Electronics in Formula 1 cars

Modern race cars in Formula 1 are simply equipped with the most sophisticated electronic systems. Despite all the new and new restrictions imposed by the FIA, the electronics control most of the car’s systems - engine, brakes, gear changes and even fuel composition. However, rarely does a race end without the descent of any pilot due to problems with the electronics.
In the car laid about a kilometer of wires and there are about 100 sensors that monitor the work of various nodes. This is controlled by the unified electronic control unit (ECU). He tries to ensure that all systems work as efficiently as possible.
')
Engine
The maximum allowed engine capacity is 2.4 liters (turbocharging is prohibited). However, he manages to give out almost 900 horsepower and accelerate the car to 360 kilometers per hour. Engine adjustments are completely changed from track to track, depending on the characteristics of the circle. For example, in Monaco, the ECU helps the driver to get more control over the gas pedal in the first half of its stroke, making it very sensitive, and the second half of the stroke of the gas pedal - less. This allows the pilot to limit the acceleration at the exit of sharp turns, not allowing the car to slip.
This is all possible due to the fact that there is no rigid connection between the gas pedal and the engine. The position of the gas pedal is controlled by the sensor, the data from which are transmitted to the ECU, and that one sends them to the engine. In addition to the gas pedal, the ECU controls the timing of the opening of the intake valve, the fuel injection system and some other elements of the engine, ensuring maximum torque.
Transmission
The ECU controls the operation of the clutch and gearbox. A racer engages the clutch only once - when it starts. After that, everything is done by electronics. It shifts gears in about 0.1 seconds, which allows the pilot not to take his foot off the gas pedal when raising the gear. The ECU also synchronizes the engine and gearbox, which prevents the machine from jerking. In addition, a special device does not allow the engine to stall in an accident or skidding.
Differential
The ECU controls the operation of the electronic differential, which tracks the difference in the speed of rotation of the rear wheels at the entrance to the turns and at the exit from them.
Steering wheel
Each steering wheel costs about $ 40 thousand and it takes about 100 hours to make. The steering wheel consists of about 120 parts and weighs 1.3 kg.
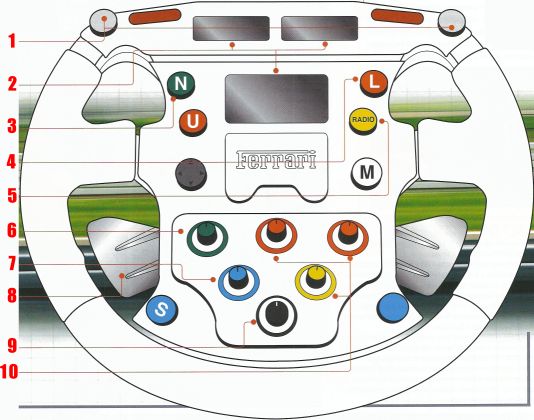
1. Multifunction buttons - the display shows which operation is performed
2. The display shows various information, such as engine speed, sector and lap time
3. Neutral gear
4. Turn on the speed limiter
5. Turning on radio communication between the racer and the boxes
6. Power steering adjustment
7. Changes in the composition of the fuel mixture
8. Gear shift.
9. Brake balance adjustment
10. The three buttons on the right serve to tune the motor.
Telemetry
Information about every aspect of the car is constantly transmitted to the pits. Formula 1 car has two types of telemetry:
1. Microwave packet signal that is sent to the engineers every time the car passes by the boxes. The signal has a size of about 4 megabytes and gives engineers the most important information about everything that happens to the car.
2. The second type is a system operating in real time. It transmits only the most basic information, such as the position on the track, the amount of fuel and simple sensor readings.
Signals are sent to the boxes via a small antenna located on the car. It is usually located on the side panel, which is closest to the boxes. However, some teams install the antenna in the side mirror so that there are no unnecessary protruding objects.
Full information about the work of the car during the race (about 40 megabytes) is already transmitted upon return to the pits. Information is loaded into a laptop connected to the car through a special socket, usually located in the side panel or near the neck of the fuel tank.
By the way, for each race, teams bring about 30 kg of equipment to process the information received.
BY
Almost all teams use software received from their partners. Some teams have such giants as Hewlett Packard, Compaq, TAG Electronics. The exception is McLaren, who developed their own ATLAS (Advanced Telemetry Linked AcquisitionSystem) system. It is considered that ATLAS is an advanced system in Formula 1.
As an epilogue, I would like to say that very many systems used in Formula 1, over time, moved into the ordinary auto industry. Starting from the ABS, which is in every new car, and ending with the permanent telemetry systems that are just appearing in concepts.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/86008/
All Articles