Why simple website design is better scientifically

A study by Google had two key findings:
- The user needs only 1/50 to 1/20 of a second to evaluate whether a site is beautiful or not.
- "Visually complex" sites are rated as less beautiful than their simple counterparts.
In other words, research has shown that the simpler the design, the better.
')
But why?
In this article, we will look at examples of the role of cognitive fluency and visual information processing theory, which play an important role in simplifying your web design and help increase conversion .
Let's get started!
What is a "prototype" of the site?
If I say “furniture”, what image will appear in your head?
If you are like 95% of people, you will think of a chair.
If I ask what color is associated with “boy”, you think “blue” (and the girl is “pink”, etc.)
A prototype is the basic mental image that your brain creates to classify everything that you interact with. From furniture to sites, your brain has a pattern of how everything should look and feel.
On the web, prototypes fall into smaller categories. You have different, but specific psychological images for social networks, sites, e-commerce, and blogs. If on any of these sites something is missing in your mental image, you close the site on a conscious and subconscious level.
If I said “website for fashionable women’s clothing”, you could imagine something like this:

Now, let's look at the prototype sites of the “online clothing store”, notice that they are all very similar and have a similar site structure? (even if this site is from another country).

The similarity does not mean at all that the sites lack originality or that they “stole” one from another. With such a structure, they live up to your expectations regarding how an e-commerce site should look.
What is cognitive fluency?
The basic idea behind cognitive fluency is that the brain prefers to think about things that are easy to think about. That's why you prefer to visit sites whose design and structure you instinctively understand.
Cognitive fluency springs from another area of behavior known as the “ Simple Effect Effect, ” which states that people prefer things they know.
This rule also applies online. We are used to the fact that the subscription on the site is located in the right corner of the site, and the company logo in the upper left corner.
If your visitors are determined by the specific design of sites in your category, deviating from them may subconsciously put you in the “less beautiful” category.
This does not mean at all that you should simply "do what everyone else does." You need to know which site design options are the prototypes for your category. Be sure to check and find evidence that this particular design is the prototype in your category.
Without doing research, many designers make poor choices. For example, many e-commerce sites use an automatic product image scroll slider, but study by study shows that the automatic slider ruins conversion .
What happens when you live up to expectations?
A site with a high level of fluency will feel familiar enough, so visitors do not need to spend mental effort to find the right product or button, and instead they can focus on why they came to your site.
However, when fluency is low, you will immediately feel it. Take the Skinny Ties online tie shop, which before the redesign didn’t look like an e-commerce site:
Before:

After:

Several key changes have led to tremendous results:
- Simple and understandable website design and structure;
- A much more “open” design with competent use of spaces;
- Images contain one high-resolution product with contrasting colors.
Let's get acquainted with the statistics of this redesign.
In just two and a half weeks, the results were stunning:

The redesign itself, although pretty, is not revolutionary. The site exactly matches the expectations of what a modern online clothing store should be like. He is "open", responsive and has a single style on all pages.
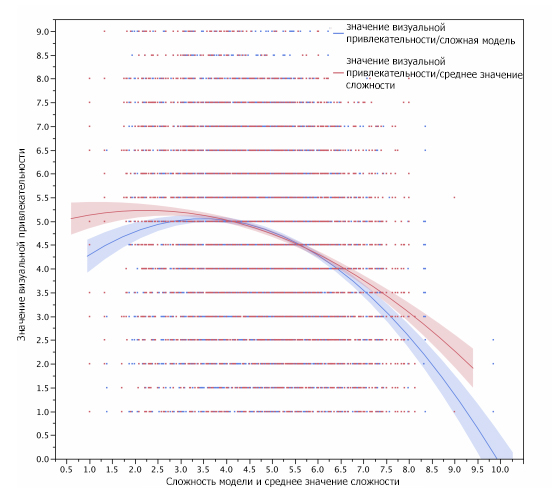
Visual processing of information and site complexity
In this joint study by Harvard University, the University of Maryland, and the University of Colorado, researchers found a strong correlation of “aesthetically attractive” sites among different demographic groups.
For example, doctoral students did not like very colorful websites.
As a result of the study, no specific universal design principles were developed. The only thing that was universal was that a visually sophisticated website had less visual appeal.
Why simple design is scientifically easier to handle
The reason why "visually light" websites are considered more beautiful is partly due to the fact that with low complexity, our eyes and brain do not need to work as hard to decode, store and process information.
Watch this short video on how the eye sends information to the brain to understand what I mean:
Essentially, your retina converts visual information from the real world into electrical impulses. These pulses are then sent through the corresponding photoreceptor cells to transmit color and light information to the brain.
The more color and light variations on the page (i.e., the greater the visual complexity), the more work the eye has to do to transmit information to the brain.
Each element conveys subtle information.
When developing a site, be aware that each element - text, logo and color choice - conveys subtle brand information.
When these elements do not do their job, the webmaster often compensates for this by adding unnecessary elements or images, which increases the visual complexity of the website and breaks the overall aesthetics.
Optimizing a page for processing visual information, in particular, simplifying the flow of information from the eye to the brain, is the transfer of as much information as possible with a minimum number of elements.
Consider the redesign of the MailChimp logo as an example.
When they wanted the brand to "grow", they did not add the usual "We have been working with email since 2001! Three million people trust us! That's why we are cool! Blah blah blah…"
It was:

It became:

Instead, they simplified the spelling, simplified the website (the top heading just reads “Send better Email”) and added an even simpler animation for the main product.
Mailchimp went through another logo redesign in 2018:

What were the guidelines for the second major redesign?
Simplicity was paramount :
The Freddy badge has long been the main brand of our brand.
We simplified it a bit, made changes to its shape and worked out small details to make it look great at any size.
In the process of iteration and refinement, we developed a font that is in harmony with the Freddy icon.
“Working Memory” and the Holy Grail of Conversion
According to a study by Princeton psychologist George A. Miller, an adult's brain is capable of storing from five to nine “pieces” of information in its short-term or “working” memory.
Working memory is the part of your brain that temporarily stores and processes information for several seconds. This is what allows you to focus, resist distractions and, most importantly, guide the decision-making process.

On a “low complexity and prototype website,” five to nine “bits” of working memory can handle things like warranties, product descriptions, prices, or offers, rather than wasting time figuring out where to click.
When you deviate from your expectations - the price is higher than expected, the color scheme is not healthy and there is no symmetry, the site has been loading for a long time , the photos were of poor quality - working memory processes these unnecessary "pieces" instead of doing important things.

This is because working memory calls up long-term memory to use what it already knows to complete the task. When long-term memory cannot help with information processing, the flow is interrupted , and working memory is turned off and moves on.
That is why it is very important to know your visitors if you want to “hack” their working memory using design.
The blogs they read, the sites they shop on, their browser, age, gender and physical location - all this will help you make the design “familiar” and create the right first impression.
7 Ways to Create a Simple Website
- Explore your audience and the sites they visit the most.
Check out case studies about design changes in your category. - Create a collage for your site with all the “working” components that you discover.
- Follow the rules of cognitive fluency.
Place items where visitors expect to find them. - Do not add unnecessary items if they do not report what excites your visitor.
- Less is more. One large image is usually better than several small ones; one column instead of three; more spaces instead of more “elements”.
- Make sure your site meets expectations for pricing, aesthetics, speed, etc.
- Keep originality. A “prototype” of a site does not mean that every aspect of your site must conform to this form.
Do not think of your site as a unique work of art.
Make it simple and familiar to users.
Conclusion
If a visitor, when interacting with your site, cannot rely on his previous experience, he does not think about how innovative your site is. He just wonders why things are not where they “should be”.
By creating a design with cognitive fluency, you allow visitors to process more important things with their working memory so that it is easier for them to say “yes”.
More such articles can be read on my telegram channel (proroas). I write about marketing and web analytics.
Your high conversions!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/461819/
All Articles