How I broke Telegram
Once I hacked one of the telegram servers. Not that it was something interesting, and the vulnerabilities themselves are standard. Surprise is rather a fact of how telegrams relate to security and why, for many years, no one has exploited vulnerabilities. But the one who does nothing is not mistaken!

Back in May 2017, kyprizel drew attention to the fact that the telegram desktop can download ZIP archives to itself on the tdesktop.com server. As it turned out later, not only ZIP, but inside there is information about the fall of the application, so that the developer can learn under what circumstances the fall occurred. In addition, the developer gets access to them through a web interface, judging by the form of authentication. I added the host to the notes and safely forgot.

')
I remembered him about a year later, when we discussed the upcoming research in the chat. At that time, the error_log file was in the root, in which, as you might guess, errors were written. At a minimum, there were full paths to the files, but beyond that, the favorite error was “You have an error in your SQL syntax”. But we are all lazy, and I generally try not to participate in bug bounty, so everything remains as it is.

Another year passed, I was invited to speak at the #PartyHack conference in Kazan. And when you do not have material for the performance - you look in the notes. What is there with us? Suspicious Telegram Host
Since PHP was used on the server, as crash.php showed, I decided to sort through the files with this extension, then I came across info.php, where the contents of the phpinfo () function were located. The first thing I noticed was the use of the Apache web server. How so? The whole telegraph nginx, and here Apache! And who uses apache in 2019?

What first comes to mind when you hear Apache? I immediately remember about mod_status, which is going with it by default. This module generates a page with the current state of the server, about system resources, requests to the server, the speed of their processing. Most often, the path to it is / server-status, rarely just / status. To understand how popular this administration error is, it suffices to recall that it has been hanging on apache.org for many years.

For many years I have been collecting paths to potentially dangerous files and directories in the fuzz.txt project, so the server-status was naturally there.
In general, in server-status, it is noteworthy that it also shows the IP addresses of clients who send requests to the server. But in this case, all requests were from 127.0.0.1 to the virtual domain preston-desktop.com. Nginx on the front end simply proxied all requests for local apache, so there was no disclosure of user information. However, it was worthwhile to put the server-status on monitoring, here is a small script made on the knee, which puts unique lines in the sqlite database. For a short period of time, a lot of unique links were collected, but mostly they were requests for updates (with the version indicated), and there were almost no downloads. After a while I saw the admin.
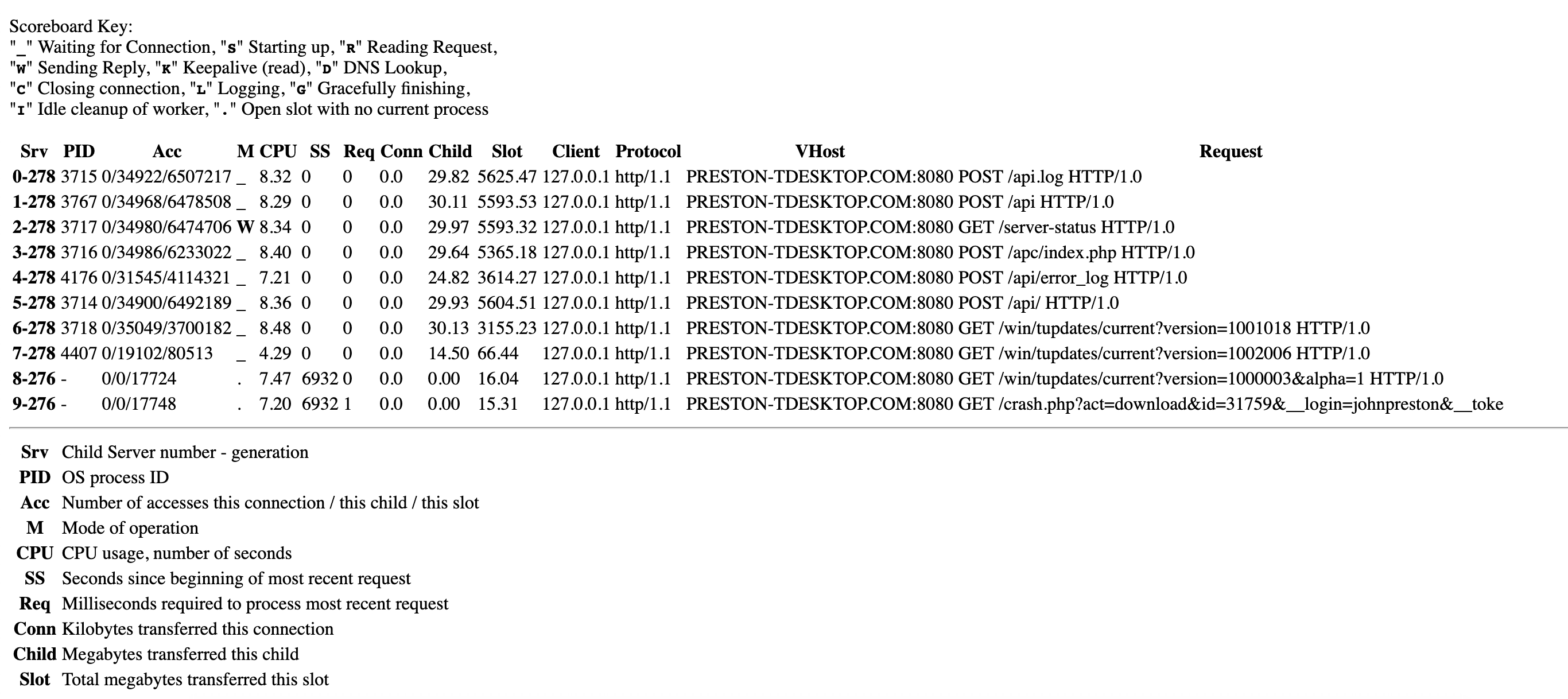
Despite the fact that we have a limited line length, it is clear from the logs that the administrator occasionally downloads the crash logs for further analysis, with funny parameters __login, and __token passed there. And the POST requests on the screenshot are mine.
Looking at the source, you can see two interesting methods.
The first is query_report , which has additional parameters apiid, version, dmp and platform. It returns whether you need more logs about the fall of the application, or the version is already fresh and known about errors. The mechanism is created not to get too much, and only correct the current.

The second is the report itself. Already without additional parameters. If a word is returned to the previous request, which indicates the need to send a dump, the file is sent.

There you can see that the data is sent using multipart, where the file name is report.telegramcrash, and its Content-type application / octet-stream.

Thus, it was possible to try pozalivat own files and test the vulnerabilities associated with unpacking ZIP and other upload-pieces.

And I would continue to try to send a different load to find at least some vulnerability, if not for one trick. If we substitute the well-known parameter names from another request, the valid values of which we took from server-status, to the report method, we can try to apply the secret attack of all web hackers.
Using the power of megazord (single quote) in the platform parameter, one could observe the anomalous behavior of the resource.

There is a quote - an error, no quotes - everything is fine. To check the validity, you can write some logical expression, for example, platform = mac 'AND' a '=' a. In the answer Done, as with a successful file upload.
Well, it’s not for nothing that they came up with automation, so I’m playing sqlmap, which is already dusty from inactivity. Anticipating questions - everything else was well tuned, the user in the DBMS is not privileged.

I sent it to security@telegram.org, a little later I received the coveted letter about the $ 30,000 reward.
Just kidding, $ 2,000 per sqli, and $ 500 for phpinfo and server-status, which is not bad either. And the wolves are safe and the sheep are fed, or vice versa.

I didn’t hack users (your correspondence is safe), I couldn’t further develop the attack, the server with random user dumps (crash dumps without information about the IT in the telegram, phone, messages and chat rooms) is of dubious value. In theory, it would be possible to pump crashes and study and exploit them yourself. Having learned how the telegrams are dropped, it was possible to drop it from the victim, and then study everything that can be squeezed out of the fall logs, if at all they could be downloaded via this injection.
Unique original .

Back in May 2017, kyprizel drew attention to the fact that the telegram desktop can download ZIP archives to itself on the tdesktop.com server. As it turned out later, not only ZIP, but inside there is information about the fall of the application, so that the developer can learn under what circumstances the fall occurred. In addition, the developer gets access to them through a web interface, judging by the form of authentication. I added the host to the notes and safely forgot.

')
I remembered him about a year later, when we discussed the upcoming research in the chat. At that time, the error_log file was in the root, in which, as you might guess, errors were written. At a minimum, there were full paths to the files, but beyond that, the favorite error was “You have an error in your SQL syntax”. But we are all lazy, and I generally try not to participate in bug bounty, so everything remains as it is.

Another year passed, I was invited to speak at the #PartyHack conference in Kazan. And when you do not have material for the performance - you look in the notes. What is there with us? Suspicious Telegram Host
Since PHP was used on the server, as crash.php showed, I decided to sort through the files with this extension, then I came across info.php, where the contents of the phpinfo () function were located. The first thing I noticed was the use of the Apache web server. How so? The whole telegraph nginx, and here Apache! And who uses apache in 2019?

What first comes to mind when you hear Apache? I immediately remember about mod_status, which is going with it by default. This module generates a page with the current state of the server, about system resources, requests to the server, the speed of their processing. Most often, the path to it is / server-status, rarely just / status. To understand how popular this administration error is, it suffices to recall that it has been hanging on apache.org for many years.

For many years I have been collecting paths to potentially dangerous files and directories in the fuzz.txt project, so the server-status was naturally there.
In general, in server-status, it is noteworthy that it also shows the IP addresses of clients who send requests to the server. But in this case, all requests were from 127.0.0.1 to the virtual domain preston-desktop.com. Nginx on the front end simply proxied all requests for local apache, so there was no disclosure of user information. However, it was worthwhile to put the server-status on monitoring, here is a small script made on the knee, which puts unique lines in the sqlite database. For a short period of time, a lot of unique links were collected, but mostly they were requests for updates (with the version indicated), and there were almost no downloads. After a while I saw the admin.

Despite the fact that we have a limited line length, it is clear from the logs that the administrator occasionally downloads the crash logs for further analysis, with funny parameters __login, and __token passed there. And the POST requests on the screenshot are mine.
Looking at the source, you can see two interesting methods.
The first is query_report , which has additional parameters apiid, version, dmp and platform. It returns whether you need more logs about the fall of the application, or the version is already fresh and known about errors. The mechanism is created not to get too much, and only correct the current.

The second is the report itself. Already without additional parameters. If a word is returned to the previous request, which indicates the need to send a dump, the file is sent.

There you can see that the data is sent using multipart, where the file name is report.telegramcrash, and its Content-type application / octet-stream.

Thus, it was possible to try pozalivat own files and test the vulnerabilities associated with unpacking ZIP and other upload-pieces.

And I would continue to try to send a different load to find at least some vulnerability, if not for one trick. If we substitute the well-known parameter names from another request, the valid values of which we took from server-status, to the report method, we can try to apply the secret attack of all web hackers.
Using the power of megazord (single quote) in the platform parameter, one could observe the anomalous behavior of the resource.

There is a quote - an error, no quotes - everything is fine. To check the validity, you can write some logical expression, for example, platform = mac 'AND' a '=' a. In the answer Done, as with a successful file upload.
Well, it’s not for nothing that they came up with automation, so I’m playing sqlmap, which is already dusty from inactivity. Anticipating questions - everything else was well tuned, the user in the DBMS is not privileged.

I sent it to security@telegram.org, a little later I received the coveted letter about the $ 30,000 reward.
Just kidding, $ 2,000 per sqli, and $ 500 for phpinfo and server-status, which is not bad either. And the wolves are safe and the sheep are fed, or vice versa.

I didn’t hack users (your correspondence is safe), I couldn’t further develop the attack, the server with random user dumps (crash dumps without information about the IT in the telegram, phone, messages and chat rooms) is of dubious value. In theory, it would be possible to pump crashes and study and exploit them yourself. Having learned how the telegrams are dropped, it was possible to drop it from the victim, and then study everything that can be squeezed out of the fall logs, if at all they could be downloaded via this injection.
Unique original .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/460655/
All Articles