Administering WEB SQL DB in Chrome
Having read this post once, after having rummaged through w3c drafts, I began to try to figure it out.
At once I will make a reservation that the technology of data storage on the client side is not a new thing. And in this version, so also, to a greater degree, webkit ( webkit ) and even under html5, so it can scare away many.
I will not tell you how it works (there are links a little higher, everything is described in detail there), but I would like to turn my attention to database administration using the Chrome browser above ...
Well, let's get started. Let me remind you that in order to launch our “admin panel” just press Ctrl + Shift + I
The window is divided into 3 parts: in the left - the list of databases with tables, in the right - the window for entering sql-scripts, in the bottom - the window for entering js-scripts
In order to create (or connect our previously created database), you need to write the following js script in the console
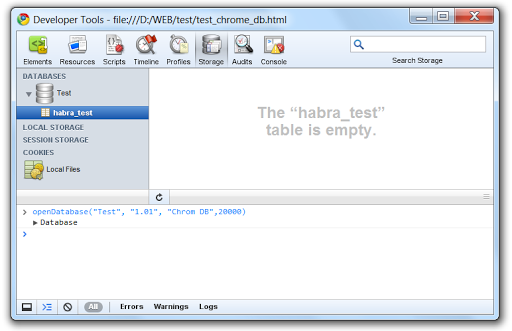
openDatabase("Test", "1.01", "Chrome DB",20000)(about syntax more here )
')
and further by a simple algorithm:
create a table

as we see it is a bit empty ...

... fill it by writing the usual insert
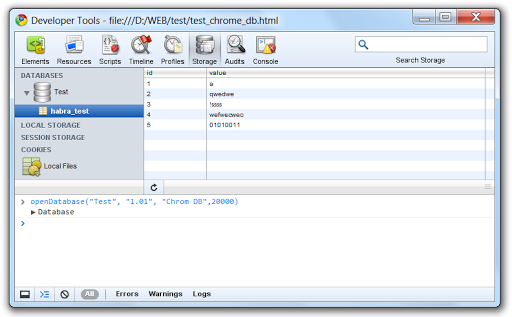
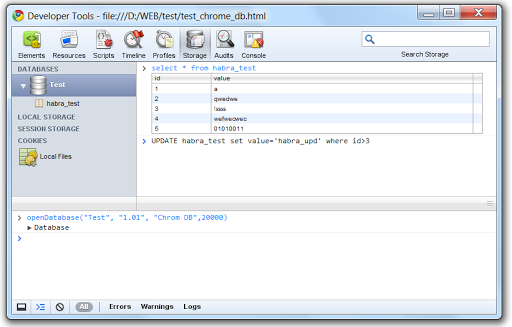
When the table is ready, we can perform various manipulations with it (select, update ...)
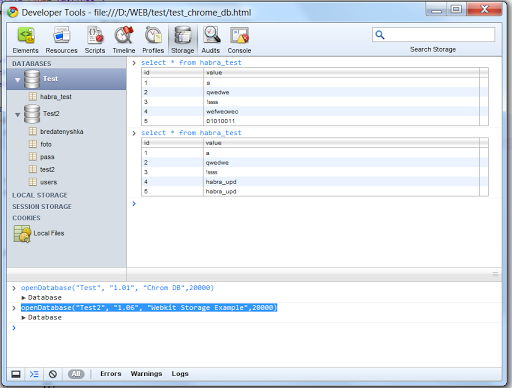
In addition to how to create, with the same command we can attach a previously created database with ready, “work tables”
Database files are stored in XP at
C:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\databases\file__0\It's so easy to administer (even if it's loud, but the term is a term) web sql db with the help of our favorite chrome.
I hope this little knowledge will help you create interesting local applications for your purposes, as well as beautiful, powerful extensions.
Thanks for attention!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/92677/
All Articles