Reflexion web
 This article deals with security issues in general and web resources in particular. The main problem of protection against deliberate attacks is that it is impossible to defend against them. Each new security system generates new vulnerabilities. Every day new holes of different software versions open up and, as a result, the process of ensuring security is the process of continuously patching holes. If the qualification and enthusiasm of a specialist who provides safety of resources is a cut above potential hackers, then he runs faster in this marathon, and we can talk about some “security” of the resource. Otherwise, the administrator has to learn from their own mistakes.
This article deals with security issues in general and web resources in particular. The main problem of protection against deliberate attacks is that it is impossible to defend against them. Each new security system generates new vulnerabilities. Every day new holes of different software versions open up and, as a result, the process of ensuring security is the process of continuously patching holes. If the qualification and enthusiasm of a specialist who provides safety of resources is a cut above potential hackers, then he runs faster in this marathon, and we can talk about some “security” of the resource. Otherwise, the administrator has to learn from their own mistakes.This whole situation has long caused a certain skepticism of the uninitiated in IT security issues of people about this IT security. I often hear the opinion that investing money in new technologies and information protection products is a waste, as any protection breaks and any new one is no exception.
This situation made me think about fundamentally new approaches to ensuring security, which are fundamentally different from the traditional ones in that they protect the system even from unknown vulnerabilities today . This idea may seem absurd, but only at first glance. Suffice it to recall that behind any attacks on the Internet is a man the same as we are with you. A network attack is a combination of some targeted actions with receiving feedback. It is based on a priori information of the attacker and information obtained in the process of research. But there is nothing difficult in making this information irrelevant to reality. And this is not about simple misinformation, but about protecting systems from research .
')
To understand what it is, you must try to imagine how a person receives information about the world. As a matter of fact, any information belongs to certain categories (classifications), which can correspond to reality only according to indicators of certain parameters (stereotypical scheme). In order not to load the reader with scientific vocabulary, I will give a simple example. There is, for example, a chair. There is a generally accepted stereotype of a chair - four legs, on them a certain surface and the back of a chair. Everyone will know him and say for sure that this is a “chair”. But if you make it fundamentally different, without legs, surface and back (for example, the first soft, shapeless chairs), then no one will call it a chair, although it will perform the same function. Changing things like this beyond recognition, you can hide their functional purpose. And by hiding their functional purpose, you can hide certain activities and even entire business processes. We have a person in Russia who claims that he has long been engaged in such a “concealment” of events and even the activities of entire companies! However, I did not see such a reality, and I do not know how to alter ordinary objects beyond recognition. But the IT industry provides us with quite suitable grounds for such activities, because you can programmatically write anything you want.
And so the protection technology from system research was born, which makes it possible to make a unique one out of any standard process, introducing into it some meaningless parameters from the point of view of the objective function of the process. This makes a small additional load on computing resources (those resources that go to create "uniqueness"), but it performs the main task from the point of view of security - any a priori information about the operation of the system simply becomes incorrect . In order to investigate the system, the attacker has to rely on some additional assumptions that can also be made incorrect and thus lead the system into a state of complete chaos for an external observer. At the same time, the objective function of the system remains unchanged, but a step to the left, a step to the right - and nothing is clear ...
How does this happen in reality? Well, the attacker is trying to check the site for the vulnerability of SQL injections and, for simplicity, enters into parameters a quote or expression like ... id = 1 + 1 and looks at what is happening. And incredible! - the system adds the numbers and displays the page by id = 2. The conclusion is made - the vulnerability of SQL injection is open. However, later when trying to display information from the database, he discovers that the system in some strange way displays the wrong information and inadequately responds to the input parameters. After some time, he finds a new relationship, but then he realizes again that it does not correspond to reality and continues the senseless process of research.
According to this principle, the modules developed within the Reflexion Web project (Reflexive Web) work . The operation scheme of the PRIS Mirror module is shown in the figure.
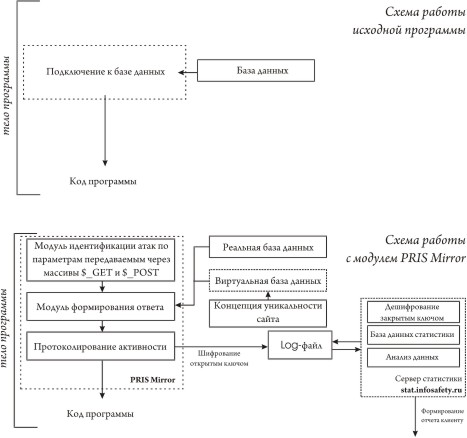
Intercepting the values of the $ _GET and $ _POST arrays, it filters out those that the “normal user” cannot enter and executes queries on them, taking into account the customized concept of the system's uniqueness. The result is that we create vast spaces of vulnerabilities in which a potential intruder will get bogged down without even suspecting that in reality he is already being watched. In terms of observation, this technology is similar to the already well-known HoneyPot system, but it is fundamentally different from the latter that observation is not the main task of the module. The main task is to make each system fundamentally different in functional processes from the other, and thereby reduce the residual risks where this cannot be done so far.
At this stage, the project is open and we welcome any new ideas, suggestions and development assistance!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/80269/
All Articles