VNC - remote access to the computer over the network
Introduction to VNC. The material is aimed at an inexperienced user.
VNC is a widely accepted method of remotely accessing a computer’s desktop over a network. Data on keystrokes and mouse movement performed by the user on their own computer is transmitted over the network to a remote computer and they perceive actions with its own keyboard and mouse. Information from the remote computer screen is displayed on the user's computer screen. Working on VNC via the Internet with a remote computer located in the opposite point of the world looks to the user as if this computer is directly in front of him. Especially VNC is convenient when working with a graphical interface - with a desktop and programs for the desktop operating systems Windows, Linux and others.
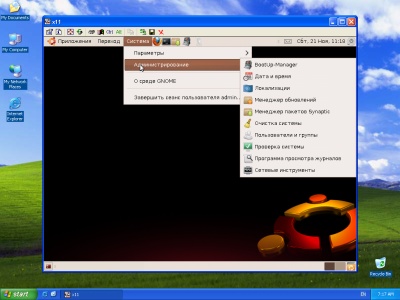
1. VNC-client on the user's computer running Windows, with an open desktop VDS (virtual server), running Ubuntu 9.10.
For novice users, administration of a Unix server via VNC will be much easier than via the command line via SSH or the control panel with a web interface. Programs with a graphical interface, as a rule, are well structured and more intuitive in understanding than editing configuration files according to instructions. Server administration looks almost the same as setting up the desktop version of the operating system, be it Linux or Windows. You can even install on your own computer a similar version of the operating system for training, and proceed to administering VDS / VPS after the basic principles of system setup are clear.
')
To administer your own server via VNC, it is enough for a user to be able to work with a graphical window interface and have a basic understanding of the main components of the operating system — the file system, the network, and the services (daemons).
A remote server program (VNC server) must be running on the remote computer, which acts as a keyboard, mouse, and monitor, and communicates with the user's computer. Access to the VNC server can be password protected.
A client program (VNC client, VNC viewer) must be running on the user's computer, which transmits information on keystrokes and mouse movements to the remote computer, receives an image from it and displays it on the screen. VNC clients exist for Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and many other platforms. There are also VNC clients for PDAs and mobile phones. When launching a VNC client, it is sufficient to specify the DNS name or IP address of the remote computer, and a password if access to the VNC server is password protected.
The main volume of data transmitted via VNC falls on graphic information displayed on the screen. To work requires the bandwidth of the channel from 32 Kbps to 2 Mbps. For comfortable work in full-color mode with a screen resolution of 1024x768, the channel speed should be 1-2 Mbps. With a decrease in the quality of graphics, with a decrease in the number of colors and with some additional optimization methods, an acceptable convenience can provide a speed of 128 Kbps. The channel is fully engaged only when updating large areas of the screen, when printing text, the traffic is noticeably less, and the rest of the time the channel is practically not used. If during transmission via the channel, there are large packet transfer delays (slow channels, satellite communication, long distances), this causes a deterioration in the response time for pressing the keys and moving the mouse, which greatly reduces the comfort of work.
Other articles in this series:
Connecting to a remote computer via VNC. Work with the VNC client.
Installing a VNC server on VDS and tuning recommendations
PS We are now writing instructions and other background information for working with VDS on VNC . Further, the articles "Working with VNC-client and tuning recommendations", "Installing VNC-server on VDS and tuning recommendations", "Administering VDS by VNC" are planned.
VNC is a widely accepted method of remotely accessing a computer’s desktop over a network. Data on keystrokes and mouse movement performed by the user on their own computer is transmitted over the network to a remote computer and they perceive actions with its own keyboard and mouse. Information from the remote computer screen is displayed on the user's computer screen. Working on VNC via the Internet with a remote computer located in the opposite point of the world looks to the user as if this computer is directly in front of him. Especially VNC is convenient when working with a graphical interface - with a desktop and programs for the desktop operating systems Windows, Linux and others.

1. VNC-client on the user's computer running Windows, with an open desktop VDS (virtual server), running Ubuntu 9.10.
For novice users, administration of a Unix server via VNC will be much easier than via the command line via SSH or the control panel with a web interface. Programs with a graphical interface, as a rule, are well structured and more intuitive in understanding than editing configuration files according to instructions. Server administration looks almost the same as setting up the desktop version of the operating system, be it Linux or Windows. You can even install on your own computer a similar version of the operating system for training, and proceed to administering VDS / VPS after the basic principles of system setup are clear.
')
To administer your own server via VNC, it is enough for a user to be able to work with a graphical window interface and have a basic understanding of the main components of the operating system — the file system, the network, and the services (daemons).
A remote server program (VNC server) must be running on the remote computer, which acts as a keyboard, mouse, and monitor, and communicates with the user's computer. Access to the VNC server can be password protected.
A client program (VNC client, VNC viewer) must be running on the user's computer, which transmits information on keystrokes and mouse movements to the remote computer, receives an image from it and displays it on the screen. VNC clients exist for Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and many other platforms. There are also VNC clients for PDAs and mobile phones. When launching a VNC client, it is sufficient to specify the DNS name or IP address of the remote computer, and a password if access to the VNC server is password protected.
The main volume of data transmitted via VNC falls on graphic information displayed on the screen. To work requires the bandwidth of the channel from 32 Kbps to 2 Mbps. For comfortable work in full-color mode with a screen resolution of 1024x768, the channel speed should be 1-2 Mbps. With a decrease in the quality of graphics, with a decrease in the number of colors and with some additional optimization methods, an acceptable convenience can provide a speed of 128 Kbps. The channel is fully engaged only when updating large areas of the screen, when printing text, the traffic is noticeably less, and the rest of the time the channel is practically not used. If during transmission via the channel, there are large packet transfer delays (slow channels, satellite communication, long distances), this causes a deterioration in the response time for pressing the keys and moving the mouse, which greatly reduces the comfort of work.
Other articles in this series:
Connecting to a remote computer via VNC. Work with the VNC client.
Installing a VNC server on VDS and tuning recommendations
PS We are now writing instructions and other background information for working with VDS on VNC . Further, the articles "Working with VNC-client and tuning recommendations", "Installing VNC-server on VDS and tuning recommendations", "Administering VDS by VNC" are planned.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/76237/
All Articles