Zero houses
Energy efficient homes are becoming increasingly popular in the world. The construction of such houses is not only a tribute to modern fashion, the desire to stand out, to build something unusual, ultramodern. The growing popularity of “zero homes” is also due to purely economic considerations, an opportunity to save on utility bills in the future. The article describes examples of the construction of energy-saving buildings in China.
Buildings with zero energy balance - “zero homes” - are gradually conquering the world. It is believed that such houses can function completely autonomously and generate heat and electricity for their own needs on their own. Such structures do not depend or almost do not depend on centralized electrical and heating networks. Solar collectors and batteries, wind generators and bioreactors are integrated into cottages, pavilions, skyscrapers and even stadiums; special systems of ventilation and rainwater collection are used, elements of solar architecture and a number of other solutions are applied. All this allows you to significantly save on the operation of such buildings, and also makes not only safe, but also comfortable to stay in them person.
')
Examples of “zero houses”
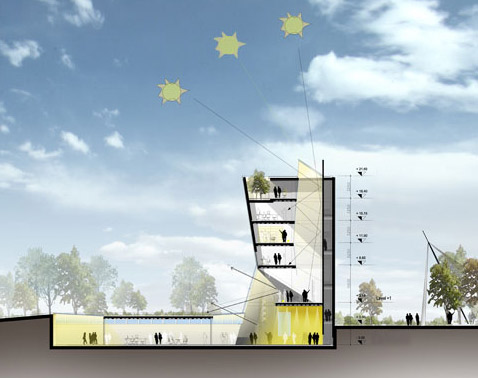
On September 20, 2008, the ceremonial opening of the Energy Technology Center in Ningbo (PRC) took place on the campus of the Chinese branch of the British University of Nottingham. The building of the Center was designed by the Italian company Mario Cucinella Architects. During the design, the principles of the “zero house” were used, allowing the maximum use of the natural possibilities for thermoregulation and lighting of the building.

The building houses audiences and offices, a small exhibition hall, as well as several laboratories: stands for testing facades, a thermal laboratory for testing structural materials, a climate chamber and a wind tunnel, a laboratory for modeling solar lighting. The total area of the building is 1300 square meters and is provided with energy due to photovoltaic batteries combined into a solar farm, as well as wind turbines. The building is equipped with batteries that are able to provide the entire structure with electricity for two weeks.
Proper distribution of air and light flux depending on the height and position of the sun above the horizon is provided by the special architecture of the building. The building has five above ground and one underground floor. All of them are interconnected by a wide shaft overlooking the roof. This element allows the reflected rays of the sun to penetrate deeper, reducing the need for electric lighting, and also sets the path for air flow. The Center spends only 7-8 kWh per 1 sq.m / year for its own cooling.
Another example of a “zero” facility in the PRC is an energy-efficient building built for Xinhua University in Beijing. The building is designed to minimize heating and cooling costs. On the one hand, a roof canopy creates a shadow in hot sunny weather, on the other, it produces electricity using solar panels installed here.

The 300-meter “Pearl River Tower” in Guangzhou, designed by the American company Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, should become the largest “zero” structure in China. The 300-meter 69-story Pearl River Tower is designed as a zero-energy building, that is, it will not consume electricity from an external network. The tower will be made special double glazing of the southern facade (with ventilation between the glass), to reduce the heating of the building.

Automatic blinds will be installed in the Building, turning to the desired angle as the Sun travels across the sky, and also opening in cloudy weather to increase the natural lighting of the offices. All this will reduce the cost of air conditioning.
Solar panels will generate electricity, the excess of which is stored in special batteries. In addition to photovoltaic panels, solar thermal collectors are also mounted here that heat the water for the inhabitants of the skyscraper.
The Americans also planned for the “Pearl River” a rainwater harvesting system and a system for cleaning and recycling industrial water (used, for example, to flush toilets), which should minimize the need for a building for an external source of moisture.
Smooth curves of the walls of the skyscraper are designed to direct the wind through the building through 2 technical floors, where wind turbines will be installed to produce electricity. In this case, the building is specially designed for the prevailing winds.
In the cooling system of the building, which will work in a hot and humid climate, the architects used a number of new products to minimize the cost of maintaining the microclimate of the building.
This includes passive ventilation air dryers (ventilation channels are located in the floors of the building) and air cooling system in offices with high efficiency. Unlike common centralized air conditioning systems, it is based on the circulation of refrigerant through numerous ramified channels that also penetrate the floors on all floors.
Source - unfortunately, to make a topic-link for some reason did not work
Related information
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/70407/
All Articles