Some aspects of optimizing LINQ queries in C # .NET for MS SQL Server
LINQ entered .NET as a new powerful data manipulation language. LINQ to SQL as part of it allows you to quite comfortably communicate with the DBMS using for example the Entity Framework. However, quite often applying it, developers forget to look at what kind of SQL query will generate a queryable provider, in your case - the Entity Framework.
Let us examine two main points by example.
To do this, create a database Test in SQL Server, and create two tables in it using the following query:
Ref :
Customer :
, 1 , - 10 .
Visual Studio Visual C# Console App (.NET Framework):
, Entity Framework.
, Manage NuGet Packages:
NuGet- «Entity Framework» Entity Framework :

App.config configSections :
connectionString .
3 :
BaseEntity , :
:
UserContext:
LINQ to SQL EF MS SQL Server:
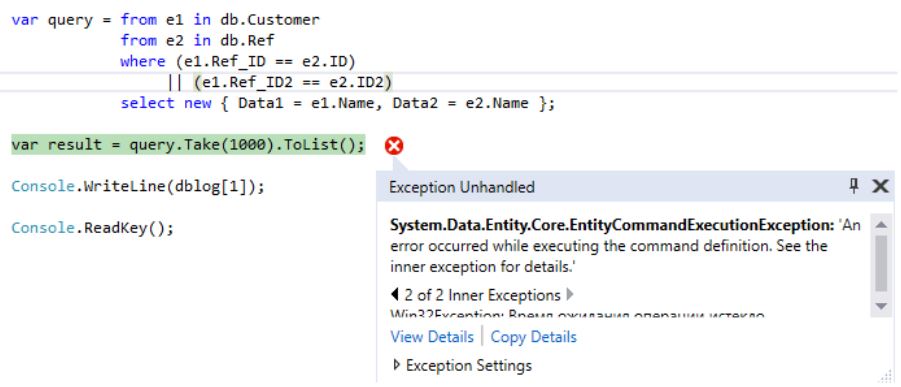
Program.cs :
.
:
. . LINQ- SQL- MS SQL Server.
LINQ-:
.
, 30 :
LINQ:
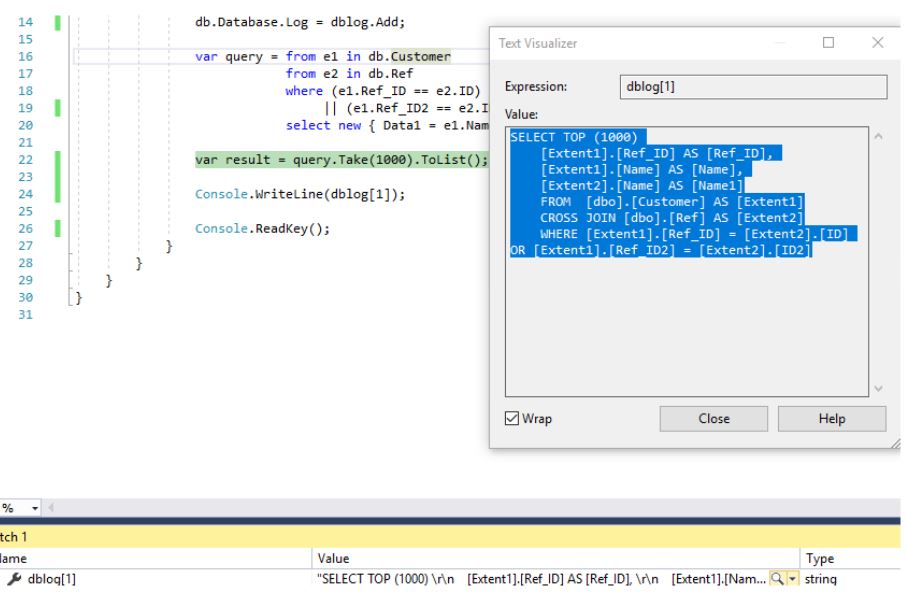
, , ():
LINQ- :
SQL-:
, LINQ- , Union .
, , . , .
:
, LINQ- , .
LINQ- :
SQL-, 1 :
LINQ to Objects :
:
:
, Para :
LINQ- MS SQL Server.
.NET- , , . , .
.
- , TEST, .
Plans .
Let us examine two main points by example.
To do this, create a database Test in SQL Server, and create two tables in it using the following query:
Creating tables
USE [TEST]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Ref](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[ID2] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](255) NOT NULL,
[InsertUTCDate] [datetime] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Ref] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Ref] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Ref_InsertUTCDate] DEFAULT (getutcdate()) FOR [InsertUTCDate]
GO
USE [TEST]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](255) NOT NULL,
[Ref_ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[InsertUTCDate] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[Ref_ID2] [int] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Customer] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Customer] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Customer_Ref_ID] DEFAULT ((0)) FOR [Ref_ID]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Customer] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Customer_InsertUTCDate] DEFAULT (getutcdate()) FOR [InsertUTCDate]
GO
Ref :
Ref
USE [TEST]
GO
DECLARE @ind INT=1;
WHILE(@ind<1200000)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Ref]
([ID]
,[ID2]
,[Name])
SELECT
@ind
,@ind
,CAST(@ind AS NVARCHAR(255));
SET @ind=@ind+1;
END
GO
Customer :
Customer
USE [TEST]
GO
DECLARE @ind INT=1;
DECLARE @ind_ref INT=1;
WHILE(@ind<=12000000)
BEGIN
IF(@ind%3=0) SET @ind_ref=1;
ELSE IF (@ind%5=0) SET @ind_ref=2;
ELSE IF (@ind%7=0) SET @ind_ref=3;
ELSE IF (@ind%11=0) SET @ind_ref=4;
ELSE IF (@ind%13=0) SET @ind_ref=5;
ELSE IF (@ind%17=0) SET @ind_ref=6;
ELSE IF (@ind%19=0) SET @ind_ref=7;
ELSE IF (@ind%23=0) SET @ind_ref=8;
ELSE IF (@ind%29=0) SET @ind_ref=9;
ELSE IF (@ind%31=0) SET @ind_ref=10;
ELSE IF (@ind%37=0) SET @ind_ref=11;
ELSE SET @ind_ref=@ind%1190000;
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Customer]
([ID]
,[Name]
,[Ref_ID]
,[Ref_ID2])
SELECT
@ind,
CAST(@ind AS NVARCHAR(255)),
@ind_ref,
@ind_ref;
SET @ind=@ind+1;
END
GO
, 1 , - 10 .
Visual Studio Visual C# Console App (.NET Framework):

, Entity Framework.
, Manage NuGet Packages:

NuGet- «Entity Framework» Entity Framework :

App.config configSections :
<connectionStrings>
<add name="DBConnection" connectionString="data source=__MSSQL;Initial Catalog=TEST;Integrated Security=True;" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
connectionString .
3 :
- IBaseEntityID
namespace TestLINQ { public interface IBaseEntityID { int ID { get; set; } } } - IBaseEntityName
namespace TestLINQ { public interface IBaseEntityName { string Name { get; set; } } } - IBaseNameInsertUTCDate
namespace TestLINQ { public interface IBaseNameInsertUTCDate { DateTime InsertUTCDate { get; set; } } }
BaseEntity , :
BaseEntity
namespace TestLINQ
{
public class BaseEntity : IBaseEntityID, IBaseEntityName, IBaseNameInsertUTCDate
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime InsertUTCDate { get; set; }
}
}
:
- Ref
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace TestLINQ { [Table("Ref")] public class Ref : BaseEntity { public int ID2 { get; set; } } } - Customer
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace TestLINQ { [Table("Customer")] public class Customer: BaseEntity { public int Ref_ID { get; set; } public int Ref_ID2 { get; set; } } }
UserContext:
UserContex
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace TestLINQ
{
public class UserContext : DbContext
{
public UserContext()
: base("DbConnection")
{
Database.SetInitializer<UserContext>(null);
}
public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; }
public DbSet<Ref> Ref { get; set; }
}
}
LINQ to SQL EF MS SQL Server:

Program.cs :
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace TestLINQ
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (UserContext db = new UserContext())
{
var dblog = new List<string>();
db.Database.Log = dblog.Add;
var query = from e1 in db.Customer
from e2 in db.Ref
where (e1.Ref_ID == e2.ID)
&& (e1.Ref_ID2 == e2.ID2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name };
var result = query.Take(1000).ToList();
Console.WriteLine(dblog[1]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
}
.
:
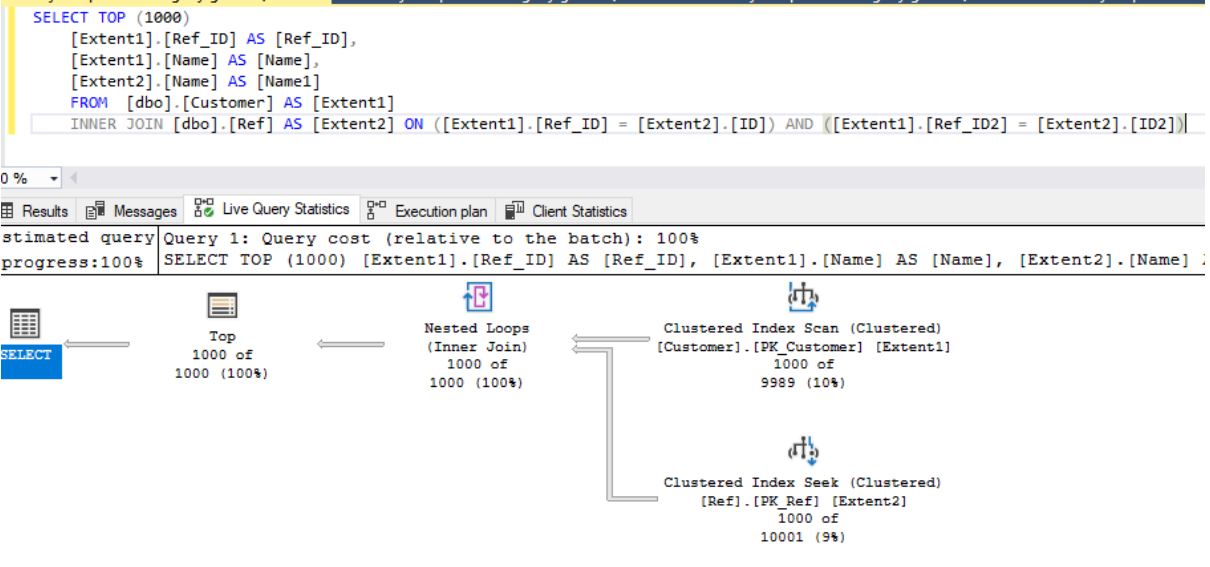
SQL-
SELECT TOP (1000)
[Extent1].[Ref_ID] AS [Ref_ID],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2] ON ([Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID]) AND ([Extent1].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent2].[ID2])
. . LINQ- SQL- MS SQL Server.
LINQ-:
LINQ-
var query = from e1 in db.Customer
from e2 in db.Ref
where (e1.Ref_ID == e2.ID)
|| (e1.Ref_ID2 == e2.ID2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name };
.
, 30 :

LINQ:

, , ():
SQL-
SELECT TOP (1000)
[Extent1].[Ref_ID] AS [Ref_ID],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
CROSS JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2]
WHERE [Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID] OR [Extent1].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent2].[ID2]
LINQ- :
LINQ-
var query = (from e1 in db.Customer
join e2 in db.Ref
on e1.Ref_ID equals e2.ID
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name }).Union(
from e1 in db.Customer
join e2 in db.Ref
on e1.Ref_ID2 equals e2.ID2
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name });
SQL-:
SQL-
SELECT
[Limit1].[C1] AS [C1],
[Limit1].[C2] AS [C2],
[Limit1].[C3] AS [C3]
FROM ( SELECT DISTINCT TOP (1000)
[UnionAll1].[C1] AS [C1],
[UnionAll1].[Name] AS [C2],
[UnionAll1].[Name1] AS [C3]
FROM (SELECT
1 AS [C1],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2] ON [Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID]
UNION ALL
SELECT
1 AS [C1],
[Extent3].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent4].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent3]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent4] ON [Extent3].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent4].[ID2]) AS [UnionAll1]
) AS [Limit1]
, LINQ- , Union .
, , . , .
:
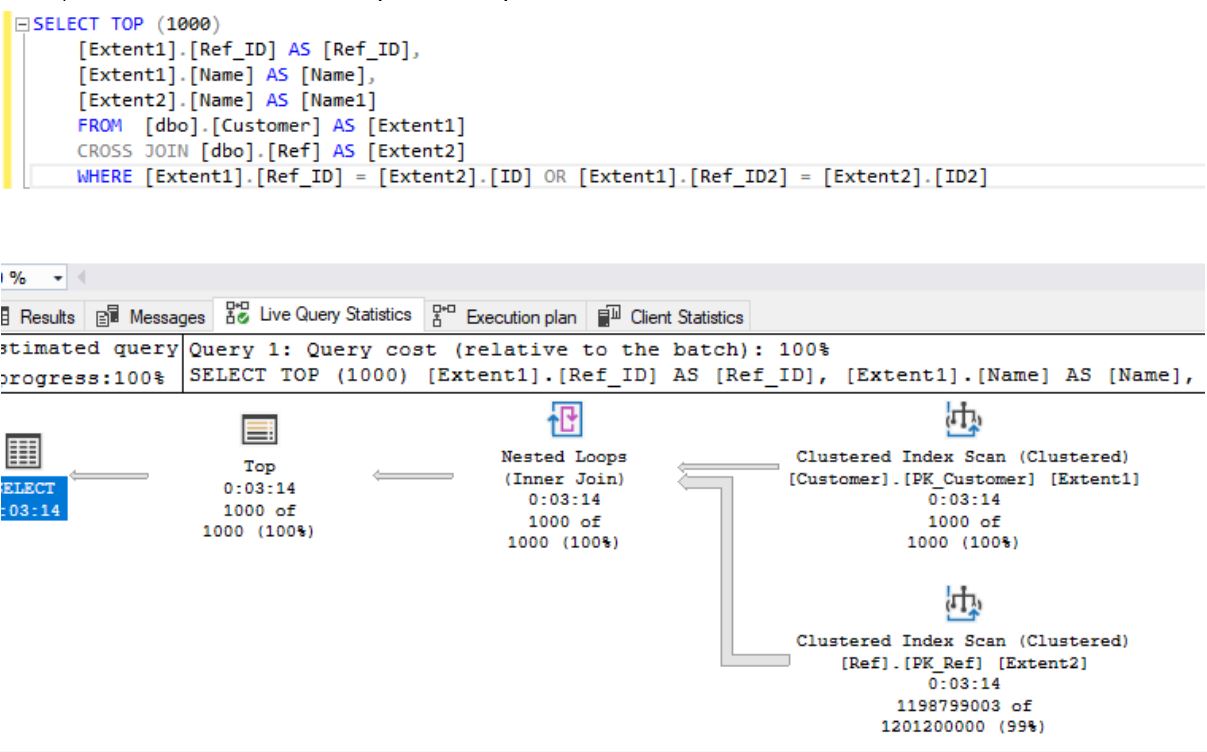
- CROSS JOIN 195 :
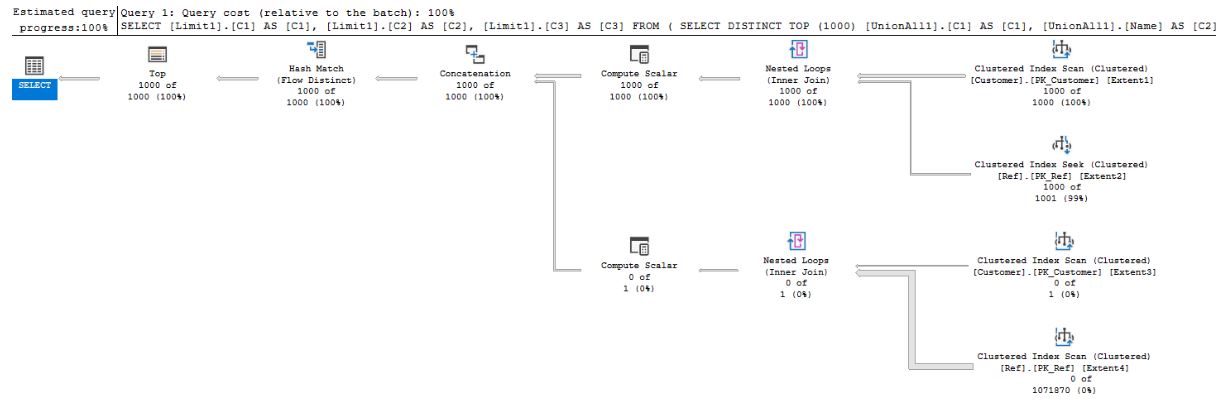
- INNER JOIN-UNION 24 :
, LINQ- , .
LINQ- :
LINQ-
var query = from e1 in db.Customer
from e2 in db.Ref
where (e1.Ref_ID == e2.ID)
&& (e1.Ref_ID2 == e2.ID2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name };
SQL-, 1 :

LINQ to Objects :
LINQ- (1- )
var query = from e1 in seq1
from e2 in seq2
where (e1.Key1==e2.Key1)
&& (e1.Key2==e2.Key2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Data, Data2 = e2.Data };
:
LINQ- (2- )
var query = from e1 in seq1
join e2 in seq2
on new { e1.Key1, e1.Key2 } equals new { e2.Key1, e2.Key2 }
select new { Data1 = e1.Data, Data2 = e2.Data };
:
Para[] seq1 = new[] { new Para { Key1 = 1, Key2 = 2, Data = "777" }, new Para { Key1 = 2, Key2 = 3, Data = "888" }, new Para { Key1 = 3, Key2 = 4, Data = "999" } };
Para[] seq2 = new[] { new Para { Key1 = 1, Key2 = 2, Data = "777" }, new Para { Key1 = 2, Key2 = 3, Data = "888" }, new Para { Key1 = 3, Key2 = 5, Data = "999" } };
, Para :
Para
class Para
{
public int Key1, Key2;
public string Data;
}
LINQ- MS SQL Server.
.NET- , , . , .
.
- , TEST, .
Plans .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/459716/
All Articles