Mastery of targeted use of keywords and page optimization
Post published at the request of a good person.
If you are a SEO (SEO), then you often hear this question. Unfortunately, there is no definite answer. But, nevertheless, there is a set of useful techniques that will help to get closer to the answer to this question. In this post, I will share our best recommendations for achieving “perfection” page optimization and keyword placement. Or at least something close to it. Some of our tips are supported by data, research and testing results, others are based on intuition and general experience. As with all CEO tips, we recommend constant testing and honing, but this post will help you begin the optimization process.
An example of a “perfect” page optimization with the key phrase “chocolate donuts”:

')
HTML Head Tags
Naturally, the use of a keyword or phrase at the very beginning of the page header has a direct correlation with high wounds *, while shifting keywords leads to a decrease in the wound.
URL
Body Tags
Internal links and location in the site architecture
Page structure
The answer is quite simple. The truth is that in the process of issuing excellent web content we sometimes forget, sometimes ignore, and sometimes deliberately do not obey these rules the best SEO optimization. Optimizing the page, while undoubtedly important, is only part of a larger ranking formation puzzle:
Components of the Google ranking algorithm (based on a survey of 72 optimizers in SEOmoz's Biennial Search Ranking Factors survey):
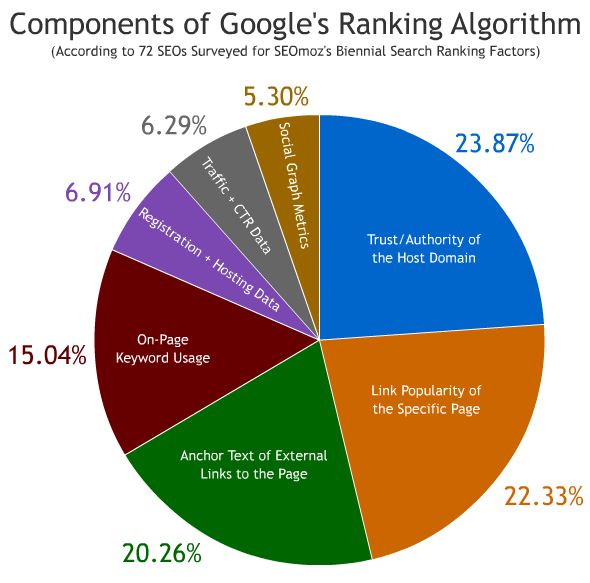
Naturally, the correct optimization of the page gives a tangible result, but, in my opinion, it follows the 80 to 20 rule. If you manage to apply 20% of the most important elements (title, URLs, internal links) that are described in this article, then you get 80% (or even more) of the maximum possible result from page optimization.
Interestingly, page optimization (on-page optimization) does not play the most important role in the quest to achieve the top ranking. In fact, the complete list that leads to the first position looks like this:
Translation into Russian - A. Savin, comments and additions - A. Fayustov.
* Note: the article uses terms that I do not know how to properly translate. For example, I translate the ranking as a ranking, and this word, in my opinion, is more beautiful and logical than the conventional “issue”.
Written at the request of d3sp
All the bumps him :)
How to create the most optimized web page?
If you are a SEO (SEO), then you often hear this question. Unfortunately, there is no definite answer. But, nevertheless, there is a set of useful techniques that will help to get closer to the answer to this question. In this post, I will share our best recommendations for achieving “perfection” page optimization and keyword placement. Or at least something close to it. Some of our tips are supported by data, research and testing results, others are based on intuition and general experience. As with all CEO tips, we recommend constant testing and honing, but this post will help you begin the optimization process.
An example of a “perfect” page optimization with the key phrase “chocolate donuts”:

')
HTML Head Tags
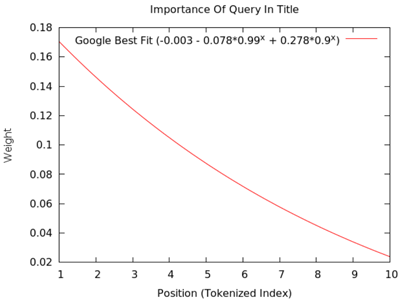
- Title is the most important page element that should use keywords or phrases at the very beginning of the tag. In our studies of correlation data, we came up with the following graph:
The importance of the query in the Title tag. The horizontal axis is the position of the keyword in the page title, the vertical is the weight for Google. Accordingly, the closer the keyword is to the beginning of the title, the greater its weight.

Naturally, the use of a keyword or phrase at the very beginning of the page header has a direct correlation with high wounds *, while shifting keywords leads to a decrease in the wound.
- Meta Description - although this information is not used for ranking by any of the leaders of search engines, this tag is an important place to use a keyword or phrase because it is highlighted in a short piece of text (snippet), which is displayed in the list of search results. The use of this tag also helps to increase the click rate (CTR or click-through rate) from the search results, thus increasing traffic from search engines regardless of the page rank.
- Meta Keywords - Yahoo! is the only search engine that uses the meta keyword tag for page recognition, but not for ranking. And now, when the Bing system of Microsoft replaces the search for Yahoo !, the last of the reasons for using this tag goes into oblivion. This fact, as well as the danger of using keywords in this tag for competition research, has led to the fact that SEOmoz never recommends using this tag.
- Meta Robots - tag is also optional for use. The only thing that this tag should not contain is the instructions for restricting access to search engines.
- Rel = "Canonical" - the larger and more complex the site (and, therefore, the more complex the organization that works on it), the more often we recommend using the canonical URL tag to prevent the creation of duplicate pages, inadvertently added URL strings, which will lead to problems with search engines and will lead to the wasting of potential "link juiciness" (link juice).
- Other Meta tags - tags offered by DCMI or FGDC look attractive, but currently do not carry any benefits for SEO with the main search engines, as well as create unnecessary complications and increase page loading speed.
URL
- Length - short URLs “perform” better in search results, and also most likely will copy them, rather than long ones, in order to share or link them.
- Keyword Locations - The closer the keywords are to the domain name in the URL, the better. Thus, site.com/keyword performs better than site.com/folder/subfolder/keyword, and thus this is the most recommended optimization method (although it will not be of great benefit in ranking)
- Subdomains or Pages? - Despite the slight advantage of using keywords in a subdomain over folders or pages, the algorithms of popularity of search engine links shift the balance towards the advantage of folders / pages rather than towards subdomains.
- Slo-delimiters - Dashes (or hyphens) still occupy the “kings” niche among the delimiters in URLs, and despite promises that underscores get the same weight, inconsistencies with other methods lead to the fact that you must use a dash ( hyphen).
Body Tags
- Number of Keyword Repeats - It is not possible to specify the exact or optimal number of times a keyword is used on a page. But here is a rule that has served us for a long time. "2-3 times on a short page, 4-6 times on a big one, and never more than common sense requires in the context of the information on the page." The resulting effect from another use of the keyword is so low that the aggressive use of this parameter is simply unwise.
- Keyword Density - Being no more than a myth, this algorithmic component of keyword density nevertheless tries to capture the minds of even real SEO SEOs. Although using more frequent keywords can potentially increase rankings, there is no doubt that keyword density has never been a formula for calculating ranking relevance.
- Using variations of Keywords - The suspected influence of this parameter on the ranking of search engines, which, incidentally, has never been studied deeply enough, can nevertheless help optimize the content, which means that it should be paid attention. We recommend using at least one or two variations of the keyword, as well as the separation of key phrases in the text.
- H1 Title - This H1 tag has long been considered very important for page optimization. Our latest correlation studies show that this parameter has very little connection with high wounds (almost none, in fact). But, despite the indisputable proof of the insignificance of the connection between H1 and the ranking, we still recommend using it as the title of the page, as well as using the keyword in this title
- H2 / H3 / H4 / Hx Tags - Even less significant than H1, and therefore it is recommended to use these tags only when necessary. These tags have (almost) no weight in SEO optimization.
- Alt attribute - Unexpectedly, this attribute, long considered insignificant, showed a rather serious connection with high wounds in the course of our research. Thus, we strongly recommend the use of graphic components (images, photos, etc.) on important landing pages along with the key phrase in the ALT attribute in the IMG tag.
- File name of the picture - Due to the fact that searching by pictures can bring a sufficiently large amount of traffic to your page, the use of keywords used on the page is recommended in the file names.
- Bold selection - The use of keywords in bold selection (bold) has a very sooooo little weight in SEO, however, highlighting keywords at least once is recommended.
- Oblique selection - Unexpectedly, the selection by tilt (Italic) shows a higher correlation with high wounds than the selection by bold, and therefore it is recommended to use this parameter on keywords or phrases in the text.
- Internal Link Anchors - None of the testing has yet proven that search engines take this text into account in their log rhythms. Or, speaking in the slang of SEOs, the title of anchors is not taken into account by search engines during internal linking.
- HTML Comments - As above, it is obvious that search engines ignore text in comments.
Internal links and location in the site architecture
- Clicks-Depth - The general recommendation is that the keyword phrase will take the larger the rank, the higher it will be in the structure of the site, and thus, the less clicks need to be made to get to this URL.
- Number and percentage of internal links - The pages most often referred to have a HIGHER WEIGHT. Therefore, a greater number of links to a page can help in ranking (yes, internal links are also taken into account).
- Links in content and permanent navigation - It turns out that Google and other search engines are trying to recognize the position on the page as an element in the parsing links. Thus, the use of links in the style of Wikipedia in the body of the page, rather than in permanent navigation, can give a certain bonus. Do not forget that Google considers only the first link to the page that it sees in HTML.
- Linking to sidebars and footers (Sidebars & Footers) - Recent patent applications, search engine publications, and SEOmoz and other SEO practitioners' experience suggest that Google is likely to stop using footers and to a lesser extent in sidebars . Thus, if a link is used in permanent navigation, it makes sense to use the top navigation menu (above content) for SEO optimization purposes.
Page structure
- Keyword Location - It is recommended that important keywords be encountered in the first 50-100 words, or even earlier, of the page content. Search engines seem to prefer those pages where keywords appear earlier in the text.
- Content Structure - Some SEO practices claim that the content format — introduction, body, examples, conclusions OR the journalistic style of the story, data, conclusions or allegory — affects the optimization, but there is no specific data supporting this fact. Nevertheless, the format that is most suitable for content and visitors is considered ideal.
Why do we not always obey these rules?
The answer is quite simple. The truth is that in the process of issuing excellent web content we sometimes forget, sometimes ignore, and sometimes deliberately do not obey these rules the best SEO optimization. Optimizing the page, while undoubtedly important, is only part of a larger ranking formation puzzle:
Components of the Google ranking algorithm (based on a survey of 72 optimizers in SEOmoz's Biennial Search Ranking Factors survey):

Naturally, the correct optimization of the page gives a tangible result, but, in my opinion, it follows the 80 to 20 rule. If you manage to apply 20% of the most important elements (title, URLs, internal links) that are described in this article, then you get 80% (or even more) of the maximum possible result from page optimization.
Practical ranking tips
Interestingly, page optimization (on-page optimization) does not play the most important role in the quest to achieve the top ranking. In fact, the complete list that leads to the first position looks like this:
- Accessibility - the content that search engines will not see or to which they will not get, will never be able to influence the formation of the ranking. So, the availability of content plays the largest role.
- Content - your site should contain highly attractive, high-quality material that will not only attract interest, but also encourage visitors to share this information. Content virality is the most important factor in ranking calculation, because it will create the highest link conversion rate (the ratio of those who visited the site to those who made a link to it after viewing).
- Basic Page Elements (On-Page Elements) - correctly using keywords in the most important elements (headings, URL, internal links) gives a big bonus for ranking the page.
- Visitor's experience - the user experience, the interface and the overall impression of the site greatly influence the creation of links and quotes, as well as the conversion rate and navigation through the site from incoming traffic.
- Marketing - I want to say that "great content will not replace great marketing." An excellent marketing machine or a powerful campaign has the power to attract far more links than, say, content can deserve it. And although this may seem dishonest, this is the principle on which capitalism has worked for the last hundreds of years. Spreading information is often as important (and even more important) than being right, being honest, or being valuable.
- Deep Page Optimization - neatly attaching all 5 points just above - is really useful. But, for better or worse, deservedly being at the bottom of the list, this optimization does not give the same value for the ranking than the first 5 points.
Translation into Russian - A. Savin, comments and additions - A. Fayustov.
* Note: the article uses terms that I do not know how to properly translate. For example, I translate the ranking as a ranking, and this word, in my opinion, is more beautiful and logical than the conventional “issue”.
Written at the request of d3sp
All the bumps him :)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/88070/
All Articles