Live and learn. Part 1. School and vocational guidance
I have a friend from Grenoble, the son of Russian émigrés - after school (collège + lycée) he moved to Bordeaux and got a job at the port, a year later he went to the flower shop SMM-shchikom, a year later he graduated from short courses and became someone like the referent manager. After two years of work, at 23, he went to the SAP office for a lower position, received a university education and now became an engineer of corporate systems. When asked whether it was not scary to make such a “gap” in education, he replied that it was scary to leave the university at 22 and not know who you are and what you want. Familiar? In general, if you are a parent or relative of a schoolboy or a schoolboy himself, you are under the cat. However, the rest is also a good reason for nostalgia.

Fragmentary articles about education, the need for a diploma, postgraduate study, and other aspects of education have repeatedly appeared on Habré - it is not for nothing that there are hubs about the educational process, career, education abroad, etc. The topic is really serious, especially in conditions of a greatly changed labor market and inquiries to specialists. We decided to summarize our experience, asked for help a specialist who gave education to people for 8 years, 25 years for ourselves, including school :-) and IT for 10 years. We have prepared 5 articles that will be published in our blog.
Cycle "Live and learn"
')
Part 1. School and vocational guidance
Part 2. University
Part 3. Additional education
Part 4. Education inside work
Part 5. Self-education
Share your experience in the comments - maybe, thanks to the efforts of the RUVDS team and Habr's readers, someone's first September will be a little more conscious, more correct and more fruitful.
On average, a school throughout the country is a very interesting element of education, especially now. Completely different worlds crossed in it:
All 4 groups are fighting between themselves and groups against other groups, within such a community there is a lot of misunderstanding and the invisible hand of the main and authoritative tutor - the Internet. And you know what I tell you? This is very good, just need a special approach. And I will say that the conflict of generations is eternal as well as the laziness of schoolchildren, only the scenery changes.
Until now, in most schools in Russia (in Moscow, the situation is better), the vocational guidance of schoolchildren is reduced to essays on the subject of a future profession and not quite adequate vocational guidance tests, some of which are reduced to an approximate definition of a student’s inclinations in one area or another. At the same time, such specialties as bioinformatics, informatics in medicine, etc. are not discussed. - that is, in-demand and promising areas for versatile and advanced children. Schoolchildren themselves remain primarily children, romantics and dreamers. Today they want to treat people or serve in the Ministry of Emergency Situations, tomorrow to be an entrepreneur, and in a week - a programmer or engineer who builds the cars of the future. And it is important to listen, to ponder, what are the reasons for the choice - in the charm of Dr. House, the charisma of Ilon Mask or in the real need and vocation of a young man.
Perspectivity is perhaps the most difficult metric. What seems promising right now, before graduation and the university can turn into the most overheated area (hello to lawyers and economists of 2000-2002 of admission!) Or disappear altogether. Therefore, it is necessary to make it clear to your child and realize that there must be a base around which you can repeatedly change your specialization. For example, a software engineer who owns C / C ++ can easily pass into the world of the development of neural networks, industrial development, science, etc., but in five years the writing (applied informatics) can be out of the stack on which was trained. Again, an economist with a specialization in Financial Management is much more promising in terms of lateral movements than Banking or Real Estate Appraisal . To evaluate the future, study the list of future professions, look at the programming language ratings (if it’s about IT), read specialized publications (for example, 15-17 years ago in medical journals the scientific community actively discussed eye microsurgery, robots in medicine, laparoscopic manipulations, and today it is a daily reality). Another way is to see which faculties have opened in universities in the last 2-3 years, as a rule, this is the top that you will manage to get into.
Real profitability is a simpler metric. You open "My Circle" or "Headhunter", evaluate the average level of earnings in the specialty (sometimes ready analytics is also available). The indexation of wages in business happens to 10% per year, in the public sector about 5% per year. It's easier to count, but do not forget that in N years there will be an adjustment for the depth of demand, the change in the landscape of the sphere, etc.
The speed of development and career growth for each sphere is different. Moreover, it is not everywhere and it is not worth romanticizing: sometimes it is better to move horizontally, study a new specialty and work not on a record in the workbook, but on the real level of earnings (which is fraught, but more on that in the next series). The main thing is to convey to the student that he will not become the head immediately, he will have to work, and the real pros sometimes cost more than their head.
Growth flexibility and professional evolution is an important continuation for the previous metric. The professional studies continuously, until the last day at work (and sometimes after). Therefore, it is necessary to relate the schoolchild's tendency to study and the requirements of the desired profession ( for example, a boy dreams of becoming a doctor, has 5 in chemistry and biology, but being lazy about learning is a signal that he may have problems with professional development in the future ) , but do not dwell on it: often after a university, an adult is happy to learn and continue education, and at school there was not laziness, but hatred of history and boring geography.
Choosing a profession, you must help your child, but do not decide for him (I guarantee - you will not get “thanks”). At the same time it is important not to miss a single detail and, perhaps, even to look at your close, dear person a little from the outside, strictly and objectively (relatively speaking, the ability to twist your booty under Lambada is not yet class B in ballroom dancing, no matter how much you want ).
It happens that parents are confident that their child does not want anything, does not have aspirations and inclinations, does not seek to choose a university, does not think about the future. In fact, it does not happen, there is always what you like - and from this you need to make a start. If you think that there are real difficulties, talk to the teachers, listen to their advice, contact a social psychologist who is engaged in vocational guidance for teens (there are very cool private traders - see below for them). My classmate has a 15-year-old daughter, a very early child, my mother is an inert housewife with no education and looks at her daughter as “nothing-not-want”. The girl served a delicious brewed coffee, gracefully bent napkins, offered the cake "Anthill", which she made. - Kate, don't you think that she should try herself as a pastry chef or work in a cafe? - What are you, she is not a plebeian to serve all sorts, I will force her to go to an accountant. A curtain.

When you are a schoolboy, you always try to hide the true motives of your behavior or choice, so as not to appear immature or led. Therefore, it is very difficult for parents to figure out where the craving for a particular profession has come from, especially if it is sudden. And do not do it, it is better to convey certain rules of the game.

It turned out such a bit of a philosophical section, but this is precisely the support of the student’s vocational guidance from the parents, the first beginnings of his self-esteem as a future specialist.
Career guidance is a process that determines the rest of life, so you need to rely on third-party methods and the help of professionals.
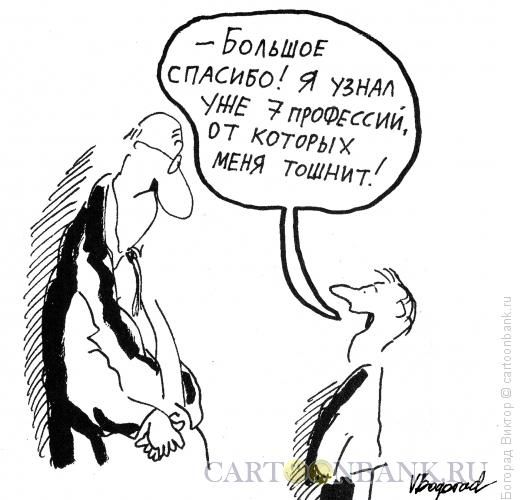 After working with a career counselor, this is also the result!
After working with a career counselor, this is also the result!
When you collect and compare these data, it will be much easier to determine how to help a teenager choose his direction.
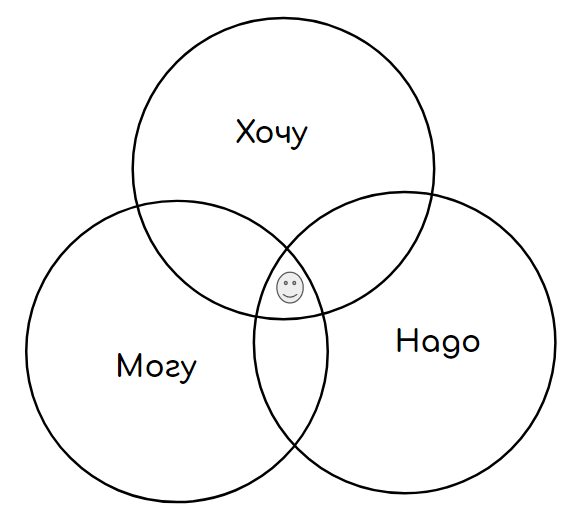 This is a classic career counseling diagram, from which it is clear that a successful career will develop at the intersection of desires, opportunities (including physical ones) and the needs of the labor market.
This is a classic career counseling diagram, from which it is clear that a successful career will develop at the intersection of desires, opportunities (including physical ones) and the needs of the labor market.
If a teenager (and even better a child under 12) has certain abilities for logical thinking, algorithms, an engineering view of things, do not miss the time and pay special attention to some things:
But behind gamification and enthusiasm you should not forget about the fundamental fundamentals of physics, mathematics and computer science, they are simply obliged to be present in the life of a schoolboy with a burden to develop (and indeed any educated person).
Of course, even if you are a child-oriented child from the first grade and are confident in his future, this does not mean that you should give up school and focus on one thing.
How to learn "profile" subjects?
Exceptionally in-depth, with the use of additional literature, problem books and reference books. The purpose of training is not just to pass the USE well, but also to come to the university prepared, with an understanding of the subject and its place in a future profession.
How to treat non-core items?
Within the framework of reasonable and personal ambitions - to teach, donate, write tests, do not spend too much time on them. Exceptions: Russian and foreign languages, they are specialized for any specialty, so pay special attention to them.
How to work with additional load?
The tasks of increased complexity and Olympiad are the beginning of a career, without exaggeration. They pump thinking, learn to focus at short distances and intensively solve the problem, give the skill of self-presentation and the ability to win / take a punch. Therefore, if you want a career expectancy in a particular university or teenager, you should take part in competitions, conferences, and student research contests.
At the same time, health should be above all, this is an important point that parents forget, but children do not realize yet.
Do I go to college after grade 8/9?
Only the decision of the parents and the student. In education according to the scheme of college + university there is nothing wrong, even more advantages. But learning is somewhat more difficult.
Should I change school to profile?
It is desirable to change - so the student will have more chances to pass the exam for a high score (well, the same story with the entrance exams, if they return everywhere in the future - the chance is still higher). You shouldn’t be afraid of psychological trauma, the team change has a great advantage: the future student will know some part of his classmates and classmates much earlier, and this is great for adapting to the university. But if a teenager is not directly torn off and the school world is the most expensive of all - of course, you should not be torn off, it is better to devote time to additional classes.
Factors choosing a university?
A lot of factors: from moving to other cities to the internal features of the university, it is all very individual. But you should pay attention to the practice base (if you don’t have your people in mind), to the degree of language learning at the university, to the main scientific profile (scientific laboratories), to the presence of a military department (to whom this is relevant).
When to start working?
This is the big question - is it worth starting work in school, and the answer to it is also individual. But, in my opinion, it is worth trying to work in the summer between 9 and 10, 10 and 11 classes - purely in order to understand how the interaction in the work collective is arranged, how responsibilities are distributed, what degrees of freedom / lack of freedom exist.But in the summer of admission to the university of stress and stress is too much - so enrolled and rest, the more the better.
In fact, this topic can be talked about forever, and it requires a deeply individual approach. But it seems that if every parent listens to at least some moments from the article, schoolchildren will find it easier to choose their future profession, and mom and dad will be able to avoid the charge “I didn’t want to go to this university, you decided for me.” The task of adults is not just to feed their children with a fish, but to give them a fishing rod and teach it to use. The school period is a huge foundation for the whole future life, so you should take it responsibly and follow three main rules: respect, guide and love. Believe me, you will be back a hundredfold.
In the next series, we will go through five / sixcorridors. university courses and finally decide whether he needs or “maybe to hell with a diploma?” Don't miss it!
By the way, we forgot about the important point - if you want to grow as an IT specialist, you should get acquainted with open source projects at school. This does not mean that you need to contribute to the largest developments, but it's time to start cutting and nurturing your pet-project by analyzing the theory in practice. And if you have already grown and you lack something for development, for example, a good powerful VPS , go to the RUVDS website - we have a lot of interesting things.


Prologue - where does this article come from
Fragmentary articles about education, the need for a diploma, postgraduate study, and other aspects of education have repeatedly appeared on Habré - it is not for nothing that there are hubs about the educational process, career, education abroad, etc. The topic is really serious, especially in conditions of a greatly changed labor market and inquiries to specialists. We decided to summarize our experience, asked for help a specialist who gave education to people for 8 years, 25 years for ourselves, including school :-) and IT for 10 years. We have prepared 5 articles that will be published in our blog.
Cycle "Live and learn"
')
Part 1. School and vocational guidance
Part 2. University
Part 3. Additional education
Part 4. Education inside work
Part 5. Self-education
Share your experience in the comments - maybe, thanks to the efforts of the RUVDS team and Habr's readers, someone's first September will be a little more conscious, more correct and more fruitful.
School: old song about the main thing
Groupings
On average, a school throughout the country is a very interesting element of education, especially now. Completely different worlds crossed in it:
- the teachers of the old formation, at a very solid age, are mostly not ready to accept new realities and forms of education, not ready to listen to the students;
- young and rather indifferent teachers from the 90s, when they went to the pedagogical school, with rare exceptions, out of despair and inability to enroll in another university (due to the level of training or lack of money);
- parents with a range of age from the 70s to the 90s, that is, from people of the way of life of the USSR to reckless representatives of the so-called “lost generation”;
- children 15-17 years old (we mostly talk about them) - children of the digital age, automated and computerized, introverted and virtual, with their own thinking and special organization of the psyche and memory.
All 4 groups are fighting between themselves and groups against other groups, within such a community there is a lot of misunderstanding and the invisible hand of the main and authoritative tutor - the Internet. And you know what I tell you? This is very good, just need a special approach. And I will say that the conflict of generations is eternal as well as the laziness of schoolchildren, only the scenery changes.
What problems do schoolchildren experience?
- Knowledge is completely divorced from practice. The school program does not provide information in conjunction with practice. That is why you can meet questions about whether a mathematician is needed by a programmer or which programming language to choose in order to get around the questions of mathematics. While on the same algebra you can touch on the problem of neural networks, machine learning, game development (think for how cool it is to learn that the favorite characters of the world of games move according to the laws of physics, and each trajectory is described by a mathematical formula). Splicing theory and practice within the subject could increase the interest of the student, overcome boredom in the classroom and at the same time help in primary vocational guidance (which takes place in grades 6-9). At the same time, it is not necessary to require an expensive material base, it is enough to have a desire, a blackboard and chalk / marker.
- The real level of knowledge does not match the estimates in the diaries and certificates. The eternal problem of insinuations, encouragement and demotivation with assessments, rivalry leads to the fact that schoolchildren are chasing the cherished figure, and parents and teachers encourage this race. It is not surprising that in the first year of high school students in high school students roll down into triples in higher mathematics and troechnikas hold a strong 4 - they have an understanding of the subject, and not a jagged part that took off right after the USE.
- Free access to information is , in fact, a big problem. No need to memorize, search, analyze - just open Wikipedia or google and everything, the information in front of you. This is bad, because the memorization function is really reduced, the correct educational basis is not formed. The very basis that teaches to grab the problem, find the missing puzzle and then use the reference book or the Internet. Simply put, constantly google, the student does not learn to understand what it is necessary to google. Meanwhile, it is the primary educational basis that underlies the future career, serves as a platform for the skills of analysis and synthesis.
- Unnecessary knowledge in school is. Probably, the teacher reading this post now wants to find and tear the author apart, but the steeper the school, the more, I'm sorry, the stuff is stuffed into the curriculum. From the game I have met: 4 years of Latin, 7 years of foreign literature (with a deepening), 4 years (!) OBZH, 2 years of philosophy, as well as various literature, Greek, theory of physical culture, history of mathematics, etc. Of course, the general erudition, school championships for "What? Where? When? ”, The ability to keep up the conversation is invaluable and even very pleasant and useful, but in such volumes the hours of classes take the student’s brain away from the core subjects and from the most important educational part (you look at the modern spelling, but at least on the same Habré!) . There is a solution: to make such items optional and without assessments.
- The complex pace of education is a question that has been standing since the beginning of the existence of schools and whose solution is very difficult to find. In one class, even “strong” or “weak”, students have a different pace of mastering the material, solving problems, and a different rate of “swinging.” And in the end, you have to either go to leveling and lose potentially strong ones, or hammer on the weak and make them even weaker. I had a student who perfectly solved problems in mathematical statistics, but did it very slowly, because He was looking for the best solution, optimized solution. As a result, out of five tasks I managed to solve three. What do you want him to bet? That's the same thing. Meanwhile, you can find a small workshop: giving more tasks to the independent solution, giving them the right to mentor and teach their classmates under the supervision of the teacher - this greatly increases responsibility, reduces the fear of error and allows students to demonstrate the basics of teamwork.
- The problem of socialization is a painful and serious problem that drags a dozen others. The virtual communication environment, game interactions, social networks and instant messengers rob children (yes, they are children under 18, children, and after, alas, children) the ability to communicate and social interaction. No problem solving skills, no teamwork, no relationships within a group of people, nothing — a peer-to-peer social network, simple conversations. And this is where the task of the school is to show how cool the “person-to-person” system looks: to organize team games, to organize communications.
How to choose a profession?
Until now, in most schools in Russia (in Moscow, the situation is better), the vocational guidance of schoolchildren is reduced to essays on the subject of a future profession and not quite adequate vocational guidance tests, some of which are reduced to an approximate definition of a student’s inclinations in one area or another. At the same time, such specialties as bioinformatics, informatics in medicine, etc. are not discussed. - that is, in-demand and promising areas for versatile and advanced children. Schoolchildren themselves remain primarily children, romantics and dreamers. Today they want to treat people or serve in the Ministry of Emergency Situations, tomorrow to be an entrepreneur, and in a week - a programmer or engineer who builds the cars of the future. And it is important to listen, to ponder, what are the reasons for the choice - in the charm of Dr. House, the charisma of Ilon Mask or in the real need and vocation of a young man.
How to evaluate a profession?
Perspectivity is perhaps the most difficult metric. What seems promising right now, before graduation and the university can turn into the most overheated area (hello to lawyers and economists of 2000-2002 of admission!) Or disappear altogether. Therefore, it is necessary to make it clear to your child and realize that there must be a base around which you can repeatedly change your specialization. For example, a software engineer who owns C / C ++ can easily pass into the world of the development of neural networks, industrial development, science, etc., but in five years the writing (applied informatics) can be out of the stack on which was trained. Again, an economist with a specialization in Financial Management is much more promising in terms of lateral movements than Banking or Real Estate Appraisal . To evaluate the future, study the list of future professions, look at the programming language ratings (if it’s about IT), read specialized publications (for example, 15-17 years ago in medical journals the scientific community actively discussed eye microsurgery, robots in medicine, laparoscopic manipulations, and today it is a daily reality). Another way is to see which faculties have opened in universities in the last 2-3 years, as a rule, this is the top that you will manage to get into.
Real profitability is a simpler metric. You open "My Circle" or "Headhunter", evaluate the average level of earnings in the specialty (sometimes ready analytics is also available). The indexation of wages in business happens to 10% per year, in the public sector about 5% per year. It's easier to count, but do not forget that in N years there will be an adjustment for the depth of demand, the change in the landscape of the sphere, etc.
The speed of development and career growth for each sphere is different. Moreover, it is not everywhere and it is not worth romanticizing: sometimes it is better to move horizontally, study a new specialty and work not on a record in the workbook, but on the real level of earnings (which is fraught, but more on that in the next series). The main thing is to convey to the student that he will not become the head immediately, he will have to work, and the real pros sometimes cost more than their head.
Growth flexibility and professional evolution is an important continuation for the previous metric. The professional studies continuously, until the last day at work (and sometimes after). Therefore, it is necessary to relate the schoolchild's tendency to study and the requirements of the desired profession ( for example, a boy dreams of becoming a doctor, has 5 in chemistry and biology, but being lazy about learning is a signal that he may have problems with professional development in the future ) , but do not dwell on it: often after a university, an adult is happy to learn and continue education, and at school there was not laziness, but hatred of history and boring geography.
What to consider?
Choosing a profession, you must help your child, but do not decide for him (I guarantee - you will not get “thanks”). At the same time it is important not to miss a single detail and, perhaps, even to look at your close, dear person a little from the outside, strictly and objectively (relatively speaking, the ability to twist your booty under Lambada is not yet class B in ballroom dancing, no matter how much you want ).
- The inclinations of a child in general terms are the very basis of vocational guidance that we spoke about above: “man”, “nature”, “machine”, “information systems”. There are no people without inclinations and some vector of wishes for their future, therefore it is important to recognize which mechanism prevails. Even station wagons have certain changes in one direction or another. Pay attention to what the student says, what subjects and why he is given easier, what he focuses on in the conversation, whether he has algorithmic thinking, how well developed logic or imagination. Moreover, such an observation of involuntary reactions is much more accurate than tests, because a schoolboy of 13-17 years old can easily guess how to respond in order to get the desired result at that time and deceive the system and adults :-)
- The wishes of the student must be taken into account and encouraged, maybe even give a "pain" to the dream of the profession - so he quickly determined. In no case do not prevent him from choosing, do not expose the profession in a negative light ( "all programmers are zadroty", "the girl has no place in the automotive department", "ha ha, psychology, you're crazy, you will be treated for something," "A taxi driver? Yes they will kill you" - based on real events ). If possible, let your child try a specialty, or at least a part of it: arrange to work for the summer, ask for help related to the profession, ask friends to take a few days to work. If there is such an opportunity, it works simply flawlessly: either cooling and disappointment comes, or enthusiasm and approval in the plans for the future.
- Family features cannot be left out of our difficult components: if the whole family, the building engineers and daughter are distinguished from their concrete marks since childhood, knows the thickness of the reinforcement, distinguishes the masonry types and at 7 years can explain how the heating works ... this does not mean that the building is waiting for it , no, but you should not wait for falling in love with Akhmatova and the early works of Petrarch, it's just not her environment. Although there are exceptions. However, nepotism should not put pressure on the student, force him to become someone, because these are his parents. Yes, your benefit is obvious: it is easier to train, help, get a job, etc. But the benefit is yours, and the life is your child, and probably the choice of a dynasty does not suit him.
It happens that parents are confident that their child does not want anything, does not have aspirations and inclinations, does not seek to choose a university, does not think about the future. In fact, it does not happen, there is always what you like - and from this you need to make a start. If you think that there are real difficulties, talk to the teachers, listen to their advice, contact a social psychologist who is engaged in vocational guidance for teens (there are very cool private traders - see below for them). My classmate has a 15-year-old daughter, a very early child, my mother is an inert housewife with no education and looks at her daughter as “nothing-not-want”. The girl served a delicious brewed coffee, gracefully bent napkins, offered the cake "Anthill", which she made. - Kate, don't you think that she should try herself as a pastry chef or work in a cafe? - What are you, she is not a plebeian to serve all sorts, I will force her to go to an accountant. A curtain.

What should the schoolboy know about the profession?
When you are a schoolboy, you always try to hide the true motives of your behavior or choice, so as not to appear immature or led. Therefore, it is very difficult for parents to figure out where the craving for a particular profession has come from, especially if it is sudden. And do not do it, it is better to convey certain rules of the game.
- Any work includes a share of the routine (up to 100% of the entire work) - the student must understand that, along with some desired or visual attributes, he will receive many routine tasks, the execution of which can make up most of the work: the programmer does not write entire programs ( if he is not a business owner or freelancer), but works on his part of the code; the doctor is obliged to fill a pile of papers, even if he is an ambulance officer or a surgeon; an astronaut trains for a long time, studies a lot of things and is obliged to perform a huge number of tasks in space, etc. It is necessary to understand that there is no profession without such specificity, it is not worth romanticizing work.
- Work is the daily work of a specialist. If you connect your life with a profession, then with a high degree of probability, it is forever: every day, with a short vacation, bosses, Mondays, complex subordinates, and so on.
- Fashion and prestige of the profession can change - and earlier than he graduates from the university. And then there will be two ways: to change qualifications or to become the best in the profession in order to guarantee demand for the labor market.
- It is impossible to transfer the attitude towards a person to the attitude towards the whole field of activity - if you like the profession, because it is owned by dad / uncle / brother / filmstroke, this does not mean that you yourself will feel as comfortable in it. Each person must choose what he likes and what he is ready for. Examples can be, idols should not be.
- Work should like, should like its components. Each work is divided into several components: the main activity and its goals, colleagues, work environment, infrastructure, “customers” of work, the external environment and its relation to the activity. You can not take one thing and give up everything else, deny the existence of external factors. In order to work well and get satisfaction, it is important to find positive things in all the listed components and, turning off the alarm clock, to know for what you turned it off now (for the sake of which, except money).
- A great path begins with a chain of small steps - one cannot immediately become great and famous, experienced and guiding. There will be mistakes, reproaches, mentors and rivals, the first steps will seem inconspicuous, tiny. But in fact, behind each such step there will be a breakthrough - the foundation of experience. You do not need to be afraid to go or rush from work to work for insignificant reasons: the stone is cluttered on the spot, and the road will be mastered by a walker.

- The beginning of a career is almost always boring - no one will entrust the novice with complex interesting tasks, you will have to approach everything from the periphery, from the basics, learn, master, repeat some terribly boring things every day. But it is precisely thanks to the mastery of these things that the young specialist is able to dive into the deep foundations of the profession. This boredom is inevitable, so you will need to learn how to find some fan in it.
- Managing money is also work. This is the thesis that our parents did not exactly convey to us, and we are somehow far from it. It is important not just to earn or even save, it is important to be able to manage money and to be able to live on the amount that you have in this period of time. This is a valuable skill that also teaches respecting your professional ego and skill, not working for a penny, but also adequately name your price.
It turned out such a bit of a philosophical section, but this is precisely the support of the student’s vocational guidance from the parents, the first beginnings of his self-esteem as a future specialist.
What and who will help?
Career guidance is a process that determines the rest of life, so you need to rely on third-party methods and the help of professionals.
- A private vocational guidance specialist is a person who can really find the most hidden aspirations and abilities in a child. Often these are not just social psychologists, but practicing HR specialists, through whom hundreds of applicants pass and they can soberly assess what your child is ready for and what horizons you should count on.

- Introspection: you need to determine what you really like, what you are ready for (the same routine), what you don’t like, what you’re not ready for for any incentives. This is best written on paper and saved to return to another iteration later. Such a table will help to understand what skills the profession should be at.
- A map of suitable professions - write out all professions that suit the student in some way, discuss each one, highlight the advantages and disadvantages, and relate to the possibilities of entering the appropriate university. Thus, we can confine ourselves to several areas and argue in the key to further professional development (for example, the professions of a videographer, programmer, automotive engineer and long-distance captain have remained, among them there is one vector - technical specialties, connection with some equipment; you can already explore prospects for each profession, evaluate what it will be at the time of leaving the university, etc. Although the spread still remains very large).
- School teachers are important observers and witnesses of the growth of your child, sometimes they can see what parents do not notice. In fact, they see a schoolboy primarily from an intellectual point of view, see his potential as a future specialist. Talk with them, discuss the issue of professional development, their observations can be a really weighty factor.
When you collect and compare these data, it will be much easier to determine how to help a teenager choose his direction.

But we liked her another variation - you can't argue!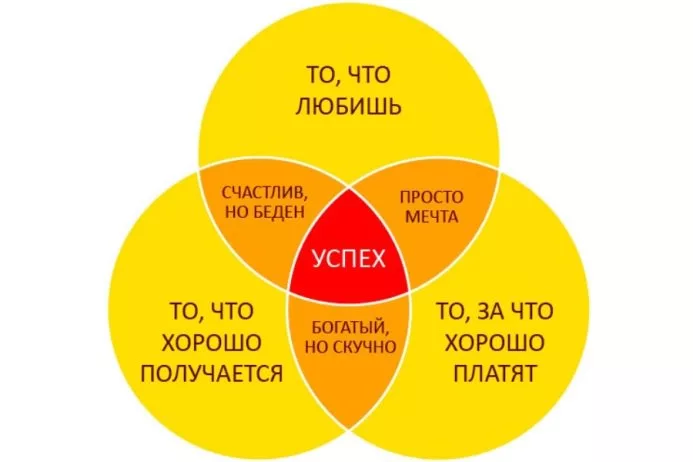

How to grow an IT person?
If a teenager (and even better a child under 12) has certain abilities for logical thinking, algorithms, an engineering view of things, do not miss the time and pay special attention to some things:
- books, namely books, computer science and mathematics - firstly, these are necessary subjects, and secondly, your student will get used to working with professional literature; in professional life, a good programmer rarely goes without books;
- circles on robotics and programming - tutors in a game form will teach the child the basic algorithms, functions, concepts from the IT sphere (stack, memory, programming language, interpreter, testing, etc.);
- English language - you need to learn the language very seriously, to take care of the diversity and depth of vocabulary, about the conversational component (from communicating with peers in applications and via Skype to learning on holidays in foreign language schools or camps);
- about robots and designers at home - now there are programmable robots in any price segment, it is important to analyze homework with a student, deepen knowledge;
- if you are also ready to dig deeper with Arduino and entice a teenager with it - then everything is almost done.
But behind gamification and enthusiasm you should not forget about the fundamental fundamentals of physics, mathematics and computer science, they are simply obliged to be present in the life of a schoolboy with a burden to develop (and indeed any educated person).
Learning - we must not forget about it: question-answer
Of course, even if you are a child-oriented child from the first grade and are confident in his future, this does not mean that you should give up school and focus on one thing.
How to learn "profile" subjects?
Exceptionally in-depth, with the use of additional literature, problem books and reference books. The purpose of training is not just to pass the USE well, but also to come to the university prepared, with an understanding of the subject and its place in a future profession.
How to treat non-core items?
Within the framework of reasonable and personal ambitions - to teach, donate, write tests, do not spend too much time on them. Exceptions: Russian and foreign languages, they are specialized for any specialty, so pay special attention to them.
How to work with additional load?
The tasks of increased complexity and Olympiad are the beginning of a career, without exaggeration. They pump thinking, learn to focus at short distances and intensively solve the problem, give the skill of self-presentation and the ability to win / take a punch. Therefore, if you want a career expectancy in a particular university or teenager, you should take part in competitions, conferences, and student research contests.
At the same time, health should be above all, this is an important point that parents forget, but children do not realize yet.
Do I go to college after grade 8/9?
Only the decision of the parents and the student. In education according to the scheme of college + university there is nothing wrong, even more advantages. But learning is somewhat more difficult.
Should I change school to profile?
It is desirable to change - so the student will have more chances to pass the exam for a high score (well, the same story with the entrance exams, if they return everywhere in the future - the chance is still higher). You shouldn’t be afraid of psychological trauma, the team change has a great advantage: the future student will know some part of his classmates and classmates much earlier, and this is great for adapting to the university. But if a teenager is not directly torn off and the school world is the most expensive of all - of course, you should not be torn off, it is better to devote time to additional classes.
Factors choosing a university?
A lot of factors: from moving to other cities to the internal features of the university, it is all very individual. But you should pay attention to the practice base (if you don’t have your people in mind), to the degree of language learning at the university, to the main scientific profile (scientific laboratories), to the presence of a military department (to whom this is relevant).
When to start working?
This is the big question - is it worth starting work in school, and the answer to it is also individual. But, in my opinion, it is worth trying to work in the summer between 9 and 10, 10 and 11 classes - purely in order to understand how the interaction in the work collective is arranged, how responsibilities are distributed, what degrees of freedom / lack of freedom exist.But in the summer of admission to the university of stress and stress is too much - so enrolled and rest, the more the better.
In fact, this topic can be talked about forever, and it requires a deeply individual approach. But it seems that if every parent listens to at least some moments from the article, schoolchildren will find it easier to choose their future profession, and mom and dad will be able to avoid the charge “I didn’t want to go to this university, you decided for me.” The task of adults is not just to feed their children with a fish, but to give them a fishing rod and teach it to use. The school period is a huge foundation for the whole future life, so you should take it responsibly and follow three main rules: respect, guide and love. Believe me, you will be back a hundredfold.
In the next series, we will go through five / six
Greedy postscript
By the way, we forgot about the important point - if you want to grow as an IT specialist, you should get acquainted with open source projects at school. This does not mean that you need to contribute to the largest developments, but it's time to start cutting and nurturing your pet-project by analyzing the theory in practice. And if you have already grown and you lack something for development, for example, a good powerful VPS , go to the RUVDS website - we have a lot of interesting things.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/459336/
All Articles