalls his childhood :)
Konstantin Zamkov , an enterprise technology specialist, deals with what is called presale at Intel, his main task is to provide technical advice to major customers on processors, platforms and technologies in both HPC and traditional IT environments. Konstantin helps the customer to integrate these solutions in their IT infrastructure. In the photo before kata Konstantin recalls his childhood :)')

 Andrei Semin is Intel Technical Director for High Performance Computing in the EMEA region. Engaged in HPC at Intel for over 10 years, since 1999. Until 2004, he worked in the Moscow office, and then moved to Munich to lead a group of engineers who help to use and apply HPC technologies based on Intel platforms as developers, vendors and users of software (for example, many commercial companies develop their own supercomputer software for their needs) and end users of HPC systems - from corporate customers from the automotive industry or oil and gas to government organizations such as meteorological services.
Andrei Semin is Intel Technical Director for High Performance Computing in the EMEA region. Engaged in HPC at Intel for over 10 years, since 1999. Until 2004, he worked in the Moscow office, and then moved to Munich to lead a group of engineers who help to use and apply HPC technologies based on Intel platforms as developers, vendors and users of software (for example, many commercial companies develop their own supercomputer software for their needs) and end users of HPC systems - from corporate customers from the automotive industry or oil and gas to government organizations such as meteorological services.Andrew, since you have such a big and serious position, can you look back and try to formulate what has changed in the last 5-7 years in the field of high-performance computing in Russia?
 : The Russian market is closer to me than any other in Europe, so I rather closely follow what is happening to it. In the early 2000s, Russia was practically not represented in the supercomputer industry, there was only one large center, MSC RAS , which has been working on HPC for 20 years. There were smaller centers, for example, in the Siberian branch of the Academy of Sciences and in the Kurchatov Institute, but these were smaller initiatives. scales, not included in the Top500 supercomputer list .
: The Russian market is closer to me than any other in Europe, so I rather closely follow what is happening to it. In the early 2000s, Russia was practically not represented in the supercomputer industry, there was only one large center, MSC RAS , which has been working on HPC for 20 years. There were smaller centers, for example, in the Siberian branch of the Academy of Sciences and in the Kurchatov Institute, but these were smaller initiatives. scales, not included in the Top500 supercomputer list .Toward the mid-2000s, a turning point for the industry took place, and Russian systems began to appear in the Top500: first there were 2-3, then 6-8, in the last June list of such supercomputers 11. In many respects, it is due to the fact that government funding supercomputer program has become more focused. In 2002, the SKIF program was created, which gradually began to finance the creation of clusters in universities: in Tomsk State, South Ural, Moscow State and so on.
In parallel with this, the industrial part began to catch up; in Russia, it is concentrated in those companies that are engaged in the development of high technology products. For example, aircraft engine developers use high-performance computing, because it is almost impossible to create modern competitive aircraft engines without modern modeling methods. In Russia, enterprises engaged in these are created on the basis of the Salyut and Saturn factories, which develop aircraft engines for Russian aircraft and sell them in Russia and abroad.
It is curious that the last edition of the Top500 list in the Russian academic sector turned out to be 5 systems, and the remaining 6 systems — more than half of the Russian ones — turned out to be in the commercial sector: in banks and in other companies that use HPC to conduct business. This suggests that, on the one hand, there were specialists who know how to exploit supercomputer systems, and on the other hand, people began to appear in the commercial sector who understand the importance of using high-performance systems. For example, in the banking sector, HPCs are commonly used to assess the risk of investment portfolios.
Summarizing - now in Russia there is a steady growth of the HPC market; Systems began to appear in the commercial sector, which suggests that high-performance computing is being democratized and there are people who know how to exploit supercomputers and understand their importance for specific, real-world applications.
Any examples of high-tech customers?
 : Yes, for example, the Russian company Rock Flow Dynamics , which creates specialized software for the oil and gas industry. We are very good friends with RFD, they always try our most recent developments, in particular the newest processors.
: Yes, for example, the Russian company Rock Flow Dynamics , which creates specialized software for the oil and gas industry. We are very good friends with RFD, they always try our most recent developments, in particular the newest processors.Rock Flow Dynamics is a Russian team of 20 mathematicians, physicists and engineers who develop tNavigator, a specialized product for computer modeling of oil and gas fields.

RFD is a unique case in domestic and international practice; For five years working on tNavigator, former Yukos immigrants have created advanced software that easily competes with software industry leader Schlumberger (80 thousand people in the state and an annual turnover of more than $ 20 billion in 2009). tNavigator is an interactive visual application that is radically different from the command-line programs used in the oilfield services industry. However, the growing interest in tNavigator is also due to the fact that the package is well optimized for multi-core desktop systems based on Intel processors. Vasily Shelkov , RFD Director:

We got acquainted with Intel at the very beginning of our journey, in 2005, and the company's employees convinced us that the future belongs to multi-core processors and parallel programming, so we started development, already on the assumption that our package will run on multi-core hardware. The software of our competitors, such as Schlumberger , had already existed on the market for 20-30 years. It is clear that computational realities then and now differ markedly, so even with all the power and parallelism of their decisions in practice, they lose factor 2 on modern systems due to the fact that they do not use all the technologies that can be used in software development.

An example of tNavigator's work on the latest Intel Xeon Series 7500 could be a project for VolgoUralNIPIgaz: a field model that the previous generation of equipment and other software performed was calculated for more than 12 hours; tNavigator in conjunction with the Xeon 7500 solves the same problem in an hour and twenty minutes.

Who in Russia is developing and implementing HPC solutions?
 : In Russia, there are two main companies involved in the development of their own supercomputer design: the T-Platform company and the RSK SKIF . There are several companies that make high-performance clusters based on standard components, such as R-Style, Storus, Aquarius and Kraftway. They also have an impact on the market, although they use standard components in their decisions.
: In Russia, there are two main companies involved in the development of their own supercomputer design: the T-Platform company and the RSK SKIF . There are several companies that make high-performance clusters based on standard components, such as R-Style, Storus, Aquarius and Kraftway. They also have an impact on the market, although they use standard components in their decisions.Recently, Intel has updated its line of server processors. One gets the impression that for high-performance solutions, Intel is trying to preserve as much as possible the processor sockets and other strapping on the motherboards. How new are compatible with old equipment?
 : The socket is indeed compatible, but with motherboards there are nuances associated, for example, with the voltage regulators of the processors. Since there are a lot of manufacturers, some of them are better, while others follow worse the recommendations or reference designs provided by Intel. For those who follow our recommendations more carefully, compatibility is better. Unfortunately, this cannot be said about all manufacturers.
: The socket is indeed compatible, but with motherboards there are nuances associated, for example, with the voltage regulators of the processors. Since there are a lot of manufacturers, some of them are better, while others follow worse the recommendations or reference designs provided by Intel. For those who follow our recommendations more carefully, compatibility is better. Unfortunately, this cannot be said about all manufacturers.In the end, it turns out that some manufacturers manage the BIOS update, after which the new hardware works fine, while others have to release new revisions of motherboards. The question is, what will this mean for the end customer? If he has already purchased the systems and just wants to replace the processors in them, which is not such a common case in itself, everything will depend on the particular manufacturer of the solution.
Among the updated Xeon was presented a fault-tolerant processor, which in the event of a critical failure does not bring down the system.
 A: Yes, this is the Xeon Series 7500, codenamed Nehalem-EX. One of the applications of this family of processors is what is called mission critical applications.
A: Yes, this is the Xeon Series 7500, codenamed Nehalem-EX. One of the applications of this family of processors is what is called mission critical applications.Are there examples of the use of mission critical solutions?
 : A classic example is billing systems. Suppose, for example, billing of cellular operators - as you know, the technology of data exchange between operators about the cost of roaming services is somewhat imperfect, so if the billing system of an individual operator falls, this means that such data will go nowhere and the company will lose money. I can only guess at the scale of the problem, but the idle time of such a system can mean the loss of hundreds of thousands of dollars.
: A classic example is billing systems. Suppose, for example, billing of cellular operators - as you know, the technology of data exchange between operators about the cost of roaming services is somewhat imperfect, so if the billing system of an individual operator falls, this means that such data will go nowhere and the company will lose money. I can only guess at the scale of the problem, but the idle time of such a system can mean the loss of hundreds of thousands of dollars. : By the way, the Xeon 7500 platform is interesting not only for mission critical, but also for HPC applications because compared to the previous platform built on the Xeon 7400 base, the memory bandwidth of the same number of processors of the Xeon 7500 increased 8 times .
: By the way, the Xeon 7500 platform is interesting not only for mission critical, but also for HPC applications because compared to the previous platform built on the Xeon 7400 base, the memory bandwidth of the same number of processors of the Xeon 7500 increased 8 times .But this is a bottleneck in many HPC systems?
 A: Yes, for HPC applications, memory performance is very important because the amount of data being processed is huge, so an eightfold increase in memory bandwidth has a very positive effect on application performance.
A: Yes, for HPC applications, memory performance is very important because the amount of data being processed is huge, so an eightfold increase in memory bandwidth has a very positive effect on application performance.There are many vertical markets for applying HPC solutions: the chemical industry, bioinformatics, finance, oil and gas, and so on. Inside some verticals there are areas where there are no alternatives to using platforms like the Xeon 7500. Examples here are some tasks in the manufacturing sphere, modeling of aerodynamic or gas-dynamic properties, fluid flows, and so on. Creating grids is usually not parallelized into a cluster of several nodes. As a rule, it is most efficient to use one system with a sufficiently large amount of memory - up to terabytes of memory in one server. In this case, the creation of the grid, the very time of the bill may take several hours or even days, depending on the model. Accordingly, if in the course of this work the server fails - the disk crashes, the memory module crashes, just something happens, then you have to start all the work over. In such cases, a combination of fault tolerance properties is required along with other indicators (for example, all the same amounts of memory).
Another area where fault-tolerant systems are used is in the chemical industry, where some modeling packages have been written for a long time. These software products are 20-25 years old. They have been tested, tested over the past decades and have a large number of certificates, they are very difficult to change according to business criteria. Packages such as GAUSSIAN effectively use up to 32 cores, and after 32 cores on most models do not give a performance boost, but they require large amounts of memory (terabytes), and the counting time of models lasts several days or even tens of days.
One example that we can talk about publicly is the case of the German chemical company BASF. They had software packages that worked on the same server without ceasing for several days from the beginning of the application and until the result was obtained. Accordingly, any stop during these one and a half months led to the fact that it was necessary to start work anew. BASF and I took measures to optimize their software and reduced the counting time to about one day, but even one day for a server running under full load is quite a stressful mode of operation, so all components of such a system should be fault-tolerant, handle errors and self-repair .
The application could not adequately scale to a large number of cores?
 A: Yes, they had an application that did not scale to the cluster, because it used input and output very strongly, reading and writing dozens of terabytes of data to the file system. Parallelizing these operations between nodes was very inefficient, so practically the work was limited to one node with a very large file system. A read cycle of several hundred gigabytes from a disk, their processing, a writeback cycle. This data processing process lasted several days, until the system came to the desired result.
A: Yes, they had an application that did not scale to the cluster, because it used input and output very strongly, reading and writing dozens of terabytes of data to the file system. Parallelizing these operations between nodes was very inefficient, so practically the work was limited to one node with a very large file system. A read cycle of several hundred gigabytes from a disk, their processing, a writeback cycle. This data processing process lasted several days, until the system came to the desired result.How are SSDs used in HPC?
 : SSD has several advantages, first of all - a high number of I / O operations, which is important because HPC has a lot of applications that actually use active I / O - the example of BASF is indicative here. In many other areas the same picture: real-world applications use large amounts of data. These data volumes are created either by some kind of physical experiment, or by a simulation method at a workstation, and then processed in a software package.
: SSD has several advantages, first of all - a high number of I / O operations, which is important because HPC has a lot of applications that actually use active I / O - the example of BASF is indicative here. In many other areas the same picture: real-world applications use large amounts of data. These data volumes are created either by some kind of physical experiment, or by a simulation method at a workstation, and then processed in a software package.SSDs are not always an effective way to solve data storage problems, because at the price per bit, SSD information is more expensive than regular drives. But many HPC applications get quite a big performance boost due to the use of SSD. We had an example of such use for applications such as NASTRAN, such applications are concerned with structural mechanics. NASTRAN - software package for analyzing the stability of structures to various kinds of mechanical deformations. With the use of SSD on the Nehalem platform, we received about 20% of the performance gain - and all this without changing the processors, only due to the SSD.
If we talk about the broader applications of SSD, they are actively used in parallel file systems, such as Luster or GPFS, on metadata servers for storing information about files and directories. As a rule, in this case the quality of SSD is used, that they allow you to effectively make a sufficiently large number of small disk operations. Accordingly, if a certain process scans a directory in which there are a lot of files, then it causes a huge number of file attribute request operations, and these are a lot of small disk accesses, which are many times more efficiently done on SSD.
How do Intel's HPC programs connect to the academic world?
 : Intel in Russia is investing a lot of effort in support of HPC. We already have a HPC infrastructure, so Intel sees its role in a greater democratization of HPC, in that high-performance computing becomes available to a wider range of users.
: Intel in Russia is investing a lot of effort in support of HPC. We already have a HPC infrastructure, so Intel sees its role in a greater democratization of HPC, in that high-performance computing becomes available to a wider range of users.Now the question is to expand the scope of HPC beyond the typical industries - oil and gas, weather modeling, etc. There are several such initiatives in the academic field, for example, using HPC in linguistics to analyze texts, to analyze human speech, and so on. In addition, we hold various contests to understand where HPC can be applied. In particular, the third contest called “ Impossible became possible: real applications for HPC ” is held, its main goal is to find and support the development of applications in areas of science and technology that have certain tasks that were previously considered unsolvable. This year the competition is held with the support of Rosnano and the SKIF consortium for the third time. It should be said that a half million processor hours on a supercomputer are added to a decent prize pool , so that the winners can calculate their applied tasks on leading Russian supercomputers. For the first place, the author will receive 250,000 rubles from Intel, as well as gifts from other partners.

Why do you do HPC?
 : For me, high performance computing (HPC) is a tool that allows you to solve problems that were previously considered completely unsolvable. Just imagine, you can give an example of what a large supercomputer is: a large supercomputer Jaguar, which ranks first on the Top500 list, for each second performs such a number of operations that six billion people working without stopping all day would require 47 years. This is a huge computational power that allows you to find a numerical solution for problems that cannot be found analytically using scientific methods. The result of all these calculations means improving the quality of life of people: the creation and use of new drugs, the creation of safer and faster cars, the cheapening of various kinds of materials and products.
: For me, high performance computing (HPC) is a tool that allows you to solve problems that were previously considered completely unsolvable. Just imagine, you can give an example of what a large supercomputer is: a large supercomputer Jaguar, which ranks first on the Top500 list, for each second performs such a number of operations that six billion people working without stopping all day would require 47 years. This is a huge computational power that allows you to find a numerical solution for problems that cannot be found analytically using scientific methods. The result of all these calculations means improving the quality of life of people: the creation and use of new drugs, the creation of safer and faster cars, the cheapening of various kinds of materials and products.What kind of questions will you be interested to discuss with readers?
NB : A lot of technical issues about Xeon processors are regularly discussed in online chat rooms with Intel experts . Perhaps an exhaustive answer to your question is already there.
 : I am pleased to talk about server processors, platforms, solutions and servers from different manufacturers. But you can touch on other topics: desktops and laptops, and something related to Intel vPro processor technology.
: I am pleased to talk about server processors, platforms, solutions and servers from different manufacturers. But you can touch on other topics: desktops and laptops, and something related to Intel vPro processor technology. : Any ideas on the use of HPC, even the most incredible, are very important to us. When I studied at the Moscow University in the Faculty of Physics in the early nineties, we were engaged in mathematical methods for solving various problems.A very popular topic was the use of various statistical methods to predict the behavior of financial markets, forecast the status of investment portfolios, and so on. Then it was exotic, no one seriously talked about it, and supercomputers in banks were not used so widely. And now, no serious financial institution, be it an insurance company, a bank, or an investment company, can’t do without HPC for such methods, and in fact a little less than 20 years passed from the moment these ideas appeared on the market to turn them into a product. We would be very interested to discuss such ideas.
: Any ideas on the use of HPC, even the most incredible, are very important to us. When I studied at the Moscow University in the Faculty of Physics in the early nineties, we were engaged in mathematical methods for solving various problems.A very popular topic was the use of various statistical methods to predict the behavior of financial markets, forecast the status of investment portfolios, and so on. Then it was exotic, no one seriously talked about it, and supercomputers in banks were not used so widely. And now, no serious financial institution, be it an insurance company, a bank, or an investment company, can’t do without HPC for such methods, and in fact a little less than 20 years passed from the moment these ideas appeared on the market to turn them into a product. We would be very interested to discuss such ideas. By the way, last week, dedicated to the story about Intel Labs , the "winner" was the user of Rule , with which we congratulate him.
By the way, last week, dedicated to the story about Intel Labs , the "winner" was the user of Rule , with which we congratulate him.Do not forget to connect to the company's blog on Habré!
Icons by Yusuke Kamiyamane
To be continued.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/98001/
All Articles