The adventures of electronic signature in Russia
States intervene in the once geek information area more and more and establish rules there. One of the institutions of state regulation in the information space is the mechanism of a “qualified electronic signature”, a conditionally non-existent trusted identifier of a subject with which it can certify various types of transactions in electronic form on its own behalf in the information space. In fact, the idea of ES is not new and has been developing for a long time, but in Russia at some point something went a bit wrong. This article is a subjective lengthy argument on the subject of the institution of electronic signatures in Russia without being immersed in the technological materiel. Well, a little heyte, as without it.

CC-BY-SA, Vadim Rybalko
What is a deal? In Russia, as in most developed and not-so-developed countries, there is a whole stack of laws and by-laws, a kind of “tree” of regulatory legal acts (NLA) governing the daily lives of citizens and associations. Dropping the detail: we have the main law of the country - the Constitution of the Russian Federation; through it, there is a mass of federal laws, including codes (in the context of our reasoning - the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and various laws and regulations affecting the electronic signature (of which the main one is the Federal Law “ On Electronic Signature”). ”Dated 04.04.2011 No. 63-FZ).
The concept of "transaction" is governed by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation: in general, these are the actions of individuals to establish relationships with each other, resulting in the emergence of civil rights and obligations. Transactions are an incredible number of types, in general, they are united by the fact that the party to the transaction certifies it for its part with its own handwritten signature (but not always), as a sign that the party’s participation in this transaction corresponds to its free will.
Now, as for the electronic signature. At the dawn of the formation of electronic signature in Russia, it was called an “electronic digital signature” (EDS), apparently, as a tracing paper with an English-language digital signature. Then the word digital was digested and dissolved, leaving an “electronic signature”. In general, according to the current legislation, anything can be called an electronic signature, even if it is a scan of a handwritten signature, therefore, detailed concepts have been introduced. The law defined three concepts of ES:
The following discussion will focus solely on enhanced qualified electronic signature, UKEP - it is this type of signature that is used in a legally significant electronic document management in Russia.
If you try to explain on your fingers what an electronic signature is and how the hell it works, you will get something like a thesis description.
There is a group of asymmetric public key cryptographic algorithms. The owner forms an interconnected pair of two keys: the private and the public key. The private or private key is kept strictly with the owner and is secret.
An open or public key is inseparable from a private key and can be freely transferred to anyone. Using the public key, you can encrypt certain information so that only the owner of the private key can decipher it and no one else (even the one who encrypted the data).
Using the private key, you can create a signature of the original information, when transferring such a file together with the signature, the recipient, who has the owner's public key in advance, can calculate that the file has not been modified in the process and is signed by the person who owns the private key.

CC-BY-SA , Illustration of signing and verifying signatures when applying asymmetric encryption, Wikipedia.
Obviously, the trust point - did the owner give his public key earlier or who else? In order for everyone not to establish with each pre-peering trust relationship, a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure, public key infrastructure) was invented.
To ensure that the public key of the sender, the owner of the ES key, is trusted by the recipient by default without establishing a relationship, it can be signed by the general participant entrusted by both parties. It is called the “certification center”, CA. Technically, the CA adds a set of additional properties to the owner’s public key (usually: expiration date, text description of the owner, a set of service identifiers), after which this sandwich is already signed with its private key. The resulting file is called an ES certificate. Owning in advance the public key of the CA, the file and the electronic signature of the sender, the recipient of the signature can calculate whether the file has undergone changes after signing.
The public key of the CA can also be certified by the public key of another CA (sometimes several, this is called cross-signature). Thus, the recipient may not have the public key directly to the sender’s CA, or it may have the public key of the higher-level CA, which in turn signed the sender’s public key. The verification chain will be extended, but it will still be possible to build a chain of trust.
In addition, an important ingredient is added to this sandwich when forming an ES for the document - a time stamp, timestamp. This is a real-time tag from a trusted source, also signed by the EA of the time server. It is unique and is created for a specific document. This allows you to make sure that the signature was formed at a specific point in time and does not allow the signature to be regenerated “backdating.
This is how PKI (read: electronic signature) works around the world in various implementations: HTTPS for websites, corporate authentication in VPN and Wi-Fi, registration of SIM-cards in the network, chip and contactless bank cards, DNSSec and RPKI, validation of passports, EP in Russia and analogues abroad, etc.
It is worth noting that the private key of the ES is a key element of the system, because its compromise will allow the unauthorized creation of the ES without the knowledge of the owner. The key is guarded by industrially recognized algorithms, quite a lot of them have been developed in the history of applied cryptography. The most common key algorithm is RSA , which has been in use for 40 years. It has a rather oak mathematical apparatus, and is still reliable at the expense of simplicity and elegance of the solution, just like an ax (when used correctly). Younger and more promising algorithms are based on the mathematics of elliptic curves, of which ECDSA (and a whole string of “ curves ” under the hood), perspective ED25519 , both of our GOSTs (both old, 2001, and new, from 2012). All this protects the private key from its “recovery” based on the public one. Protection against direct copying of the private key is provided by modern smart card mechanisms: the private key is generated inside the cryptographic chip and never leaves its limits, including during operations with it; and special mechanisms of self-destruction make it almost impossible to mechanically break the chip.
In a number of civilized countries, the key of an ES is issued to citizens along with a plastic identity identifier. Since the ID is issued by the state authority, the key of the EA as part of the ID is also issued by the state and equals the validity period of the certificate itself. In most cases, those who wish to use an electronic signature, it is enough to purchase a penny smart card reader and install a software package on the computer to interact with the key and work with the electronic signature. Such certificates use industrially standardized parameters, since their release is “looked after” by the international standardization body ICAO . ICAO (ICAO) is in fact not designed to do standardization of identity cards, as this is actually the International Civil Aviation Organization that standardizes everything in aviation. But it so happened that citizens' migration control is a considerable part of the obligations of air carriers and ground air services, so ICAO took up the standardization of travel documents, including all types of passports and ID cards, releasing a series of 9303 standards in 12 parts . And since the majority of states began to introduce electronic signature as an additional application on a smart card of a personal identity card, this provided at least some compatibility of the electronic component of such IDs from country to country, including in terms of electronic signature algorithms.
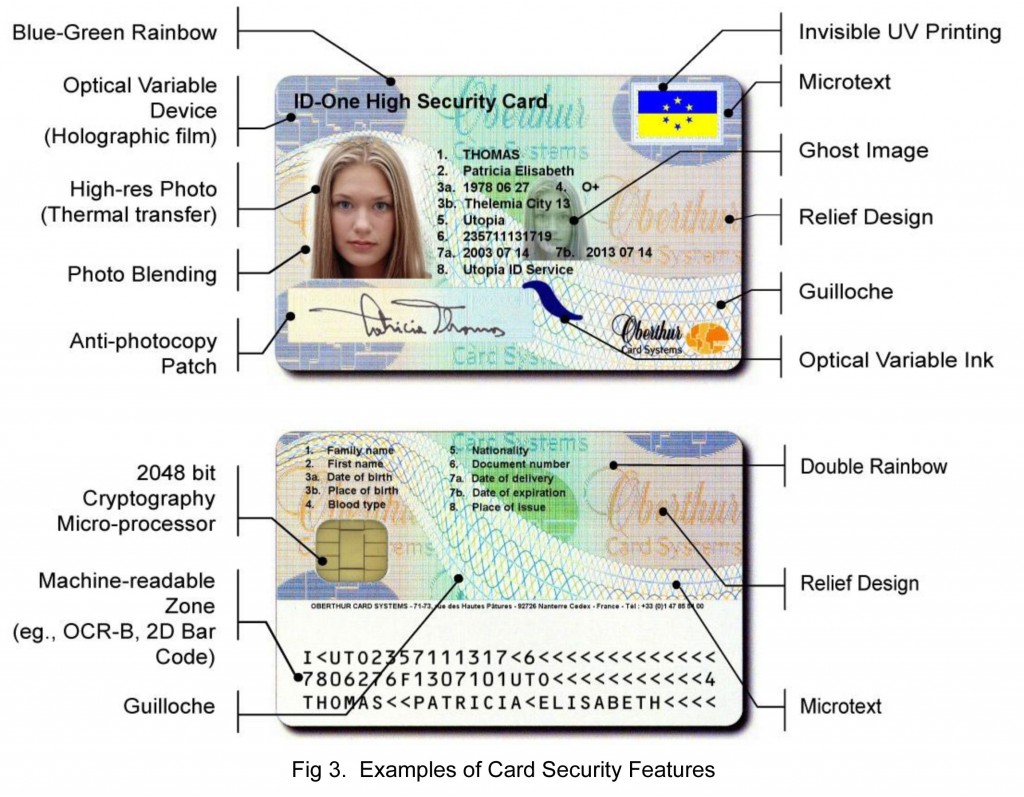
The main attributes of an identification card complying with the ICAO standard. A sample document of a major plastic card manufacturer Oberthur
On the other hand, the main operating systems contain embedded software implementations of globally recognized cryptoalgorithms, which makes it possible to exchange signed documents and check ES among counterparties from different countries.
There are several standards in Russia that describe national EP algorithms recognized by our legislation. Two of them (GOST R 34.10-94 and GOST R 34.10-2001) are currently not valid (from 2001 has a limited effect in legacy mode), the worker is GOST R 34.10-2012 . All DPEC must use the algorithm GOST R 34.10-2012 or GOST R 34.10-2001 to be considered legally recognized. In general, our algorithms are considered to be quite good, built just on the basis of elliptic curves (not counting completely outdated from 94 years). However, for a number of reasons they did not become generally accepted international standards. The most interesting thing is that GOST R 34.10-2001 managed to leak into the DNSSec standard, but could not achieve any tangible share. But mastered to write RFC within IETF - for it plus in karma.
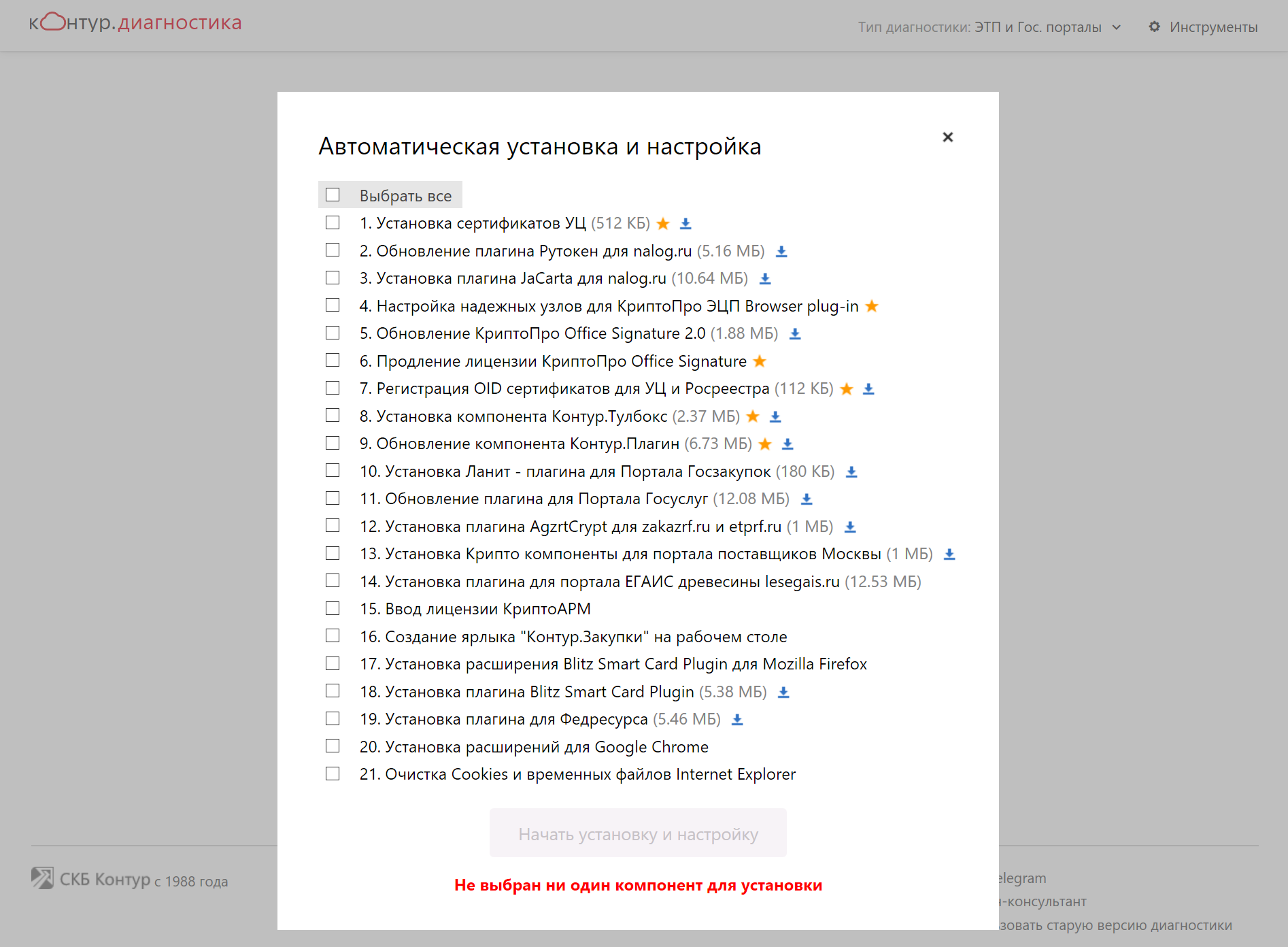
At some point, our legislators began to nail the UKEC with nails to different segments of civil relations in Russia. We started, of course, with one of the most obscene groups of subjects - legal entities. In general, the idea is sound: translate the document flow into an electronic form, remove the queues from different control firms, again, undermine the business of pulp mills and save nature by reducing the amount of paper. But, since laws are being passed, including without proper study and examination (and sometimes even in the interests of a certain circle of people, according to the sensations), so at some point everything went wrong. The state obliged businessmen to receive and renew an EDS every year (the normal key is valid for 12-15 months), while withdrawing itself from the very process of issuing such an important attribute as the EDS key, giving it to the merchant organizations - authorized certification centers; 445 with valid accreditation, not counting branches and representative offices. At the same time, besides the fact that the issuance of the DECK key itself is not free, a very strange software and hardware solution was chosen. It was decided to replace the normal protected cryptographic media for the private key with cheaper ones, which allow copying the key (in fact, not so cheap). Since such media do not know how to work with the key themselves, but in fact are flash drives with a password, software merchants who sell software layers for operating systems that carry out manipulations with the ES closed key, copying it into the computer’s main memory (SIC!), And while stably worth the money.
The piquancy was added by the total ignorance of voluntarily-imposed users of ES and the enormity of software solutions for working with it. For example, to set up a working computer of an average ES user to work with accounting portals of all stripes and electronic trading platforms, you need to perform about 20 operations: downloads / installs of a heap of various software of dubious quality, CA certificates, making specific settings so that it all interacts and something worked. It is not even worth mentioning that this heap of govnokod works more or less confidently only in the Windows environment (and not always the latest versions), it works extremely limitedly and with eerie crutches in some gos-linux and absolutely does not work on MacOS. For example, the tax site only less than a year ago learned to work only with Internet Explorer! And this FTS is a department that is considered relatively advanced in IT and is an operator of a big government big data solution.
CC-BY-SA, Vadim Rybalko, Approximate list of actions that the software auto-installer script performs to use the DPEC. UT SKB Kontur though there is such a service, some CA just give instructions in the DOC file.
The average usecase with the EECC in a company: someone (courier or enikeyshchik) receives, under a power of attorney from the head of the organization in TC, the key, hands it to the conditional aunt Mane to the accountant, who “signs” the documents on behalf of the manager. It should be understood that the essence of UKEP is an analogue of a handwritten signature, and not the signature of the conditional uncle Vasya. That is, the use in this form has already undergone significant mutations. We must not forget that even though the key was issued and the organization for working with electronic reporting, it contains as qualifying values and the data of the natural person - the manager, in whose name this key was created. This permits an attack vector against a given individual, the only limiting factor of which is the underdevelopment of electronic services with ES for individuals. And even physical control of a token with a key is a fiction, since any person (the same accountant) can, relatively invisibly to the owner, simply copy the key “to the registry” because “it’s more convenient”. And this is not to mention the default PIN codes of the form 12345678. Darkness and decadence.
Separately, you should write about the electronic signature for trading platforms. In order to make deals with budget and near-budget structures: to sell something or provide services, it is necessary to go through the tender mechanism. The tender is carried out on electronic trading platforms (ETP): special sites where orders are placed, something like an auction. There are many sites, as a rule, their holders are large, near - state organizations . To be an accredited participant of the ETP, you must have an electronic signature, but only the CEEC, whatever it is official and recognized by the state, will not work. No, the conversation is not about trusting the EECC, but the owners of trading platforms earn money from this. Technically, the electronic signature for the sites is the same as the CEEP, but the certificate additionally includes additional identifiers, OIDs , which give the right to use this key CEAP on a specific site. This was done with the aim to receive significantly more money for issuing such an electronic signature than for issuing a regular CCEP. It comes to a ridiculous scenario: in order to sell something to Russian Railways, you need to go through a tender, for which you need to get an electronic signature key from a particular CA, not any. Russian Railways can buy not only rail cars and cast-iron bridges, but also fairly inexpensive goods or order services in small quantities. Technically, it is possible to carry out an inexpensive deal without a tender, but representatives of the Russian Railways are afraid to do so, they can push a hat. Therefore, they offer the potential supplier to register on their own pocket trading platform and respond to the order specially prepared for the supplier. Naturally, such a scheme, in principle, smacks of violation of the principles of tender, but for the employees of the corporation the main thing is to observe bureaucratic regulations. Naturally, the Russian Railways marketplace works only for those who have an electronic signature key, but unlike the larger ETP, it cooperates only with four accredited CAs , of which there is not one with an extensive network of offices in Russia, and one is just an operator (owner ) the site itself. But if the representatives of Russian Railways really need to get a unique service and it’s easier for the supplier to refuse this circus with their ETP, then sometimes they can spit on their tender regulations and order a deal directly (based on a true story). It turns out that, on the one hand, it seems to be a normal PCEC, but it is not suitable for a number of actions, for which it is necessary to receive essentially the same ECU from another CA with a different set of additional attributes. As a result, a bunch of tokens that are difficult to follow and that need to be renewed annually, passing the quest with confirmation of authority.
A number of authorized CAs are generally suspected of negligent attitudes towards verification of the subject’s personal data when issued to the ECEC. This was supposed to happen, given the number of CAs that have deployed their activities throughout the country. It would be desirable to hope that these cases only describe the fact of inattention, and not intentional actions. And yes, if someone successfully tries to get the PDE on false documents in my name, I will not even know about it! And I own my personalized PECD, that is, the key double will appear. There is no opportunity to find out from the consolidated register that an ECRE has been issued to a certain person, each CA has its own register and procedures for accessing it. In fact, there is no available mechanism for recalling the CEEC on the application without sending out letters with a notarial application to the addresses of all existing CAs. Moreover, such cases are not uncommon, for example, PaulZi found itself in a situation when several dummy organizations were registered for it by obtaining the EECC on forged documents.
At one time, a real example of data disclosure was on the service of the State Service, which could be accessed via the CEEC issued to the head of the organization, in his personal account on the portal. It was difficult to mess things up there, but still it would be unpleasant for someone. And, for example, the same Rosreestr, after a series of scandals with the re-registration of ownership rights to real estate with the help of the EECC, was forced to push through the bill (not yet adopted, by the way), prohibiting to make real estate transactions using the EEMC, unless such operations were previously allowed physical person. That is, first we make a frank architectural sieve, and then we do not change it, but simply put the patches.
When developing the next project with the use of DECK, EGAIS , the developers went a little more towards the bright side: only those DECA were allowed to work in the system, and they are in non-recoverable form on honest cryptographic tokens. This is a glimpse of common sense, it’s a pity that cryptographic nihilism continues to dominate only in the market of the classic CEEC. Yes, it was always possible, but the financial interests of the vendors of software layers also need to be serviced. And the annual release of a key to each legal entity as a certification center is also a good financial aid.
By the way, non-recoverable hardware keys have long and successfully used a number of banks in their remote banking services solutions for organizations. A separate benefit of such solutions is the relative abstraction of cryptographic calculations with a specific crypto-algorithm from the support of this algorithm by the operating system. It can be said that the OS is no longer required to be able to work with a specific algorithm, but simply issues tasks: create a signature for this, or encrypt it, and the firmware on the hardware key already performs the specified actions. And at once you don't need any paid twilight software and everything works fine in any browsers, and even on a Mac.
Well, it is impossible not to mention a very strange project for cramming GOST algorithms into mobile telephony, namely, in a SIM card. This hotelka of a certain circle of people from among Russian silovik and controlled “licensed” vendors of crypto-equipment does not give in to a sound analysis. It’s good if it’s just a matter of state orders and landing another amount of money in the right direction, but this gives another reason for conspiracy discussion of the unfortunate and so not very handshaking “sovereign” cryptoalgorithm.
While preparing the article, I was surprised to find several more representatives of the club of seekers of my path. By a strange coincidence, they are here, side by side: the Belarusians invented their own algorithm STB 34.101.45-2013 (very similar to GOST), and the Ukrainians - DSTU 4145-2002 . The features of the algorithms are painted in the excellent post NeverWalkAloner . Both countries did not even bother to describe their standards in the IETF RFC, unlike GOST . There, most likely, their mice with cacti are in practical application, which we do not know about, but we also have enough of our own.
There is an opinion about the decline of "classical" cryptography as the development of quantum computing. At a certain point, it will be possible to bypass the basic principle of protecting a private key - the impossibility of its recovery from the public key in a sane period of time. This issue relates to the field of cryptography - post-quantum cryptography . In general, approaches to PKI do not change this much; this question is more related to the choice of specific cryptographic algorithms.
Another mechanic of identity verification is biometric authentication . Like any biometrics, such data cannot act as a private key generation vector, since a priori biometric parameters are available for reading without the owner’s control, as they are always in sight of everyone (fingerprints, iris pattern, voice profile). The technology of reading biometric data from their owner is constantly under the pressure of technical methods of reproducing this data without the participation of the owner on the basis of a previously made record. This is a fully functioning technology that has certain limitations. That is, it is not a replacement for the electronic signature and the PKI model, but a separate mechanism with its niche of use.
We should also briefly tell you about the " cloud electronic signature ". Like all terms that include the word “cloud”, this technology is not something magical: it’s just storing the key pair of the owner (including the private key) on a server on the Internet. Cryptographic operations are similarly performed on a remote computer, in fact, the owner of the ES does not control his private key in any way. Cloud signature services appeared in Russia, one of the first to provide the FTS for the personal account of individuals, and now these services are provided by some cloud accounting providers. In fact, this appeared solely due to the compatibility problems of our DPEC with computers and other electronic devices of end users. Whatever the assurances given by the suppliers of such services, the real security of such decisions against illegal actions of the supplier, its employees or third parties remains only on the conscience of such a supplier. Most technically savvy people mark this technology as a profanation of cryptography, including aimed at removing the private signature key from the owner of this key under any plausible pretext and putting it in an accessible storage for the necessary services.
Well, what article can do without mentioning Blockchain? In fact, the technology of the self-signed registry is already used in PKI implementations, the same transparency log is actively used by a number of certification authorities. And do not forget that the Blockchain itself is an application for cryptography, including on asymmetric algorithms. And, in general, the ideas of processing IDs in the blockchain plane look tempting, although frightening because of the registry's excessive transparency. Even under the idea, some designers came up with their vision.
Actually there is. Of course, the use of electronic signature should be developed - this is good. In my opinion, the institution of authorized CA should go. This is an unnecessary link, and, moreover, is poorly controlled. The sole authority responsible for issuing the EECC should be the authority, as in most countries. The most rational scenario seems to be the scenario of some countries: the issuance of the PDEC as part of an electronic ID card, which will immediately limit the number of attack vectors, since the PDEC will be one per person and in a manner precluding the deliberate transfer of the key to another person on an ongoing basis. The same transfer of a key to a conditional accountant is ignorance, it is necessary to transfer authority, and the accountant to make his key in his name (and with the EEPC on the ID card it is enough to transfer authority, the accountant will have his own key at this point). But for now, perhaps no one bothers about this. Naturally, the key from this card should not be retrievable. Unnecessary software layers should also be on the dustbin of history. Develop intelligible open standards for containers for transferring ES, preferably opensource . Look towards the Estonian decision , as the most progressive and elegant.
There is a separate pain about a normal plastic ID card instead of a morally outdated Russian internal passport. With the inability to take and do everything (and everything is invented before us), we invent our own special way with birch sap and kokoshniks, we design some monsters in the interests of a commercial bank (SIC!) - this is a stone in the UEC garden. The story of the adventure of Sberbank with UEC pulls on one more review, as there is a lot of pain in it. Today, they again started talking about ID-cards, but now Rostelecom is pulling the blanket over to its side and offers another Frankenstein, instead of taking the ICAO specification, smearing it with their favorite GOST (smart cards and not experienced this) and put it into trial operation.
Here then we will live (if we will live)!
A little about myself: a system and network administrator, a crypto-enthusiast, I collect bank cards (about two thousand pieces) and identity cards of various countries, I drown my common sense.

CC-BY-SA, Vadim Rybalko
Achtung! This is a longrid and it can take away a piece of your life!
Disclaimer
')
I tried not to hurt anyone, even when I wanted to. But still, if someone is ready to be offended: please save your psyche and go read the post with an overview of the next cloud hosting or about docker, for example. Feel better. If you are ready to discuss or have something to add - write boldly in the comments or in person.
First, a little abstract legal materiel
What is a deal? In Russia, as in most developed and not-so-developed countries, there is a whole stack of laws and by-laws, a kind of “tree” of regulatory legal acts (NLA) governing the daily lives of citizens and associations. Dropping the detail: we have the main law of the country - the Constitution of the Russian Federation; through it, there is a mass of federal laws, including codes (in the context of our reasoning - the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and various laws and regulations affecting the electronic signature (of which the main one is the Federal Law “ On Electronic Signature”). ”Dated 04.04.2011 No. 63-FZ).
The concept of "transaction" is governed by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation: in general, these are the actions of individuals to establish relationships with each other, resulting in the emergence of civil rights and obligations. Transactions are an incredible number of types, in general, they are united by the fact that the party to the transaction certifies it for its part with its own handwritten signature (but not always), as a sign that the party’s participation in this transaction corresponds to its free will.
Now, as for the electronic signature. At the dawn of the formation of electronic signature in Russia, it was called an “electronic digital signature” (EDS), apparently, as a tracing paper with an English-language digital signature. Then the word digital was digested and dissolved, leaving an “electronic signature”. In general, according to the current legislation, anything can be called an electronic signature, even if it is a scan of a handwritten signature, therefore, detailed concepts have been introduced. The law defined three concepts of ES:
- A simple electronic signature - any codes, passwords, scans, SMS verification. It has limited legal recognition, including only in the case when the parties to the contract have agreed in advance to use this type of signature and define the parameters of use.
- Reinforced unqualified electronic signature - a signature made using any cryptographic means of information protection, with the participation of the ES key. When recognizing such a signature, it is important that such a signature could be used to identify the signatory and ensure the cryptographic strength of the signed document (in order to detect the fact that changes were made to the document after it was signed).
- Reinforced qualified electronic signature (UKEP) - corresponds to the characteristics of the reinforced unqualified electronic signature, but with the condition that the key of the signature of the signing party is certified by the state authority along the trust chain (authorized certifying center).
The following discussion will focus solely on enhanced qualified electronic signature, UKEP - it is this type of signature that is used in a legally significant electronic document management in Russia.
The generalized principle of the EP
If you try to explain on your fingers what an electronic signature is and how the hell it works, you will get something like a thesis description.
There is a group of asymmetric public key cryptographic algorithms. The owner forms an interconnected pair of two keys: the private and the public key. The private or private key is kept strictly with the owner and is secret.
An open or public key is inseparable from a private key and can be freely transferred to anyone. Using the public key, you can encrypt certain information so that only the owner of the private key can decipher it and no one else (even the one who encrypted the data).
Using the private key, you can create a signature of the original information, when transferring such a file together with the signature, the recipient, who has the owner's public key in advance, can calculate that the file has not been modified in the process and is signed by the person who owns the private key.

CC-BY-SA , Illustration of signing and verifying signatures when applying asymmetric encryption, Wikipedia.
Obviously, the trust point - did the owner give his public key earlier or who else? In order for everyone not to establish with each pre-peering trust relationship, a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure, public key infrastructure) was invented.
To ensure that the public key of the sender, the owner of the ES key, is trusted by the recipient by default without establishing a relationship, it can be signed by the general participant entrusted by both parties. It is called the “certification center”, CA. Technically, the CA adds a set of additional properties to the owner’s public key (usually: expiration date, text description of the owner, a set of service identifiers), after which this sandwich is already signed with its private key. The resulting file is called an ES certificate. Owning in advance the public key of the CA, the file and the electronic signature of the sender, the recipient of the signature can calculate whether the file has undergone changes after signing.
The public key of the CA can also be certified by the public key of another CA (sometimes several, this is called cross-signature). Thus, the recipient may not have the public key directly to the sender’s CA, or it may have the public key of the higher-level CA, which in turn signed the sender’s public key. The verification chain will be extended, but it will still be possible to build a chain of trust.
In addition, an important ingredient is added to this sandwich when forming an ES for the document - a time stamp, timestamp. This is a real-time tag from a trusted source, also signed by the EA of the time server. It is unique and is created for a specific document. This allows you to make sure that the signature was formed at a specific point in time and does not allow the signature to be regenerated “backdating.
This is how PKI (read: electronic signature) works around the world in various implementations: HTTPS for websites, corporate authentication in VPN and Wi-Fi, registration of SIM-cards in the network, chip and contactless bank cards, DNSSec and RPKI, validation of passports, EP in Russia and analogues abroad, etc.
It is worth noting that the private key of the ES is a key element of the system, because its compromise will allow the unauthorized creation of the ES without the knowledge of the owner. The key is guarded by industrially recognized algorithms, quite a lot of them have been developed in the history of applied cryptography. The most common key algorithm is RSA , which has been in use for 40 years. It has a rather oak mathematical apparatus, and is still reliable at the expense of simplicity and elegance of the solution, just like an ax (when used correctly). Younger and more promising algorithms are based on the mathematics of elliptic curves, of which ECDSA (and a whole string of “ curves ” under the hood), perspective ED25519 , both of our GOSTs (both old, 2001, and new, from 2012). All this protects the private key from its “recovery” based on the public one. Protection against direct copying of the private key is provided by modern smart card mechanisms: the private key is generated inside the cryptographic chip and never leaves its limits, including during operations with it; and special mechanisms of self-destruction make it almost impossible to mechanically break the chip.
How are they?
In a number of civilized countries, the key of an ES is issued to citizens along with a plastic identity identifier. Since the ID is issued by the state authority, the key of the EA as part of the ID is also issued by the state and equals the validity period of the certificate itself. In most cases, those who wish to use an electronic signature, it is enough to purchase a penny smart card reader and install a software package on the computer to interact with the key and work with the electronic signature. Such certificates use industrially standardized parameters, since their release is “looked after” by the international standardization body ICAO . ICAO (ICAO) is in fact not designed to do standardization of identity cards, as this is actually the International Civil Aviation Organization that standardizes everything in aviation. But it so happened that citizens' migration control is a considerable part of the obligations of air carriers and ground air services, so ICAO took up the standardization of travel documents, including all types of passports and ID cards, releasing a series of 9303 standards in 12 parts . And since the majority of states began to introduce electronic signature as an additional application on a smart card of a personal identity card, this provided at least some compatibility of the electronic component of such IDs from country to country, including in terms of electronic signature algorithms.

The main attributes of an identification card complying with the ICAO standard. A sample document of a major plastic card manufacturer Oberthur
On the other hand, the main operating systems contain embedded software implementations of globally recognized cryptoalgorithms, which makes it possible to exchange signed documents and check ES among counterparties from different countries.
How about us?
There are several standards in Russia that describe national EP algorithms recognized by our legislation. Two of them (GOST R 34.10-94 and GOST R 34.10-2001) are currently not valid (from 2001 has a limited effect in legacy mode), the worker is GOST R 34.10-2012 . All DPEC must use the algorithm GOST R 34.10-2012 or GOST R 34.10-2001 to be considered legally recognized. In general, our algorithms are considered to be quite good, built just on the basis of elliptic curves (not counting completely outdated from 94 years). However, for a number of reasons they did not become generally accepted international standards. The most interesting thing is that GOST R 34.10-2001 managed to leak into the DNSSec standard, but could not achieve any tangible share. But mastered to write RFC within IETF - for it plus in karma.
At some point, our legislators began to nail the UKEC with nails to different segments of civil relations in Russia. We started, of course, with one of the most obscene groups of subjects - legal entities. In general, the idea is sound: translate the document flow into an electronic form, remove the queues from different control firms, again, undermine the business of pulp mills and save nature by reducing the amount of paper. But, since laws are being passed, including without proper study and examination (and sometimes even in the interests of a certain circle of people, according to the sensations), so at some point everything went wrong. The state obliged businessmen to receive and renew an EDS every year (the normal key is valid for 12-15 months), while withdrawing itself from the very process of issuing such an important attribute as the EDS key, giving it to the merchant organizations - authorized certification centers; 445 with valid accreditation, not counting branches and representative offices. At the same time, besides the fact that the issuance of the DECK key itself is not free, a very strange software and hardware solution was chosen. It was decided to replace the normal protected cryptographic media for the private key with cheaper ones, which allow copying the key (in fact, not so cheap). Since such media do not know how to work with the key themselves, but in fact are flash drives with a password, software merchants who sell software layers for operating systems that carry out manipulations with the ES closed key, copying it into the computer’s main memory (SIC!), And while stably worth the money.
The piquancy was added by the total ignorance of voluntarily-imposed users of ES and the enormity of software solutions for working with it. For example, to set up a working computer of an average ES user to work with accounting portals of all stripes and electronic trading platforms, you need to perform about 20 operations: downloads / installs of a heap of various software of dubious quality, CA certificates, making specific settings so that it all interacts and something worked. It is not even worth mentioning that this heap of govnokod works more or less confidently only in the Windows environment (and not always the latest versions), it works extremely limitedly and with eerie crutches in some gos-linux and absolutely does not work on MacOS. For example, the tax site only less than a year ago learned to work only with Internet Explorer! And this FTS is a department that is considered relatively advanced in IT and is an operator of a big government big data solution.
CC-BY-SA, Vadim Rybalko, Approximate list of actions that the software auto-installer script performs to use the DPEC. UT SKB Kontur though there is such a service, some CA just give instructions in the DOC file.
The average usecase with the EECC in a company: someone (courier or enikeyshchik) receives, under a power of attorney from the head of the organization in TC, the key, hands it to the conditional aunt Mane to the accountant, who “signs” the documents on behalf of the manager. It should be understood that the essence of UKEP is an analogue of a handwritten signature, and not the signature of the conditional uncle Vasya. That is, the use in this form has already undergone significant mutations. We must not forget that even though the key was issued and the organization for working with electronic reporting, it contains as qualifying values and the data of the natural person - the manager, in whose name this key was created. This permits an attack vector against a given individual, the only limiting factor of which is the underdevelopment of electronic services with ES for individuals. And even physical control of a token with a key is a fiction, since any person (the same accountant) can, relatively invisibly to the owner, simply copy the key “to the registry” because “it’s more convenient”. And this is not to mention the default PIN codes of the form 12345678. Darkness and decadence.
Separately, you should write about the electronic signature for trading platforms. In order to make deals with budget and near-budget structures: to sell something or provide services, it is necessary to go through the tender mechanism. The tender is carried out on electronic trading platforms (ETP): special sites where orders are placed, something like an auction. There are many sites, as a rule, their holders are large, near - state organizations . To be an accredited participant of the ETP, you must have an electronic signature, but only the CEEC, whatever it is official and recognized by the state, will not work. No, the conversation is not about trusting the EECC, but the owners of trading platforms earn money from this. Technically, the electronic signature for the sites is the same as the CEEP, but the certificate additionally includes additional identifiers, OIDs , which give the right to use this key CEAP on a specific site. This was done with the aim to receive significantly more money for issuing such an electronic signature than for issuing a regular CCEP. It comes to a ridiculous scenario: in order to sell something to Russian Railways, you need to go through a tender, for which you need to get an electronic signature key from a particular CA, not any. Russian Railways can buy not only rail cars and cast-iron bridges, but also fairly inexpensive goods or order services in small quantities. Technically, it is possible to carry out an inexpensive deal without a tender, but representatives of the Russian Railways are afraid to do so, they can push a hat. Therefore, they offer the potential supplier to register on their own pocket trading platform and respond to the order specially prepared for the supplier. Naturally, such a scheme, in principle, smacks of violation of the principles of tender, but for the employees of the corporation the main thing is to observe bureaucratic regulations. Naturally, the Russian Railways marketplace works only for those who have an electronic signature key, but unlike the larger ETP, it cooperates only with four accredited CAs , of which there is not one with an extensive network of offices in Russia, and one is just an operator (owner ) the site itself. But if the representatives of Russian Railways really need to get a unique service and it’s easier for the supplier to refuse this circus with their ETP, then sometimes they can spit on their tender regulations and order a deal directly (based on a true story). It turns out that, on the one hand, it seems to be a normal PCEC, but it is not suitable for a number of actions, for which it is necessary to receive essentially the same ECU from another CA with a different set of additional attributes. As a result, a bunch of tokens that are difficult to follow and that need to be renewed annually, passing the quest with confirmation of authority.
A number of authorized CAs are generally suspected of negligent attitudes towards verification of the subject’s personal data when issued to the ECEC. This was supposed to happen, given the number of CAs that have deployed their activities throughout the country. It would be desirable to hope that these cases only describe the fact of inattention, and not intentional actions. And yes, if someone successfully tries to get the PDE on false documents in my name, I will not even know about it! And I own my personalized PECD, that is, the key double will appear. There is no opportunity to find out from the consolidated register that an ECRE has been issued to a certain person, each CA has its own register and procedures for accessing it. In fact, there is no available mechanism for recalling the CEEC on the application without sending out letters with a notarial application to the addresses of all existing CAs. Moreover, such cases are not uncommon, for example, PaulZi found itself in a situation when several dummy organizations were registered for it by obtaining the EECC on forged documents.
At one time, a real example of data disclosure was on the service of the State Service, which could be accessed via the CEEC issued to the head of the organization, in his personal account on the portal. It was difficult to mess things up there, but still it would be unpleasant for someone. And, for example, the same Rosreestr, after a series of scandals with the re-registration of ownership rights to real estate with the help of the EECC, was forced to push through the bill (not yet adopted, by the way), prohibiting to make real estate transactions using the EEMC, unless such operations were previously allowed physical person. That is, first we make a frank architectural sieve, and then we do not change it, but simply put the patches.
When developing the next project with the use of DECK, EGAIS , the developers went a little more towards the bright side: only those DECA were allowed to work in the system, and they are in non-recoverable form on honest cryptographic tokens. This is a glimpse of common sense, it’s a pity that cryptographic nihilism continues to dominate only in the market of the classic CEEC. Yes, it was always possible, but the financial interests of the vendors of software layers also need to be serviced. And the annual release of a key to each legal entity as a certification center is also a good financial aid.
By the way, non-recoverable hardware keys have long and successfully used a number of banks in their remote banking services solutions for organizations. A separate benefit of such solutions is the relative abstraction of cryptographic calculations with a specific crypto-algorithm from the support of this algorithm by the operating system. It can be said that the OS is no longer required to be able to work with a specific algorithm, but simply issues tasks: create a signature for this, or encrypt it, and the firmware on the hardware key already performs the specified actions. And at once you don't need any paid twilight software and everything works fine in any browsers, and even on a Mac.
Well, it is impossible not to mention a very strange project for cramming GOST algorithms into mobile telephony, namely, in a SIM card. This hotelka of a certain circle of people from among Russian silovik and controlled “licensed” vendors of crypto-equipment does not give in to a sound analysis. It’s good if it’s just a matter of state orders and landing another amount of money in the right direction, but this gives another reason for conspiracy discussion of the unfortunate and so not very handshaking “sovereign” cryptoalgorithm.
Are we alone such D'Artagnan?
While preparing the article, I was surprised to find several more representatives of the club of seekers of my path. By a strange coincidence, they are here, side by side: the Belarusians invented their own algorithm STB 34.101.45-2013 (very similar to GOST), and the Ukrainians - DSTU 4145-2002 . The features of the algorithms are painted in the excellent post NeverWalkAloner . Both countries did not even bother to describe their standards in the IETF RFC, unlike GOST . There, most likely, their mice with cacti are in practical application, which we do not know about, but we also have enough of our own.
Perspectives
There is an opinion about the decline of "classical" cryptography as the development of quantum computing. At a certain point, it will be possible to bypass the basic principle of protecting a private key - the impossibility of its recovery from the public key in a sane period of time. This issue relates to the field of cryptography - post-quantum cryptography . In general, approaches to PKI do not change this much; this question is more related to the choice of specific cryptographic algorithms.
Another mechanic of identity verification is biometric authentication . Like any biometrics, such data cannot act as a private key generation vector, since a priori biometric parameters are available for reading without the owner’s control, as they are always in sight of everyone (fingerprints, iris pattern, voice profile). The technology of reading biometric data from their owner is constantly under the pressure of technical methods of reproducing this data without the participation of the owner on the basis of a previously made record. This is a fully functioning technology that has certain limitations. That is, it is not a replacement for the electronic signature and the PKI model, but a separate mechanism with its niche of use.
We should also briefly tell you about the " cloud electronic signature ". Like all terms that include the word “cloud”, this technology is not something magical: it’s just storing the key pair of the owner (including the private key) on a server on the Internet. Cryptographic operations are similarly performed on a remote computer, in fact, the owner of the ES does not control his private key in any way. Cloud signature services appeared in Russia, one of the first to provide the FTS for the personal account of individuals, and now these services are provided by some cloud accounting providers. In fact, this appeared solely due to the compatibility problems of our DPEC with computers and other electronic devices of end users. Whatever the assurances given by the suppliers of such services, the real security of such decisions against illegal actions of the supplier, its employees or third parties remains only on the conscience of such a supplier. Most technically savvy people mark this technology as a profanation of cryptography, including aimed at removing the private signature key from the owner of this key under any plausible pretext and putting it in an accessible storage for the necessary services.
Well, what article can do without mentioning Blockchain? In fact, the technology of the self-signed registry is already used in PKI implementations, the same transparency log is actively used by a number of certification authorities. And do not forget that the Blockchain itself is an application for cryptography, including on asymmetric algorithms. And, in general, the ideas of processing IDs in the blockchain plane look tempting, although frightening because of the registry's excessive transparency. Even under the idea, some designers came up with their vision.
Is there a light at the end of the tunnel?
Actually there is. Of course, the use of electronic signature should be developed - this is good. In my opinion, the institution of authorized CA should go. This is an unnecessary link, and, moreover, is poorly controlled. The sole authority responsible for issuing the EECC should be the authority, as in most countries. The most rational scenario seems to be the scenario of some countries: the issuance of the PDEC as part of an electronic ID card, which will immediately limit the number of attack vectors, since the PDEC will be one per person and in a manner precluding the deliberate transfer of the key to another person on an ongoing basis. The same transfer of a key to a conditional accountant is ignorance, it is necessary to transfer authority, and the accountant to make his key in his name (and with the EEPC on the ID card it is enough to transfer authority, the accountant will have his own key at this point). But for now, perhaps no one bothers about this. Naturally, the key from this card should not be retrievable. Unnecessary software layers should also be on the dustbin of history. Develop intelligible open standards for containers for transferring ES, preferably opensource . Look towards the Estonian decision , as the most progressive and elegant.
There is a separate pain about a normal plastic ID card instead of a morally outdated Russian internal passport. With the inability to take and do everything (and everything is invented before us), we invent our own special way with birch sap and kokoshniks, we design some monsters in the interests of a commercial bank (SIC!) - this is a stone in the UEC garden. The story of the adventure of Sberbank with UEC pulls on one more review, as there is a lot of pain in it. Today, they again started talking about ID-cards, but now Rostelecom is pulling the blanket over to its side and offers another Frankenstein, instead of taking the ICAO specification, smearing it with their favorite GOST (smart cards and not experienced this) and put it into trial operation.
Here then we will live (if we will live)!
A little about myself: a system and network administrator, a crypto-enthusiast, I collect bank cards (about two thousand pieces) and identity cards of various countries, I drown my common sense.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/460153/
All Articles