Solution of the task with pwnable.kr 01 - fd. File Descriptors and Processes

In this article we will analyze: what a file descriptor is, how processes get access to certain input / output streams, and we will solve the first task from pwnable.kr
Organizational information
Especially for those who want to learn something new and develop in any of the areas of information and computer security, I will write and talk about the following categories:
In addition, I will share my experience in computer forensics, analysis of malware and firmware, attacks on wireless networks and local area networks, pentesting and writing exploits.
So that you can learn about new articles, software and other information, I created a channel in Telegram and a group to discuss any issues in the field of i & kb. I will also personally consider your personal requests, questions, suggestions and recommendations and answer all .
')
All information is presented solely for educational purposes. The author of this document does not bear any responsibility for any damage caused to anyone as a result of using the knowledge and methods obtained as a result of studying this document.
- PWN;
- cryptography (crypto);
- network technologies (Network);
- reverse (Reverse Engineering);
- steganography (Stegano);
- search and exploitation of WEB-vulnerabilities.
In addition, I will share my experience in computer forensics, analysis of malware and firmware, attacks on wireless networks and local area networks, pentesting and writing exploits.
So that you can learn about new articles, software and other information, I created a channel in Telegram and a group to discuss any issues in the field of i & kb. I will also personally consider your personal requests, questions, suggestions and recommendations and answer all .
')
All information is presented solely for educational purposes. The author of this document does not bear any responsibility for any damage caused to anyone as a result of using the knowledge and methods obtained as a result of studying this document.
File descriptors
A file descriptor is a non-negative number that is an identifier for any I / O stream that can be associated with files, directories, or sockets.

The System File Table (SFT) and the Inode Table (INode Table) contain the information necessary for the process to access the file data. If several processes request access to the same file, each of these processes will receive its own element of the system file table, despite the fact that they will work with the same file.
The kernel provides the process with a file descriptor when it accesses the file. We can say that a file descriptor is an index of an array of open files that is unique to each process. But the first three indices are rigidly fixed:
- 0 - standard input (stdin);
- 1 - standard output (stdout);
- 2 - standard error stream (stderr).
So, the gets () and printf () functions from the standard C library use stdin and stdout, which allows the shells to redirect input and output processes correctly.
Solution fd
We click on the first icon with the signature fd, and we are told that we need to connect via SSH with the guest password.
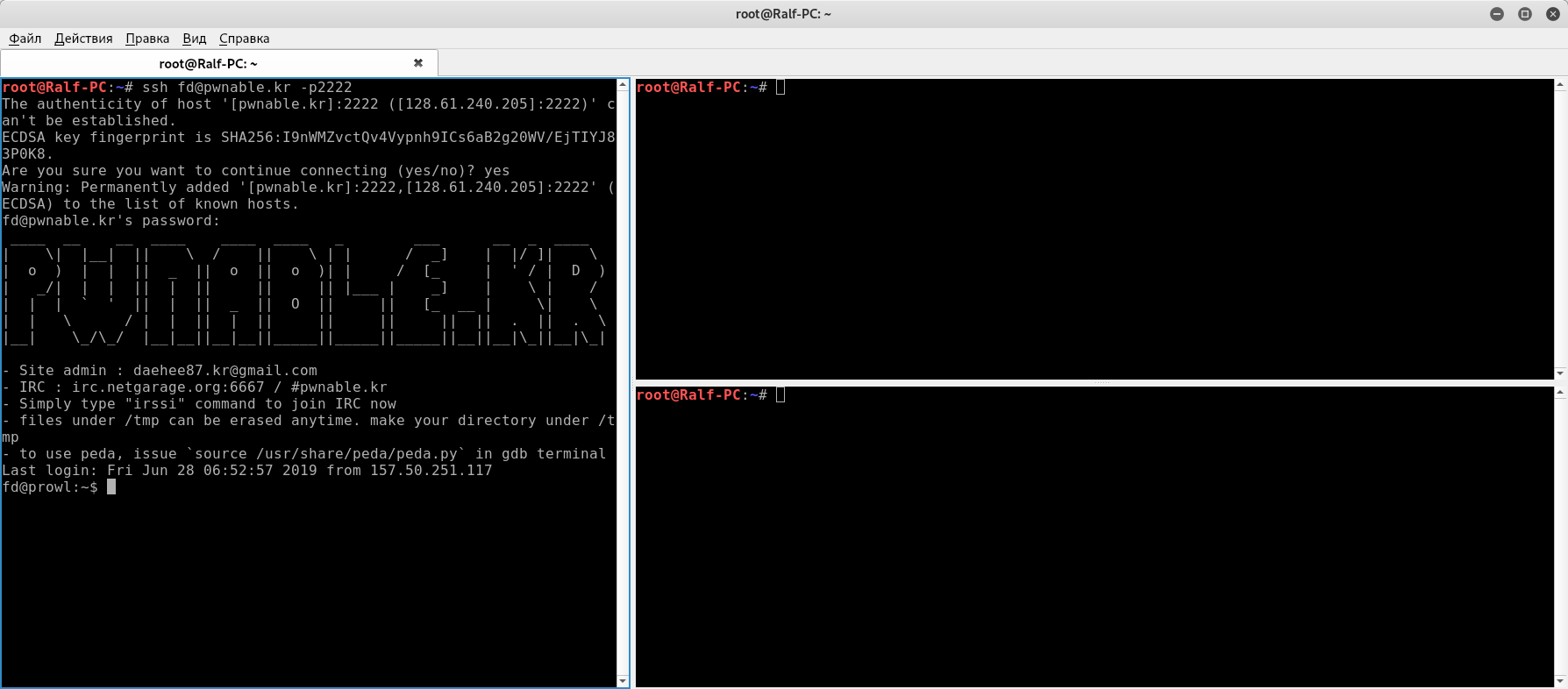
When connected, we see the appropriate banner.
Let's find out what files are on the server, as well as what rights we have.
ls -l 
Thus, we can read the source code of the program, since there is a right to read for everyone, and execute the fd program with the owner's rights (the sticky bit is set). Let's review the source code.

From the code it follows that the program takes a number as a parameter, takes 0x1234 from it and uses as a descriptor to get a string that must be equal to "LETMEWIN".
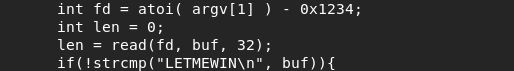
Thus, we need to send the program the string "LETMEWIN" through the standard input stream (stdin). For this, the descriptor that is passed to the read () function must be equal to 0. That is, the number 0x1234 must be used as a program parameter. Translate it to decimal.
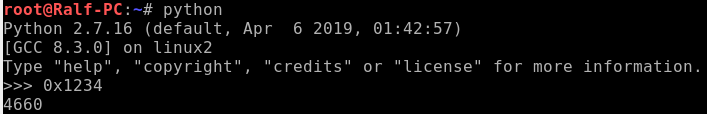
Now run the program with parameter 4660, drop the desired line and pick up the flag.
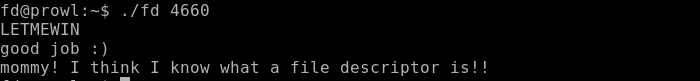
As a result, we get the first point.

Here with such an easy task, thanks to which it was necessary to deal with the descriptors, pwnable.kr begins. See you in the next articles!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/458346/
All Articles