RDMA inside the data center in the implementation of Huawei
Under the cut, what approach does Huawei offer when organizing remote direct memory access using AI Fabric technology and how does it differ from InfiniBand and “pure” Ethernet-based RDMA.
Distributed computing is used in a wide variety of industries. This research and technical development like facial recognition or autopilot, and industry. In general, data analysis is finding more and more applications, and one can say with confidence that it will not lose popularity in the near future. In fact, we are now experiencing a transition from the era of cloud computing, where the most important factors were application and speed of service deployment, to the era of data monetization, including through the use of artificial intelligence algorithms. According to our internal data (report GIV 2025: Unfolding the Industry Blueprint of an Intelligent World ) by 2025, 86% of companies will use AI in their work. Many of them view this direction as a key to modernizing activities and, possibly, a basic tool for making business decisions in the future. And this means that each of these companies will need some kind of raw data processing - most likely through distributed clusters.
With the growing popularity of distributed calculations, the amount of traffic exchanged between individual data center machines increases. Traditionally, when discussing networks, attention is focused on the growth of traffic between the data center and end users on the Internet, and it is really growing. But the growth of horizontal traffic within distributed systems far exceeds that generated by users. According to Facebook, the traffic between their internal systems doubles in less than a year.
')

In attempts to cope with this traffic, you can increase the clusters, but you can not do this indefinitely. Therefore, predicting the growth of computational load on clusters, it is necessary to increase processing efficiency — first of all, find and eliminate bottlenecks within these distributed networks.
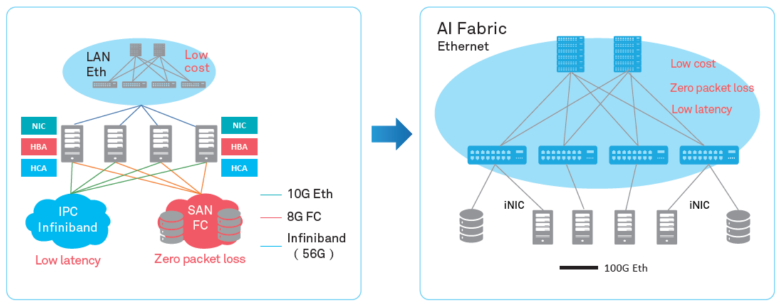
If earlier the “weak link” of distributed systems was the resources of each of these systems separately, while the constantly developing data transmission networks even overtook the needs, today network communications are the main source of the problem. The usual TCP / IP protocol stack and tree topology no longer correspond to the tasks. Therefore, more and more data centers are abandoning the centralized and moving to a new CLOS-architecture that provides greater bandwidth and better cluster scalability, as, for example, Facebook did a few years ago.

At the same time, it is necessary to optimize the process at another level - at the level of interaction of two separate systems. In this article we want to talk about what optimization tools provides data center Huawei Ai Fabric. This is our proprietary technology that accelerates data exchange between nodes.
The main “trick” of Huawei Ai Fabric is the reduction of overhead costs for transferring data packets between systems within the cluster through the implementation of RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) - direct memory access by the systems included in the cluster.
RDMA is not a new idea. The technology provides direct data exchange between the memory and the network interface, reducing waiting time and eliminating unnecessary copying of data to the buffers. Its roots go back to the 1990s of Compaq, Intel, and Microsoft.
There are three types of delays in transmitting a packet from one system to another:

To reduce losses throughout this chain, back in the 1990s, it was proposed to use direct memory access for interacting systems — the abstract Virtual Interface Architecture model. Its main idea is that applications running on two interacting systems completely fill their local memory and establish a P2P data connection without affecting the OS. Thus it is possible to significantly reduce delays in the transmission of packets. In addition, since the VIA model did not imply the placement of transmitted data into intermediate buffers, it saved the resources needed for the copy operation.

With respect to the abstract model, VIA RDMA, as a technology, has gone a step further towards the optimal utilization of resources. In particular, it does not wait for the buffer to complete the connection and allows connections with several computers simultaneously. Due to this, the technology allows reducing transmission delays to 1 ms, reducing the load on the processor.
The two main implementations of RDMA on the market, the proprietary transport protocol InfiniBand and the “pure” Ethernet-based RDMA, unfortunately, are not without flaws.
The InfiniBand transport protocol has a built-in packet delivery control mechanism (protection against data loss), but is supported by specific equipment and is not compatible with Ethernet. In fact, using this protocol closes the data center at one hardware vendor, which carries certain risks and promises complexity from the point of view of service (since InfiniBand has a small market share, finding specialists will not be so easy). And, of course, when implementing a protocol, it is impossible to use already existing equipment of IP networks.
RDMA over Ethernet allows you to use existing equipment on the network, supports Ethernet networks, and thus it will be easier to find service technicians. Against the background of Infiniband it significantly reduces the cost of ownership of the infrastructure, simplifies its deployment.
The only serious flaw that impeded the widespread use of RDMA over Ethernet is the lack of mechanisms to protect against packet loss, which limits the bandwidth of the entire network. To reduce packet loss or prevent network congestion, third-party mechanisms should be used. We went just this way by offering our own intelligent algorithms for compensating for the disadvantages of RDMA over Ethernet while maintaining its advantages in the new tool - Huawei Ai Fabric.
AI Fabric implements RDMA over Ethernet, complemented by its own intelligent network congestion control algorithm, which ensures zero packet loss, high network bandwidth and low transmission delay for RDMA streams.
Huawei Ai Fabric is built on open standards and supports a range of different equipment that optimizes the implementation process. However, some additional tools - add-ons over open standards that allow for more efficient data exchange, which we will discuss in subsequent publications - are available only for Huawei devices. The CloudEngine series of switches supports the solution, integrates a chip that analyzes traffic characteristics and dynamically adjusts network parameters, which makes it possible to use the switch buffer more efficiently. The collected characteristics are also used to predict traffic patterns in the future.
Huawei Ai Fabric allows you to get a profit on two levels.
On the one hand, the solution allows optimizing the data center architecture - reducing the number of nodes (due to more optimal utilization of resources), creating a converged environment without the traditional division into separate subnets that are difficult and expensive to service in parts. Using the tool, you do not have to allocate separate subnets for each type of service in the domain controller (with its own network requirements). You can create a unified environment that ensures the provision of all services.

On the other hand, AI Fabric allows you to increase the speed of distributed computing, especially where you often need to access the memory of remote systems. For example, the introduction of AI in any field implies a period of learning of the algorithm, which can include millions of operations, so a gain in delay for each such operation will result in a serious acceleration of the process.
The effect of the introduction of a specialized tool, such as Huawei Ai Fabric, will be noticeable in the data center with six or more switches. But the greater the volume of the data center, the higher the profit - due to the optimal utilization of resources, a cluster of the same scale with Ai Fabric will provide higher performance. For example, a cluster of 384 nodes can achieve the performance of a “normal” cluster of 512 nodes. At the same time, the solution has no restrictions on the number of physical switches within the infrastructure. There may be tens of thousands of them (if you forget that projects are usually limited to the scope of the administrative domain).

Distributed computing is used in a wide variety of industries. This research and technical development like facial recognition or autopilot, and industry. In general, data analysis is finding more and more applications, and one can say with confidence that it will not lose popularity in the near future. In fact, we are now experiencing a transition from the era of cloud computing, where the most important factors were application and speed of service deployment, to the era of data monetization, including through the use of artificial intelligence algorithms. According to our internal data (report GIV 2025: Unfolding the Industry Blueprint of an Intelligent World ) by 2025, 86% of companies will use AI in their work. Many of them view this direction as a key to modernizing activities and, possibly, a basic tool for making business decisions in the future. And this means that each of these companies will need some kind of raw data processing - most likely through distributed clusters.
The evolution of architecture
With the growing popularity of distributed calculations, the amount of traffic exchanged between individual data center machines increases. Traditionally, when discussing networks, attention is focused on the growth of traffic between the data center and end users on the Internet, and it is really growing. But the growth of horizontal traffic within distributed systems far exceeds that generated by users. According to Facebook, the traffic between their internal systems doubles in less than a year.
')

In attempts to cope with this traffic, you can increase the clusters, but you can not do this indefinitely. Therefore, predicting the growth of computational load on clusters, it is necessary to increase processing efficiency — first of all, find and eliminate bottlenecks within these distributed networks.
If earlier the “weak link” of distributed systems was the resources of each of these systems separately, while the constantly developing data transmission networks even overtook the needs, today network communications are the main source of the problem. The usual TCP / IP protocol stack and tree topology no longer correspond to the tasks. Therefore, more and more data centers are abandoning the centralized and moving to a new CLOS-architecture that provides greater bandwidth and better cluster scalability, as, for example, Facebook did a few years ago.

At the same time, it is necessary to optimize the process at another level - at the level of interaction of two separate systems. In this article we want to talk about what optimization tools provides data center Huawei Ai Fabric. This is our proprietary technology that accelerates data exchange between nodes.
Networking Changes
The main “trick” of Huawei Ai Fabric is the reduction of overhead costs for transferring data packets between systems within the cluster through the implementation of RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) - direct memory access by the systems included in the cluster.
RDMA - a way to reduce transmission delays
RDMA is not a new idea. The technology provides direct data exchange between the memory and the network interface, reducing waiting time and eliminating unnecessary copying of data to the buffers. Its roots go back to the 1990s of Compaq, Intel, and Microsoft.
There are three types of delays in transmitting a packet from one system to another:
- due to the processor processing required, for example, for buffering data in the OS and calculating the check sums;
- due to busses and data transmission channels (it is technically impossible to significantly increase the bandwidth);
- because of network equipment.

To reduce losses throughout this chain, back in the 1990s, it was proposed to use direct memory access for interacting systems — the abstract Virtual Interface Architecture model. Its main idea is that applications running on two interacting systems completely fill their local memory and establish a P2P data connection without affecting the OS. Thus it is possible to significantly reduce delays in the transmission of packets. In addition, since the VIA model did not imply the placement of transmitted data into intermediate buffers, it saved the resources needed for the copy operation.

With respect to the abstract model, VIA RDMA, as a technology, has gone a step further towards the optimal utilization of resources. In particular, it does not wait for the buffer to complete the connection and allows connections with several computers simultaneously. Due to this, the technology allows reducing transmission delays to 1 ms, reducing the load on the processor.
InfiniBand vs Ethernet
The two main implementations of RDMA on the market, the proprietary transport protocol InfiniBand and the “pure” Ethernet-based RDMA, unfortunately, are not without flaws.
The InfiniBand transport protocol has a built-in packet delivery control mechanism (protection against data loss), but is supported by specific equipment and is not compatible with Ethernet. In fact, using this protocol closes the data center at one hardware vendor, which carries certain risks and promises complexity from the point of view of service (since InfiniBand has a small market share, finding specialists will not be so easy). And, of course, when implementing a protocol, it is impossible to use already existing equipment of IP networks.
RDMA over Ethernet allows you to use existing equipment on the network, supports Ethernet networks, and thus it will be easier to find service technicians. Against the background of Infiniband it significantly reduces the cost of ownership of the infrastructure, simplifies its deployment.
The only serious flaw that impeded the widespread use of RDMA over Ethernet is the lack of mechanisms to protect against packet loss, which limits the bandwidth of the entire network. To reduce packet loss or prevent network congestion, third-party mechanisms should be used. We went just this way by offering our own intelligent algorithms for compensating for the disadvantages of RDMA over Ethernet while maintaining its advantages in the new tool - Huawei Ai Fabric.
Huawei AI Fabric - your way
AI Fabric implements RDMA over Ethernet, complemented by its own intelligent network congestion control algorithm, which ensures zero packet loss, high network bandwidth and low transmission delay for RDMA streams.
Huawei Ai Fabric is built on open standards and supports a range of different equipment that optimizes the implementation process. However, some additional tools - add-ons over open standards that allow for more efficient data exchange, which we will discuss in subsequent publications - are available only for Huawei devices. The CloudEngine series of switches supports the solution, integrates a chip that analyzes traffic characteristics and dynamically adjusts network parameters, which makes it possible to use the switch buffer more efficiently. The collected characteristics are also used to predict traffic patterns in the future.
Who is it useful?
Huawei Ai Fabric allows you to get a profit on two levels.
On the one hand, the solution allows optimizing the data center architecture - reducing the number of nodes (due to more optimal utilization of resources), creating a converged environment without the traditional division into separate subnets that are difficult and expensive to service in parts. Using the tool, you do not have to allocate separate subnets for each type of service in the domain controller (with its own network requirements). You can create a unified environment that ensures the provision of all services.

On the other hand, AI Fabric allows you to increase the speed of distributed computing, especially where you often need to access the memory of remote systems. For example, the introduction of AI in any field implies a period of learning of the algorithm, which can include millions of operations, so a gain in delay for each such operation will result in a serious acceleration of the process.
The effect of the introduction of a specialized tool, such as Huawei Ai Fabric, will be noticeable in the data center with six or more switches. But the greater the volume of the data center, the higher the profit - due to the optimal utilization of resources, a cluster of the same scale with Ai Fabric will provide higher performance. For example, a cluster of 384 nodes can achieve the performance of a “normal” cluster of 512 nodes. At the same time, the solution has no restrictions on the number of physical switches within the infrastructure. There may be tens of thousands of them (if you forget that projects are usually limited to the scope of the administrative domain).
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/458104/
All Articles