3D model of the ribosome at the atomic level
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009
Studies of the functions and structure of ribosomes.
Venkatraman Ramakrishnan (Venkatraman Ramakrishnan), USA; Thomas Steitz, USA; Ada Yonath, Israel.
As you know, the structure of any organism is programmed initially in the genetic code and is stored in DNA. According to this program (after copying it into RNA), every molecule of our body is produced. Directly compiling proteins involved ribosomes - a kind of robotic mini-factories that are present in each cell. Until the 21st century, science did not know the details of this process, but it became much clearer thanks to the work that the current Nobel laureates had almost simultaneously performed and published in 2000. They filmed the ribosome in the smallest detail using a cryo-electron microscope and made a functional 3D map of this organoid. For which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009.
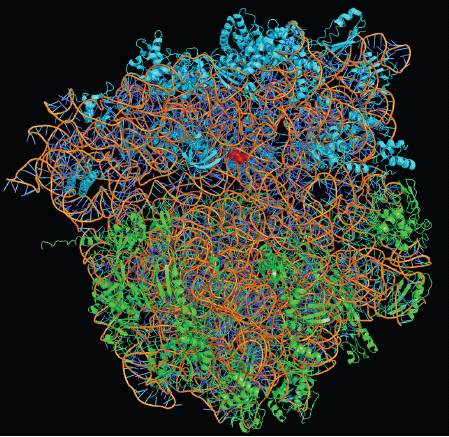
Ramakrishnan and Yonat removed the ribosome of the bacteria Haloarcula marismortui. In the illustration above, its three-dimensional model at the atomic level (parts with different functionalities are highlighted in different colors, for decoding see the explanatory note from the Nobel Committee).
On the page of the Nobel laureate Ada Yonat you can see even more animated 3D models of the ribosome (each GIF and SWF file on that page is several megabytes in size, so they are all in the archive, 17 MB ).
')

A few words about patents. The announcement by the Nobel Committee of the laureates of the prize in the field of chemistry was yet another proof of how patented modern biology is along and across, even its most fundamental components. As soon as the functional of the ribosomes was modeled, it immediately became clear how the ribosomes react to other molecules of different structure. It became possible to simulate on the computer the action of various artificial molecules (drugs) that may affect the work of the ribosomes in one way or another, including disrupting their work. This is how antibiotics tetracycline, neomycin and others work. They kill harmful cells in the body by joining their ribosomes and stopping them.
Patents for all drugs created using this model, which has now received the Nobel Prize, belong to pharmaceutical corporations, which deduct their interest, including Nobel Prize winner Thomas Steitz.
However, patents have always been a part of science. Actually, the Nobel Prize itself is issued from the money received from a patent for dynamite, which Alfred Nobel registered in 1867.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/71851/
All Articles