Connecting to a remote computer via VNC
Work with the VNC client. The material is aimed at an inexperienced user.
1. Install the VNC client
2. Connecting a VNC client to a remote computer
3. Disconnect the VNC client from a remote computer
4. Tuning VNC-client
5. Frequent problems
To work with a remote computer via VNC on the user's computer, you need to run the client program (VNC viewer, VNC client). This program transmits data on keystrokes and mouse movements made by the user to the remote computer and shows the information intended for display on the screen.
For Windows, you can download and install the UltraVNC and TightVNC VNC client for free.
')
Mac OS X since version 10.5 has support for the VNC client in RemoteDesktop . For previous versions you can use Jollys FastVNC and Chicken VNC clients.
For the Linux branch of Debian (Ubuntu), the VNC client is installed from the repository with the command:
For the RedHat branch (CentOS, Fedora) - with the command:
For FreeBSD, the VNC client (TightVNC) is installed from packages with the command:
To connect a VNC client to a remote computer, you need to specify its IP address or DNS name, and the display number (by default, 0) or the TCP port number (by default, 5900). If the VNC server requires authorization, then when connecting to it, the VNC client will request a password. Please note that the password for access to the VNC server is not associated with any account (user account) on the remote computer, but serves only to limit access to the display of the VNC server.
After the connection is established and the screen is opened, depending on the settings of the VNC server, it may be necessary to authorize the user on the virtual server or the already started working session of a user may be opened.
Since several VNC servers can work simultaneously on a computer, the display number parameter is used to separate them. For example, one VNC server can be started on the display: 0, the other on the display: 1. Each display number corresponds to a TCP port number on which the VNC server accepts connections. The port number for the display is obtained by adding the display number to the base port number - 5900. Display: 0 corresponds to TCP port 5900, display: 1 - port 5901.
When closing the VNC client window or after leaving the environment using the desktop, depending on the settings of the VNC server, the user's work session can be closed with stopping all used programs, or continue working and be available again when reconnecting to the VNC server.
A large amount of information transmitted to the screen entails increased requirements for the speed of the channel - its bandwidth and packet transmission time. A lack of bandwidth leads to uncomfortable delays in case of large changes in information displayed on the screen - opening new windows, scrolling, etc. Especially large delays will occur when showing photos and other images or interface elements that have a large number of colors and complex shapes.
The main parameter that affects the amount of data transmitted is the coding algorithm for the transmitted graphics. To reduce the volume and, consequently, accelerate the work, it is recommended to use the algorithms Tight, ZLib, ZRLE - compared to uncompressed data (Raw), they provide compression tenfold, significantly loading the processor. These coding algorithms ensure comfortable operation even on channels with a speed of 256-512 Kbps.
To reduce the amount of information transmitted over the network, you can also set a high level of compression (Compression Level, Compression Value), a low quality level of JPEG (JPEG Quality) and enable the mode of reducing the number of colors (-bgr233, Restricted colors). The biggest effect of them with a noticeable decrease in image quality is given by the mode of reducing the number of colors - the amount of transmitted information decreases 1.5-3 times, respectively, the display on the screen accelerates 1.5-3 times.
JPEG is used by the Tight encoding algorithm to compress screen sections containing photographs and other complex images with a large number of colors. Using Tight + JPEG reduces the amount of transmitted data by 2-5 times. Other JPEG encoding algorithms do not support.
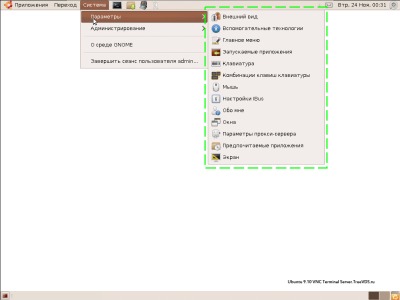
1. Drop-down menu "System -> Parameters"
The volume of transmitted data and the display speed on the 1 Mbit / s channel when opening the drop-down menu “System -> Parameters” (in the menu picture is highlighted with a green dotted line):
Need to check:
If the VNC client cannot reconcile with the VNC server using a graphics encoding algorithm with data compression, the default algorithm is Raw, which transmits data without compression. Also, coding without compression or with a low compression level can be automatically selected by the VNC client when working through a fast local area network. This problem can be corrected by forcing the encoding algorithm with a high compression level — ZLib, ZRLE, Tight — in the VNC client settings.
However, for some client and server combinations, this solution may be useless due to errors in the coding algorithm matching. For example, a TightVNC client with a RealVNC server can often only work with Raw encoding. The solution in this case is to change the VNC-client or VNC-server.
Other articles in this series:
VNC - remote access to the computer over the network. Introduction to VNC.
Installing a VNC server on VDS and tuning recommendations
PS If there are comments, additions, questions - write in the comments, I will add an article on them.
1. Install the VNC client
2. Connecting a VNC client to a remote computer
3. Disconnect the VNC client from a remote computer
4. Tuning VNC-client
5. Frequent problems
To work with a remote computer via VNC on the user's computer, you need to run the client program (VNC viewer, VNC client). This program transmits data on keystrokes and mouse movements made by the user to the remote computer and shows the information intended for display on the screen.
1. Install the VNC client
For Windows, you can download and install the UltraVNC and TightVNC VNC client for free.
')
Mac OS X since version 10.5 has support for the VNC client in RemoteDesktop . For previous versions you can use Jollys FastVNC and Chicken VNC clients.
For the Linux branch of Debian (Ubuntu), the VNC client is installed from the repository with the command:
apt-get install vncviewerFor the RedHat branch (CentOS, Fedora) - with the command:
yum install vncFor FreeBSD, the VNC client (TightVNC) is installed from packages with the command:
pkg_add -r tightvnc2. Connecting a VNC client to a remote computer
To connect a VNC client to a remote computer, you need to specify its IP address or DNS name, and the display number (by default, 0) or the TCP port number (by default, 5900). If the VNC server requires authorization, then when connecting to it, the VNC client will request a password. Please note that the password for access to the VNC server is not associated with any account (user account) on the remote computer, but serves only to limit access to the display of the VNC server.
After the connection is established and the screen is opened, depending on the settings of the VNC server, it may be necessary to authorize the user on the virtual server or the already started working session of a user may be opened.
Since several VNC servers can work simultaneously on a computer, the display number parameter is used to separate them. For example, one VNC server can be started on the display: 0, the other on the display: 1. Each display number corresponds to a TCP port number on which the VNC server accepts connections. The port number for the display is obtained by adding the display number to the base port number - 5900. Display: 0 corresponds to TCP port 5900, display: 1 - port 5901.
3. Disconnect the VNC client from a remote computer
When closing the VNC client window or after leaving the environment using the desktop, depending on the settings of the VNC server, the user's work session can be closed with stopping all used programs, or continue working and be available again when reconnecting to the VNC server.
4. Tuning VNC-client
A large amount of information transmitted to the screen entails increased requirements for the speed of the channel - its bandwidth and packet transmission time. A lack of bandwidth leads to uncomfortable delays in case of large changes in information displayed on the screen - opening new windows, scrolling, etc. Especially large delays will occur when showing photos and other images or interface elements that have a large number of colors and complex shapes.
The main parameter that affects the amount of data transmitted is the coding algorithm for the transmitted graphics. To reduce the volume and, consequently, accelerate the work, it is recommended to use the algorithms Tight, ZLib, ZRLE - compared to uncompressed data (Raw), they provide compression tenfold, significantly loading the processor. These coding algorithms ensure comfortable operation even on channels with a speed of 256-512 Kbps.
To reduce the amount of information transmitted over the network, you can also set a high level of compression (Compression Level, Compression Value), a low quality level of JPEG (JPEG Quality) and enable the mode of reducing the number of colors (-bgr233, Restricted colors). The biggest effect of them with a noticeable decrease in image quality is given by the mode of reducing the number of colors - the amount of transmitted information decreases 1.5-3 times, respectively, the display on the screen accelerates 1.5-3 times.
JPEG is used by the Tight encoding algorithm to compress screen sections containing photographs and other complex images with a large number of colors. Using Tight + JPEG reduces the amount of transmitted data by 2-5 times. Other JPEG encoding algorithms do not support.

1. Drop-down menu "System -> Parameters"
The volume of transmitted data and the display speed on the 1 Mbit / s channel when opening the drop-down menu “System -> Parameters” (in the menu picture is highlighted with a green dotted line):
| Full color mode | 256 colors (BGR233) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume | Time | Volume | Time | |
| Zlib | 11 Kb | 0.09 seconds | 7 Kb | 0.06 seconds |
| HexTile | 208 Kb | 1.6 sec | 118 Kb | 0.95 sec |
| Raw | 248 Kb | 2 sec | 128 Kb | 1 sec |
5. Frequent problems
Unable to connect to the VNC server
Need to check:
- Is there access to the Internet?
- Does the virtual server respond to pings?
- whether the VNC server is running on the virtual server;
- Is there a firewall along the path that blocks access to the VNC server TCP port;
- Is the display number or TCP port of the VNC server correct (port number = 5900 + display number).
Slow work through a fairly fast channel
If the VNC client cannot reconcile with the VNC server using a graphics encoding algorithm with data compression, the default algorithm is Raw, which transmits data without compression. Also, coding without compression or with a low compression level can be automatically selected by the VNC client when working through a fast local area network. This problem can be corrected by forcing the encoding algorithm with a high compression level — ZLib, ZRLE, Tight — in the VNC client settings.
However, for some client and server combinations, this solution may be useless due to errors in the coding algorithm matching. For example, a TightVNC client with a RealVNC server can often only work with Raw encoding. The solution in this case is to change the VNC-client or VNC-server.
Other articles in this series:
VNC - remote access to the computer over the network. Introduction to VNC.
Installing a VNC server on VDS and tuning recommendations
PS If there are comments, additions, questions - write in the comments, I will add an article on them.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/76343/
All Articles