The sun is simple. Part Four: Fluctuations on the Sun's Surface
In my previous parts: 1 2 and 3 I talked about research tools, radio emission mechanisms and briefly spoke about solar flares. Today I will continue this series of topics and talk about helioseismology, that is, the oscillations on the sun. Below is a video of the oscillating portion of the active region of the Sun:
Earth seismology is based on the peculiarities of the propagation of sound under the ground. However, a seismograph (a device that records the fluctuations of the soil) cannot be placed on the Sun. Therefore, the fluctuations of the sun are measured by completely different methods. The main one is based on the Doppler effect. Since the solar surface rhythmically descends and rises (oscillates), its approach and removal affects the spectrum of the emitted light. Studying the spectra of different parts of the solar disk, get a picture of the velocity distribution; Of course, over time it changes - the waves run. The periods of these waves lie in the range of about 3 to 10 minutes. When they were first opened, the period found was approximately 5 minutes. Since then, all these fluctuations are called "five-minute." In the sixties of the XX century, astronomers found that the upper layer of the solar atmosphere rises and falls every five minutes.
A new path to the study of the inner layers of the Sun has opened helioseismology. Constant wave motion, like seismic waves on Earth, shakes the bowels of the sun. As geophysicists study seismic waves in order to understand the conditions inside the Earth, so solar physicists use the oscillations observed on the surface of the Sun to get information about its internal structure. In the gaseous medium of the Sun, waves of compression and rarefaction — acoustic waves — and internal gravitational waves, in which the force of gravity is the restoring force, can propagate. The focus is on acoustic waves, as they are best observed. The propagation of acoustic waves inside the Sun cannot be directly observed. However, under the influence of waves reaching the surface of the Sun, the outer layer of gas begins to rise and fall. This leads to a change in the frequency of the spectral lines in the emitted light and in changes in temperature and brightness on the surface.
Helioseismology consists of three areas:
1. Seismology of the Sun as a whole.
2. Seismology of photospheric structures.
3. Seismology of coronal structures.
')
The crown is the topmost, hottest part of the solar atmosphere, whose structure is determined by magnetic fields.

The corona of the Sun consists of almost completely ionized plasma of a mixture of hydrogen and helium with a temperature of more than a million degrees.

1. Open coronal structures
- Coronal holes;
- Streamers;
- Feathers inside coronal holes;
2. Closed coronal structures
- Hot and tight loops
3. Other
- Jets
- Prominences

More than twenty examples of such fluctuations were found, one of which is shown in the video at the very top of the post. For their enormous size and the outstanding amount of energy released, the flash has even been called “Bastille Day”.
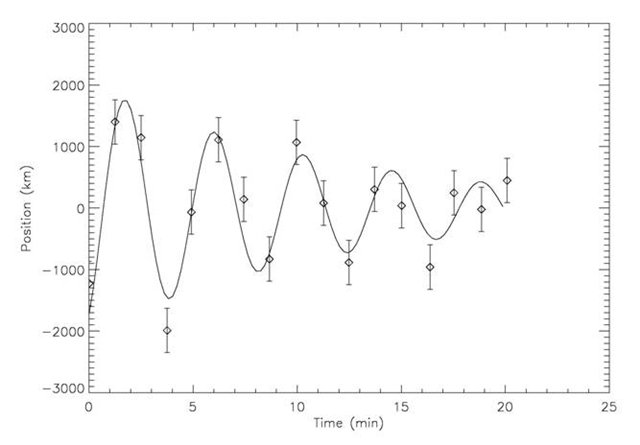
The periods of the received oscillations are about 4 minutes, the oscillations are close to harmonic, the decay time is 3-4 periods.
Wiki for the article:
1. Seismology - the science of the spread of seismic waves.
2. The Doppler effect - the change in frequency and wavelengths recorded by the receiver, caused by the movement of their source and / or movement of the receiver.
3. The protuberances are dense condensations of relatively cold (compared to the solar corona) substances that rise and are held above the surface of the sun by a magnetic field.
4. Oscillations - oscillations.
Article literature:
1. Zheleznyakov V.V. "Radiation in astrophysical plasma".
2. Kraus J.D. "Radio astronomy".
Earth seismology is based on the peculiarities of the propagation of sound under the ground. However, a seismograph (a device that records the fluctuations of the soil) cannot be placed on the Sun. Therefore, the fluctuations of the sun are measured by completely different methods. The main one is based on the Doppler effect. Since the solar surface rhythmically descends and rises (oscillates), its approach and removal affects the spectrum of the emitted light. Studying the spectra of different parts of the solar disk, get a picture of the velocity distribution; Of course, over time it changes - the waves run. The periods of these waves lie in the range of about 3 to 10 minutes. When they were first opened, the period found was approximately 5 minutes. Since then, all these fluctuations are called "five-minute." In the sixties of the XX century, astronomers found that the upper layer of the solar atmosphere rises and falls every five minutes.
A new path to the study of the inner layers of the Sun has opened helioseismology. Constant wave motion, like seismic waves on Earth, shakes the bowels of the sun. As geophysicists study seismic waves in order to understand the conditions inside the Earth, so solar physicists use the oscillations observed on the surface of the Sun to get information about its internal structure. In the gaseous medium of the Sun, waves of compression and rarefaction — acoustic waves — and internal gravitational waves, in which the force of gravity is the restoring force, can propagate. The focus is on acoustic waves, as they are best observed. The propagation of acoustic waves inside the Sun cannot be directly observed. However, under the influence of waves reaching the surface of the Sun, the outer layer of gas begins to rise and fall. This leads to a change in the frequency of the spectral lines in the emitted light and in changes in temperature and brightness on the surface.
Helioseismology consists of three areas:
1. Seismology of the Sun as a whole.
2. Seismology of photospheric structures.
3. Seismology of coronal structures.
')
Seismology of coronal structures
What is the crown of the sun?
The crown is the topmost, hottest part of the solar atmosphere, whose structure is determined by magnetic fields.

The corona of the Sun consists of almost completely ionized plasma of a mixture of hydrogen and helium with a temperature of more than a million degrees.
Coronal structures

1. Open coronal structures
- Coronal holes;
- Streamers;
- Feathers inside coronal holes;
2. Closed coronal structures
- Hot and tight loops
3. Other
- Jets
- Prominences
Oscillation of coronal loops generated by flashes

More than twenty examples of such fluctuations were found, one of which is shown in the video at the very top of the post. For their enormous size and the outstanding amount of energy released, the flash has even been called “Bastille Day”.

The periods of the received oscillations are about 4 minutes, the oscillations are close to harmonic, the decay time is 3-4 periods.
Wiki for the article:
1. Seismology - the science of the spread of seismic waves.
2. The Doppler effect - the change in frequency and wavelengths recorded by the receiver, caused by the movement of their source and / or movement of the receiver.
3. The protuberances are dense condensations of relatively cold (compared to the solar corona) substances that rise and are held above the surface of the sun by a magnetic field.
4. Oscillations - oscillations.
Article literature:
1. Zheleznyakov V.V. "Radiation in astrophysical plasma".
2. Kraus J.D. "Radio astronomy".
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/85448/
All Articles