Progressbar and threads in PyGTK
Recently there was a need and desire to get acquainted with PyGTK. There is practically no literature in Russian on this issue, and what Google finds in various blogs is a bit obsolete. Also I was surprised to find that the PyGTK theme is not very popular in Habré either.
So, I will not talk about the layout of the interface elements, because such articles already exist. I’ll tell you about the next step: creating an application that does some work, displaying its progress in the process.
For example, let's write a primitive GUI for two functions of the convert utility (ImageMagick package). Our program will take four values:
The interface itself will create in the glade. Importantly , the project must be in GtkBuilder format.

')
Then two examples of code, the first - ordinary, and the second, with the creation of a separate thread for image processing. Examples two - to visually make sure whether there is a sense of messing with the threads.
Skeleton of the program:
We will add the main on_start method, which displays the progress bar, receives user instructions, generates a list of files (we exclude directories) and is directly involved in processing.
We display our dialog box, load the values from the GUI and generate a list of files. Next, run a loop with a search through the list of files.
First of all, we check if the stop flag indicates that the processing stops if self.stop (set by the on_progressdialog_close button on the Cancel button or close the dialog box). Further, in the process we change the text and the percentage of processing in the progress bar, and also run the convert utility itself with the necessary parameters.
Important piece of code
Without it, our dialog box simply does not appear, and the interface will freeze until processing is complete. This is because our loop blocks the interface redrawing (main loop) until it completes. The above code returns control to the main loop for a short time.
Also, I specifically added time.sleep (5), and if someone has a fast computer, they may not notice that during the actual processing (or sleep) the interface does not respond to events.
With threads in PyGTK, unknowingly had to tinker. In the beginning, you need to call gtk.gdk.threads_init (), and all further gtk calls should be framed with gtk.threads_enter () and gtk.threads_leave (), such is the specifics.
Our code has changed a bit. We have created the self.dialog dictionary, which is useful to us below, and the on_start method, now only prepares the data and launches a new thread, in which the non-blocking interface of our program is directly processed.
Create a class Worker:
We had to override the constructor (__init__) so that it took parameters. These are dialog dictionaries (I said, it will be useful), data (size, quality, and two directories) and a list of files.
In the run method we put what needs to be performed at the start - i.e. processing itself.
That's all, as they say "The result on the face."
I want to note, in this example, the calculation of the percentage of completion and its change for the dialogue, occur directly in the working thread. This is considered a bad tone, and if the thread were not one, it would not have worked (it would have worked with errors more precisely).
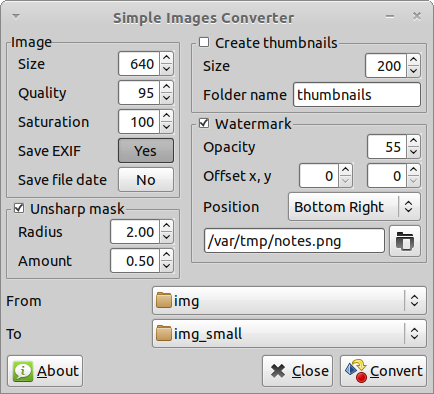
A slightly enhanced version of our program looks like this.
You can read about the features and download it here .
Archive source .
UPD:
alex3d recalled that if you match the manual, in Worker.run the lines
need to wrap in
gtk.threads_enter () / gtk.threads_leave ().
So, I will not talk about the layout of the interface elements, because such articles already exist. I’ll tell you about the next step: creating an application that does some work, displaying its progress in the process.
For example, let's write a primitive GUI for two functions of the convert utility (ImageMagick package). Our program will take four values:
- size, how to reduce the image
- quality
- catalog with the images themselves
- directory where to save
The interface itself will create in the glade. Importantly , the project must be in GtkBuilder format.

')
Then two examples of code, the first - ordinary, and the second, with the creation of a separate thread for image processing. Examples two - to visually make sure whether there is a sense of messing with the threads.
Skeleton of the program:
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8
try :
import sys , pygtk
pygtk . require ( '2.0' )
except :
print ' PyGTK'
sys . exit ( 1 )
import gtk , os , time
class GUI ( object ) :
def __init__ ( self ) :
self . wTree = gtk . Builder ( )
#
self . wTree . add_from_file ( "convert.glade" )
#
self . wTree . connect_signals ( self )
self . window1 = self . wTree . get_object ( "window1" )
self . progressdialog = self . wTree . get_object ( "progressdialog" )
self . progressbar_label = self . wTree . get_object ( "progressbar_label" )
self . window1 . show ( )
#
self . wTree . get_object ( "size" ) . set_value ( 100 )
self . wTree . get_object ( "quality" ) . set_value ( 95 )
self . progressbar = self . wTree . get_object ( "progressbar" )
def on_cancel ( self , widget ) :
gtk . main_quit ( )
def on_progressdialog_close ( self , * args ) :
self . stop = True
self . progressdialog . hide ( )
return True
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
app = GUI ( )
gtk . main ( )
We will add the main on_start method, which displays the progress bar, receives user instructions, generates a list of files (we exclude directories) and is directly involved in processing.
def on_start ( self , widget ) :
self . progressdialog . show ( )
self . stop = False
# GUI
self . size = int ( self . wTree . get_object ( "size" ) . get_value ( ) )
self . quality = int ( self . wTree . get_object ( "quality" ) . get_value ( ) )
self . from_dir = self . wTree . get_object ( "from_dir" ) . get_current_folder ( )
self . to_dir = self . wTree . get_object ( "to_dir" ) . get_current_folder ( )
files = [ ]
all_files = os . listdir ( self . from_dir )
for f in all_files :
fullname = os . path . join ( self . from_dir , f )
if os . path . isfile ( fullname ) :
files . append ( f )
count = len ( files )
i = 1.0
for file in files :
#
if self . stop :
break
self . progressbar_label . set_text ( file )
self . progressbar . set_fraction ( i / count )
os . popen ( 'convert -resize ' + str ( self . size ) + ' -quality ' + str ( self . quality ) + ' ' + os . path . join ( self . from_dir , file ) + ' ' + os . path . join ( self . to_dir , file ) )
#
while gtk . events_pending ( ) :
gtk . main_iteration ( )
time . sleep ( 5 )
i + = 1
self . progressdialog . hide ( )
We display our dialog box, load the values from the GUI and generate a list of files. Next, run a loop with a search through the list of files.
First of all, we check if the stop flag indicates that the processing stops if self.stop (set by the on_progressdialog_close button on the Cancel button or close the dialog box). Further, in the process we change the text and the percentage of processing in the progress bar, and also run the convert utility itself with the necessary parameters.
Important piece of code
while gtk . events_pending ( ) :
gtk . main_iteration ( )
Without it, our dialog box simply does not appear, and the interface will freeze until processing is complete. This is because our loop blocks the interface redrawing (main loop) until it completes. The above code returns control to the main loop for a short time.
Also, I specifically added time.sleep (5), and if someone has a fast computer, they may not notice that during the actual processing (or sleep) the interface does not respond to events.
Threads
With threads in PyGTK, unknowingly had to tinker. In the beginning, you need to call gtk.gdk.threads_init (), and all further gtk calls should be framed with gtk.threads_enter () and gtk.threads_leave (), such is the specifics.
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8
try :
import sys , pygtk
pygtk . require ( '2.0' )
except :
print ' PyGTK'
sys . exit ( 1 )
import threading , gtk , os , time
class GUI ( object ) :
def __init__ ( self ) :
self . wTree = gtk . Builder ( )
#
self . wTree . add_from_file ( "convert.glade" )
#
self . wTree . connect_signals ( self )
self . window1 = self . wTree . get_object ( "window1" )
self . dialog = {
"progressdialog" : self . wTree . get_object ( "progressdialog" ) ,
"progressbar_label" : self . wTree . get_object ( "progressbar_label" ) ,
"progressbar" : self . wTree . get_object ( "progressbar" )
}
self . window1 . show ( )
#
self . wTree . get_object ( "size" ) . set_value ( 100 )
self . wTree . get_object ( "quality" ) . set_value ( 95 )
def on_cancel ( self , widget ) :
gtk . main_quit ( )
def on_progressdialog_close ( self , * args ) :
self . work . stop ( )
self . dialog [ 'progressdialog' ] . hide ( )
return True
def on_start ( self , widget ) :
self . dialog [ 'progressdialog' ] . show ( )
#
self . data = {
'size' : int ( self . wTree . get_object ( "size" ) . get_value ( ) ) ,
'quality' : int ( self . wTree . get_object ( "quality" ) . get_value ( ) ) ,
'from_dir' : self . wTree . get_object ( "from_dir" ) . get_current_folder ( ) ,
'to_dir' : self . wTree . get_object ( "to_dir" ) . get_current_folder ( )
}
files = [ ]
all_files = os . listdir ( self . data [ 'from_dir' ] )
for f in all_files :
fullname = os . path . join ( self . data [ 'from_dir' ] , f )
if os . path . isfile ( fullname ) :
files . append ( f )
self . work = Worker ( self . dialog , self . data , files )
self . work . start ( )
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
gtk . gdk . threads_init ( )
app = GUI ( )
gtk . gdk . threads_enter ( )
gtk . main ( )
gtk . gdk . threads_leave ( )
Our code has changed a bit. We have created the self.dialog dictionary, which is useful to us below, and the on_start method, now only prepares the data and launches a new thread, in which the non-blocking interface of our program is directly processed.
Create a class Worker:
class Worker ( threading . Thread ) :
#
stopthread = threading . Event ( )
def __init__ ( self , dialog , data , files ) :
threading . Thread . __init__ ( self )
self . dialog = dialog
self . data = data
self . files = files
def run ( self ) :
count = len ( self . files )
i = 1.0
for file in self . files :
#
if ( self . stopthread . isSet ( ) ) :
self . stopthread . clear ( )
break
self . dialog [ 'progressbar' ] . set_fraction ( i / count )
self . dialog [ 'progressbar_label' ] . set_text ( file )
os . popen ( 'convert -resize ' + str ( self . data [ 'size' ] ) + ' -quality ' + str ( self . data [ 'quality' ] ) + ' ' + os . path . join ( self . data [ 'from_dir' ] , file ) + ' ' + os . path . join ( self . data [ 'to_dir' ] , file ) )
time . sleep ( 2 )
i + = 1
#
self . stopthread . clear ( )
#
self . dialog [ 'progressdialog' ] . hide ( )
def stop ( self ) :
self . stopthread . set ( )
We had to override the constructor (__init__) so that it took parameters. These are dialog dictionaries (I said, it will be useful), data (size, quality, and two directories) and a list of files.
In the run method we put what needs to be performed at the start - i.e. processing itself.
That's all, as they say "The result on the face."
I want to note, in this example, the calculation of the percentage of completion and its change for the dialogue, occur directly in the working thread. This is considered a bad tone, and if the thread were not one, it would not have worked (it would have worked with errors more precisely).
A slightly enhanced version of our program looks like this.

You can read about the features and download it here .
Archive source .
UPD:
alex3d recalled that if you match the manual, in Worker.run the lines
self.dialog['progressbar'].set_fraction(i/count)
self.dialog['progressbar_label'].set_text(file)need to wrap in
gtk.threads_enter () / gtk.threads_leave ().
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/72431/
All Articles