Mobile radio - PTT
The progress of the development of technologies for mobile networks does not stand still, and with each new standard and technology for mobile networks, new possibilities of using the network are opening up to the final subscribers. In our talk today about mobile technologies, we will discuss additional functionality based on voice data packet transmission - Push-To-Talk (PTT, P2T, Press-To-Transmit).
PTT technology or, to be precise, PoC (PTT over Cellular) is not at all a new service in mobile networks, but the feature of providing this technology involves the introduction of new elements into the GSM network architecture of operators that are “borrowed” from IMS architecture and thereby ultimately promote introducing more efficient methods of transmitting information to the operator’s network, as well as to some extent simplifying the evolution of the network to newer standards.
Let's see what is this technology in general.
')
So ... ROC technology (similar technology Walkie-Talkie) allows us to use the phone as a walkie-talkie in the usual sense and allows you to send a voice message to an active group / subscriber. Just like a regular walkie-talkie, you need to press and hold during a conversation a special key, called the "tangent". At the same time, the main difference from regular circuit-switched conversation will be that your short voice message will be transmitted via packet data channels, i.e. GPRS / EDGE and naturally will be much cheaper for the end user. Each piece of voice data is delivered to the recipient via a dedicated PTT server in the mobile operator’s network. For speech encoding, the AMR codec (5.15 Kb / s) is used. The user can use voice data transfer to another user (unicast) or group of users (multicast).
In the case of PTT, the optimal response time is determined at the level of 1-1.5 seconds, and the transmission time of a voice message (delay) is calculated at a level of up to 2 seconds. To interfere with the transmission of voice information is impossible, as in the "classic" radio broadcast using radio. In the case of a lively transmission, the interlocutors will be serviced in turn, in the sequence to which they will press and hold the “Conversation” button (the “Tangent” key).
The conversation is carried out in the classic half-duplex mode (simultaneous one-way communication), i.e. the interlocutor hears you only when you hold down the “Talk” key, in turn you will be able to hear other members of your group only when you have released “Tangenta”.
The main advantage of this technology over “classic” portable radio stations is of course the distance at which you are available to other participants, because in this case, the restriction is only the coverage area of the mobile operator.
At the same time, the talk mode is very similar to the implementation scheme of voice services in IP-telephony, since the same protocols are used - SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol):
The general scheme for the implementation of the PTT service can be presented as follows:
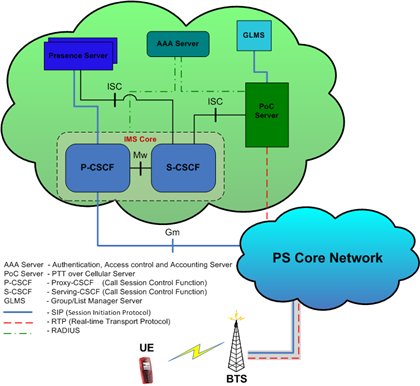
The main functions of the GCS server include terminal SIP signaling, voice message delivery, message service for user groups and an individual subscriber, collection and transmission of billing data.
The GLMS or group management server contains information about group membership, access lists, and permissions for members of each group.
The P-CSCF and S-CSCF are part of the IMS (IP Multimedia System) and are the gateway between the operator’s network and the IMS itself. We will not go deep into the details of IMS, because this goes beyond our discussion today and will be covered in more detail in the relevant IMS article.
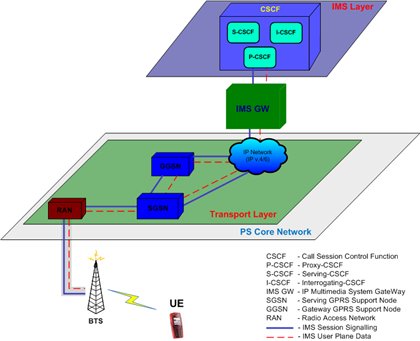
We only note that there are several levels of separation and the main network elements of the mobile operator are located on the so-called. transport layer ( Transport Layer ), and IMS elements - on a higher level ( IMS Layer ). For "communication" between levels there is a certain IMS Gateway .
In case of support by the mobile network Traffic Class Streaming , a separate PDP Context is activated for RTP / RTCP packets, and so-called SIP and http requests are used for signaling. Traffic Class Interactive. If the Streaming class is not supported by the network, then it is possible to use two separate PDP Contexts for signaling and RTP data, respectively. It is also possible to use one PDP Context for both signaling and RTP data.
The scheme of establishing a session with another subscriber / group of subscribers can be represented as a diagram below. At the same time, we will assume that the subscriber has already performed GPRS Attach and activated at least one PDP Context (these two procedures are discussed in more detail in the article: “Inside GPRS. Part 2” ).
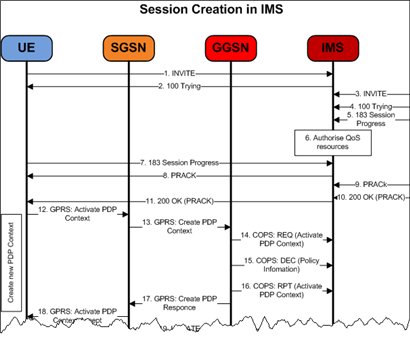
As we see, the establishment of a session with another subscriber, i.e. the transmission of a voice message on air is very similar to the transmission of voice information in IP-telephony, since SIP protocol is used.
It should be noted that in the mobile device market there is a rather wide selection of those supporting the PoC service, most of the devices are represented by Nokia and Motorola, which widely developed and promoted the PoC standard.
The ROS service is in demand for taxi services, tourist organizations, groups of subscribers constantly exchanging short voice data, is a kind of alternative to conference calls.
The introduction of the service itself shows the gradual transition of operators to the concept of IMS, which in itself is a good indicator. Further development of the PoC service involves deeper integration with multimedia services, for example, a subscriber can find another subscriber using the so-called LBS (Location-Based Services), then will be able to send him a short message using the PoC service, possibly send him a short text message (MIM) or multimedia message (MMS).
Another direction of PoC service development is the provision of so-called. Push-to-video [PTV] of services that allow you to send / start a video message to another subscriber / group of subscribers using a mobile terminal.
A small assistant:
AAA Server - Authentication, Authorization & Accounting Server
BTS - Base Transceiver Station
ISC - InterSystem Communication
MIM - Mobile Instant Messaging
MMS - Multimedia Messaging Service
PS Core - Packet Switched Core
RADIUS - Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
RTCP - RTP Control Protocol
RTP - Real-time Transport Protocol
UE - User Equipment
Related links (en):
Intro
PTT technology or, to be precise, PoC (PTT over Cellular) is not at all a new service in mobile networks, but the feature of providing this technology involves the introduction of new elements into the GSM network architecture of operators that are “borrowed” from IMS architecture and thereby ultimately promote introducing more efficient methods of transmitting information to the operator’s network, as well as to some extent simplifying the evolution of the network to newer standards.
Let's see what is this technology in general.
')
So ... ROC technology (similar technology Walkie-Talkie) allows us to use the phone as a walkie-talkie in the usual sense and allows you to send a voice message to an active group / subscriber. Just like a regular walkie-talkie, you need to press and hold during a conversation a special key, called the "tangent". At the same time, the main difference from regular circuit-switched conversation will be that your short voice message will be transmitted via packet data channels, i.e. GPRS / EDGE and naturally will be much cheaper for the end user. Each piece of voice data is delivered to the recipient via a dedicated PTT server in the mobile operator’s network. For speech encoding, the AMR codec (5.15 Kb / s) is used. The user can use voice data transfer to another user (unicast) or group of users (multicast).
In the case of PTT, the optimal response time is determined at the level of 1-1.5 seconds, and the transmission time of a voice message (delay) is calculated at a level of up to 2 seconds. To interfere with the transmission of voice information is impossible, as in the "classic" radio broadcast using radio. In the case of a lively transmission, the interlocutors will be serviced in turn, in the sequence to which they will press and hold the “Conversation” button (the “Tangent” key).
The conversation is carried out in the classic half-duplex mode (simultaneous one-way communication), i.e. the interlocutor hears you only when you hold down the “Talk” key, in turn you will be able to hear other members of your group only when you have released “Tangenta”.
The main advantage of this technology over “classic” portable radio stations is of course the distance at which you are available to other participants, because in this case, the restriction is only the coverage area of the mobile operator.
At the same time, the talk mode is very similar to the implementation scheme of voice services in IP-telephony, since the same protocols are used - SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol):
- SIP is used as a signaling protocol
- RTP to transfer voice data directly
The general scheme for the implementation of the PTT service can be presented as follows:

The main functions of the GCS server include terminal SIP signaling, voice message delivery, message service for user groups and an individual subscriber, collection and transmission of billing data.
The GLMS or group management server contains information about group membership, access lists, and permissions for members of each group.
The P-CSCF and S-CSCF are part of the IMS (IP Multimedia System) and are the gateway between the operator’s network and the IMS itself. We will not go deep into the details of IMS, because this goes beyond our discussion today and will be covered in more detail in the relevant IMS article.

We only note that there are several levels of separation and the main network elements of the mobile operator are located on the so-called. transport layer ( Transport Layer ), and IMS elements - on a higher level ( IMS Layer ). For "communication" between levels there is a certain IMS Gateway .
QoS requirements for RoS
In case of support by the mobile network Traffic Class Streaming , a separate PDP Context is activated for RTP / RTCP packets, and so-called SIP and http requests are used for signaling. Traffic Class Interactive. If the Streaming class is not supported by the network, then it is possible to use two separate PDP Contexts for signaling and RTP data, respectively. It is also possible to use one PDP Context for both signaling and RTP data.
The scheme of establishing a session with another subscriber / group of subscribers can be represented as a diagram below. At the same time, we will assume that the subscriber has already performed GPRS Attach and activated at least one PDP Context (these two procedures are discussed in more detail in the article: “Inside GPRS. Part 2” ).

As we see, the establishment of a session with another subscriber, i.e. the transmission of a voice message on air is very similar to the transmission of voice information in IP-telephony, since SIP protocol is used.
Summary
It should be noted that in the mobile device market there is a rather wide selection of those supporting the PoC service, most of the devices are represented by Nokia and Motorola, which widely developed and promoted the PoC standard.
The ROS service is in demand for taxi services, tourist organizations, groups of subscribers constantly exchanging short voice data, is a kind of alternative to conference calls.
The introduction of the service itself shows the gradual transition of operators to the concept of IMS, which in itself is a good indicator. Further development of the PoC service involves deeper integration with multimedia services, for example, a subscriber can find another subscriber using the so-called LBS (Location-Based Services), then will be able to send him a short message using the PoC service, possibly send him a short text message (MIM) or multimedia message (MMS).
Another direction of PoC service development is the provision of so-called. Push-to-video [PTV] of services that allow you to send / start a video message to another subscriber / group of subscribers using a mobile terminal.
A small assistant:
AAA Server - Authentication, Authorization & Accounting Server
BTS - Base Transceiver Station
ISC - InterSystem Communication
MIM - Mobile Instant Messaging
MMS - Multimedia Messaging Service
PS Core - Packet Switched Core
RADIUS - Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
RTCP - RTP Control Protocol
RTP - Real-time Transport Protocol
UE - User Equipment
Related links (en):
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/86342/
All Articles