Kaspersky KryptoStorage from and to
 In December 2009, Kaspersky Lab announced the release of the commercial release of Kaspersky KryptoStorage. This program was created based on InfoWatch CryptoStorage and adapted for use on home PCs. In this article I will try to go beyond the usual review and most fully describe the program, warn about pitfalls, give general advice on its use. Kaspersky KryptoStorage is needed for:
In December 2009, Kaspersky Lab announced the release of the commercial release of Kaspersky KryptoStorage. This program was created based on InfoWatch CryptoStorage and adapted for use on home PCs. In this article I will try to go beyond the usual review and most fully describe the program, warn about pitfalls, give general advice on its use. Kaspersky KryptoStorage is needed for:- protect confidential information from third parties;
- prevent data leakage when the operating system stores service information on the disk (for example, memory dumps);
- delete data without the possibility of recovery.
- Protected folder . This is a special folder created by the program in the NTFS file system. When you connect it, you can work with it as with a regular folder, with some reservations.
- H protected container . This is a special file created by the program. When you connect a container, you can work with it as a logical drive. This file can be copied to flash, burned onto a CD / DVD, sent via e-mail, laid out on a phonoexchanger and used on any PC where the program is installed and the password for connecting the container is known.
- Protected partition (disk) . This is an existing partition or disk converted (encrypted) by the program. After a protected partition / disk is connected using Kaspersky KryptoStorage, it becomes possible to work with it as with a regular partition / disk. It is also possible to encrypt system and / or boot partitions and Mass Storage class devices (Flash drives, USB storage devices, etc.).
Installing Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Before installing the program, you need to make sure that the platform on which the program will run meets the requirements.Hardware Requirements:
- Intel Celeron 1 GHz or higher processor or equivalent
- 256 MB free RAM
- 10 MB of free disk space for installing the application
Software Requirements:
- Windows 2000 SP4 operating system (with all updates) ...
- ... either Windows XP SP2 ...
- ... either Windows 2003 Server ...
- ... either Windows Vista SP1 ...
- ... either Windows 7
Run the installer program. The installation process does not differ from the installation of any other program, the user goes through the same steps of accepting the license agreement, choosing the installation site (the default is% ProgramFiles% \ Kaspersky Lab \ KryptoStorage \), and the installation wizard completes. At the end, it is proposed to restart the computer and after the restart, the application is fully operational. Important! During the reboot, it is highly recommended not to turn off the computer. This can cause a crash and an error every time you reboot! If, for some reason, a failure has nevertheless occurred, then you need to use the download option of the last successful configuration and reinstall the application.
')
Let's start working with the program. Here’s what the main window looks like:

Group Data Encryption . In this group there are three buttons with which you can create a protected folder , a protected container , or encrypt a disk (disk partition) . Let's do it!
Encrypting a folder in Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Create a secure folder . Click on the desired button. A window appears where you need to specify the folder (disk), where the protected folder will be located, the name for the protected folder , password and password hint. By default, it is proposed to create a "New Protected Folder" in the current user's "My Documents".
By clicking on OK folder is created. What you need to know about the protected folder ?
- All files and folders inside the protected are also encrypted and protected. That is, if you copy the file that lies outside it to a protected folder , the copy will be protected.
- Performing any actions on the protected folder (copying, moving, deleting, renaming, archiving, writing, reading) and its contents is possible only when this folder is connected.
- Access to a protected folder over the network is prohibited, but the connected folder is available to all users and programs that can work with the computer locally on behalf of the person who has connected. For example, you can work with the connected folder via RDP .
- If the file is copied from the protected folder to the outside, the copy becomes unprotected. In this case, the protection of the original file is preserved
- The program does not allow the following actions to be performed with protected folders and their contents:
- delete to trash
- move within the same volume files and folders containing files. When you try to move to the destination, an empty folder will be created with the same name as the original
- However, some file managers (for example, Total Commander), when moving, first make a copy of the object, and then delete the original one. In this case, the movement will be successful.
- Within one volume, you can move unprotected folders containing protected, or other unprotected folders without restrictions. Connecting a protected folder is not required, but protection is preserved. In other words, there is the usual folder "A", which contains the protected folder "B" and there is the usual folder "C". Moving "A" to "B" will take place without any restrictions. Connection "B" is not required, and protection will be preserved.
- An unprotected folder with protected subfolders can be moved to the recycle bin if the sub protected folders are connected. The folder moved to the trash can be deleted and restored. When restoring protected folders will be connected.
- Some file managers (for example, Total Commander) cannot move such a folder to the recycle bin.
- Working with a protected folder is possible if the Protected folders subsystem is enabled. The status can be viewed in the main window in the KryptoStorage Subsystem block.
- Creating a protected folder is possible only on non-write protected media.
- The user must have rights to create a folder.
- A protected folder can only be created on the NTFS file system.
- The full name of the folder should not exceed 255 characters.
- A protected folder cannot be created inside another protected folder .
- A secure folder cannot be created inside an EFS protected folder.
- A protected folder can be created on a hard disk, removable media, as well as on a program protected disk or in an encrypted container (when a disk or container is connected).
- The password can be no more than eight characters .

That is, in a free space (not on a folder, not on a file), right-click, Create - Kaspersky KryptoStorage Folder .
Recommendations for compiling strong passwords.
- the password must not be less than six characters (maximum, I remind you, eight)
- passwords may include numbers, latin letters, spaces and special characters
- It is desirable that the password consists of both numbers and letters (in upper and lower case), and specials. characters.
- common words and stable combinations
- a set of characters representing keyboard shortcuts arranged in a row on the keyboard (qwertyui, 12345678, qazxswed, etc.)
- personal data (names, surnames, dates of birth, passport numbers, insurance, etc.)
- passwords from other programs and services (mail, forums, etc.)
So, the folder is created. Let's try to protect the photos, the role of which will play the desktop wallpaper.
Video №1
I will explain what happened in the video.
- I copied the objects to be protected to the clipboard (moving, as I described above, is not possible)
- Connect the protected folder
- For demonstration of the help entered incorrect data. As you can see, the hint meets two main requirements: it is clear to me, it says nothing to others
- Pasted files into a protected folder
- Unmounted protected folder
- Launched a permanent removal of source files
Creating a secure container in Kaspersky KryptoStorage
What you need to know about the protected container ?- The device on which the container is created (container file) should not be write protected.
- The container cannot be created on a CD / DVD, but it can be written there as a file when it has already been created.
- The user creating the container must have rights to create files.
- Working with a container is possible only if Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed on the system and the Protected Containers subsystem is running.
- The container can be created on a hard disk, on flash, inside another container (when it is connected), inside a protected folder (when it is connected), inside a protected disk (when it is connected), and also copied to all these places.
- Restrictions on the size of the container are imposed only by the file system itself:
- for FAT16 - 2 GB
- for FAT32 - 4 GB
- for exFAT - 256 TB
- for NTFS - 16 TB
- You can create a container, as well as a protected folder in two ways:
- from the program window
- from the context menu
- By default, containers are suggested to be assigned the .kde extension. This extension is associated in the system with the program at the installation stage. If you use this extension, you can mount the container by double-clicking the mouse or from the context menu. If you use a different extension, you can mount the container only from the context menu of the container file (Kaspersky KryptoStorage item - Connect container).
- There is no auto unmount function.
- The connected container can be shared (moreover, the system will remember the sharing, if the same letter is used for mounting). Accordingly, the following scenario is possible: the user logs into the system, connects the container and leaves it, while the container remains shared and accessible over the network.
- Because Since the container is a regular file, you can protect it from deletion by placing it in a protected folder or on a protected disk .
After creating the container, the program will offer to format it. Without formatting, nothing can be written to the container. If you refuse to format at this stage, the request will appear every time after mounting and when accessing the mounted drive from the Explorer (try to open it).
When formatting you need to keep in mind:
- If you select the fast formatting mode and the FAT16 / FAT32 / exFAT file system, then the container file will have the minimum possible size and increase to the specified size during creation as it is filled. This will save space where the container file is located.
- When you select the NTFS file system, the container file will immediately have the specified size
- when fully formatted, regardless of the file system, the container file will immediately have the size specified at creation

The container is connected as a disk (hard or removable) and therefore it needs to assign a letter. All available drive letters will be listed in the Logical Disk drop-down menu. Connection mode will be unavailable until the container is formatted.
Container connection modes:
- only for reading. In this mode, nothing can be written to the mounted container and nothing can be deleted from it.
- the checkbox is set automatically and cannot be cleared if the container file has the "Read Only" attribute
- In MS Windows 2000, it is impossible to work in read-only mode with containers formatted in NTFS
- Connect as a removable disk. If the box is checked, then the disk is connected as removable. If the box is unchecked, the disk is mounted as fixed (hard disk).
- In MS Windows Vista, the container can only be connected as a removable disk.
Demonstration of working with a protected container :
Video # 2
Please note that it takes some time to dismount. However, you can restart or turn off the computer when containers are mounted; after the OS is booted, they will be removed.
Disk Encryption in Kaspersky KryptoStorage
What you need to know about disk encryption?- If protection is placed on a partition that is bootable / system, then you will need to log in to access it before loading the operating system.
- If the system and boot partitions are on different logical drives and both are protected, then each of these partitions must be connected.
- Installing protection on the system partition of the hard disk protects the memory dump file (crash dump), as well as the contents of the RAM when it goes into hibernate mode.
- Working with a protected disk or removable media is possible if the Protected disks subsystem is running on a computer with installed Kaspersky KryptoStorage system.
- If a protected system and / or boot partition of a hard disk is located on the computer, the system configurator does not allow to disable the Protected disks subsystem. In this case, in the main window of Kaspersky KryptoStorage in the KryptoStorage Subsystems section, the Protected Drives block is not available for making changes.
- It is not recommended to use Kaspersky KryptoStorage on computers with multiple operating systems and at the same time protect the disk partitions required for booting installed operating systems.
- Kaspersky KryptoStorage data about all protected logical partitions of physical media (physical hard disk, Flash storage, etc.) are located in the root directory of the first logical partition of physical media in the iwcs.bin file . If the partition containing the iwcs.bin file is formatted, or if this file is deleted, replaced, or damaged, access to all protected logical partitions of the physical media may be lost.
- Installing protection on logical partitions of hard drives and removable media is possible if the corresponding device has a sector size of 512 bytes (the standard sector size for most devices of this type).
- Installing protection on dynamic partitions is not supported.
- Protection can only be installed on local drives. Network drive protection is not supported.
- Installation / deletion / reinstallation of protection for several logical partitions cannot be simultaneously launched on the same physical disk. You can work with logical partitions of different disks simultaneously.
- Protecting the logical partition of a hard disk on which Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed is allowed only if this partition is system and / or boot.
- Installation of protection is allowed provided that the protected partition is allowed to write.
- You can start installing protection on a removable disk only if the files on the removable disk are not used by any programs. In the process of installing protection, it is possible to use files on a removable disk.
- Kaspersky KryptoStorage does not support CD / DVD protection.
- Resizing logical partitions on a hard disk (exactly like their division, merging) can lead to data loss. If these changes are necessary, then remove the protection sections before starting work.
There are two ways to install security:
- From the main program window, the Encrypt disk button.
- From the context menu of the object, the Kaspersky KryptoStorage item - Install protection to disk.

Upon successful completion, the user receives a notification.
Until the protection is installed, you can click on the "Stop" button. Then the authorization window will appear (where you need to enter the password to access the object). The next window will be a message about the successful interruption of the installation of protection.
In case of interruption of the protection installation (manually, or the system went into standby / sleep mode, or the computer was de-energized), the object remains partially encrypted, but is considered protected. Therefore, working with this object is possible only by connecting it and entering a password. Of course, if the protection was not installed to the end, then some of the information remains unencrypted. In this situation, you can either resume the installation of protection or cancel its installation.
To resume the installation of protection, you need to connect the object (if it has been disabled) and select Kaspersky KryptoStorage in its context menu - Continue installing protection on the disk . The process of installing the protection will continue.
To cancel the installation of the protection of an object, select Kaspersky KryptoStorage in the context menu of the object . Cancel installation of the disk protection . To perform the operation will require authorization.
To work with a protected object, you must first connect it. To do this, in the context menu of the object, select the Kaspersky KryptoStorage item - Map disk . The procedure requires an authorization. Upon completion of work with the object, it is recommended to disable it, since A connected object is not a protected object. To do this, select the Kaspersky KryptoStorage item in the context menu - Disconnect Disk . Objects will also be disabled if the OS rebooted.
Booting from the system and / or boot disk protected by Kaspersky KryptoStorage is possible only after authorization. The authorization request will appear during the PC boot process before the OS boots:
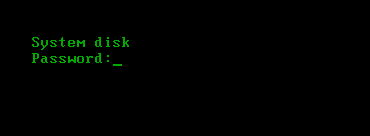
After successful authorization the OS will be loaded. If you make a mistake when entering the password, a message appears about the incorrect password and a suggestion to press any key. If a hint was set during the installation of protection, it will be displayed:

You can try to enter again. If the prompt was not set, then to repeat the authorization procedure, you will need to restart the computer using the Ctrl + Alt + Del combinations.
To remove protection from an object, select the Kaspersky KryptoStorage item in its context menu - Remove protection from disk . The procedure requires authorization, and the object must be previously connected. The process of removing protection, as well as the installation of protection, can be interrupted and resumed. The algorithm works also similar to the algorithms for the installation of protection.
Kaspersky KryptoStorage settings
Let's go back to the main window. Below the Data Encryption block is the Kaspersky KryptoStorage Subsystem block. Each of the subsystems protects objects of a certain type: disks, containers, folders. If the subsystem of some type of object is stopped, then the possibility of working with this type of object disappears. The subsystem status (running or disabled) is indicated in the second column of the block. The third column allows you to change this status. To stop the work with protected folders subsystem, you need to uncheck the "Autostart" checkbox on this subsystem and restart the computer. To start the subsystem, this checkbox must be checked and also the computer is restarted.In the Settings for connecting objects section, there is only one setting that is responsible for auto-opening of connected objects in Explorer. You can either turn off the opening of objects at once, by clearing the Open objects checkbox using the explorer in a new window after connecting , or enable it for all at once. It is impossible to configure auto - opening of the protected folder and at the same time prohibiting auto-opening for the protected container .
The Licenses button opens the license management window:

The license can be in the form of an activation code, it can be a file. The license file is created automatically with activation code. The license is perpetual for the program. Validity period means that there will be no user support, but the functionality remains.
The Disk Recovery button is needed to free up space on the hard disk, logical partition, flash, etc., when access to them is lost. To perform operations, local Administrator rights are required. Such a situation may arise if:
- lost access keys to a protected partition, so you can’t connect or unprotect it
- The protected partition was formatted after uninstalling Kaspersky KryptoStorage with the Protected drives subsystem running. After reinstalling the program with the Protected Disk subsystem running by default, access to the formatted object becomes impossible
- The size of the protected partition has been changed. As a result, a mismatch arose between the size taken into account by Kaspersky KryptoStorage and the actual size of the protected partition. For correct resizing, you must first remove the protection from the object, resize, and then install the protection again
- complete all operations associated with installing, reinstalling and removing protection on all partitions of a physical disk or removable media
- disable protected partitions of a physical disk, information about which should be deleted from Kaspersky KryptoStorage
To make available disk space occupied by a protected partition, you need to:
- In the main window, click the Disk Recovery button.
- In the "Restore Disks" window, specify the protected partition whose information you want to delete from the disk.
- In the context menu of the section, select Delete encrypted area information.
- In the window with a warning about the loss of encrypted information, click "Yes".

On this I consider my article complete and will gladly read your comments. Additionally, I inform you that Kaspersky KryptoStorage is included in Kaspersky PURE , whose commercial release is not far off.
For writing an article, the Knowledge Base of the product on the Kaspersky Lab technical support site was actively used.
UPD 1. Now clarified an important detail. When the license ends, you can put minor program updates, but not major ones. If after the expiration of the license had to reinstall the OS, then this license can again be used. That is, there is no limit on the number of its uses (or there is, but a large one). Validity applies only to the ability to contact technical support and major updates.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/81083/
All Articles