Windows Server 2008 R2 - The King Is Dead, Long Live The King
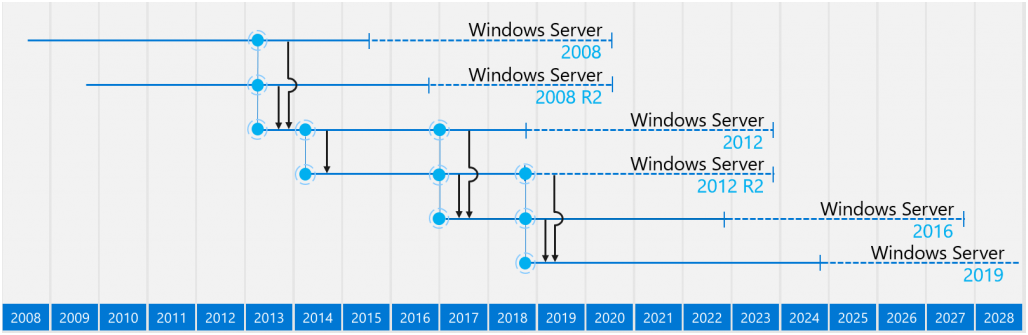
Hi, Habr! 14/01/2020 is approaching and this date marks the end of extended support for Windows Server 2008 R2, and if you are still using Windows Server 2008 R2, you should think about migrating to a more up-to-date platform.
Under the cat there is a small comparison of the consumed resources of the old and new Windows Server platforms - the role of RDSH. First of all, I was interested in the opportunity to continue using the already available HP G6 / G7 servers running VMware Vsphere 5.5.
')
Information about Windows Server Lifecycle is available at this link Search Product Lifecycle .
I will have two test stands:
- HP DL120 G7, 1 * cpu Intel Xeon E3-1240
- HP ML350 G6,2 * cpu Intel Xeon E5620
Servers will run under VMware ESXi 5.5, VMware-ESXi-5.5.0-Update1-1746018-HP-5.75.4-Dec2014 image. I also tried using the VMware-ESXi-5.5.0-Update3-3116895-HP-550.9.4.26-Nov2015 image, but this does not affect the results.
But the image of VMware-ESXi-5.5.0-Update2-2403361-HP-550.9.2.40.2-Sep2015 gives distorted results, for some reason, the statistics shown by the server differ from the real one by two times. With this image, the maximum that the server shows is 50 percent of the load on the processor, apparently some kind of bug. At first I was delighted when I received the first results, but then I realized that something was wrong ...
It should also be mentioned that support for VMware Vsphere 5.5 is also not eternal, and the platform is no longer relevant, and it is worth thinking about the update. Information about VMware Lifecycle is available in this VMware Lifecycle Product Matrix document.
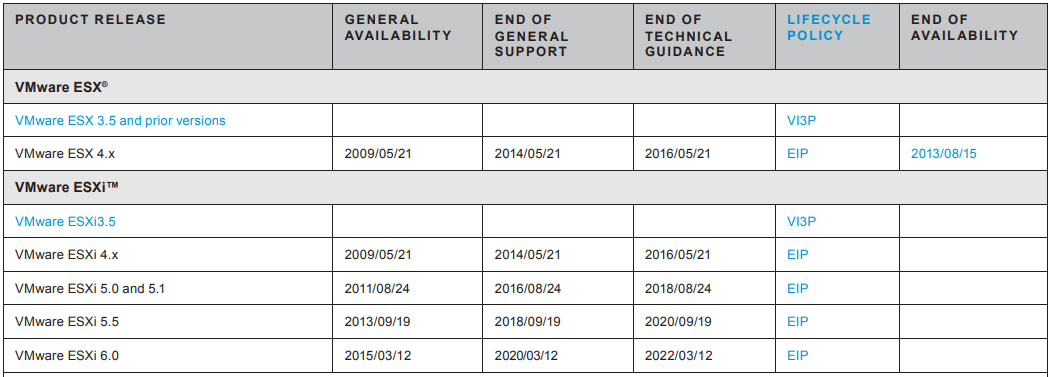
And do not forget about the VMware Compatibility Guide . If we talk about the server HP DL120 G7, this server has never been present in the compatibility matrices, but on the server HP ML350 G6 is officially allowed to install ESXi 5.5 U3.
Guest OS
Information about ESXi compatibility with guest OSs is also available in the VMware Compatibility Guide .
ESXi 5.5 U3 allows you to install Windows Server 2016 as a guest OS, and even version 5.5 will be enough for this. But to install Windows Server 2019, you will need ESXi version 6+, but this will not prevent me from testing my plans.
I will have the following test VMs: WS2008R2SP1, WS2012R2, WS2016, and WS2019.
VMware Tools 5.5.0-10.2.5.8068406 are installed on all VMs. Installed all updates from Microsoft in May 2019, and even some in June 2019, after which the update service was disabled.
For my tests, I performed the minimum tuning, I want everything to work with the most standard parameters. For this, I will use local group policies, a little more detail about this, I will write at the end.
- disconnected "desktop composition"
- allowed audio and video redirect
- Enabled RemoteFX for WS2008R2SP1 and WS2008R2SP1 Clients
- disabled font smoothing
- limited the color depth of the color palette to 32
- limited the number of monitors to 1
In order for the RemoteFX codec to start working on WS2008R2SP1, you must install the RDSH role, for newer versions this can be not done. Perhaps, RemoteFX is used on WS2008R2SP1 without installing RDSH, but there are no events in the logs about the activation of this codec.
Test 1
As a test, I will use a 720p YouTube movie , the BRK2242 .
On each of the servers, I will in turn open one rdp session and a test video in Chrome (version 75.0.3770.80 (64bit)).
In this test, the HP t510 thin client running on the HP ThinOS 4.4 OS and with the Freerdp-1.1hp10d-all-4.4-x86-SQ package will be used as a client. This unit is connected to a Full HD monitor, and the thin client profile has been reset to factory.
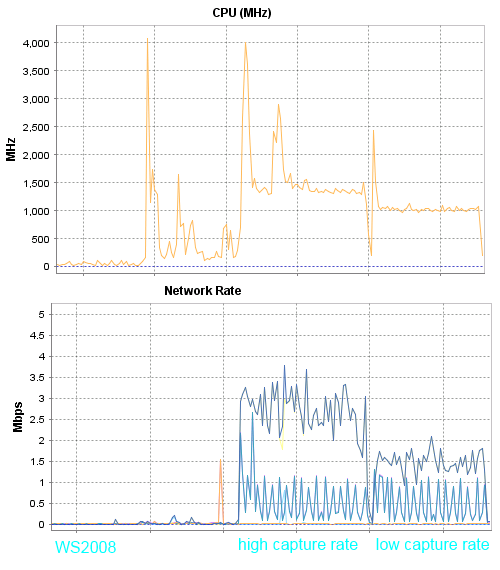
I shot the graphs from the host; all the first tests will be performed on the HP DL120G7 server.

Comments on the results of the first test:
In this test, ws2008 consumes three times less CPU resources, but at the same time three times more traffic than other test participants.
With current traffic, one gigabit can be placed 66 sessions, but the transition to the new version of the server will probably reduce three times the number of users who can work with this processor consumption.
Visually, the picture in this presentation is acceptable on all versions of Windows Server. Of course, if you run something more dynamic, the newer versions of the servers show a much better picture. I suppose that this is due to the number of frames, more frames = smooth playback = more CPU load.
Test 2
The script for the second test remains unchanged, except for the use of Firefox (version 67.0.2 (64bit))

Comments on the results of the second test:
Firefox paired with ws2019 shows not a bad result, consumes slightly more CPU and noticeably less traffic than ws2008.
Test 3
In this test, Chrome will be used, but the client will already be a laptop with Windows 10 1903, the laptop is connected to a monitor with FullHD resolution.
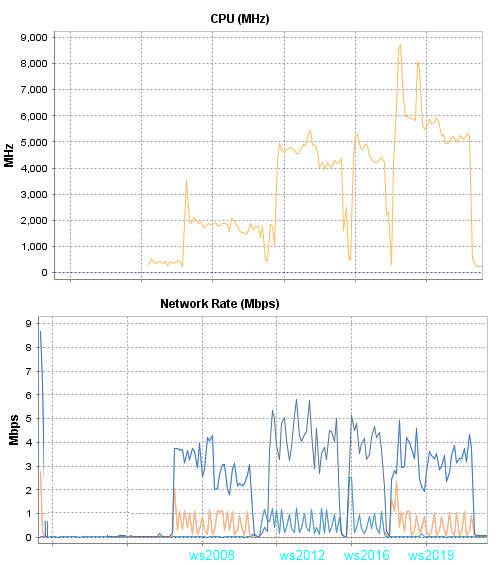
Comments on the results of the third test:
In the cases with ws2008 less traffic is consumed, other changes are not significant ...
I also noticed that Chrome, when displaying a progress bar on the background of a video, consumes 1,000 MHz more, but I did not notice this effect in Firefox, and drawing the progress of the bar does not affect the amount of resources consumed.
Test 4
Laptop with Windows 10 paired with Firefox

Comments on the results of the fourth test:
In this combination of server-client-browser, ws2019 + Firefox consumes less resources than with Chrome, but began to consume significantly more processor compared to the results of Test 2.
In the cases with ws2012 and ws2016, the results of all tests performed are much smoother, there is no such spread as ws2019.
Test 5
This test is concluded in running the maximum number of rdp sessions and launching the presentation in each of the sessions. Remote Desktop Connection Manager will help me in this, RDCM will run on a laptop with Windows 10.
Resolution sessions had to be reduced to 1440 * 900. As results, I’ll just give a summary table:

Comments on the results of the fifth test:
Suddenly, the 2019 server showed worse results than ws2012 and ws2016. Server 2008 was able to open 8 sessions while 2012/2016 servers could open 4 sessions, and the 5th one increases the load to 100%. Server 2019 was able to work with a maximum of 4 sessions.
Firefox is not a priority browser for me, and therefore I only ran it in ws2019 to verify the numbers I received.
Test 6
In this test, the HP ML350G6 server with two E5620 processors comes into play, I will test only 2008 and 2019 servers. The test is the same, the launch of the maximum number of sessions will be used only by Chrome.
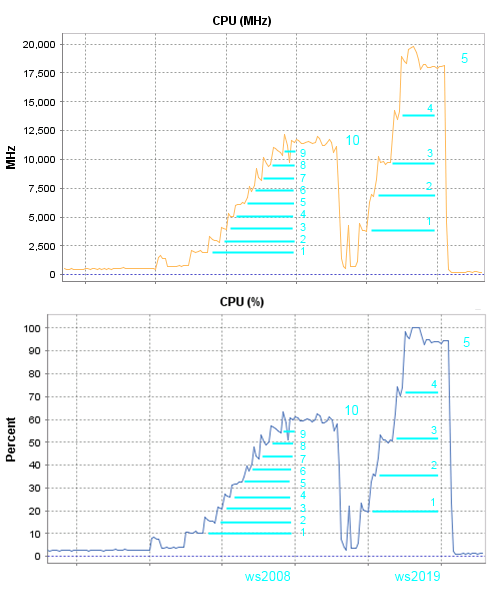
Comments on the results of the sixth test:
To run 10 sessions on server 2008, it took 60 percent of the processor resources, and to launch just 5 sessions on 2019 the server needs more than 90 percent.
The final part - Tuning
I returned all the test VMs to the HP DL120G7 server and as a client I used a laptop with Windows 10 and its regular screen with a resolution of 1366 * 768.
Unfortunately, I would not have called attempts to reduce CPU consumption successful, but I can’t say that there are no results either. Here is a list of all available parameters of local group policies that can be used for tyunig:

In Windows Server 2008R2, the “Optimize visual experience when using RemoteFX” parameters allow you to control the picture quality and the number of frames, and this gives a noticeable result. Reducing the number of frames reduces the load on the processor and network. For Windows Server 2019, these options do not work.
The quality of the picture in Windows Server 2019 can be controlled by the parameter “Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics”, but there is nothing to change the number of frames, or I have not found such a parameter.
I tried various combinations of parameters, but I could get noticeable changes in the results only in a few cases. And the most interesting thing is that you can notice changes in traffic, but at the same time the load on the processor varies only slightly.
- Prioritization of H.264 / AVC 444 increased the load on the processor, but at the same time the traffic significantly decreased from 2x to 1 megabit.
This policy setting prioritizes the H.264 / AVC 444 graphics mode for non-RemoteFX vGPU scenarios. H.264 / AVC 444 server can use H.264 / AVC 444 when you use it.
- Disabling RDP compression did not reduce the load on the processor, but traffic increased from 2x to 7 megabits.
- The inclusion of the Losles parameter for image quality results in inadequate traffic consumption, without changing the processor load. For which scenarios, this option was added to me is not entirely clear.
If you use the RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics uses lossless encoding. In this mode, it is not impacted. However, this is a significant increase in network bandwidth consumption. We recommend that you set this for very specific cases only.

Results
If earlier for the work of 10 active users there were enough 8 nuclear servers and there was still free space, now such a server is only enough for 5 users.
I think it's time to prepare to replace the HP G6 and G7 generation servers. It is a pity to part with servers in which> 100 GB of RAM is installed, I assumed that they would serve further.
I do not rule out that the old processors do not have enough hardware instructions, so I plan to get a modern server to the test in the near future. But to be honest, my forecast is pessimistic, I think that getting the desired result will be possible only by brute force, an increase in the number of processor cores, and this will entail an increase in the number of licenses and cost.
The end
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/459068/
All Articles