Quantum computing can change everything, and IBM competes with Microsoft, Intel, and Google to master it.
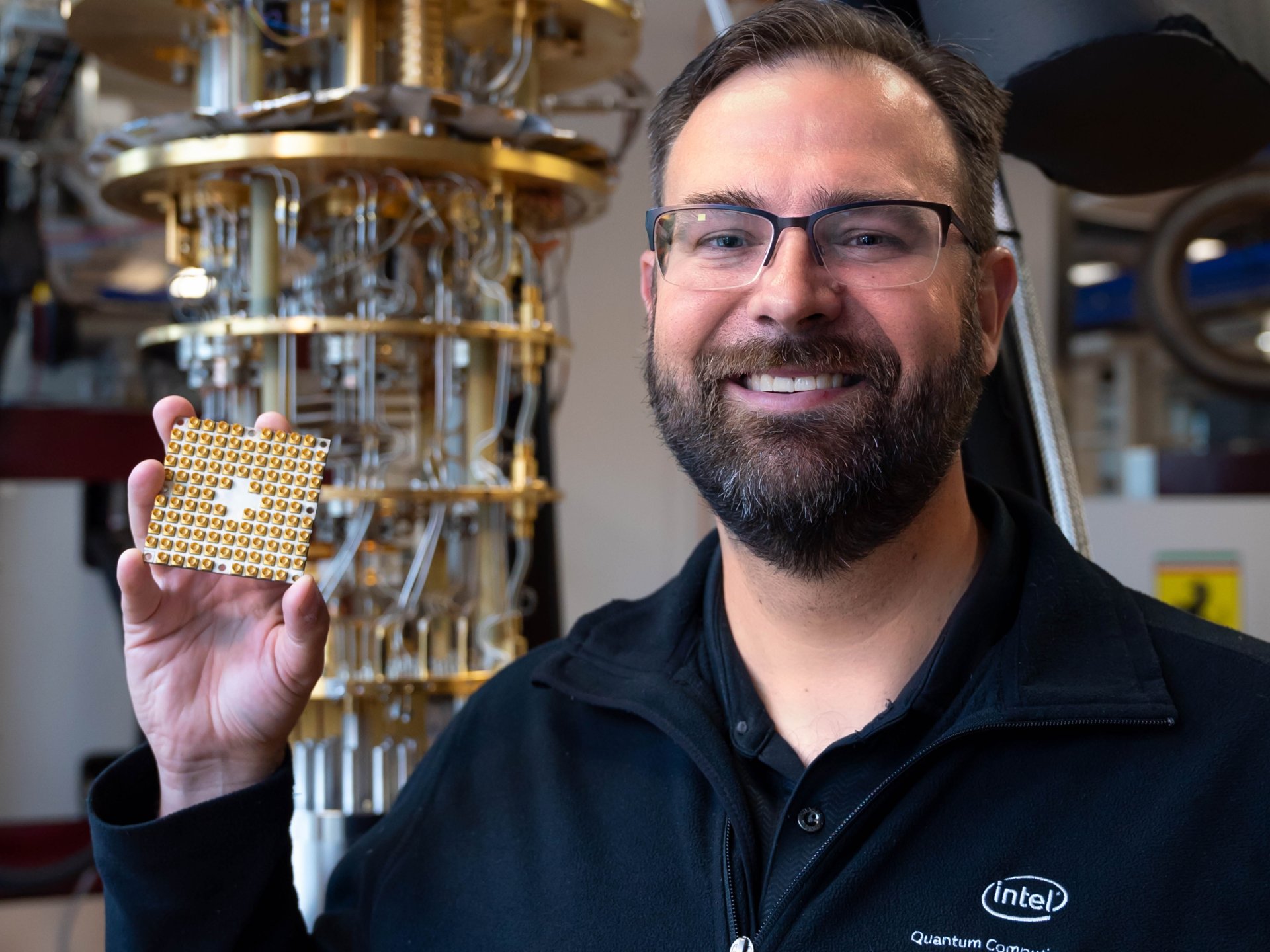
Jim Clark, director of quantum equipment for Intel, with one of the company's quantum processors. A photo; Intel
- Quantum computers are an extremely exciting technology that shows promise in creating powerful computational capabilities to solve previously unsolvable problems.
- Experts say that IBM was the leader in quantum computing, so Google, Intel, Microsoft and many startups are under its influence.
- Investors are attracted to quantum computing startups, including IonQ, ColdQuanta, D-Wave Systems and Rigetti, who can change this market.
- However, there is a catch: modern quantum computers, as a rule, are not as powerful and not as reliable as the existing supercomputers today, and they also require special conditions for launching and loading.
In January, IBM made a splash when it announced the release of the IBM Q System One, the world's first quantum computer model available for business. The device was placed in a sleek glass body with a volume of 9 cubic feet.
This is an important milestone for quantum computers, which are still located in research laboratories. According to IBM, buyers already intend to take into their hands this technology, promising in various areas: chemistry, materials science, food production, aerospace industry, drug development, stock market forecasting, and even in the fight against climate change.
')
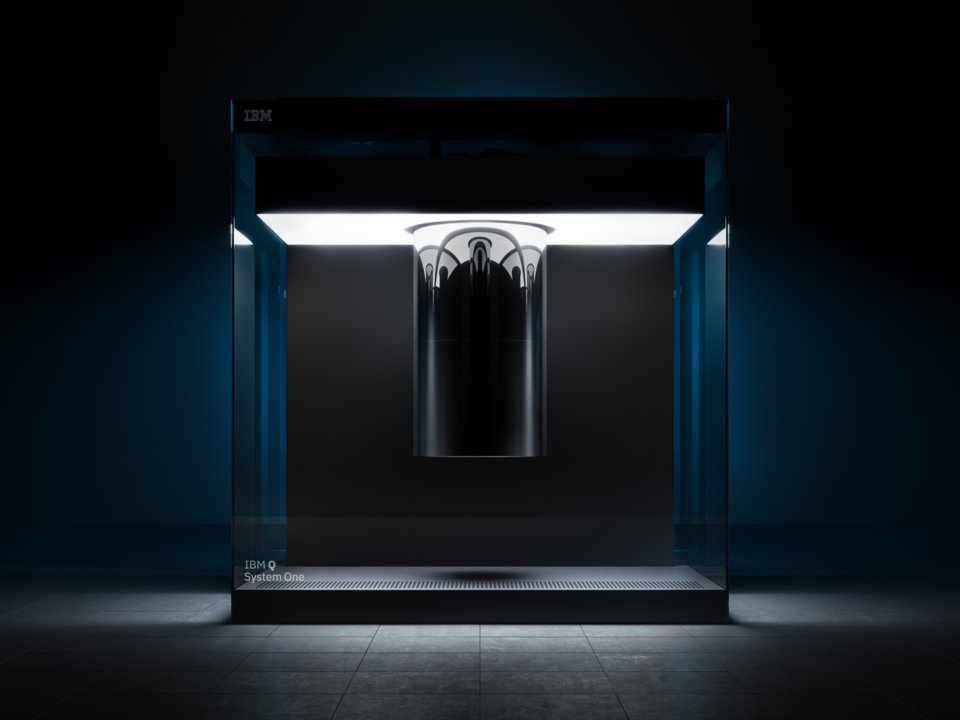

IBM Q System One. Photo: IBM
The reason for the unrest lies in the fact that a quantum computer has seemingly magical properties that allow it to process exponentially more information. A quantum computer is not just a very fast computer; rather, it is a completely different computing paradigm that requires a radical rethinking.
The winner in the technology race will be the company that takes advantage of the opportunities offered by this technology. IBM, Microsoft, Google, and other technical giants, as well as startups, rely on this technology.
Business Insider asked a couple of questions to IBM Q vice president of Strategy and Ecosystem Bob Sutor about how to make these systems accessible to people: how will people get access to them? How can a lot of people learn how to use quantum computers to perform their tasks?
Little chance of seeing quantum computers in the office anytime soon. Experts with whom we spoke, believe that, despite the fact that they are available to IBM, it will take another five to ten years before quantum computing really becomes mainstream. IBM Q System One is currently available only as a cloud computing service for select customers. It will take some time before something like that people can acquire and make work for personal purposes.
Indeed, experts assure that quantum computers offer great promise, but they are far from mass production. They are extremely fragile and require special working conditions. Moreover, quantum computers today are not as reliable and not as powerful as the computers that we already have.
"We believe that in about ten years, a quantum computer will change your life or mine," said Jim Clark, director of quantum equipment at Intel, for Business Insider. - In fact, we are now only at the first mile of the marathon. This does not mean that we are not concerned about this. ”
What is a quantum computer?
Once Bill Gates said that the mathematics underlying the quantum was beyond his comprehension, but not everyone agreed.
“It’s somewhat erroneous to believe that quantum physics is also physics and it’s too complicated,” says Business Insider Chris Monroe, CEO and co-founder of IonQ. - Incomprehensible to many people, it is done by the fact that it is incomprehensible, but it is also incomprehensible to me, as it is to you. If something can be in superposition, it means that it can be in two states at the same time. This is strange because we do not encounter the like in the real world. "
The computers that we used display the data in the form of a string 1 or 0, called binary code. However, a quantum computer can represent data in the form of 1, 0 or, most importantly, both numbers at the same time.
When a system can be in more than one state at a time, this is called a “superposition” —one of the seemingly magical properties of quantum computing. Another key principle here is “entanglement,” which is a quantum property that allows two particles to move absolutely synchronously, no matter how far they are physically separated.
As an article in Scientific American explains, these two qualities are combined into a computer that can process much more data at the same time than any system on the market today.
The power of a quantum computer is measured in qubits, the basic unit of measurement in a quantum computer. Just as modern computers have 32-bit or 64-bit processors (a measure of how much data they can process at the same time) a quantum computer with a large number of qubits has a much larger amount of computing power.
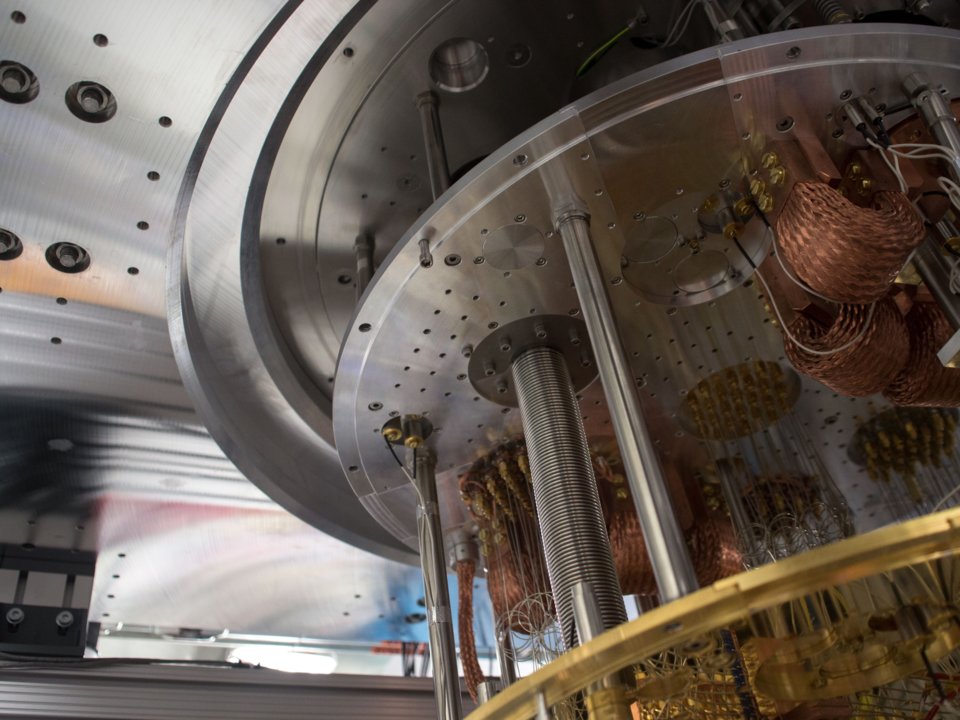

Inside a quantum computer. Photo: IBM
The sky is the limit
All this means that a quantum computer can solve problems that were previously limited by computing power.
For example, a quantum computer can coarsely solve the famous traveling salesman problem — a complex computational problem that requires finding the shortest route between several cities before returning home. It sounds simple, but if you look at it from the point of view of mathematics, finding the only optimal path becomes more difficult when you add more cities to its route.
Similarly, a quantum computer could sneak through the most cunning, most time-consuming tasks, sifting out huge amounts of financial, pharmaceutical, or climatological data to find optimal solutions. Indeed, the D-Wave quantum startup is already working with Volkswagen to analyze motion patterns and weed out a tremendous amount of interference in order to get to the point.
Discusses its usefulness in the field of cryptography. A quantum computer is able to master an encryption method that is different from the previously known cipher, which allows it to easily decipher even state secrets. There is great interest from world governments in this useful feature, while activists fear that the advent of quantum computing may destroy confidentiality.
Physical challenge
“Since quantum computing is still in the early stages of its development, there is a lot of information that still remains unproven,” said Matthew Briss, Gartner’s vice president of research and development. “But buyers are already looking for applications to determine the competitive advantage of quantum computing for their business,” he says.
Despite all the hype, experts believe that quantum computers are as far from leading positions as PCs in the 1950s. Of course, they are gaining momentum, but slowly.
"Quantum computing can be compared to a slow moving train," said Brian Hopkins, Forrester vice president and principal analyst, with Business Insider. - If it passes one inch per second, then in a month it will pass already two inches per second. Pretty soon he will start moving faster. ”
The big problem now is that a quantum computer cannot do anything that a classic computer could not do. Industry is looking forward to the moment, called quantum superiority, when quantum computers go beyond current limits.
“When customers come to us, the main thing that they tell us is that they don’t care what model they are, if only it would be useful for their business,” said analyst Briss. - There is no model that could outperform the classical algorithms. We really need to wait for the quantum computer hardware to improve. ”
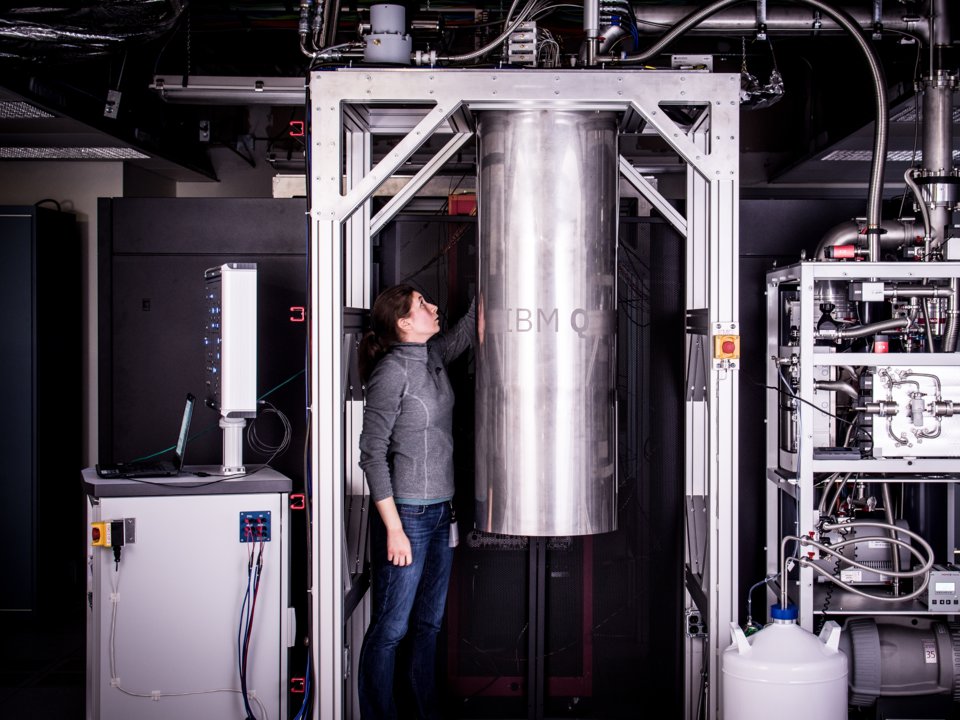

IBM Research Officer Kathy Puli examines a cryostat that helps quantum computers keep their temperatures low. Photo: Andy Aaron, IBM
A big problem is the lack of computing power. It is assumed that the quantum superiority will require a computer with a power of 50 qubit. Although this frontier was overcome in the laboratory, it is not constant and cannot be maintained. Indeed, qubits can either be subject to errors or be non-permanent, which leads to problems with their generation and lowers their potential.
Another important factor is more material. Quantum computers must be completely isolated from the environment in order to function, and they require very low temperatures. Even the weakest vibrations can lead to the destruction of qubits, removing them from superposition, just as a child, knocking on a table, causes rotating coins to fall on the table.
Previous quantum computers, such as the IBM Q System One, are so cumbersome that the necessary isolation and cooling conditions become a real problem. This problem is aggravated by the lack of necessary components: superconducting cables and low-temperature refrigerators. They are in strong deficiency.
Ultimately, this means that although knowledge is improving and technology evolves, quantum computing is still practically impracticable.
“One of the problems in my workgroup is the manipulation of materials, silicon, and metals, so that we can create a very homogeneous environment,” said Clark of Intel. - This is basically the best semiconductor technology. The technologies that we need to create quantum computing on a large scale do not yet exist. ”
Another problem is that quantum computers have undeniable potential to provide unpredictable computing power. However, in this world there are not so many people who actually have experience in programming or managing these systems, and fascinated potential buyers are trying to figure out how to actually use it.
Great quantum race
Analysts claim that IBM is currently leading the quantum computing race due to the limited commercial availability of the IBM Q System One. Because it is accessed through the cloud, IBM can support these special conditions in order for this quantum computer to function, while at the same time allowing selected customers to use it.
“I think [IBM's quantum computer] is swinging,” said analyst Briss. - I think that the quantum computing model as a service is a valid model. By placing it in a container and addressing specific tasks, they are really trying to improve its quality. ”
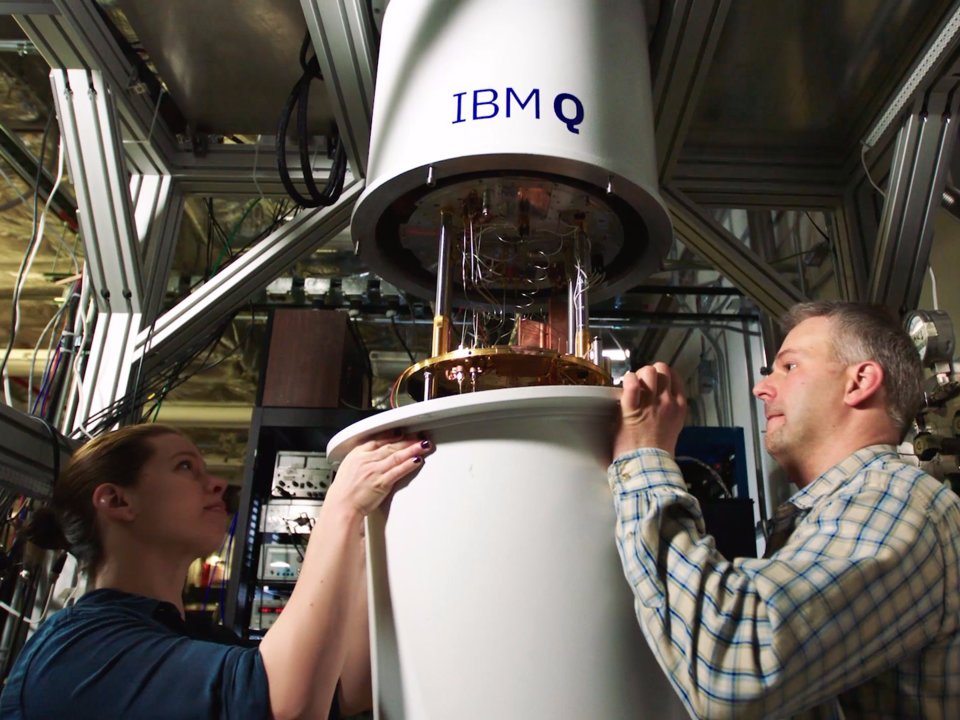

Sarah Sheldon and Pat Humane from IBM are working on a dilution refrigerator that cools quantum computers. Photo: IBM
At the same time, analysts say that any of the players in this market can have a breakthrough at any moment that will allow them to get ahead, and that this is still a necessary rivalry.
Different IT giants have a different approach to this problem. Intel, IBM, Google and Rigetti, a quantum computing startup, build systems based on superconducting circuits based on modern supercomputers.
Microsoft uses a completely different and possibly more risky approach, trying to create a better qubit. The topological qubit that Microsoft is trying to create fragments electrons to store information in several places at the same time, making it more stable and less susceptible to destruction. According to analyst Hopkins, this is less reliable than what his competitors are trying to create, but the result will be an important step forward for the entire field of quantum computing.
"They got involved in the adventure and many believe that they will never succeed," Hopkins says.
As for adventures, startups such as IonQ and D-Wave, rely on advanced technologies such as ion capture and quantum annealing. Simply put, they are trying in different ways to achieve greater performance and stability from each qubit, using completely new methods.
“This allows us to create a quantum computer that solves complex problems and continuously progresses in this,” said Business Insider Mark Johnson, vice president of design and development of processors and quantum products at D-Wave.
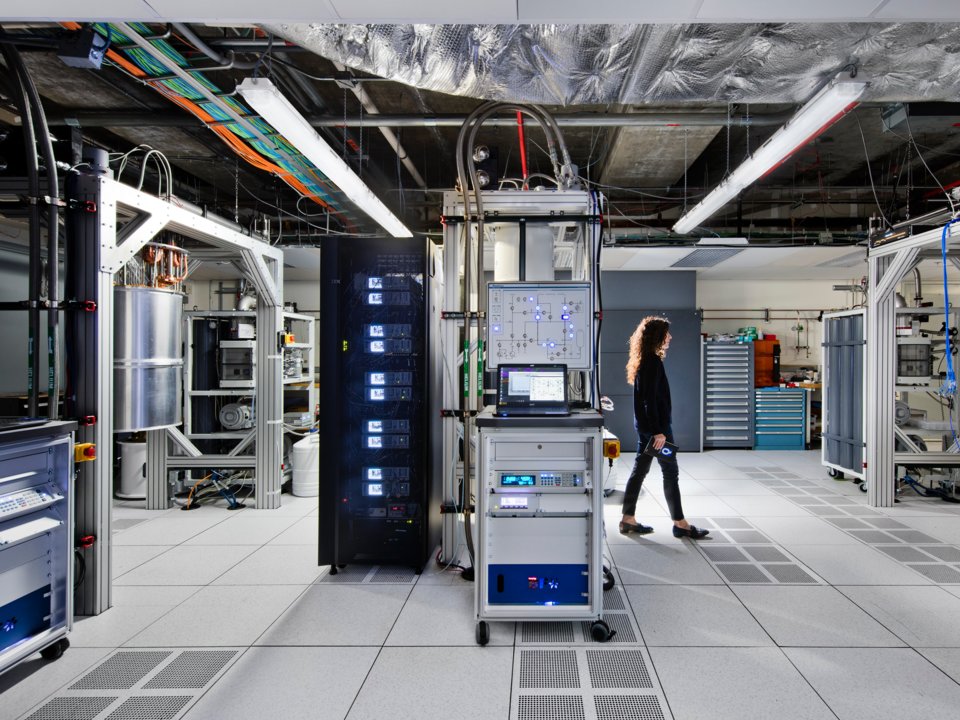

The IBM Quantum Technology Specialist is walking through the IBM Q Computing Center at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York. Photo: Connie Zhou for IBM
Quantum startups
The rise in quantum computing has sparked a wave of investor interest in related startups. According to estimates by Robert Sütor from IBM, there are about 100 startups in the field of quantum software, hardware and even consulting in the world. This is not much compared to the huge startup market, but much more than before.
“I have been in this field for a very long time, from the very beginning,” said Monroe of IonQ. - For a long time, it was in its infancy, until it drew attention to itself 5-8 years ago, and attracted huge investments. It became clear that the time had come. ”
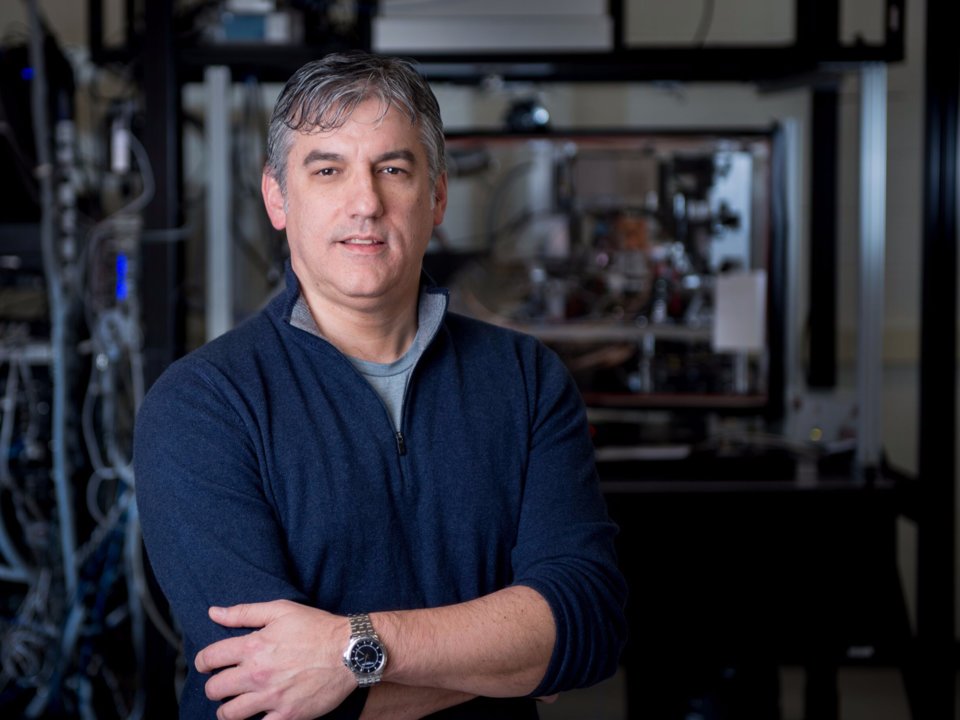

Chris Monroe, CEO and Co-Founder of IonQ Quantum Computing. Photo: IonQ
Some, like Rigetti, are ready to fight on equal terms with technical titans, sharing their own quantum chips and skilful quantum computing systems.
“This is the foundation of our business,” said Betsy Maciello, Business Insider, vice president of products at Rigetti. - In the quantum space, there are many companies that are working on software applications in the field of quantum computing. We manufacture microchips and build computing systems. ”
Matthew Kinsella, managing director of Maverick Ventures, says he is optimistic about the area of quantum computing. His company went so far as to invest in ColdQuanta, a company that manufactures equipment used in quantum systems. He expects quantum computers to outperform today's systems in five to ten years. Maverick Ventures has made a long-term view.
“I really believe in quantum computing, although it may take longer than expected before a quantum computer becomes better than a traditional computer for everyday tasks. Most likely in the next few years we will receive the advantages of quantum computers in solving small-scale problems, ”said Kinsella.
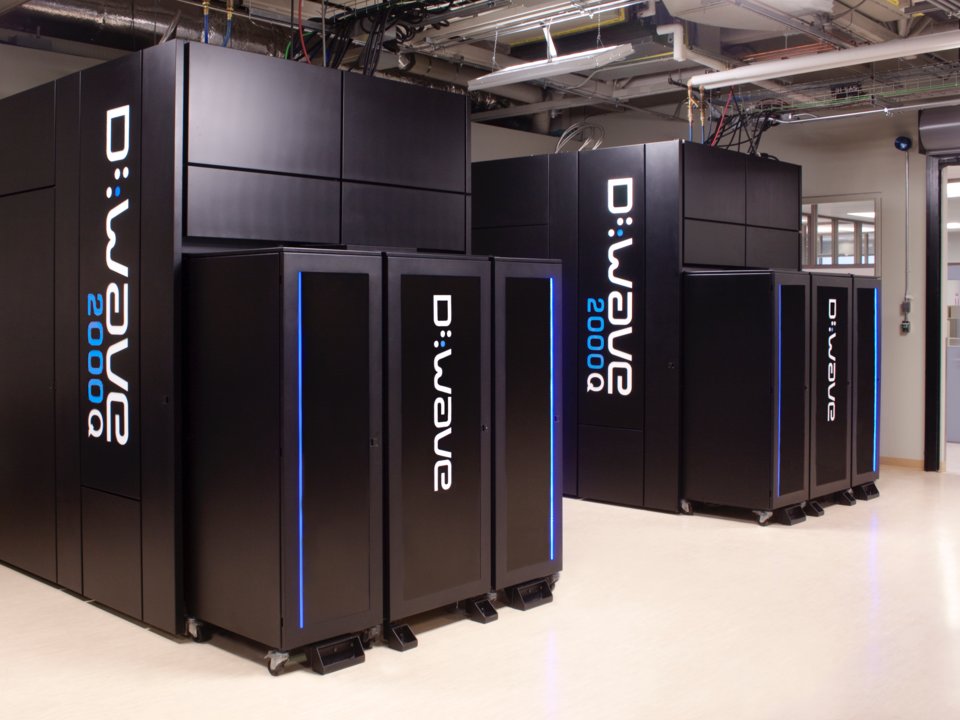

D-Wave's 2000Q Systems Lab. Photo: D-Wave
Kinsella, like the analysts with whom we spoke, awaiting the so-called "quantum winter." Around the quantum computers can be a stir, but people are encouraging themselves, experts warn. Machines are not yet perfect, and it will be years before investors see results.
In perspective
Even outside of quantum supremacy, experts assure us that there is still room for traditional computers and supercomputers. Until then, there are still worth solving problems with cost, size, reliability and computing power before we can discuss it.
“Breathe in,” said analyst Briss. - In this area, there are many exciting things that take time. This is a conglomerate of physics, computer science and, frankly, scientific analysis. We would not have to study this if we knew all the answers, but in the future we will have a large amount of research work. "
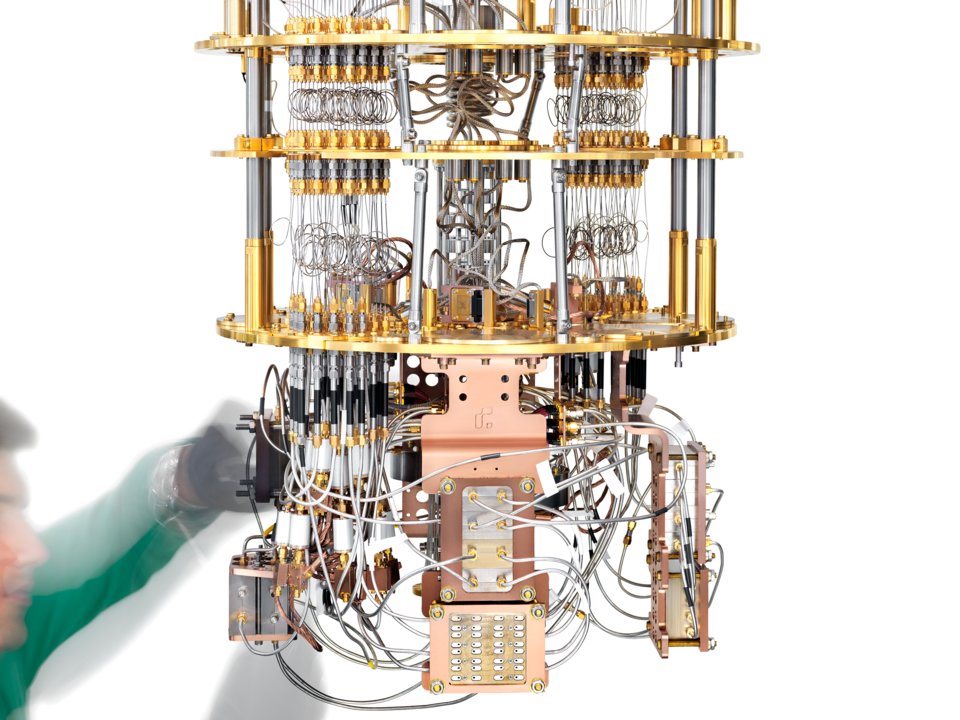
Quantum computer Rigetti. Photo: Rigetti
However, for many it is clear that this is the future. Just like the manufacturers of the first mainframe computer, they did not realize that this would ultimately lead to an increase in the number of palm-sized handheld smartphones. A quantum computer can be the first step on a completely new path.
Few, like Microsoft’s vice president of corporate governance Todd Holmdalu, are optimistic enough to say that this may be more significant than artificial intelligence and machine learning today. He used to say to his children that they should do what they are passionate about and that they can always get work in the field of artificial intelligence. Now he will say the same thing about quantum computing.
“This is an area that will develop. “We need people to fill it up and not let it go,” said Holmdal. “It plays an important role for our generation, making it possible to create amazing things in the future.”
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/458134/
All Articles