SQL Entertaining puzzles
Hello, Habr!
For more than 3 years now I have been teaching SQL in various training centers, and one of my observations is that students master and understand SQL better if they set a task, and not just talk about the possibilities and theoretical foundations.
In this article I will share with you my list of tasks that I give students as homework and over which we conduct various kinds of brainstorms, which leads to a deep and clear understanding of SQL.
')
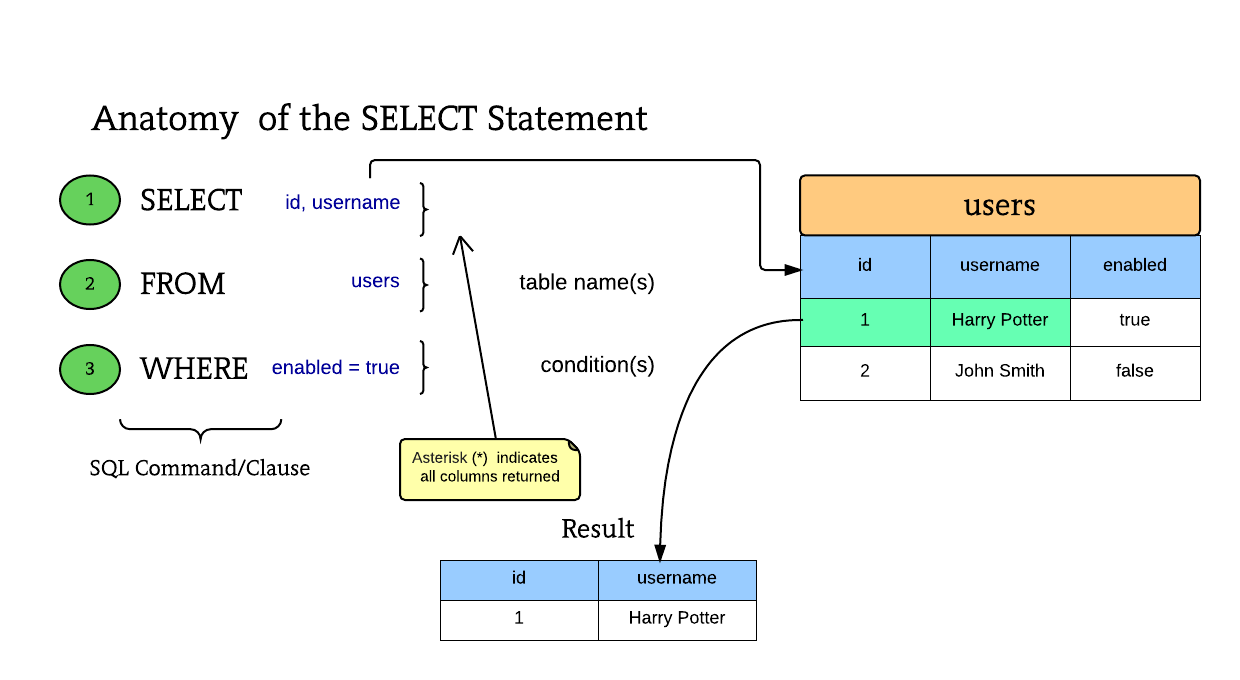
SQL (ˈɛsˈkjuˈɛl; English structured query language) is a declarative programming language used to create, modify and manage data in a relational database managed by the corresponding database management system. Learn more
You can read about SQL from various sources .
This article is not intended to teach you SQL from scratch.
So let's go.
We will use the well-known HR schema in Oracle with its tables ( more ):
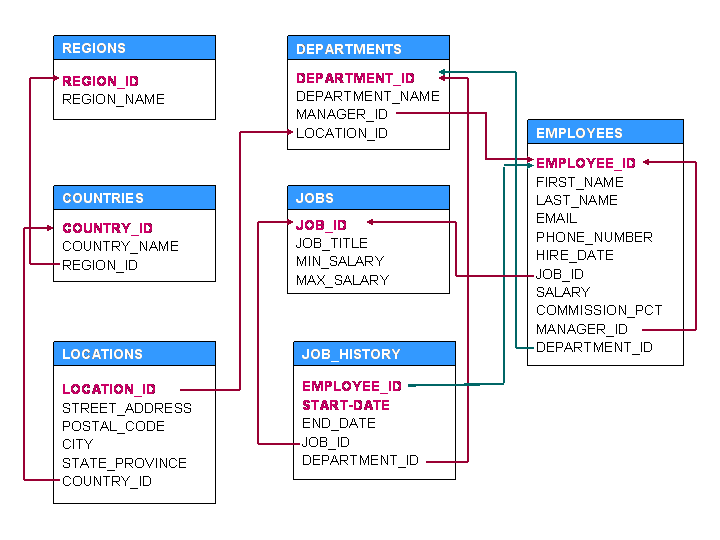
I note that we will only consider SELECT tasks. There are no problems with DML and DDL.
Restricting and Sorting Data
Employees table. Get a list with information about all employees
Employees table. Get a list of all employees named 'David'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees with job_id equal to 'IT_PROG'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 50th department (department_id) with salary (salary), more than 4000
Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 20th and from the 30th department (department_id)
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last letter in the name is 'a'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 50th and from the 80th department (department_id) who have a bonus (the value in the commission_pct column is not empty)
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains at least 2 letters 'n'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name is longer than 4 letters
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose salary is in the range from 8000 to 9000 (inclusive)
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains the character '%'
Employees table. Get a list of all ID managers
Employees table. Get a list of employees with their positions in the format: Donald (sh_clerk)
Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name is longer than 10 letters
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have the letter 'b' in their name (case insensitive)
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains at least 2 letters 'a'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose salary is a multiple of 1000
Employees table. Get the first 3-digit number of the employee’s phone number if his number is in the format XXXX.XXX.XXXX
Departments table. Get the first word from the name of the department for those with more than one word in the name
Employees table. Get the names of employees without the first and last letters in the name
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last letter in the name is 'm' and a long name greater than 5
Dual table. Get Next Friday Date
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have been working in the company for over 17 years
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last digit of the phone number is odd and consists of 3 numbers separated by a dot
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have at least 3 characters in the job_id value after the '_' sign but this value after '_' is not equal to 'CLERK'
Employees table. Get a list of all employees by replacing all '.' In the value PHONE_NUMBER. on '-'
Using Conversion Functions and Conditional Expressions
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who came to work on the first day of the month (any)
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who came to work in 2008
DUAL table. Display tomorrow's date in the format: Tomorrow is Second day of January
Employees table. Get a list of all employees and the date everyone came to work in the format: 21st of June, 2007
Employees table. Get a list of employees with increased salaries by 20%. Show salary with dollar sign
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who come to work in February 2007.
DUAL table. Take out the current date, + second, + minute, + hour, + day, + month, + year
Employees table. Get a list of all employees with full salaries (salary + commission_pct (%)) in the format: $ 24,000.00
Employees table. Get a list of all employees and information about the availability of salary bonuses (Yes / No)
Employees table. Get the salary level of each employee: Less than 5000 is considered Low level, Greater than or equal to 5000 and less than 10000 is considered Normal level, Greater than or equal to 10000 is considered High
Countries table. For each country, show the region in which it is located: 1-Europe, 2-America, 3-Asia, 4-Africa (without Join)
Reporting Aggregated Data Using the Group Functions
Employees table. Get a report on department_id with a minimum and maximum salary, with an early and late date of arrival at work and with the number of employees. Sort by number of employees (descending)
Employees table. How many employees whose names begin with the same letter? Sort by quantity. Only show where quantity is greater than 1
Employees table. How many employees who work in the same department and receive the same salary?
Employees table. Get a report of how many employees were hired on each day of the week. Sort by quantity
Employees table. Get a report of how many employees were hired by year. Sort by quantity
Employees table. Get the number of departments in which there are employees
Employees table. Get a list of department_id with more than 30 employees
Employees table. Get a list of department_id and a rounded average salary for employees in each department.
Countries table. Get a list of region_id the sum of all the letters of all country_name in which more than 60
Employees table. Get a list of department_id in which employees of several (> 1) job_id work
Employees table. Get a list of manager_id whose number of subordinates is more than 5 and the sum of all salaries of his subordinates is more than 50,000
Employees table. Get a list of manager_id for which the average salary of all his subordinates is in the range from 6000 to 9000 who do not receive bonuses (commission_pct is empty)
Employees table. Get the maximum salary from all employees job_id who ends in the word 'CLERK'
Employees table. Get the maximum salary among all average salaries in the department
Employees table. Get the number of employees with the same number of letters in the name. At the same time, show only those with a name length of more than 5 and the number of employees with that name is more than 20. Sort by name length
Displaying Data from Multiple Tables Using Joins
Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get a list of regions and the number of employees in each region
Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get detailed information about each employee:
First_name, Last_name, Departament, Job, Street, Country, Region
Employees table. Show all managers who have more than 6 employees
Employees table. Show all employees who do not report to anyone
Employees table, Job_history. The Employee table stores all employees. The Job_history table stores the employees who left the company. Get a report about all employees and their status in the company (Works or left the company with the date of departure)
Example:
first_name | status
Jennifer | Left the company at 31 of December, 2006
Clara | Currently working
Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get a list of employees who live in Europe (region_name)
Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments with more than 30 employees
Employees table, Departaments. Show all employees who are not in any department
Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments without a single employee
Employees table. Show all employees who have no subordinates
Table Employees, Jobs, Departaments. Show employees in the format: First_name, Job_title, Department_name.
Example:
First_name | Job_title | Department_name
Donald | Shipping | Clerk shipping
Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in 2005, but at the same time, these employees themselves got a job until 2005
Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in the month of January of any year and the job_title length of these employees is more than 15 characters
Using Subqueries to Solve Queries
Employees table. Get a list of employees with the longest name.
Employees table. Get a list of employees with a salary greater than the average salary of all employees.
Table Employees, Departments, Locations. Get a city in which employees earn less in total.
Employees table. Get a list of employees whose manager receives a salary of more than 15,000.
Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments without a single employee
Employees table. Show all employees who are not managers
Employees table. Show all managers who have more than 6 employees
Employees table, Departaments. Show employees who work in the IT department
Table Employees, Jobs, Departaments. Show employees in the format: First_name, Job_title, Department_name.
Example:
First_name | Job_title | Department_name
Donald | Shipping | Clerk shipping
Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in 2005, but at the same time, these employees themselves got a job until 2005
Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in the month of January of any year and the job_title length of these employees is more than 15 characters
That's all for now.
I hope the tasks were interesting and fascinating.
If possible, I will supplement this list of tasks.
I will also be glad to any comments and suggestions.
PS: If someone comes up with an interesting SELECT task, write in the comments, add to the list.
Thank.
For more than 3 years now I have been teaching SQL in various training centers, and one of my observations is that students master and understand SQL better if they set a task, and not just talk about the possibilities and theoretical foundations.
In this article I will share with you my list of tasks that I give students as homework and over which we conduct various kinds of brainstorms, which leads to a deep and clear understanding of SQL.
')

SQL (ˈɛsˈkjuˈɛl; English structured query language) is a declarative programming language used to create, modify and manage data in a relational database managed by the corresponding database management system. Learn more
You can read about SQL from various sources .
This article is not intended to teach you SQL from scratch.
So let's go.
We will use the well-known HR schema in Oracle with its tables ( more ):

I note that we will only consider SELECT tasks. There are no problems with DML and DDL.
Tasks
Restricting and Sorting Data
Employees table. Get a list with information about all employees
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees Employees table. Get a list of all employees named 'David'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'David'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees with job_id equal to 'IT_PROG'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE job_id = 'IT_PROG' Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 50th department (department_id) with salary (salary), more than 4000
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50 AND salary > 4000; Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 20th and from the 30th department (department_id)
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id = 20 OR department_id = 30; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last letter in the name is 'a'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name LIKE '%a'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees from the 50th and from the 80th department (department_id) who have a bonus (the value in the commission_pct column is not empty)
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE (department_id = 50 OR department_id = 80) AND commission_pct IS NOT NULL; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains at least 2 letters 'n'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name LIKE '%n%n%'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name is longer than 4 letters
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name LIKE '%_____%'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose salary is in the range from 8000 to 9000 (inclusive)
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary BETWEEN 8000 AND 9000; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains the character '%'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name LIKE '%\%%' ESCAPE '\'; Employees table. Get a list of all ID managers
Decision
SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL; Employees table. Get a list of employees with their positions in the format: Donald (sh_clerk)
Decision
SELECT first_name || '(' || LOWER (job_id) || ')' employee FROM employees; Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output
Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name is longer than 10 letters
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE LENGTH (first_name) > 10; Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have the letter 'b' in their name (case insensitive)
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE INSTR (LOWER (first_name), 'b') > 0; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose name contains at least 2 letters 'a'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE INSTR (LOWER (first_name),'a',1,2) > 0; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose salary is a multiple of 1000
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE MOD (salary, 1000) = 0; Employees table. Get the first 3-digit number of the employee’s phone number if his number is in the format XXXX.XXX.XXXX
Decision
SELECT phone_number, SUBSTR (phone_number, 1, 3) new_phone_number FROM employees WHERE phone_number LIKE '___.___.____'; Departments table. Get the first word from the name of the department for those with more than one word in the name
Decision
SELECT department_name, SUBSTR (department_name, 1, INSTR (department_name, ' ')-1) first_word FROM departments WHERE INSTR (department_name, ' ') > 0; Employees table. Get the names of employees without the first and last letters in the name
Decision
SELECT first_name, SUBSTR (first_name, 2, LENGTH (first_name) - 2) new_name FROM employees; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last letter in the name is 'm' and a long name greater than 5
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE SUBSTR (first_name, -1) = 'm' AND LENGTH(first_name)>5; Dual table. Get Next Friday Date
Decision
SELECT NEXT_DAY (SYSDATE, 'FRIDAY') next_friday FROM DUAL; Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have been working in the company for over 17 years
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (SYSDATE, hire_date) / 12 > 17; Employees table. Get a list of all employees whose last digit of the phone number is odd and consists of 3 numbers separated by a dot
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE MOD (SUBSTR (phone_number, -1), 2) != 0 AND INSTR (phone_number,'.',1,3) = 0; Employees table. Get a list of all employees who have at least 3 characters in the job_id value after the '_' sign but this value after '_' is not equal to 'CLERK'
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE LENGTH (SUBSTR (job_id, INSTR (job_id, '_') + 1)) > 3 AND SUBSTR (job_id, INSTR (job_id, '_') + 1) != 'CLERK'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees by replacing all '.' In the value PHONE_NUMBER. on '-'
Decision
SELECT phone_number, REPLACE (phone_number, '.', '-') new_phone_number FROM employees; Using Conversion Functions and Conditional Expressions
Employees table. Get a list of all employees who came to work on the first day of the month (any)
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'DD') = '01'; Employees table. Get a list of all employees who came to work in 2008
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'YYYY') = '2008'; DUAL table. Display tomorrow's date in the format: Tomorrow is Second day of January
Decision
SELECT TO_CHAR (SYSDATE, 'fm""Tomorrow is ""Ddspth ""day of"" Month') info FROM DUAL; Employees table. Get a list of all employees and the date everyone came to work in the format: 21st of June, 2007
Decision
SELECT first_name, TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'fmddth ""of"" Month, YYYY') hire_date FROM employees; Employees table. Get a list of employees with increased salaries by 20%. Show salary with dollar sign
Decision
SELECT first_name, TO_CHAR (salary + salary * 0.20, 'fm$999,999.00') new_salary FROM employees; Employees table. Get a list of all employees who come to work in February 2007.
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE hire_date BETWEEN TO_DATE ('01.02.2007', 'DD.MM.YYYY') AND LAST_DAY (TO_DATE ('01.02.2007', 'DD.MM.YYYY')); SELECT * FROM employees WHERE to_char(hire_date,'MM.YYYY') = '02.2007'; DUAL table. Take out the current date, + second, + minute, + hour, + day, + month, + year
Decision
SELECT SYSDATE now, SYSDATE + 1 / (24 * 60 * 60) plus_second, SYSDATE + 1 / (24 * 60) plus_minute, SYSDATE + 1 / 24 plus_hour, SYSDATE + 1 plus_day, ADD_MONTHS (SYSDATE, 1) plus_month, ADD_MONTHS (SYSDATE, 12) plus_year FROM DUAL; Employees table. Get a list of all employees with full salaries (salary + commission_pct (%)) in the format: $ 24,000.00
Decision
SELECT first_name, salary, TO_CHAR (salary + salary * NVL (commission_pct, 0), 'fm$99,999.00') full_salary FROM employees; Employees table. Get a list of all employees and information about the availability of salary bonuses (Yes / No)
Decision
SELECT first_name, commission_pct, NVL2 (commission_pct, 'Yes', 'No') has_bonus FROM employees; Employees table. Get the salary level of each employee: Less than 5000 is considered Low level, Greater than or equal to 5000 and less than 10000 is considered Normal level, Greater than or equal to 10000 is considered High
Decision
SELECT first_name, salary, CASE WHEN salary < 5000 THEN 'Low' WHEN salary >= 5000 AND salary < 10000 THEN 'Normal' ELSE 'High' END salary_level FROM employees; Countries table. For each country, show the region in which it is located: 1-Europe, 2-America, 3-Asia, 4-Africa (without Join)
Decision
SELECT country_name country, DECODE (region_id, 1, 'Europe', 2, 'America', 3, 'Asia', 4, 'Africa', 'Unknown') region FROM countries; SELECT country_name country, CASE region_id WHEN 1 THEN 'Europe' WHEN 2 THEN 'America' WHEN 3 THEN 'Asia' WHEN 4 THEN 'Africa' ELSE 'Unknown' END region FROM countries; Reporting Aggregated Data Using the Group Functions
Employees table. Get a report on department_id with a minimum and maximum salary, with an early and late date of arrival at work and with the number of employees. Sort by number of employees (descending)
Decision
SELECT department_id, MIN (salary) min_salary, MAX (salary) max_salary, MIN (hire_date) min_hire_date, MAX (hire_date) max_hire_Date, COUNT (*) count FROM employees GROUP BY department_id order by count(*) desc; Employees table. How many employees whose names begin with the same letter? Sort by quantity. Only show where quantity is greater than 1
Decision
SELECT SUBSTR (first_name, 1, 1) first_char, COUNT (*) FROM employees GROUP BY SUBSTR (first_name, 1, 1) HAVING COUNT (*) > 1 ORDER BY 2 DESC; Employees table. How many employees who work in the same department and receive the same salary?
Decision
SELECT department_id, salary, COUNT (*) FROM employees GROUP BY department_id, salary HAVING COUNT (*) > 1; Employees table. Get a report of how many employees were hired on each day of the week. Sort by quantity
Decision
SELECT TO_CHAR (hire_Date, 'Day') day, COUNT (*) FROM employees GROUP BY TO_CHAR (hire_Date, 'Day') ORDER BY 2 DESC; Employees table. Get a report of how many employees were hired by year. Sort by quantity
Decision
SELECT TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'YYYY') year, COUNT (*) FROM employees GROUP BY TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'YYYY'); Employees table. Get the number of departments in which there are employees
Decision
SELECT COUNT (COUNT (*)) department_count FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL GROUP BY department_id; Employees table. Get a list of department_id with more than 30 employees
Decision
SELECT department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id HAVING COUNT (*) > 30; Employees table. Get a list of department_id and a rounded average salary for employees in each department.
Decision
SELECT department_id, ROUND (AVG (salary)) avg_salary FROM employees GROUP BY department_id; Countries table. Get a list of region_id the sum of all the letters of all country_name in which more than 60
Decision
SELECT region_id FROM countries GROUP BY region_id HAVING SUM (LENGTH (country_name)) > 60; Employees table. Get a list of department_id in which employees of several (> 1) job_id work
Decision
SELECT department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id HAVING COUNT (DISTINCT job_id) > 1; Employees table. Get a list of manager_id whose number of subordinates is more than 5 and the sum of all salaries of his subordinates is more than 50,000
Decision
SELECT manager_id FROM employees GROUP BY manager_id HAVING COUNT (*) > 5 AND SUM (salary) > 50000; Employees table. Get a list of manager_id for which the average salary of all his subordinates is in the range from 6000 to 9000 who do not receive bonuses (commission_pct is empty)
Decision
SELECT manager_id, AVG (salary) avg_salary FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NULL GROUP BY manager_id HAVING AVG (salary) BETWEEN 6000 AND 9000; Employees table. Get the maximum salary from all employees job_id who ends in the word 'CLERK'
Decision
SELECT MAX (salary) max_salary FROM employees WHERE job_id LIKE '%CLERK'; SELECT MAX (salary) max_salary FROM employees WHERE SUBSTR (job_id, -5) = 'CLERK'; Employees table. Get the maximum salary among all average salaries in the department
Decision
SELECT MAX (AVG (salary)) FROM employees GROUP BY department_id; Employees table. Get the number of employees with the same number of letters in the name. At the same time, show only those with a name length of more than 5 and the number of employees with that name is more than 20. Sort by name length
Decision
SELECT LENGTH (first_name), COUNT (*) FROM employees GROUP BY LENGTH (first_name) HAVING LENGTH (first_name) > 5 AND COUNT (*) > 20 ORDER BY LENGTH (first_name); SELECT LENGTH (first_name), COUNT (*) FROM employees WHERE LENGTH (first_name) > 5 GROUP BY LENGTH (first_name) HAVING COUNT (*) > 20 ORDER BY LENGTH (first_name); Displaying Data from Multiple Tables Using Joins
Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get a list of regions and the number of employees in each region
Decision
SELECT region_name, COUNT (*) FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) JOIN locations l ON (d.location_id = l.location_id) JOIN countries c ON (l.country_id = c.country_id) JOIN regions r ON (c.region_id = r.region_id) GROUP BY region_name; Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get detailed information about each employee:
First_name, Last_name, Departament, Job, Street, Country, Region
Decision
SELECT First_name, Last_name, Department_name, Job_id, street_address, Country_name, Region_name FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) JOIN locations l ON (d.location_id = l.location_id) JOIN countries c ON (l.country_id = c.country_id) JOIN regions r ON (c.region_id = r.region_id); Employees table. Show all managers who have more than 6 employees
Decision
SELECT man.first_name, COUNT (*) FROM employees emp JOIN employees man ON (emp.manager_id = man.employee_id) GROUP BY man.first_name HAVING COUNT (*) > 6; Employees table. Show all employees who do not report to anyone
Decision
SELECT emp.first_name FROM employees emp LEFT JOIN employees man ON (emp.manager_id = man.employee_id) WHERE man.FIRST_NAME IS NULL; SELECT first_name FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NULL; Employees table, Job_history. The Employee table stores all employees. The Job_history table stores the employees who left the company. Get a report about all employees and their status in the company (Works or left the company with the date of departure)
Example:
first_name | status
Jennifer | Left the company at 31 of December, 2006
Clara | Currently working
Decision
SELECT first_name, NVL2 ( end_date, TO_CHAR (end_date, 'fm""Left the company at"" DD ""of"" Month, YYYY'), 'Currently Working') status FROM employees e LEFT JOIN job_history j ON (e.employee_id = j.employee_id); Employees, Departaments, Locations, Countries, Regions table. Get a list of employees who live in Europe (region_name)
Decision
SELECT first_name FROM employees JOIN departments USING (department_id) JOIN locations USING (location_id) JOIN countries USING (country_id) JOIN regions USING (region_id) WHERE region_name = 'Europe'; SELECT first_name FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) JOIN locations l ON (d.location_id = l.location_id) JOIN countries c ON (l.country_id = c.country_id) JOIN regions r ON (c.region_id = r.region_id) WHERE region_name = 'Europe'; Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments with more than 30 employees
Decision
SELECT department_name, COUNT (*) FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) GROUP BY department_name HAVING COUNT (*) > 30; Employees table, Departaments. Show all employees who are not in any department
Decision
SELECT first_name FROM employees e LEFT JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) WHERE d.department_name IS NULL; SELECT first_name FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NULL; Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments without a single employee
Decision
SELECT department_name FROM employees e RIGHT JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) WHERE first_name IS NULL; Employees table. Show all employees who have no subordinates
Decision
SELECT man.first_name FROM employees emp RIGHT JOIN employees man ON (emp.manager_id = man.employee_id) WHERE emp.FIRST_NAME IS NULL; Table Employees, Jobs, Departaments. Show employees in the format: First_name, Job_title, Department_name.
Example:
First_name | Job_title | Department_name
Donald | Shipping | Clerk shipping
Decision
SELECT first_name, job_title, department_name FROM employees e JOIN jobs j ON (e.job_id = j.job_id) JOIN departments d ON (d.department_id = e.department_id); Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in 2005, but at the same time, these employees themselves got a job until 2005
Decision
SELECT emp.* FROM employees emp JOIN employees man ON (emp.manager_id = man.employee_id) WHERE TO_CHAR (man.hire_date, 'YYYY') = '2005' AND emp.hire_date < TO_DATE ('01012005', 'DDMMYYYY'); Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in the month of January of any year and the job_title length of these employees is more than 15 characters
Decision
SELECT emp.* FROM employees emp JOIN employees man ON (emp.manager_id = man.employee_id) JOIN jobs j ON (emp.job_id = j.job_id) WHERE TO_CHAR (man.hire_date, 'MM') = '01' AND LENGTH (j.job_title) > 15; Using Subqueries to Solve Queries
Employees table. Get a list of employees with the longest name.
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE LENGTH (first_name) = (SELECT MAX (LENGTH (first_name)) FROM employees); Employees table. Get a list of employees with a salary greater than the average salary of all employees.
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG (salary) FROM employees); Table Employees, Departments, Locations. Get a city in which employees earn less in total.
Decision
SELECT city FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) JOIN locations l ON (d.location_id = l.location_id) GROUP BY city HAVING SUM (salary) = ( SELECT MIN (SUM (salary)) FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) JOIN locations l ON (d.location_id = l.location_id) GROUP BY city); Employees table. Get a list of employees whose manager receives a salary of more than 15,000.
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE manager_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE salary > 15000) Employees table, Departaments. Show all departments without a single employee
Decision
SELECT * FROM departments WHERE department_id NOT IN (SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL); Employees table. Show all employees who are not managers
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id NOT IN (SELECT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL) Employees table. Show all managers who have more than 6 employees
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees e WHERE (SELECT COUNT (*) FROM employees WHERE manager_id = e.employee_id) > 6; Employees table, Departaments. Show employees who work in the IT department
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id = (SELECT department_id FROM departments WHERE department_name = 'IT'); Table Employees, Jobs, Departaments. Show employees in the format: First_name, Job_title, Department_name.
Example:
First_name | Job_title | Department_name
Donald | Shipping | Clerk shipping
Decision
SELECT first_name, (SELECT job_title FROM jobs WHERE job_id = e.job_id) job_title, (SELECT department_name FROM departments WHERE department_id = e.department_id) department_name FROM employees e; Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in 2005, but at the same time, these employees themselves got a job until 2005
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE manager_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'YYYY') = '2005') AND hire_date < TO_DATE ('01012005', 'DDMMYYYY'); Employees table. Get a list of employees whose managers got a job in the month of January of any year and the job_title length of these employees is more than 15 characters
Decision
SELECT * FROM employees e WHERE manager_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE TO_CHAR (hire_date, 'MM') = '01') AND (SELECT LENGTH (job_title) FROM jobs WHERE job_id = e.job_id) > 15; That's all for now.
I hope the tasks were interesting and fascinating.
If possible, I will supplement this list of tasks.
I will also be glad to any comments and suggestions.
PS: If someone comes up with an interesting SELECT task, write in the comments, add to the list.
Thank.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/461567/
All Articles