Two words of three letters: TMS and VCS
Over the past month I received three calls in which these mysterious words sounded, and I was forced to explain how it works. I am deeply convinced that knowledge needs to be shared - this is the right means from degradation. Therefore, to the best of my understanding, I will try to explain to the general public what they mean. So, the following discussion will focus on three TANDBERG devices for video communication: TMS, VCS Control and VCS ExpressWay.
All three devices belong to the group of infrastructure equipment, i.e. You can start a video conference without them, but they are very useful for solving problems that go beyond the point-to-point communication.
As the name implies, this is a software package (although it can also be supplied as an assembled 1-u server) for managing terminals and video communication servers. It can generate address books for terminals, manage their updates, generate usage reports, switch between multipoint servers, etc. In short: a system that manages your entire video network.
Remarkably, it is able to manage third-party terminals (of course, not to the same extent as its relatives). The fact is that this product was developed by a company that was absorbed by TANDBERG several years ago. Obviously, the product was designed for video conferencing in general. After absorption, this functionality was decided not to be removed.
')
VCS stands for Video Control Server (not to be confused with a multipoint server). And if we discard the big words, it is a sip server and H.323 zone controller in one bottle. Sharpened by video and can connect devices from both these networks. Also, it is very useful when docking with third-party applications: ip-telephony, Cisco Unified Communications, Microsoft OCS, etc.
And this is a much more entertaining piece of iron (more precisely, an application): it serves to overcome firewalls. Firewalls, as you know, are designed to keep out. First of all, outside. Accordingly, if you try to connect because of the firewall with the remote terminal, then you will most likely be seen and heard, but the packets will not go in your direction, and you will sadly look at the dark silent screen. This is the RTP protocol.
What ExpressWay does: it sends incoming packets on the port that was initialized by the device behind the firewall, and, accordingly, can run over this connection, anything in both directions. Obviously, ExpressWay is located in a public network.
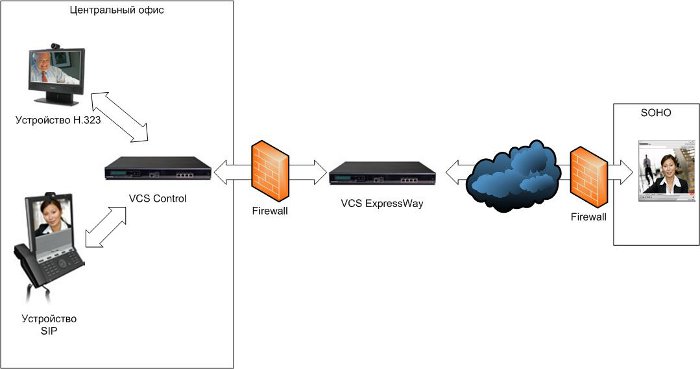
The figure shows how devices communicate with each other. I did not draw TMS, but it is implied: it is very difficult to steer this zoo without it.
I do not work for TANDBERG (now Cisco), but I believe that their equipment is the best on the market in their fields (this does not mean the cheapest). In general, as managed told. Specially did not go into how connections are initialized and packages run; This information is enough for a couple of separate topics, if there is interest - I will write.
Brief description of devices
All three devices belong to the group of infrastructure equipment, i.e. You can start a video conference without them, but they are very useful for solving problems that go beyond the point-to-point communication.
TANDBERG Management Suite or TMS
As the name implies, this is a software package (although it can also be supplied as an assembled 1-u server) for managing terminals and video communication servers. It can generate address books for terminals, manage their updates, generate usage reports, switch between multipoint servers, etc. In short: a system that manages your entire video network.
Remarkably, it is able to manage third-party terminals (of course, not to the same extent as its relatives). The fact is that this product was developed by a company that was absorbed by TANDBERG several years ago. Obviously, the product was designed for video conferencing in general. After absorption, this functionality was decided not to be removed.
')
TANBERG VCS Control
VCS stands for Video Control Server (not to be confused with a multipoint server). And if we discard the big words, it is a sip server and H.323 zone controller in one bottle. Sharpened by video and can connect devices from both these networks. Also, it is very useful when docking with third-party applications: ip-telephony, Cisco Unified Communications, Microsoft OCS, etc.
TANDBERG VCS ExpressWay
And this is a much more entertaining piece of iron (more precisely, an application): it serves to overcome firewalls. Firewalls, as you know, are designed to keep out. First of all, outside. Accordingly, if you try to connect because of the firewall with the remote terminal, then you will most likely be seen and heard, but the packets will not go in your direction, and you will sadly look at the dark silent screen. This is the RTP protocol.
What ExpressWay does: it sends incoming packets on the port that was initialized by the device behind the firewall, and, accordingly, can run over this connection, anything in both directions. Obviously, ExpressWay is located in a public network.
What it looks like
The figure shows how devices communicate with each other. I did not draw TMS, but it is implied: it is very difficult to steer this zoo without it.

When you need it
- With a large number of terminals;
- When docked with third-party services (at once I will make a reservation that you can do without all of this, but you will have to spend a lot of effort);
- In the presence of a distributed network and the inability to provide VPN at each point.
Conclusion
I do not work for TANDBERG (now Cisco), but I believe that their equipment is the best on the market in their fields (this does not mean the cheapest). In general, as managed told. Specially did not go into how connections are initialized and packages run; This information is enough for a couple of separate topics, if there is interest - I will write.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/95888/
All Articles