Search 2.0, as it may be
Take as a starting point two rather famous quotes:
Let us highlight the three main problems encountered in modern search engines.
The developers here have a special mantra for all occasions, which can be applied to the above questions - “The user himself does not know what he wants,” so we have to do what we do. Let me, when you ask your colleague or a passer-by, does he understand what you want from him?
Criticizing is the easiest thing to do, but what would you like to see in the search engines of tomorrow or in search 2.0?
And finally, a brief brief on their own attempts to solve the problems indicated at the beginning of the article (important note - all the services described below work only in English, for all are only prototypes). This is not a search 2.0, it is an optimizing add-on over Google, reformatting search results.
My first attempt to bring my own order to the search results I called Search explorer and located at newisearch.com . Among the main features:

')
The second attempt is the jabber agent agent@clisearch.net, which selects the five most appropriate paragraphs about the search subject. This is already a command line interface, but without context support and with a long response time, since a large number of resulting pages need to be processed.
Work example:
me: -q internet
agent:
1. It is a global system for interconnected computer networks (TCP / IP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of electronic and digital networking technologies. - en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
Multipurpose Wireless Computer World Wide Web - www.webopedia.com/internet.html
3. Most traditional media communications, such as telephone and Internet services, are reshaped or redefined using voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and IPTV. Newspaper publishing has been reshaped into Web sites, blogging, and web feeds. The Internet has been activated by the Internet. - en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
4. The origins of the Internet in the United States of America. This has been a globalization of the United States backbone by the National Science Foundation. applications. -http: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
5. The Internet today is a widespread information infrastructure, which is often called the National Infrastructure (or Global or Galactic) Information Infrastructure. Its history is complex and involves many aspects - technological, organizational, and community. It has been noted that it will not be a problem. - www.isoc.org/internet/history/brief.shtml
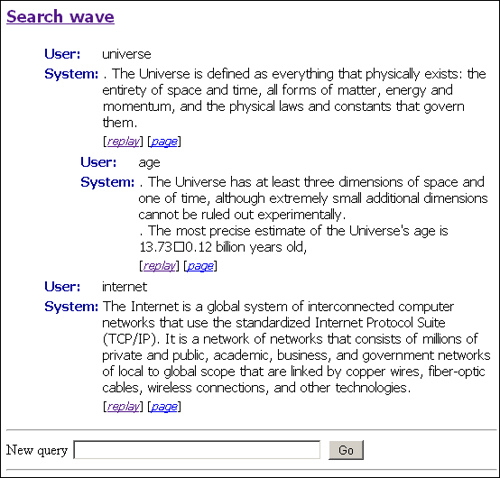
The following service implemented an attempt to build an interactive mode of operation with support for the conversation context. Since each branch of the discussion was similar to a wave in a well-known service, it was called a search wave ( newisearch.com/wave ).
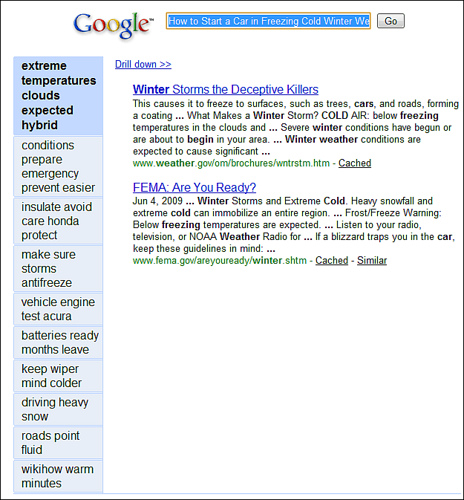
The last in this article attempt to optimize the search - Search summary ( newisearch.com/sum ), which instead of increasing the number of search results reduces them to the foreseeable number (forgive me optimizers), cutting them into topics. Among the main features:
This is where our homegrown efforts don't end, the next milestone is a semantic search. But that's another story.
- “Search engines have become one of the two new wonders of the world, giving Homo Sapiens unlimited and instant access to information.” Ilya Segalovich, “How search engines work”
- “The Internet is like a big dump: everything is there, but it’s impossible to find.” Popular wisdom
Let us highlight the three main problems encountered in modern search engines.
The main problems of finding information
- Instead of searching for information search for links to it .
Are you not tired of snippets yet? How much time is spent on a hike on the links, and the subsequent search for information on the pages. Yes, while we are spinning banners, visitor counters, etc., pleasing the owners, but no one suffers from the publication of the RSS feed? In 90 cases out of 100 we are looking for information, and we get a link where it may be located. Instead of instant access, the required information moves away from us beyond a certain barrier. - Instead of searching for the width of the search in depth .
At the request of the Internet, Yandex offers 602 million pages and this figure continues to grow. And if your interlocutor answers the question “What is the Internet”, “I heard this word 602 million times, which time are you interested in?”, You are unlikely to be satisfied. Most likely, our mental interlocutor will begin to talk about the protocols, if he is a technical specialist, or about social networks, otherwise. In any case, he will have one answer to the question. Even if this answer is completely accurate and absolutely useless, as in the well-known joke. - Mixed search results .
Ask the request "gull". You will receive in one heap information about watches, cars, birds, etc. Unified list, mixed with each other. Yes, there are timid attempts by some systems to derive a number of accompanying words or a cluster tree, but this will give rise to a new query with its local chaos. Why can not the issue be carefully cut into sections (and not accompanying words), and give the result for these sections? Birds are separate, machines are separate, otherwise the instantaneous access to information sinks under its heterogeneity.
The developers here have a special mantra for all occasions, which can be applied to the above questions - “The user himself does not know what he wants,” so we have to do what we do. Let me, when you ask your colleague or a passer-by, does he understand what you want from him?
Search Description 2.0
Criticizing is the easiest thing to do, but what would you like to see in the search engines of tomorrow or in search 2.0?
- Interface: web chat, command line interface (cli), instant messenger (im)
- Principle: dialogue between search engine and user
- Differences:
- ready information
- conversation context support ("and how much does IT cost?")
- Bonus:
- AI - the ability, at the expense of inference, to generate new information
- dialogue support (“Hello, how are you?”)
And finally, a brief brief on their own attempts to solve the problems indicated at the beginning of the article (important note - all the services described below work only in English, for all are only prototypes). This is not a search 2.0, it is an optimizing add-on over Google, reformatting search results.
Search explorer
My first attempt to bring my own order to the search results I called Search explorer and located at newisearch.com . Among the main features:
- Definition of context key phrases
- Clustering them into subject groups
- Group Navigation in Bookmark Mode
- The “I'm lucky” mode allows you to navigate not by the search results, but by the “ready-made” sites that are most relevant to the selected cluster.
- Search mode with indication of context for disambiguation. Example: the query “jaguar @car” will allow you to find results of the form “jaguar rides”, and the query “jaguar animal ” - “jaguar runs”.

')
Command line interface agent
The second attempt is the jabber agent agent@clisearch.net, which selects the five most appropriate paragraphs about the search subject. This is already a command line interface, but without context support and with a long response time, since a large number of resulting pages need to be processed.
Work example:
me: -q internet
agent:
1. It is a global system for interconnected computer networks (TCP / IP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of electronic and digital networking technologies. - en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
Multipurpose Wireless Computer World Wide Web - www.webopedia.com/internet.html
3. Most traditional media communications, such as telephone and Internet services, are reshaped or redefined using voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and IPTV. Newspaper publishing has been reshaped into Web sites, blogging, and web feeds. The Internet has been activated by the Internet. - en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
4. The origins of the Internet in the United States of America. This has been a globalization of the United States backbone by the National Science Foundation. applications. -http: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet
5. The Internet today is a widespread information infrastructure, which is often called the National Infrastructure (or Global or Galactic) Information Infrastructure. Its history is complex and involves many aspects - technological, organizational, and community. It has been noted that it will not be a problem. - www.isoc.org/internet/history/brief.shtml
Search wave
The following service implemented an attempt to build an interactive mode of operation with support for the conversation context. Since each branch of the discussion was similar to a wave in a well-known service, it was called a search wave ( newisearch.com/wave ).

Search summary
The last in this article attempt to optimize the search - Search summary ( newisearch.com/sum ), which instead of increasing the number of search results reduces them to the foreseeable number (forgive me optimizers), cutting them into topics. Among the main features:
- Breakdown of search results into a number of clusters, several snippets within each, with navigation between them.
- Opportunity to “fail” inside the selected cluster (drill down) - perform a new search with current keywords
- Further development of the project: on the right instead of snippets display sammarie

This is where our homegrown efforts don't end, the next milestone is a semantic search. But that's another story.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/94426/
All Articles