Network for small businesses on Cisco equipment. Part 1
Greetings, dear habrozhiteli and occasional guests. This series of articles focuses on building an uncomplicated network for a company that is not too demanding for its IT infrastructure, but at the same time has a need to provide its employees with high-quality Internet connection, access to shared file resources, and provide VPN access to employees. to the workplace and the connection of the video surveillance system, access to which would be available from anywhere in the world. For the small business segment, rapid growth and, accordingly, network re-planning are very characteristic. In this article we will start with one office for 15 workplaces and will continue to expand the network. So, if some topic is interesting, write in the comments, we will try to introduce it into the article. I will assume that the reader is familiar with the basics of computer networks, but I will give references to Wikipedia to all technical terms, if something is not clear, click and correct this defect.
So, let's begin. Any network begins with an inspection of the area and the receipt of customer requirements, which will later be formed in the TK. Often, the customer himself does not fully understand what he wants and what he needs for this, so he needs to be guided to what we can do, but this work is more than a sales representative, we also provide the technical part, so suppose that we got the following initial requirements:
I will not delve into the selection of the vendor, since this is a question that generates age-old disputes, we’ll dwell on the fact that the brand has already been decided, this is Cisco.
The network is based on a router (router). It is important to assess our needs, as we plan to expand the network in the future. Acquiring a router with a reserve for this will save the customer money when expanding, although it will be a bit more expensive in the first stage. Cisco for the small business segment offers the Rvxxx series, which present routers for home offices (RV1xx, most often with an integrated Wi-Fi module), which are designed to connect multiple workstations and network storage. But they are not interested in us, since they have quite limited VPN capabilities and sufficiently low bandwidth. Also, we are not interested in the built-in wireless module, since it is supposed to be placed in a technical room in a rack, Wi-Fi will be organized using an AP ( Access Point's ). Our selection will fall on the RV320, which is the youngest model in the older series. We do not need a large number of ports in the built-in switch, since we will have a separate switch in order to provide a sufficient number of ports. The main advantages of the router are a fairly high bandwidth of the VPN server (75 Mbit / s), a license for 10 VPN tunnels, the possibility of raising the Site-2-site VPN tunnel. Also important is the presence of a second WAN port to provide a backup Internet connection.
')
The router is followed by a switch (switch) . The most important parameter of a switch is the set of functions it possesses. But first we calculate the ports. In our case, we plan to connect to the switch: 17 PCs, 2 AP (Wi-Fi access points), 8 IP cameras, 1 NAS, 3 network printers. With the help of arithmetic, we get the number 31, corresponding to the number of devices initially connected to the network, we add to this 2 uplinks (we are planning to expand the network) and dwell on 48 ports. Now about the functionality: our switch should be able to VLAN , preferably all 4096, will not interfere with the SFP mines, since it will be possible to connect the switch at the other end of the building using optics, must be able to work in a closed circle, which makes it possible to reserve links ( STP-Spanning Tree Protocol ), also AR and cameras will be powered via twisted pair, therefore, PoE is required (for more information about protocols, see the wiki, the names are clickable). We do not need too complex L3 functionality, so our choice will stop on the Cisco SG250-50P, as it has enough functionality for us and at the same time does not include redundant functions. We will talk about Wi-Fi in the next article, as this is a rather extensive topic. There we will focus on the choice of AR. We do not select NAS and cameras, we assume that other people are engaged in this, we are only interested in the network.
To begin with, we will decide on which virtual networks we need (what virtual VLANs you can read on Wikipedia). So, we have several logical network segments:
Also, according to the rules of good tone, the device management interface will be rendered into a separate VLAN. You can number VLANs in any order, I will choose this:
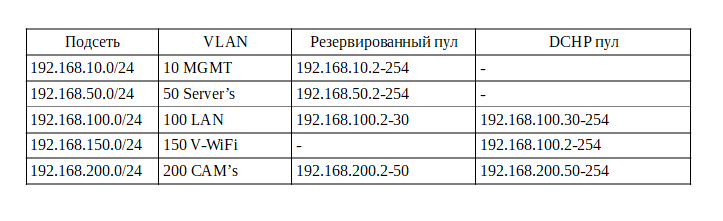
Next, we will make an IP plan, use a 24-bit mask and a 192.168.xx subnet. Let's get started
The reserved pool will contain addresses that will be configured statically (printers, servers, management interfaces, etc., will issue a dynamic address for DHCP clients).
So we figured IP, there are a couple of points that I would like to draw attention to:
Well, finally proceed to the setting. Take the patch cord and connect to one of the four LAN ports of the router. By default, the router has a DHCP server enabled and it is available at 192.168.1.1. You can check this with the console utility ipconfig, in the output of which our router will be the default gateway. Check:

In the browser we go to this address, confirm the insecure connection and log in with the cisco / cisco login / password. Immediately change the password to secure. And first of all we go to the Setup tab, the Network section, here we assign the name and domain name for the router

Now let's add VLANs to our router. Go to the Port Management / VLAN Membership. We are greeted by the default VLAN-ok tag.
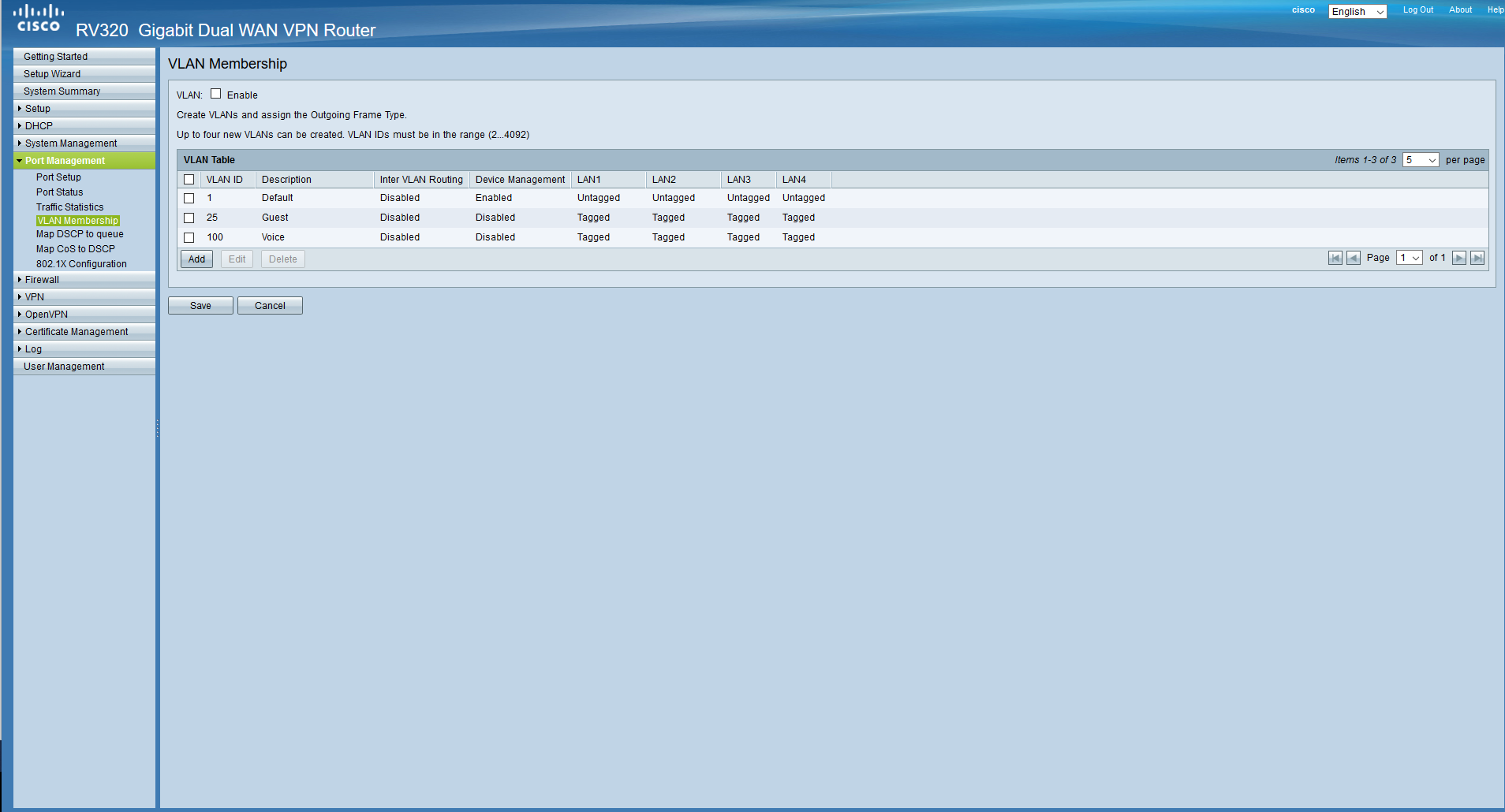
We do not need them, we will delete everything except the first one, since it is defaulted and cannot be deleted, we will immediately add the VLANs we have planned. Do not forget to tick the top. Also, device management is allowed only from the control network, and routing between networks is allowed anywhere except for the guest network. Ports configure later.
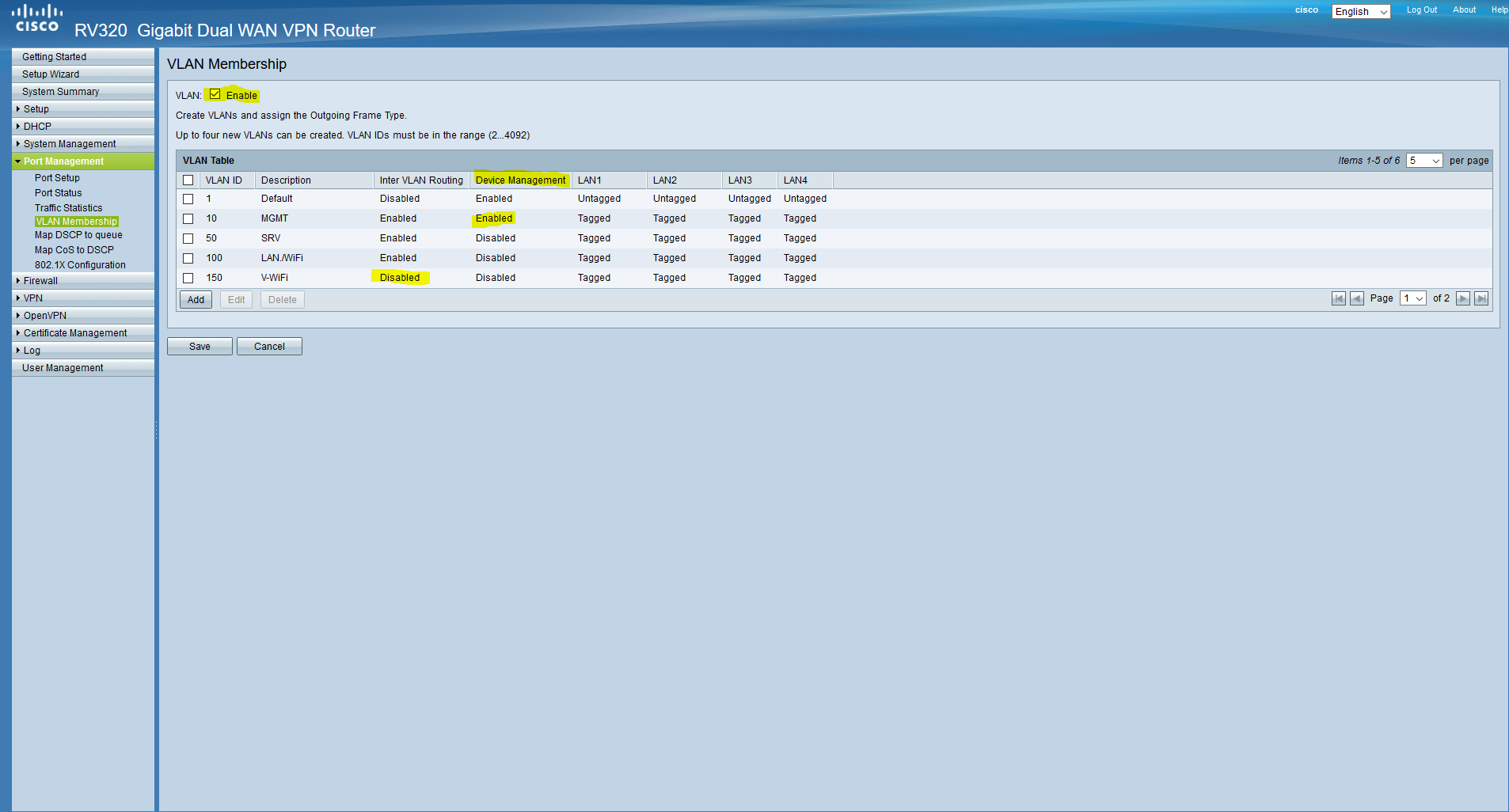
Now we will configure the DHCP server according to our table. To do this, go to the DHCP / DHCP Setup.
For networks in which DHCP will be disabled, we will only configure the gateway address, which will be the first on the subnet (respectively, the mask).

In networks with DHCP, everything is quite simple, we also configure the gateway address, below we prescribe pools and DNS keys:
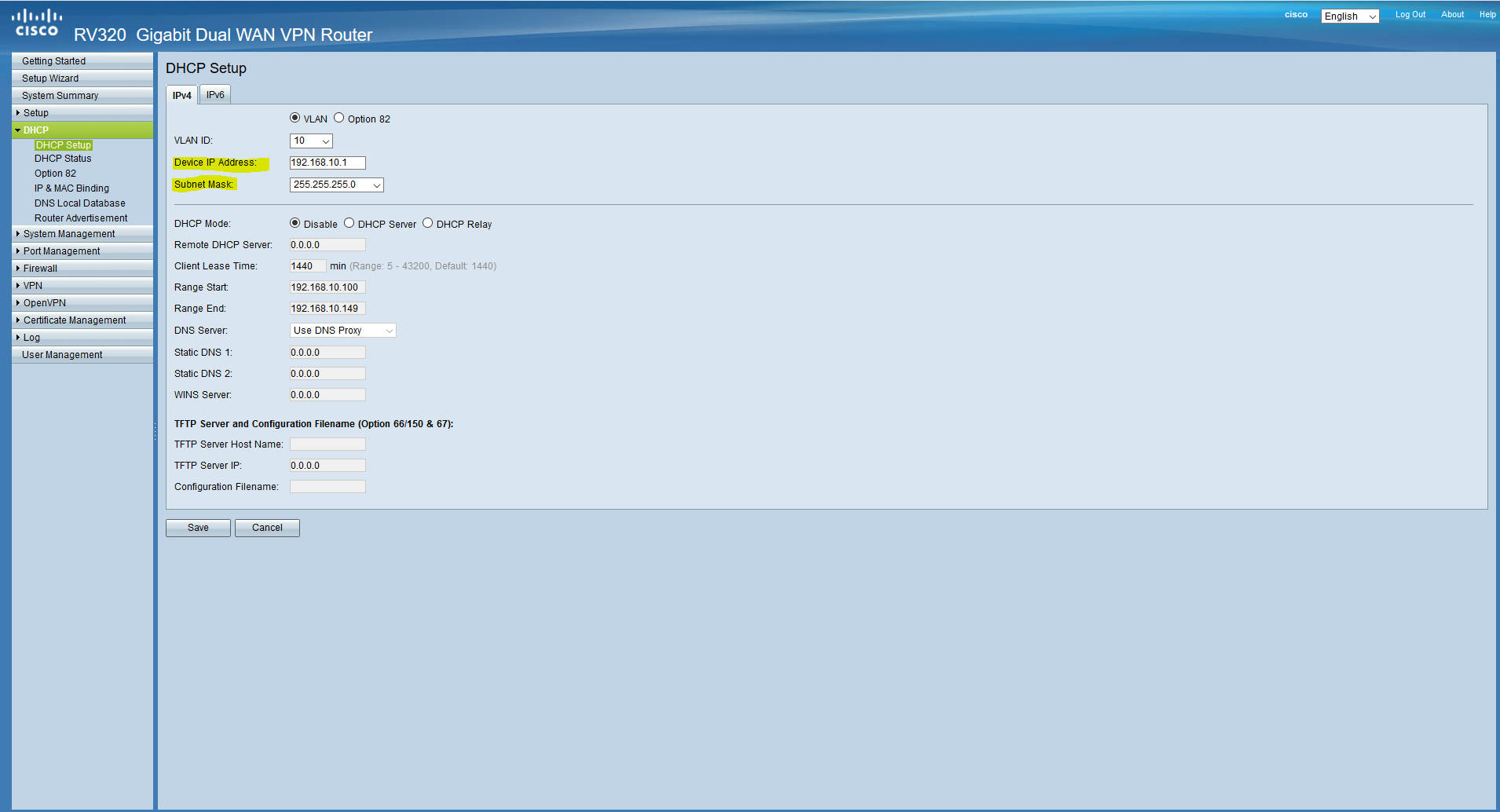
On this we figured out with DHCP, now the clients connected to the local network will receive the address automatically. Now we will configure the ports (the ports are configured according to the 802.1q standard, the link is clickable, you can familiarize yourself with it). Since it is assumed that all clients will be connected via managed switches to untagged (native) VLAN-oh on all ports will be MGMT, this means that any device connected to this port will fall into this network (more here). Go back to the Port Management / VLAN Membership and set it up. VLAN1 on all ports is Excluded, we do not need it.

Now on our network card we need to configure a static address from the management subnet, since we got into this subnet after we clicked “save”, and there is no DHCP server here. Go to the network adapter settings and configure the address. After that, the router will be available at 192.168.10.1

Set up our connection to the Internet. Suppose we got a static address from the provider. Go to Setup / Network, mark WAN1 at the bottom, click Edit. We select Static IP and we configure the address.

And the last for today - we will configure remote access. To do this, go to the Firewall / General and tick the Remote Management, if necessary, configure the port

For today, perhaps, everything. At the end of the article we have a basic configured router with which we can access the Internet. The volume of the article is more than I expected, so in the next part we will finish setting up the router, raise the VPN, configure the firewall and logging, configure the switch and will be able to start our office to work. I hope that the article was for you at least a little useful and informative. I am writing for the first time, I will be very happy for constructive criticism and questions, I will try to answer everyone and take into account your comments. Also, as I wrote at the beginning, your thoughts about what else might appear in the office and what else we will configure are welcome.
My contacts:
Telegram: hebelz
Skype / mail: kashuba@antik.sk
Add, talk.
So, let's begin. Any network begins with an inspection of the area and the receipt of customer requirements, which will later be formed in the TK. Often, the customer himself does not fully understand what he wants and what he needs for this, so he needs to be guided to what we can do, but this work is more than a sales representative, we also provide the technical part, so suppose that we got the following initial requirements:
- 17 jobs for stationary PCs
- Network Disk Storage ( NAS )
- Video surveillance system using NVR and IP cameras (8 pieces)
- Wi-Fi office coverage, two networks (internal and guest)
- You can add network printers (up to 3 pieces)
- The prospect of opening a second office at the other end of the city
Equipment selection
I will not delve into the selection of the vendor, since this is a question that generates age-old disputes, we’ll dwell on the fact that the brand has already been decided, this is Cisco.
The network is based on a router (router). It is important to assess our needs, as we plan to expand the network in the future. Acquiring a router with a reserve for this will save the customer money when expanding, although it will be a bit more expensive in the first stage. Cisco for the small business segment offers the Rvxxx series, which present routers for home offices (RV1xx, most often with an integrated Wi-Fi module), which are designed to connect multiple workstations and network storage. But they are not interested in us, since they have quite limited VPN capabilities and sufficiently low bandwidth. Also, we are not interested in the built-in wireless module, since it is supposed to be placed in a technical room in a rack, Wi-Fi will be organized using an AP ( Access Point's ). Our selection will fall on the RV320, which is the youngest model in the older series. We do not need a large number of ports in the built-in switch, since we will have a separate switch in order to provide a sufficient number of ports. The main advantages of the router are a fairly high bandwidth of the VPN server (75 Mbit / s), a license for 10 VPN tunnels, the possibility of raising the Site-2-site VPN tunnel. Also important is the presence of a second WAN port to provide a backup Internet connection.
')
The router is followed by a switch (switch) . The most important parameter of a switch is the set of functions it possesses. But first we calculate the ports. In our case, we plan to connect to the switch: 17 PCs, 2 AP (Wi-Fi access points), 8 IP cameras, 1 NAS, 3 network printers. With the help of arithmetic, we get the number 31, corresponding to the number of devices initially connected to the network, we add to this 2 uplinks (we are planning to expand the network) and dwell on 48 ports. Now about the functionality: our switch should be able to VLAN , preferably all 4096, will not interfere with the SFP mines, since it will be possible to connect the switch at the other end of the building using optics, must be able to work in a closed circle, which makes it possible to reserve links ( STP-Spanning Tree Protocol ), also AR and cameras will be powered via twisted pair, therefore, PoE is required (for more information about protocols, see the wiki, the names are clickable). We do not need too complex L3 functionality, so our choice will stop on the Cisco SG250-50P, as it has enough functionality for us and at the same time does not include redundant functions. We will talk about Wi-Fi in the next article, as this is a rather extensive topic. There we will focus on the choice of AR. We do not select NAS and cameras, we assume that other people are engaged in this, we are only interested in the network.
Planning
To begin with, we will decide on which virtual networks we need (what virtual VLANs you can read on Wikipedia). So, we have several logical network segments:
- Client Workstations (PCs)
- Server (NAS)
- CCTV
- Guest devices (WiFi)
Also, according to the rules of good tone, the device management interface will be rendered into a separate VLAN. You can number VLANs in any order, I will choose this:
- VLAN10 Management (MGMT)
- VLAN50 Server's
- VLAN100 LAN + WiFi
- VLAN150 Visitor's WiFI (V-WiFi)
- VLAN200 CAM's
Next, we will make an IP plan, use a 24-bit mask and a 192.168.xx subnet. Let's get started
The reserved pool will contain addresses that will be configured statically (printers, servers, management interfaces, etc., will issue a dynamic address for DHCP clients).

So we figured IP, there are a couple of points that I would like to draw attention to:
- In the control network, there is no point in raising DHCP, in the same way as in the server one, since all addresses are assigned manually when setting up the equipment. Some leave a small DHCP pool in case of new equipment connection, for its primary configuration, but I am used to it and advise you to configure the equipment not at the customer, but on my desk, so I don’t make this pool here.
- Some camera models may require a static address, but we assume that cameras receive it automatically.
- In the local network, the pool is reserved for printers, since the network printing service does not work very reliably with dynamic addresses.
Configure the router
Well, finally proceed to the setting. Take the patch cord and connect to one of the four LAN ports of the router. By default, the router has a DHCP server enabled and it is available at 192.168.1.1. You can check this with the console utility ipconfig, in the output of which our router will be the default gateway. Check:

In the browser we go to this address, confirm the insecure connection and log in with the cisco / cisco login / password. Immediately change the password to secure. And first of all we go to the Setup tab, the Network section, here we assign the name and domain name for the router

Now let's add VLANs to our router. Go to the Port Management / VLAN Membership. We are greeted by the default VLAN-ok tag.

We do not need them, we will delete everything except the first one, since it is defaulted and cannot be deleted, we will immediately add the VLANs we have planned. Do not forget to tick the top. Also, device management is allowed only from the control network, and routing between networks is allowed anywhere except for the guest network. Ports configure later.

Now we will configure the DHCP server according to our table. To do this, go to the DHCP / DHCP Setup.
For networks in which DHCP will be disabled, we will only configure the gateway address, which will be the first on the subnet (respectively, the mask).

In networks with DHCP, everything is quite simple, we also configure the gateway address, below we prescribe pools and DNS keys:

On this we figured out with DHCP, now the clients connected to the local network will receive the address automatically. Now we will configure the ports (the ports are configured according to the 802.1q standard, the link is clickable, you can familiarize yourself with it). Since it is assumed that all clients will be connected via managed switches to untagged (native) VLAN-oh on all ports will be MGMT, this means that any device connected to this port will fall into this network (more here). Go back to the Port Management / VLAN Membership and set it up. VLAN1 on all ports is Excluded, we do not need it.

Now on our network card we need to configure a static address from the management subnet, since we got into this subnet after we clicked “save”, and there is no DHCP server here. Go to the network adapter settings and configure the address. After that, the router will be available at 192.168.10.1

Set up our connection to the Internet. Suppose we got a static address from the provider. Go to Setup / Network, mark WAN1 at the bottom, click Edit. We select Static IP and we configure the address.

And the last for today - we will configure remote access. To do this, go to the Firewall / General and tick the Remote Management, if necessary, configure the port

For today, perhaps, everything. At the end of the article we have a basic configured router with which we can access the Internet. The volume of the article is more than I expected, so in the next part we will finish setting up the router, raise the VPN, configure the firewall and logging, configure the switch and will be able to start our office to work. I hope that the article was for you at least a little useful and informative. I am writing for the first time, I will be very happy for constructive criticism and questions, I will try to answer everyone and take into account your comments. Also, as I wrote at the beginning, your thoughts about what else might appear in the office and what else we will configure are welcome.
My contacts:
Telegram: hebelz
Skype / mail: kashuba@antik.sk
Add, talk.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/459154/
All Articles