Google Global Cache - for favorites
One of the characteristics of Google is the provision of quality services, free of charge and profitable for you.
 Google Global Cache (GGC) is one of the solutions for optimizing huge volumes of its traffic based on the CDN platform, and also with user benefits (read providers).
Google Global Cache (GGC) is one of the solutions for optimizing huge volumes of its traffic based on the CDN platform, and also with user benefits (read providers).
The explosion of broadband and rich multimedia content is constantly increasing demand from Internet service providers (ISP). GGC allows Google to provide content, primarily video, from its own network (provider). This eases the load on the network and reduces the cost of transit links, thereby saving providers money, while at the same time increasing the level of customer service.
The GGC project is in beta, so the agreement with the provider is a commercial secret, and it is forbidden to use the mention of this service for their own purposes.
')
Without GGC, every user request from the provider’s network to YouTube videos, Google Apps, etc. creates a transit of this video instance over the network, from Google to the user.
With GGC, only the first copy of the video passes through the entire network. If another user requests the same video, Google serves it from the GGC node.
- reduction of traffic through networks : the percentage of requests through cache varies depending on the usage pattern of users, but typical performance is close to 75%,
- quick response, transparent to users : Google transparently serves users requests from the cache within the network,
- easy installation : installation requires a rack (cabinet), a laptop, a copy of a CD from Google, as well as an Internet connection. Once the servers have been configured and accessible from the network, Google will do the rest of the work and monitor it remotely,
- reliability : the node has several levels of redundancy. If the GGC node is unavailable for any reason, user requests will be sent transparently to Google.
When a user requests parts of content — for example, video, web pages, or images — Google systems determine if this resource can be provided from a GGC node within the network, and if the user has access to the GGC node.
If the GGC node already has a cached version of the requested content in its local cache, it will provide the content directly to the end user, improving user experience and saving money for Internet transit.
If the content is not stored on the GGC site, the site downloads them from Google, provides it to the user, and stores it for future requests.
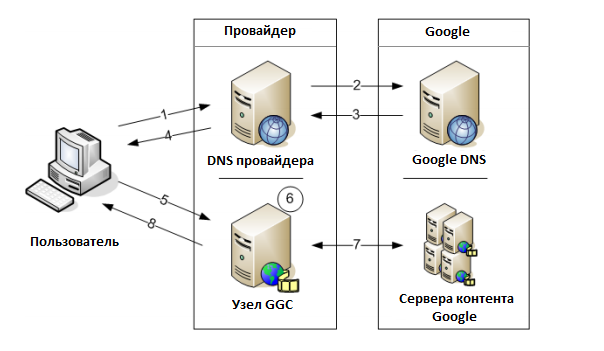
1. The user requests the link video or other content posted on Google. The computer generates a DNS query for the host address.
2. DNS provider requests Google's DNS to host IP address with content.
3. Google's DNS knows that you have GGC, so the answers contain the IP addresses of the provider’s GGC.
This is known because the provider announced the DNS resolver IP addresses to the GGC host (via BGP) and Google updated the information in its DNS.
4. DNS provider responds the GGC host IP address to the user.
5. The user's computer sends a request to the IP address that is routed to the GGC node.
6. The node confirms that the user has access to this node (done by matching the user's IP address to the list of IP blocks announced through the BGP node.) If the address is not in the list, the user is redirected to the cache on the Google network.
7. If the content is not contained on the GGC node, the node requests content from Google and caches it.
8. After the GGC node contains content, gives it to the user. Content is contained in the site, so the next request can be sent without a request to Google.
Google provides the necessary equipment, the provider must provide accommodation with its premises, power from the electrical network and an Internet connection.
GGC runs on rack mountable servers, 3-8 in each cluster.
Server specifications
• 2 RU Rack-mountable chassis
• 74cm L x 44cm Sh x x 8.64cm V
• Weight: 28 KG
• Power supply: 2x 110/220 VAC.
• 4 x 1000Base-T copper Gigabit Ethernet
• IP Addressing: dedicated subnet (one broadcast domain).

Possible configurations:
3 servers - 6RU 1200W
4 servers - 8RU 1600W
6 servers - 12RU 2400W
8 servers - 16RU 3200W
Uses ggcadmin.google.com for site configuration and shipping information. The initial user is accessing the portal from the GGC group.
After accepting the beta agreement, the user can invite additional users.
- Google retains ownership of the hardware and software that makes up the site. Google will be responsible for the maintenance, support and shipping costs associated with server hardware,
- According to Google assurances, user privacy is paramount.
Personal information (Personally Identifiable Information) or private user content is not stored on the GGC node,
- Google reserves the right to require providers of assurances of non-disclosure of the use of the service, since the project is in beta.
Why for your favorites you ask?
The fact is that Google usually offers such services only to those providers that are present at the largest traffic exchange points and if the traffic to demanding Google services (youtube, maps) make up a significant percentage of traffic (> 70%).
Related Links:
Google @ Peering DB
Google regional caching and media reaction to it
Here is an example.

 Google Global Cache (GGC) is one of the solutions for optimizing huge volumes of its traffic based on the CDN platform, and also with user benefits (read providers).
Google Global Cache (GGC) is one of the solutions for optimizing huge volumes of its traffic based on the CDN platform, and also with user benefits (read providers).But what is it all the same?
The explosion of broadband and rich multimedia content is constantly increasing demand from Internet service providers (ISP). GGC allows Google to provide content, primarily video, from its own network (provider). This eases the load on the network and reduces the cost of transit links, thereby saving providers money, while at the same time increasing the level of customer service.
The GGC project is in beta, so the agreement with the provider is a commercial secret, and it is forbidden to use the mention of this service for their own purposes.
')
System overview
Without GGC, every user request from the provider’s network to YouTube videos, Google Apps, etc. creates a transit of this video instance over the network, from Google to the user.
With GGC, only the first copy of the video passes through the entire network. If another user requests the same video, Google serves it from the GGC node.
GGC Features
- reduction of traffic through networks : the percentage of requests through cache varies depending on the usage pattern of users, but typical performance is close to 75%,
- quick response, transparent to users : Google transparently serves users requests from the cache within the network,
- easy installation : installation requires a rack (cabinet), a laptop, a copy of a CD from Google, as well as an Internet connection. Once the servers have been configured and accessible from the network, Google will do the rest of the work and monitor it remotely,
- reliability : the node has several levels of redundancy. If the GGC node is unavailable for any reason, user requests will be sent transparently to Google.
How GGC works
When a user requests parts of content — for example, video, web pages, or images — Google systems determine if this resource can be provided from a GGC node within the network, and if the user has access to the GGC node.
If the GGC node already has a cached version of the requested content in its local cache, it will provide the content directly to the end user, improving user experience and saving money for Internet transit.
If the content is not stored on the GGC site, the site downloads them from Google, provides it to the user, and stores it for future requests.
Query diagram

1. The user requests the link video or other content posted on Google. The computer generates a DNS query for the host address.
2. DNS provider requests Google's DNS to host IP address with content.
3. Google's DNS knows that you have GGC, so the answers contain the IP addresses of the provider’s GGC.
This is known because the provider announced the DNS resolver IP addresses to the GGC host (via BGP) and Google updated the information in its DNS.
4. DNS provider responds the GGC host IP address to the user.
5. The user's computer sends a request to the IP address that is routed to the GGC node.
6. The node confirms that the user has access to this node (done by matching the user's IP address to the list of IP blocks announced through the BGP node.) If the address is not in the list, the user is redirected to the cache on the Google network.
7. If the content is not contained on the GGC node, the node requests content from Google and caches it.
8. After the GGC node contains content, gives it to the user. Content is contained in the site, so the next request can be sent without a request to Google.
Equipment provided by Google
Google provides the necessary equipment, the provider must provide accommodation with its premises, power from the electrical network and an Internet connection.
GGC runs on rack mountable servers, 3-8 in each cluster.
Server specifications
• 2 RU Rack-mountable chassis
• 74cm L x 44cm Sh x x 8.64cm V
• Weight: 28 KG
• Power supply: 2x 110/220 VAC.
• 4 x 1000Base-T copper Gigabit Ethernet
• IP Addressing: dedicated subnet (one broadcast domain).

Possible configurations:
3 servers - 6RU 1200W
4 servers - 8RU 1600W
6 servers - 12RU 2400W
8 servers - 16RU 3200W
Administration
Uses ggcadmin.google.com for site configuration and shipping information. The initial user is accessing the portal from the GGC group.
After accepting the beta agreement, the user can invite additional users.
Other details
- Google retains ownership of the hardware and software that makes up the site. Google will be responsible for the maintenance, support and shipping costs associated with server hardware,
- According to Google assurances, user privacy is paramount.
Personal information (Personally Identifiable Information) or private user content is not stored on the GGC node,
- Google reserves the right to require providers of assurances of non-disclosure of the use of the service, since the project is in beta.
Why for your favorites you ask?
The fact is that Google usually offers such services only to those providers that are present at the largest traffic exchange points and if the traffic to demanding Google services (youtube, maps) make up a significant percentage of traffic (> 70%).
Related Links:
Google @ Peering DB
Google regional caching and media reaction to it
Here is an example.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/93864/
All Articles