Real virtuality: workstations ++
If 3-4 years ago I was solving automation, then today it’s a turn for virtualization: the available powerful workstations equalize the potential of transnational giants and small business. Workstations are professional computers with a set of hardware and software designed to solve a specific range of tasks: multimedia (image processing, video, sound), CAD, GIS, scientific and technical calculations, industrial applications, etc. At present, the resources of a workstation can be receive as a cloud service. It is gaining popularity with an increasing number of companies due to the ease of integration into the IT infrastructure and economic advantages. So, there is no turning back, there is only virtuality ahead? Let's figure it out.

The first workstations appeared in the late 60s and today they are widely used to work with computer-aided design and engineering systems, 2D and 3D graphics, video editing and demanding computing. With the advent of 64-bit versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems, high-performance UNIX workstations with proprietary software environments have given way to systems with MS Windows. Many vendors also offer Linux from Red Hat or SuSE as an alternative.
Workstations are a useful tool for designers and designers, financial analysts and researchers, content creators and creators. They support the most resource-demanding tasks and applications, such as rendering complex graphics, financial analysis, computational tasks and video editing, and creating other complex digital content.
')
When processing geospatial data, building three-dimensional terrain models, etc. on standard PCs, one often encounters memory shortages, delays and “hang-ups”, while workstations demonstrate high performance and do a good job of displaying data.
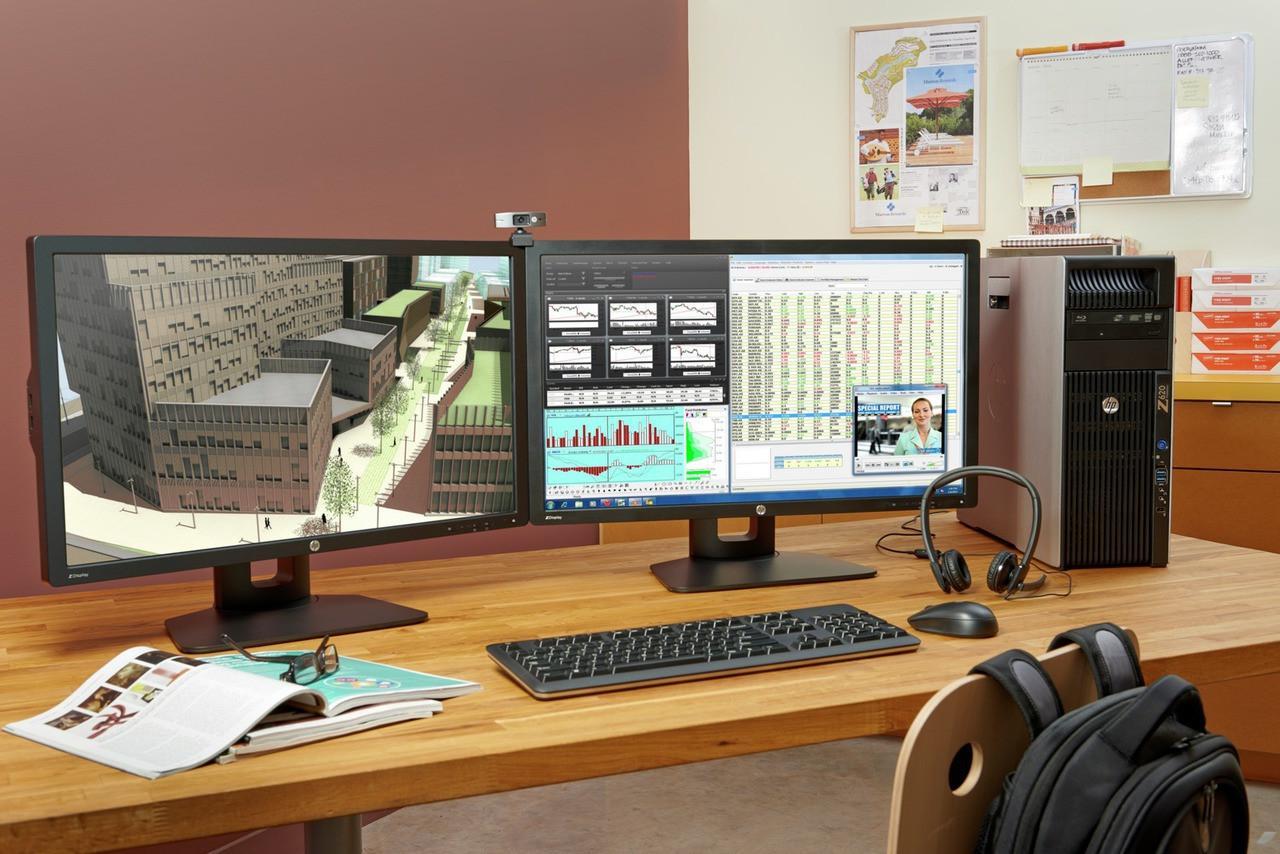

A workstation is not just a computer, it is a whole range of mechanisms designed to perform the most demanding tasks, ensure uninterrupted operation and advanced functionality.
Distinctive features of modern workstations are high speed of work with data, powerful processor, large capacity of fast RAM, integrated high-performance network controller, professional graphics subsystem.
The equipment of the workstations provides high performance in design, realistic visualization of frame and textured three-dimensional models, fast receipt of the results of scientific calculations, high-resolution video processing and the creation of various video effects.
By classes of tasks, workstations can be divided into several types:
Each subclass of professional workstations can have its inherent features and unique components that are significantly different from mass PC models: large display size / resolution and / or several displays (CAD, GIS, stock trading, Internet trading), powerful video card (film and video , animation, computer games), large capacity / performance of the storage subsystem (scientific tasks, animation), mobile or secure execution (operation in the field or in the shops of industrial enterprises), etc.
So, models equipped with NVIDIA graphics accelerators are suitable for professionals involved in 3D modeling, engineering analysis, non-linear video editing (NLE), design, as well as for finance workers.
Professional graphics cards Quadro RTX 6000 and Quadro RTX 5000, which are built on the basis of selection graphics processors on the Turing architecture, are distinguished by the support of hardware accelerated ray tracing, which is provided by specialized RT cores.
Graphic workstations (the most extensive category) are suitable for designers, artists, photographers, animators, video editors, designers, engineers, and all those who use specialized graphics packages. They have high performance when working with graphics, video and animation. Graphic stations, as a rule, use the latest NVIDIA or AMD graphic processors.
They are often equipped with multiple monitors, used for working with 2D and 3D graphics (design, engineering, etc.), data visualization (medicine, big data analytics), rendering, modeling (CAD / CAM), creating video walls, gesture recognition, GIS and others
Graphic workstations are widely used in modeling for the automotive industry, aircraft manufacturing, the oil and gas industry, the production of media content, the processing of medical data and the visualization of research results.
Workstations CAD - a subclass of graphic workstations - allow you to create design and / or technological documentation, geometric models (solid-state, three-dimensional, composite), as well as product drawings. The hardware resources of such a workstation use all the functionality of professional CAD systems: CATIA, CREO, NX, Inventor, Compass, AutoCAD, Solid Works, SolidEdge, T-Flex CAD and others.
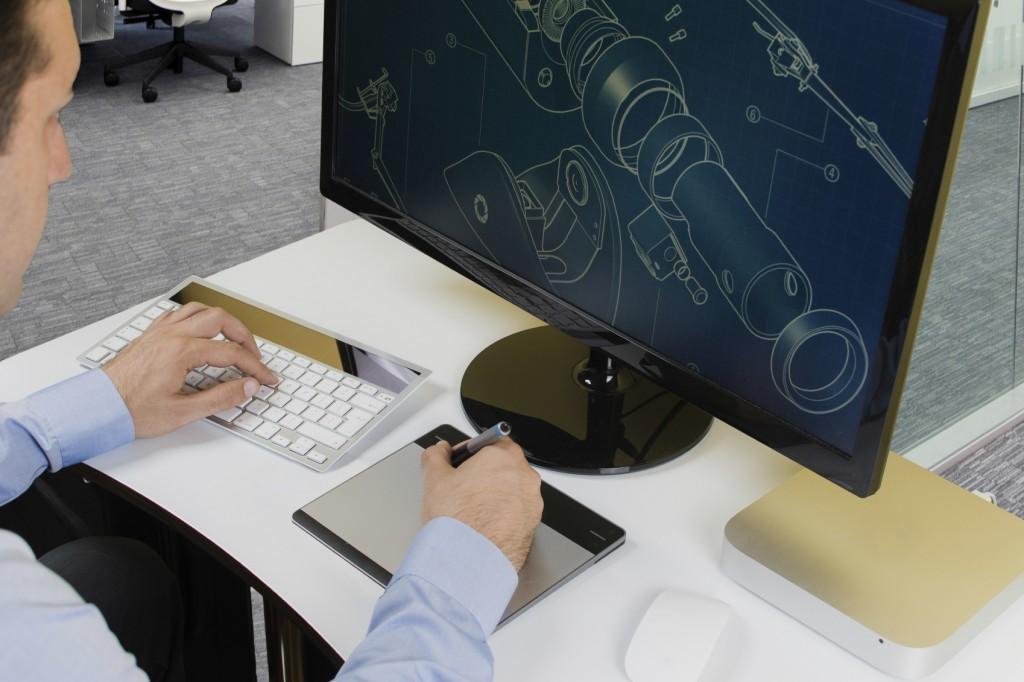

Graphic workstations for design automation systems (CAD) represent a wide class of systems for CAD (Computer Aided Design), CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) and CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) tasks.
Modern CAD workstations are conventionally divided into the following groups:
Today, when the cloud becomes the same usual element of IT infrastructure, like a server or a workstation, virtual virtual station services are gaining popularity, which solve the important problem of using graphic power from the cloud, which seemed impossible only a few years ago.
Previously, work with resource-intensive applications was assigned to powerful computers and workstations with a large set of application programs. The disadvantages of the above solutions are the high cost of ownership, the need for regular investments in upgrading and restricting user mobility.
Exit - virtual graphic stations located in a high-performance cloud environment. This technology not only provides access to virtually unlimited computing resources in the cloud, but also allows you to work simultaneously with several demanding applications online. And all this - without reference to a stationary workplace.
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) technology allows you to create a virtual IT infrastructure and deploy workstations based on server systems where many virtual machines are running. In fact, for users it looks like a familiar workplace on a PC with the necessary applications.
VDI makes it possible to create full-fledged workstations for users, functionally identical to workstations of classical architecture. VDI infrastructure involves placing virtual desktops and other user resources in the server infrastructure (in the corporate data center or in the provider cloud) and providing access to them from the company's internal network and / or via the Internet.
As a result, instead of providing users with “heavy” graphics applications with powerful workstations, you can take advantage of a more modern solution and deploy the VDI infrastructure. They will have at their disposal a virtual graphic workstation - an access service to a virtual machine with a graphics accelerator.
In fact, this is a remote terminal access to a virtual machine with a powerful graphics subsystem. The company can save, working with remote employees from regions or other countries, to collect virtual teams.
Providing a full computing core of a video card to a virtual machine allows using high-loaded applications such as AVEVA, SolidWorks, AutoCAD, SketchUP, 3DS Max, Revit, ArhiCAD, etc. on a virtual workstation. Moreover, this configuration replaces several powerful workstations.

The task of the AMD Radeon Pro V340 card is reliable graphics performance in all systems, from cloud solutions to virtually any device. The hardware solution for virtualization of graphics processors (AMD MxGPU) is based on the standard virtualization technology of SR-IOV (Single-Root I / O Virtualization) devices, which allows remotely working virtualized users (their number can reach 16 on each physical graphics processor).
Such a platform is often built on the basis of high-performance NVIDIA graphics cards or GPUs from AMD with fast storage. Windows Server is often used as a virtualization platform. To improve the performance of the disk system are usually used flash drives (SSD).
A virtual graphic station can be included in the company's existing IT infrastructure. All projects can be saved in the corporate network or in cloud storages, which can be accessed from anywhere in the Internet.
The VDI infrastructure provides a higher level of protection for the transfer and storage of important information, centralized management of the IT infrastructure of workplaces and the provision of IT services to employees. At the same time, the cost of implementing VDI is comparable to the replacement of the PC fleet.
In the VDI architecture, all data is stored on a server in the data center. This solution significantly increases the level of information security, provides much more efficient use of computational resources compared to full-featured physical workstations, and provides convenient tools for centralized administration of workstations.
One of the advantages of VDI is that, if necessary, a user workstation of any available performance is created, and when it is no longer necessary, it is deleted. Thus, in the presence of modern Internet channels, it is possible to allocate significant computing power to remote users.
By the way, as the testing shows, the speed of the 3G mobile network 17 Mbit / s (2.12 MBytes / s) is clearly not enough - it’s uncomfortable to work, not to mention HD video, which VMware Verizon simply doesn’t pull on such a channel.
In general, VDI provides the following key benefits:
The main driver for implementing VDI is data security and integrity, centralization of management and administration. A VDI system is usually deployed by fairly large companies.
You can use virtual graphic stations when you need to:
They are also convenient to use for training, testing, organization of temporary work.
VDI technology originated at the junction of three areas: terminal access, remote work with graphic stations and server virtualization.
Standard VDI infrastructure can be of three types:
Unlike terminal farms, in the latter case, VDI users have at their disposal a personal virtual machine with an installed OS and applications, and virtualization provides users with isolation and resource sharing: only those computing resources that are allocated to their virtual machine are available to the user.
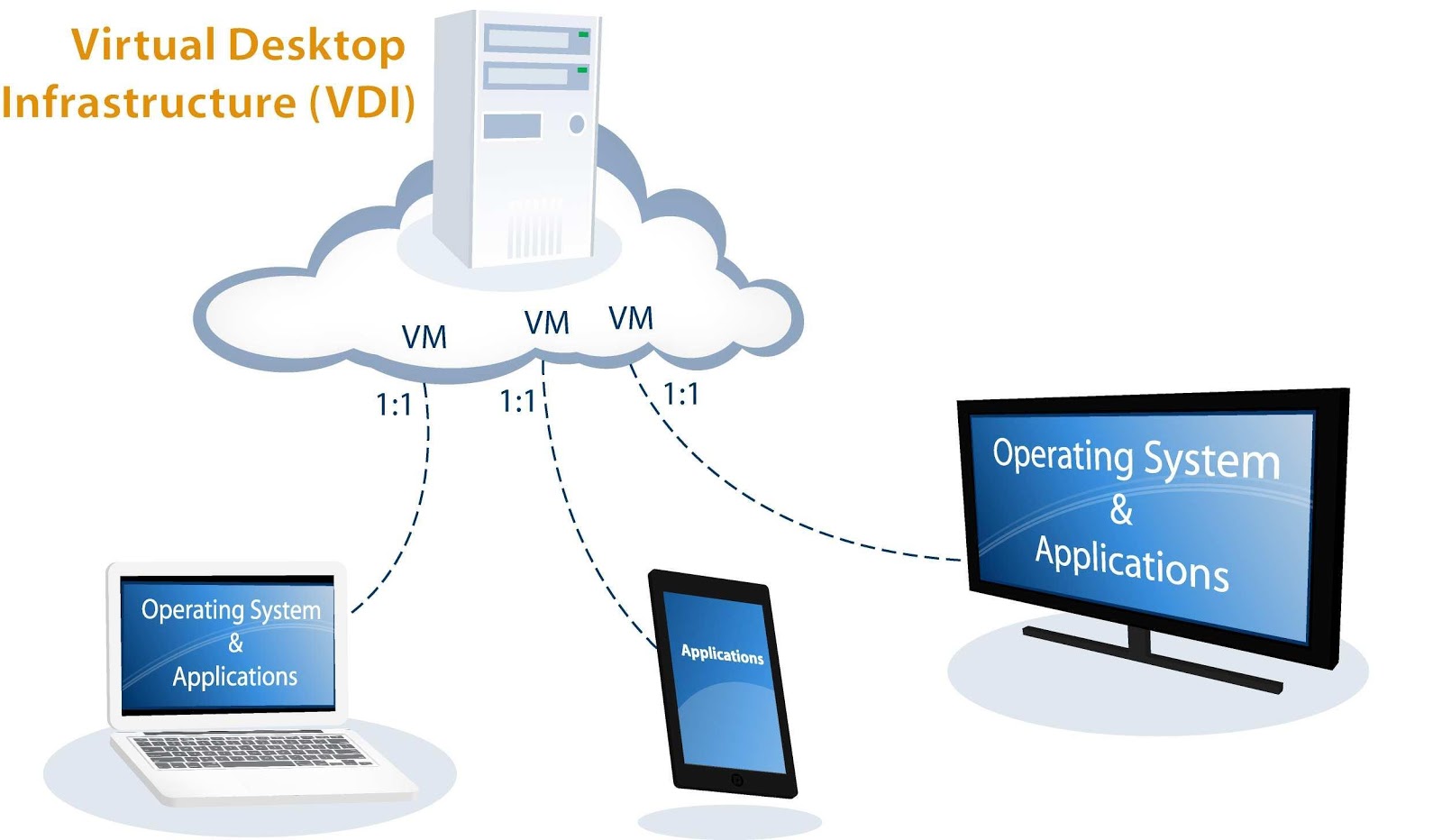
Virtual Workstation Infrastructure (VDI) is a way to access workstations working remotely in the data center.
The main consumers of VDI solutions today are the financial and banking sector, retail, healthcare and insurance, but due to the development of technology to accelerate image processing and transmission, companies from the engineering industry have become interested in VDI solutions.
The evolution of VDI can be broken down into several key stages:
This early stage is a basic approach to VDI, which has not yet become widespread in enterprises that have just begun to get acquainted with the solution and mainly used VDI for non-business-critical applications. This technology has been used primarily for call center applications. VDI configurations were fairly limited, and when running virtual machines in the data center, a lot of resources were not consumed (computing, storage, and network).
With this deployment, there were no high demands on storage I / O performance, bandwidth, or network latency. Traditional disks (HDD) quite satisfied the needs of the user.
VDI 1.0 is the first attempt to apply breakthrough virtualization technology to PCs, but it didn’t give much in terms of cost.
This is the current generation of VDI, which appeared about 2-3 years ago. This stage is likely to last several more years. VDI 2.0 is also a basic version of VDI, but of the next generation.
As enterprises managed to evaluate the benefits of VDI 1.0 in terms of security, availability, flexibility and manageability compared to physical workstations, the introduction of VDI has become more widespread, and there is every reason to believe that this trend will continue.
With the growing popularity of VDI, new scenarios for the use of this technology have appeared, it has been used in many applications. However, this has created problems at the infrastructure level, such as “boot storm” (boot storm), application of patches, rapid deployment. "Heavyweight" configuration of virtual workstations.
The I / O performance requirements of the storage subsystem were thousands of IOPS, and the HDD could no longer handle them. There have been attempts to optimize the performance of the storage environment using SAN from hundreds of magnetic media, but such solutions have proved to be not efficient either technically or economically, and the VDI tasks required different types of I / O. Flash arrays are used to eliminate these problems, but this increases the cost of the solution.
The new architectures use hyperconvergence systems (combining storage, network components and calculations) based on flash memory to meet the performance needs of the storage system. Some solutions use SSD to cache data, while other solutions, such as VMware All Flash Virtual SAN, use the entire data storage stack using various types of flash memory.
Currently, enterprises are using fully or partially flash-based solutions using the hyper-convergent approach. This trend continues in VDI 3.0.
In VDI 2.0, the scope of this infrastructure has expanded, the average cost of a virtual workstation has decreased. Began a new stage. With the spread of VDI, this approach began to be tested in the field of virtualization of high-performance workstations.
VDI 2.0 and VDI 3.0 have a lot in common. Flash memory plays a key role in technology development. With the increased use of demanding graphics applications in VDI 3.0, the storage subsystem has become even more important.
The possibilities of using high-performance workstations, such as workstations for engineering calculations or design systems (CAD), have expanded. A few years ago, it was simply unthinkable to virtualize workstations with similar requirements. However, today it is becoming a reality thanks to flash memory and graphics accelerators.
At the same time, VDI 3.0 promises acceptable performance and competitive costs even for the most complex use cases of virtual workstations.
The VDI market is a little over 10 years old. Its traditional leaders are Citrix and VMware. VMware has created a strong set of solutions for desktop virtualization through the development of its own products and the active absorption of other companies. Its VDI solutions are integrated with the vSphere virtualization platform, the vRealize Operations Manager monitoring system, software-defined NSX management software, and vSAN software repositories.
Citrix started with terminal access applications (WinFrame) and gained popularity with Citrix XenDesktop thanks to the functionality of a product that supports multiple virtualization platforms (Citrix XenServer, Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware ESXi hypervisors) and Citrix client terminal solutions.
Microsoft, Parallels, Huawei and several other vendors are also known on the VDI market. And Microsoft is actively promoting the solutions of its partner Citrix.
Large VDI installations are demanding in terms of storage capacity and performance. When deploying, running, or updating virtual workstations, the storage system is under severe stress. Modern flash arrays are designed to solve this problem, providing the necessary performance indicators.
The gaining popularity of hyperconvergent systems (HCI), which allow you to combine computational resources and data storage in a single solution. In addition, HCI provides horizontal scaling of the VDI infrastructure.
VDI, with its centralization and unification of the IT infrastructure, increasing the safety of data storage and processing, is also characterized by relatively high capital costs compared to physical workstations, the need to modernize the existing IT infrastructure.
This is one of the reasons for the growing popularity of the provision of access to virtual workstations based on a monthly subscription (for example, VMware Horizon Air and Amazon Workspaces). Represent the services of virtual workstations and a number of Russian cloud providers.
Virtual graphics station - access service to a virtual machine with a graphics accelerator. Such remote terminal access is very convenient for professionals working with graphics software. It is suitable for designers, freelance artists, employees of small studios.
The server platform is usually built on the basis of high-performance NVIDIA or AMD graphics cards with fast storage. Windows Server is used as a virtualization platform, SSD (NVMe) is used for storage subsystems. The clients are VMware, Microsoft, or Citrix.
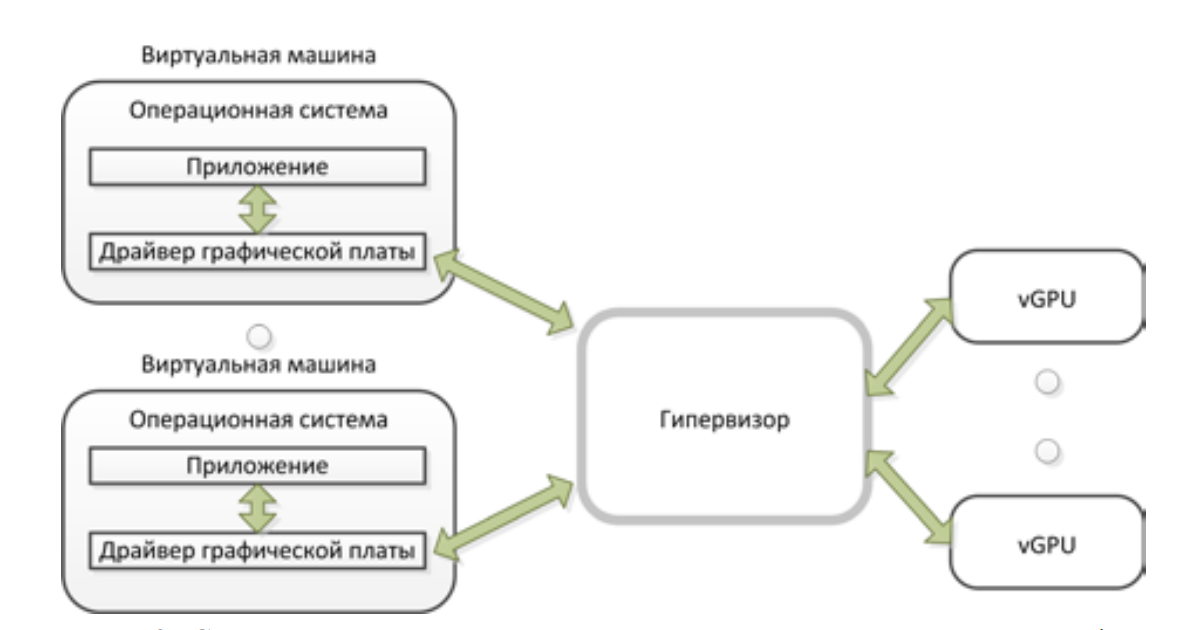
The interaction of VM and graphics cards.
NVIDIA GRID vGPU technology unleashes the potential for accelerating NVIDIA graphics in virtualized environments. The NVIDIA GRID vGPU virtual graphics processor provides high graphics performance in virtual workstations and the use of hardware acceleration of the graphics processor by several virtual workstations without sacrificing graphics quality. The graphics commands of each virtual machine are transmitted directly to the GPU without translation by the hypervisor.
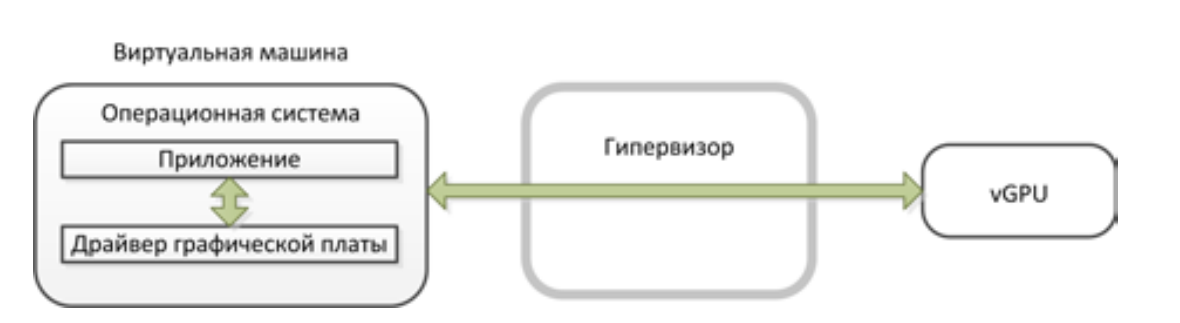
Forwarding a graphics card VM.
For teamwork or the use of demanding applications (SolidWorks, AutoCAD, 3DS Max, Revit, ArchiCAD, etc.), you can use a special GPU Pass-through mode — forwarding a card (PCIe device) to a virtual server. In this case, the VM directly receives the full computational core of the video card. This option replaces several powerful workstations.
As a client, you can use regular PCs and even thin clients, but the channel is recommended not to have 4 Mbit / s.
To “forward” a video card to a virtual server, you need to enable passthrough mode for this PCIe device in the host configuration and add the PCI device to the VM configuration. In the 3DMark test, the "forwarded" virtual map shows high results, virtually identical to the physically installed graphics card.
Such a feature of graphics acceleration technologies as the ability to “forward” a video card directly to a virtual machine not only has a positive effect on the quality and speed of working with graphics. Some applications simply will not function correctly without having full access to the graphics card.

Target audience VDI.
Using graphics technology in a VDI environment gives good results. Due to the graphics acceleration modes in VDI platforms, graphics applications work in almost the same way as on physical workstations - without delays and braking.
An important aspect is safety. Any physical workstation in the workplace is potentially unsafe, as it contains information, the loss of which can cause serious damage to the company.
Terminal access solves this problem, because the employee simply does not have the ability to upload data and carry it with him.
Another significant advantage is the efficient use of resources.
The expensive NVIDIA graphics card purchased in a limited budget will not be used 100% most of the time, and the budget does not allow providing all employees with powerful and expensive jobs. Virtualization is the way out of this situation.
Video cards can be shared. Thus, it is possible to provide each employee with a high-end video card with minimal investment and without idle capacity.
Instead of a large pool of graphic workstations, several servers with powerful video cards are used. Employees of the company can simultaneously connect to them and use CPU, RAM, SSD and GPU resources on a competitive basis. At the same time, all information (files, projects, assemblies) does not leave the limits of the data center.
 The NVIDIA graphics cards have several graphic GPUs working independently of each other. The hypervisor defines these GPUs as separate PCI devices. Some video cards have an increased amount of video memory, which is actively used, for example, in drawing models.
The NVIDIA graphics cards have several graphic GPUs working independently of each other. The hypervisor defines these GPUs as separate PCI devices. Some video cards have an increased amount of video memory, which is actively used, for example, in drawing models.
The GPU has thousands of cores for efficient parallel processing of workloads, such as 3D graphics applications, video processing and image rendering. GPU virtualization allows you to share its power between several virtual machines - each gets its own vGPU.
NVIDIA vGPU software and NVIDIA Tesla accelerators provide workstations with powerful graphics processors in data centers. As a result, applications work as they should.
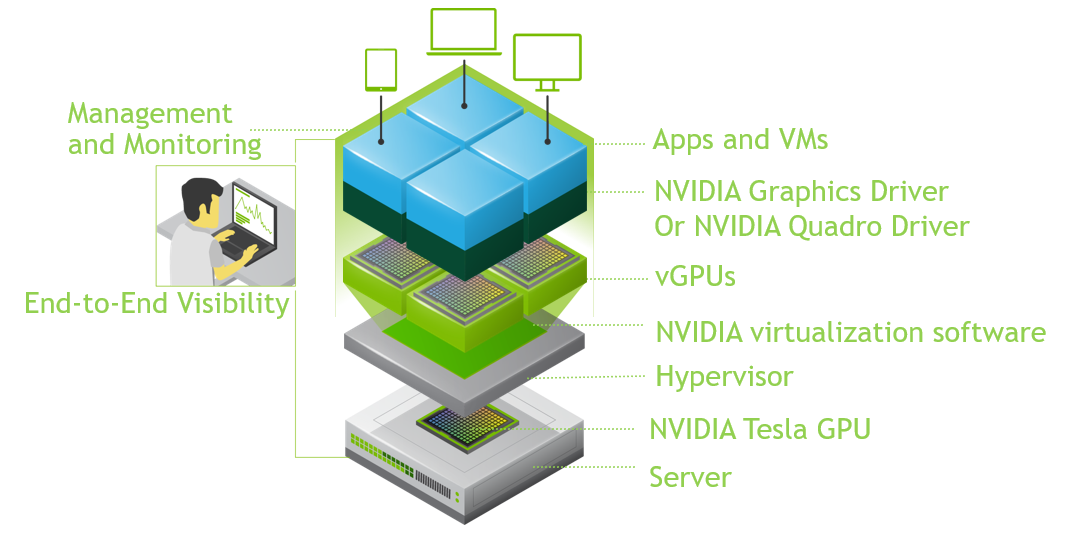
Virtualization software converts a physical graphics processor on a server into multiple vGPUs that can be shared among several virtual machines.
 The NVIDIA offerings for virtual graphics processors include several products for digital workplace organization: NVIDIA GRID virtual PCs (GRID vPC), NVIDIA GRID virtual applications (GRID vApps) and NVIDIA Quadro virtual data center workstation (Quadro vDWS) for designers, engineers and architects.
The NVIDIA offerings for virtual graphics processors include several products for digital workplace organization: NVIDIA GRID virtual PCs (GRID vPC), NVIDIA GRID virtual applications (GRID vApps) and NVIDIA Quadro virtual data center workstation (Quadro vDWS) for designers, engineers and architects.
A set of graphics virtualization technologies from VMware-Citrix-Microsoft, which can be combined with each other to optimize the required characteristics.
A virtual workstation is an invaluable tool for creators, content creators, design studio specialists and marketing agencies, as well as for all those for whom the purchase of a powerful graphic station is irrational or exceeds budget possibilities. Yes, and all other potential users can get the benefits of the service model (transfer CAPEX to OPEX).
Theoretically, the implementation of VDI in an enterprise with an extensive network helps to reduce (over time) operating costs. At least, simply because the efforts associated with solving everyday tasks (helping everyone to restore the system, update, apply a patch), IT specialists will need much less. But to realize such a project would be expensive. Yes, VDI is an expensive technology, and sometimes not the best replacement for a classic workplace. It all depends on the specific case, goals and availability of resources.
In addition, the success of VDI projects, as a rule, largely depends on their proper implementation, competent preliminary analysis on the compliance of the project objectives with real opportunities, so that expertise cannot be done here.
The experience of such projects shows that some customers are really satisfied with the results, while others have significant difficulties in implementing and operating such solutions.
If we talk about VDI as a whole, it was previously thought that virtualization of workplaces makes sense if the number of users is more than 500, then - 200 (virtualization of workstations is a special case). Today, at the cost of implementation, VDI technology has become much more affordable, Experts say that it is economically feasible to implement such systems in enterprises with more than 50 workplaces.
Meanwhile, in order to deploy a data center in my company and organize its work, it will be necessary to spend money on the purchase of equipment, as well as certified software. It may be necessary to prepare the IT infrastructure for change, optimize software for a multi-user environment, replace the old, incompatible and proprietary software with more standard solutions.
An important role, especially in the virtualization of workstations, is played by the communication channels between clients and the infrastructure of the data center - they must be with a reserve of bandwidth and preferably reserved. Particular attention should be paid to plug-in peripherals and their compatibility in the VDI environment.
Not uncommon - problems with data storage systems that must withstand a large flow of information. Also, high demands are placed on the qualifications of specialists who will have to work with the new system.
The best option for VDI is a company with a new IT infrastructure, a large number of users of the same type with modern office software, departments of organizations with a limited set of tasks, such as call centers, projects for standardizing workstations to work with various devices and from different places, with frequent moving users inside and outside the company, as well as special security requirements.
Companies with years of IT infrastructure and a huge fleet of heterogeneous user software that cannot be replaced or optimized for one reason or another are not the best choice for VDI, as well as the heterogeneity of most users, insufficient communication channels for comfortable work with VDI. In such cases, it is better to reduce the scope of the project or to postpone the VDI project as a whole.
Specific cases - when VDI is used to virtualize powerful workstations for graphics processing, for working with heavy files. Modern technologies of virtualization of workstations allow you to work together not only on typical tasks, but also with specialized software, to run CAD files, three-dimensional modeling, professional graphic editors on a VM. There are all new generation of graphics adapters NVIDIA, AMD, and soon Intel, VDI vendors optimize their software. Therefore, the performance of virtual stations is practically not inferior to physical ones. However, such projects usually do not provide savings.
The use of VDI technology (in the case of virtualization of workstations) implies the replacement of a workstation is replaced by a thin client. All workload from workstations is transferred to several servers. The user's work environment is deployed in a virtual infrastructure, and the user's workstation will be a VM.
The price of the issue on the hardware of the solution is reduced to the cost of thin clients (plus a monitor, keyboard, mouse), virtual infrastructure (several servers are required per calculation - one server for 2-3 dozens of VMs, depending on software), a separate disk storage is required. To this is added the cost of software for virtualization (for example, VMware), Windows licenses, CAL client access licenses, VDI access licenses, CAD licenses or other special software.
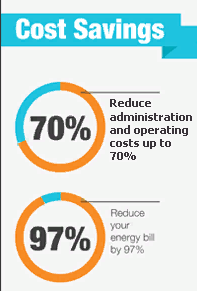
As a result, the classical scheme is the cheapest. And virtualization of workstations actually remains technology expensive. That is why it makes sense to contact the VDI provider. This is not only a translation of CAPEX to OPEX, but also a significant savings on a number of the articles listed. So, according to different sources , VDI allows you to reduce administration costs by up to 70% and energy costs by 97%.
In particular, VDI "from the cloud" will not only provide an opportunity to abandon the use of powerful workstations and personal computers, but also significantly reduce the staff of technical support by switching to remote administration or IT outsourcing.
According to different sources, VDI allows you to reduce administration costs by up to 70% and energy costs by 97%.
The cost depends on the configuration and the number of users. Here is an approximate comparison chart for 50 employees.
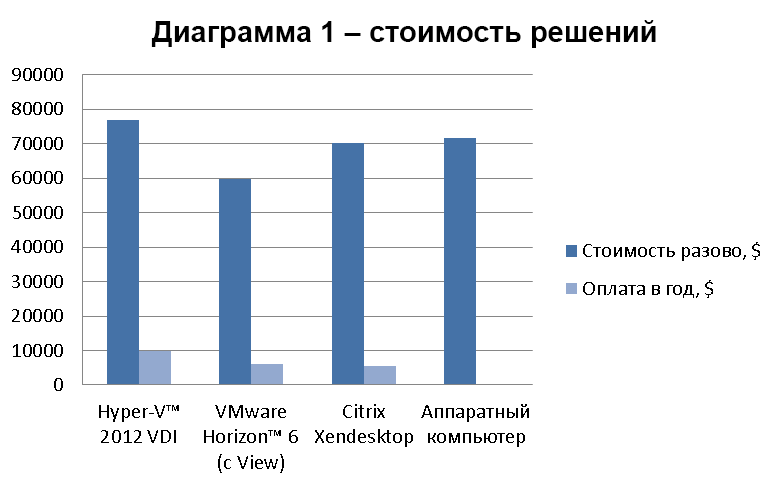
Comparative cost of virtual and physical workstations for 50 users (according to the Efsol company).
Virtual workplaces are the centralization and protection of user data, the ability to quickly and cost-effectively connect new users, for example, when expanding the company, eliminating downtime in case of equipment failure (you can immediately resume working on another device without losing data. You can integrate and standardize business processes in remote branches, standardize and unify workplaces, improve the stability of work processes. The main thing is to choose a reliable provider with suitable tariff plans .

What is a workstation?
The first workstations appeared in the late 60s and today they are widely used to work with computer-aided design and engineering systems, 2D and 3D graphics, video editing and demanding computing. With the advent of 64-bit versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems, high-performance UNIX workstations with proprietary software environments have given way to systems with MS Windows. Many vendors also offer Linux from Red Hat or SuSE as an alternative.
Workstations are a useful tool for designers and designers, financial analysts and researchers, content creators and creators. They support the most resource-demanding tasks and applications, such as rendering complex graphics, financial analysis, computational tasks and video editing, and creating other complex digital content.
')
When processing geospatial data, building three-dimensional terrain models, etc. on standard PCs, one often encounters memory shortages, delays and “hang-ups”, while workstations demonstrate high performance and do a good job of displaying data.

A workstation is not just a computer, it is a whole range of mechanisms designed to perform the most demanding tasks, ensure uninterrupted operation and advanced functionality.
Distinctive features of modern workstations are high speed of work with data, powerful processor, large capacity of fast RAM, integrated high-performance network controller, professional graphics subsystem.
Applications and Workstation Types
The equipment of the workstations provides high performance in design, realistic visualization of frame and textured three-dimensional models, fast receipt of the results of scientific calculations, high-resolution video processing and the creation of various video effects.
By classes of tasks, workstations can be divided into several types:
| Type of Workstation | Application area |
|---|---|
| Graphic | Graphics and multimedia, in particular, computer graphics and image processing, video, sound, development of computer games and digital content. |
| For engineering or architectural design | Various engineering, architectural and other CAD systems, GIS, field work and geodesy, etc. |
| For scientific and technical tasks | Scientific and engineering calculations. |
| For trading | Professional stock and online trading. |
| For industrial applications | Design, operational management and monitoring, process management. |
Each subclass of professional workstations can have its inherent features and unique components that are significantly different from mass PC models: large display size / resolution and / or several displays (CAD, GIS, stock trading, Internet trading), powerful video card (film and video , animation, computer games), large capacity / performance of the storage subsystem (scientific tasks, animation), mobile or secure execution (operation in the field or in the shops of industrial enterprises), etc.
So, models equipped with NVIDIA graphics accelerators are suitable for professionals involved in 3D modeling, engineering analysis, non-linear video editing (NLE), design, as well as for finance workers.

Professional graphics cards Quadro RTX 6000 and Quadro RTX 5000, which are built on the basis of selection graphics processors on the Turing architecture, are distinguished by the support of hardware accelerated ray tracing, which is provided by specialized RT cores.
Graphic workstations (the most extensive category) are suitable for designers, artists, photographers, animators, video editors, designers, engineers, and all those who use specialized graphics packages. They have high performance when working with graphics, video and animation. Graphic stations, as a rule, use the latest NVIDIA or AMD graphic processors.
They are often equipped with multiple monitors, used for working with 2D and 3D graphics (design, engineering, etc.), data visualization (medicine, big data analytics), rendering, modeling (CAD / CAM), creating video walls, gesture recognition, GIS and others

Graphic workstations are widely used in modeling for the automotive industry, aircraft manufacturing, the oil and gas industry, the production of media content, the processing of medical data and the visualization of research results.
| Scope of the graphic workstation | Description | Solvable tasks | Typical software |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD | Professional workstations for engineers and designers who work with computer-aided design and engineering applications (CAD / CAM / CAE). | Design, construction, production. | Autodesk AutoCAD, Autodesk Inventor, Altair HyperWorks, Siemens NX. |
| 3D graphics | Used to work in the field of 3D-animation and modeling, when you need fast interactive work with graphics. When 3D-visualization provide the fastest possible rendering results. | Modeling, animation, visualization. | Autodesk 3ds Max, Autodesk Maya, Adobe After Effects CC, Maxon CINEMA 4D. |
| Video editing | Workstations for video editing based on NVIDIA QUADRO professional graphics accelerators with CUDA technology support dozens of times faster processing and conversion of high-definition video Full HD and ULTRA HD 4K. | Video editing, working with video Full HD, Ultra HD 4K. | Adobe Premiere Pro CC, Avid Media Composer, Sony Vegas Pro, Grass Valley Edius. |
CAD workstations
Workstations CAD - a subclass of graphic workstations - allow you to create design and / or technological documentation, geometric models (solid-state, three-dimensional, composite), as well as product drawings. The hardware resources of such a workstation use all the functionality of professional CAD systems: CATIA, CREO, NX, Inventor, Compass, AutoCAD, Solid Works, SolidEdge, T-Flex CAD and others.
| View CAD | Solvable tasks |
|---|---|
| Engineering | Development of a wide range of products: from the creation of aerospace systems to the design of household appliances. |
| Microelectronics Products | Design of circuit and wiring diagrams, printed circuit boards, automatic placement of items of products, autotracing. |
| Electrotechnical | Development of schematic diagrams and electrical equipment connection diagrams, its spatial layout, maintenance of databases of finished products. |
| Architectural | 2D / 3D design of architectural and building structures, the calculation of special structures such as roofs, typical static calculations of building structures, maintenance of databases of standard elements, planning of territories for construction. |
| Equipment for industrial installations and structures | Creation of schematic diagrams of installations, spatial wiring of pipelines and cable routes, design of heating, water supply, sewerage, electricity, ventilation and air conditioning systems, maintenance of equipment databases, pipe fittings, finished electrical products. |
| Geoinformational | Digitizing field survey data, analyzing geodetic networks, building a digital elevation model, creating maps and plans in vector form, maintaining land and city cadastres, maintaining an electronic cartographic archive. |

Graphic workstations for design automation systems (CAD) represent a wide class of systems for CAD (Computer Aided Design), CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) and CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) tasks.
Modern CAD workstations are conventionally divided into the following groups:
| CAD workstations | Workstation Applications |
|---|---|
| Entry level | 2D-modeling of products, work with small assemblies in 3D; entry-level design and architectural design. |
| Mid level | 3D modeling of parts, work with small and medium assemblies; design and architectural design. |
| High-end Workstations | High performance computing using specialized software, engineering analysis and simulation modeling; preparing photorealistic images (rendering); video processing and effects overlay; work with super large assemblies. |
Today, when the cloud becomes the same usual element of IT infrastructure, like a server or a workstation, virtual virtual station services are gaining popularity, which solve the important problem of using graphic power from the cloud, which seemed impossible only a few years ago.
Virtual graphic station - the time has come
Previously, work with resource-intensive applications was assigned to powerful computers and workstations with a large set of application programs. The disadvantages of the above solutions are the high cost of ownership, the need for regular investments in upgrading and restricting user mobility.
Exit - virtual graphic stations located in a high-performance cloud environment. This technology not only provides access to virtually unlimited computing resources in the cloud, but also allows you to work simultaneously with several demanding applications online. And all this - without reference to a stationary workplace.
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) technology allows you to create a virtual IT infrastructure and deploy workstations based on server systems where many virtual machines are running. In fact, for users it looks like a familiar workplace on a PC with the necessary applications.
VDI makes it possible to create full-fledged workstations for users, functionally identical to workstations of classical architecture. VDI infrastructure involves placing virtual desktops and other user resources in the server infrastructure (in the corporate data center or in the provider cloud) and providing access to them from the company's internal network and / or via the Internet.
As a result, instead of providing users with “heavy” graphics applications with powerful workstations, you can take advantage of a more modern solution and deploy the VDI infrastructure. They will have at their disposal a virtual graphic workstation - an access service to a virtual machine with a graphics accelerator.
In fact, this is a remote terminal access to a virtual machine with a powerful graphics subsystem. The company can save, working with remote employees from regions or other countries, to collect virtual teams.
Providing a full computing core of a video card to a virtual machine allows using high-loaded applications such as AVEVA, SolidWorks, AutoCAD, SketchUP, 3DS Max, Revit, ArhiCAD, etc. on a virtual workstation. Moreover, this configuration replaces several powerful workstations.

The task of the AMD Radeon Pro V340 card is reliable graphics performance in all systems, from cloud solutions to virtually any device. The hardware solution for virtualization of graphics processors (AMD MxGPU) is based on the standard virtualization technology of SR-IOV (Single-Root I / O Virtualization) devices, which allows remotely working virtualized users (their number can reach 16 on each physical graphics processor).
Such a platform is often built on the basis of high-performance NVIDIA graphics cards or GPUs from AMD with fast storage. Windows Server is often used as a virtualization platform. To improve the performance of the disk system are usually used flash drives (SSD).
VDI benefits
A virtual graphic station can be included in the company's existing IT infrastructure. All projects can be saved in the corporate network or in cloud storages, which can be accessed from anywhere in the Internet.
The VDI infrastructure provides a higher level of protection for the transfer and storage of important information, centralized management of the IT infrastructure of workplaces and the provision of IT services to employees. At the same time, the cost of implementing VDI is comparable to the replacement of the PC fleet.
In the VDI architecture, all data is stored on a server in the data center. This solution significantly increases the level of information security, provides much more efficient use of computational resources compared to full-featured physical workstations, and provides convenient tools for centralized administration of workstations.
One of the advantages of VDI is that, if necessary, a user workstation of any available performance is created, and when it is no longer necessary, it is deleted. Thus, in the presence of modern Internet channels, it is possible to allocate significant computing power to remote users.
By the way, as the testing shows, the speed of the 3G mobile network 17 Mbit / s (2.12 MBytes / s) is clearly not enough - it’s uncomfortable to work, not to mention HD video, which VMware Verizon simply doesn’t pull on such a channel.
In general, VDI provides the following key benefits:
- the possibility of dynamic and operational management of computing resources;
- unification of the park software and arm;
- centralized administration software and AWP;
- a significant reduction in information security incidents;
- reduction of terms for provision of new AWPs;
- increasing the safety of data storage and processing;
- cost reduction with the support of remote offices.
The main driver for implementing VDI is data security and integrity, centralization of management and administration. A VDI system is usually deployed by fairly large companies.
You can use virtual graphic stations when you need to:
- Select graphics capacity for a short-term project.
- Quickly expand your current infrastructure without a long process of purchasing new graphic stations.
- To involve remote employees or freelancers to work on the project.
- Move part of the workplace in the cloud (for example, if the existing equipment is outdated, and the budget does not allow updating it).
- Get savings, including software licenses.
- Protect access and work results (you can use VPN, antivirus protection, backup options).
They are also convenient to use for training, testing, organization of temporary work.
From the history of VDI
VDI technology originated at the junction of three areas: terminal access, remote work with graphic stations and server virtualization.
Standard VDI infrastructure can be of three types:
- Terminal Sessions, streaming applications.
- Desktops on the model of queuing (Pooled Desktop).
- Personal desktops (Personal Desktop).
Unlike terminal farms, in the latter case, VDI users have at their disposal a personal virtual machine with an installed OS and applications, and virtualization provides users with isolation and resource sharing: only those computing resources that are allocated to their virtual machine are available to the user.

Virtual Workstation Infrastructure (VDI) is a way to access workstations working remotely in the data center.
The main consumers of VDI solutions today are the financial and banking sector, retail, healthcare and insurance, but due to the development of technology to accelerate image processing and transmission, companies from the engineering industry have become interested in VDI solutions.
The evolution of VDI can be broken down into several key stages:
VDI 1.0
This early stage is a basic approach to VDI, which has not yet become widespread in enterprises that have just begun to get acquainted with the solution and mainly used VDI for non-business-critical applications. This technology has been used primarily for call center applications. VDI configurations were fairly limited, and when running virtual machines in the data center, a lot of resources were not consumed (computing, storage, and network).
With this deployment, there were no high demands on storage I / O performance, bandwidth, or network latency. Traditional disks (HDD) quite satisfied the needs of the user.
VDI 1.0 is the first attempt to apply breakthrough virtualization technology to PCs, but it didn’t give much in terms of cost.
VDI 2.0
This is the current generation of VDI, which appeared about 2-3 years ago. This stage is likely to last several more years. VDI 2.0 is also a basic version of VDI, but of the next generation.
As enterprises managed to evaluate the benefits of VDI 1.0 in terms of security, availability, flexibility and manageability compared to physical workstations, the introduction of VDI has become more widespread, and there is every reason to believe that this trend will continue.
With the growing popularity of VDI, new scenarios for the use of this technology have appeared, it has been used in many applications. However, this has created problems at the infrastructure level, such as “boot storm” (boot storm), application of patches, rapid deployment. "Heavyweight" configuration of virtual workstations.
The I / O performance requirements of the storage subsystem were thousands of IOPS, and the HDD could no longer handle them. There have been attempts to optimize the performance of the storage environment using SAN from hundreds of magnetic media, but such solutions have proved to be not efficient either technically or economically, and the VDI tasks required different types of I / O. Flash arrays are used to eliminate these problems, but this increases the cost of the solution.
The new architectures use hyperconvergence systems (combining storage, network components and calculations) based on flash memory to meet the performance needs of the storage system. Some solutions use SSD to cache data, while other solutions, such as VMware All Flash Virtual SAN, use the entire data storage stack using various types of flash memory.
Currently, enterprises are using fully or partially flash-based solutions using the hyper-convergent approach. This trend continues in VDI 3.0.
VDI 3.0
In VDI 2.0, the scope of this infrastructure has expanded, the average cost of a virtual workstation has decreased. Began a new stage. With the spread of VDI, this approach began to be tested in the field of virtualization of high-performance workstations.
VDI 2.0 and VDI 3.0 have a lot in common. Flash memory plays a key role in technology development. With the increased use of demanding graphics applications in VDI 3.0, the storage subsystem has become even more important.
The possibilities of using high-performance workstations, such as workstations for engineering calculations or design systems (CAD), have expanded. A few years ago, it was simply unthinkable to virtualize workstations with similar requirements. However, today it is becoming a reality thanks to flash memory and graphics accelerators.
At the same time, VDI 3.0 promises acceptable performance and competitive costs even for the most complex use cases of virtual workstations.
VDI Market
The VDI market is a little over 10 years old. Its traditional leaders are Citrix and VMware. VMware has created a strong set of solutions for desktop virtualization through the development of its own products and the active absorption of other companies. Its VDI solutions are integrated with the vSphere virtualization platform, the vRealize Operations Manager monitoring system, software-defined NSX management software, and vSAN software repositories.
Citrix started with terminal access applications (WinFrame) and gained popularity with Citrix XenDesktop thanks to the functionality of a product that supports multiple virtualization platforms (Citrix XenServer, Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware ESXi hypervisors) and Citrix client terminal solutions.
Microsoft, Parallels, Huawei and several other vendors are also known on the VDI market. And Microsoft is actively promoting the solutions of its partner Citrix.
Large VDI installations are demanding in terms of storage capacity and performance. When deploying, running, or updating virtual workstations, the storage system is under severe stress. Modern flash arrays are designed to solve this problem, providing the necessary performance indicators.
The gaining popularity of hyperconvergent systems (HCI), which allow you to combine computational resources and data storage in a single solution. In addition, HCI provides horizontal scaling of the VDI infrastructure.
VDI, with its centralization and unification of the IT infrastructure, increasing the safety of data storage and processing, is also characterized by relatively high capital costs compared to physical workstations, the need to modernize the existing IT infrastructure.
This is one of the reasons for the growing popularity of the provision of access to virtual workstations based on a monthly subscription (for example, VMware Horizon Air and Amazon Workspaces). Represent the services of virtual workstations and a number of Russian cloud providers.
Virtual graphic station and its features
Virtual graphics station - access service to a virtual machine with a graphics accelerator. Such remote terminal access is very convenient for professionals working with graphics software. It is suitable for designers, freelance artists, employees of small studios.
The server platform is usually built on the basis of high-performance NVIDIA or AMD graphics cards with fast storage. Windows Server is used as a virtualization platform, SSD (NVMe) is used for storage subsystems. The clients are VMware, Microsoft, or Citrix.

The interaction of VM and graphics cards.
NVIDIA GRID vGPU technology unleashes the potential for accelerating NVIDIA graphics in virtualized environments. The NVIDIA GRID vGPU virtual graphics processor provides high graphics performance in virtual workstations and the use of hardware acceleration of the graphics processor by several virtual workstations without sacrificing graphics quality. The graphics commands of each virtual machine are transmitted directly to the GPU without translation by the hypervisor.

Forwarding a graphics card VM.
For teamwork or the use of demanding applications (SolidWorks, AutoCAD, 3DS Max, Revit, ArchiCAD, etc.), you can use a special GPU Pass-through mode — forwarding a card (PCIe device) to a virtual server. In this case, the VM directly receives the full computational core of the video card. This option replaces several powerful workstations.
As a client, you can use regular PCs and even thin clients, but the channel is recommended not to have 4 Mbit / s.
To “forward” a video card to a virtual server, you need to enable passthrough mode for this PCIe device in the host configuration and add the PCI device to the VM configuration. In the 3DMark test, the "forwarded" virtual map shows high results, virtually identical to the physically installed graphics card.
Such a feature of graphics acceleration technologies as the ability to “forward” a video card directly to a virtual machine not only has a positive effect on the quality and speed of working with graphics. Some applications simply will not function correctly without having full access to the graphics card.

Target audience VDI.
Using graphics technology in a VDI environment gives good results. Due to the graphics acceleration modes in VDI platforms, graphics applications work in almost the same way as on physical workstations - without delays and braking.
An important aspect is safety. Any physical workstation in the workplace is potentially unsafe, as it contains information, the loss of which can cause serious damage to the company.
Terminal access solves this problem, because the employee simply does not have the ability to upload data and carry it with him.
Another significant advantage is the efficient use of resources.
The expensive NVIDIA graphics card purchased in a limited budget will not be used 100% most of the time, and the budget does not allow providing all employees with powerful and expensive jobs. Virtualization is the way out of this situation.
Video cards can be shared. Thus, it is possible to provide each employee with a high-end video card with minimal investment and without idle capacity.
Instead of a large pool of graphic workstations, several servers with powerful video cards are used. Employees of the company can simultaneously connect to them and use CPU, RAM, SSD and GPU resources on a competitive basis. At the same time, all information (files, projects, assemblies) does not leave the limits of the data center.
 The NVIDIA graphics cards have several graphic GPUs working independently of each other. The hypervisor defines these GPUs as separate PCI devices. Some video cards have an increased amount of video memory, which is actively used, for example, in drawing models.
The NVIDIA graphics cards have several graphic GPUs working independently of each other. The hypervisor defines these GPUs as separate PCI devices. Some video cards have an increased amount of video memory, which is actively used, for example, in drawing models.The GPU has thousands of cores for efficient parallel processing of workloads, such as 3D graphics applications, video processing and image rendering. GPU virtualization allows you to share its power between several virtual machines - each gets its own vGPU.
NVIDIA vGPU software and NVIDIA Tesla accelerators provide workstations with powerful graphics processors in data centers. As a result, applications work as they should.

Virtualization software converts a physical graphics processor on a server into multiple vGPUs that can be shared among several virtual machines.
 The NVIDIA offerings for virtual graphics processors include several products for digital workplace organization: NVIDIA GRID virtual PCs (GRID vPC), NVIDIA GRID virtual applications (GRID vApps) and NVIDIA Quadro virtual data center workstation (Quadro vDWS) for designers, engineers and architects.
The NVIDIA offerings for virtual graphics processors include several products for digital workplace organization: NVIDIA GRID virtual PCs (GRID vPC), NVIDIA GRID virtual applications (GRID vApps) and NVIDIA Quadro virtual data center workstation (Quadro vDWS) for designers, engineers and architects.A set of graphics virtualization technologies from VMware-Citrix-Microsoft, which can be combined with each other to optimize the required characteristics.
Who needs VDI?
A virtual workstation is an invaluable tool for creators, content creators, design studio specialists and marketing agencies, as well as for all those for whom the purchase of a powerful graphic station is irrational or exceeds budget possibilities. Yes, and all other potential users can get the benefits of the service model (transfer CAPEX to OPEX).
Theoretically, the implementation of VDI in an enterprise with an extensive network helps to reduce (over time) operating costs. At least, simply because the efforts associated with solving everyday tasks (helping everyone to restore the system, update, apply a patch), IT specialists will need much less. But to realize such a project would be expensive. Yes, VDI is an expensive technology, and sometimes not the best replacement for a classic workplace. It all depends on the specific case, goals and availability of resources.
In addition, the success of VDI projects, as a rule, largely depends on their proper implementation, competent preliminary analysis on the compliance of the project objectives with real opportunities, so that expertise cannot be done here.
The experience of such projects shows that some customers are really satisfied with the results, while others have significant difficulties in implementing and operating such solutions.
If we talk about VDI as a whole, it was previously thought that virtualization of workplaces makes sense if the number of users is more than 500, then - 200 (virtualization of workstations is a special case). Today, at the cost of implementation, VDI technology has become much more affordable, Experts say that it is economically feasible to implement such systems in enterprises with more than 50 workplaces.
Meanwhile, in order to deploy a data center in my company and organize its work, it will be necessary to spend money on the purchase of equipment, as well as certified software. It may be necessary to prepare the IT infrastructure for change, optimize software for a multi-user environment, replace the old, incompatible and proprietary software with more standard solutions.
An important role, especially in the virtualization of workstations, is played by the communication channels between clients and the infrastructure of the data center - they must be with a reserve of bandwidth and preferably reserved. Particular attention should be paid to plug-in peripherals and their compatibility in the VDI environment.
Not uncommon - problems with data storage systems that must withstand a large flow of information. Also, high demands are placed on the qualifications of specialists who will have to work with the new system.
The best option for VDI is a company with a new IT infrastructure, a large number of users of the same type with modern office software, departments of organizations with a limited set of tasks, such as call centers, projects for standardizing workstations to work with various devices and from different places, with frequent moving users inside and outside the company, as well as special security requirements.
Companies with years of IT infrastructure and a huge fleet of heterogeneous user software that cannot be replaced or optimized for one reason or another are not the best choice for VDI, as well as the heterogeneity of most users, insufficient communication channels for comfortable work with VDI. In such cases, it is better to reduce the scope of the project or to postpone the VDI project as a whole.
Specific cases - when VDI is used to virtualize powerful workstations for graphics processing, for working with heavy files. Modern technologies of virtualization of workstations allow you to work together not only on typical tasks, but also with specialized software, to run CAD files, three-dimensional modeling, professional graphic editors on a VM. There are all new generation of graphics adapters NVIDIA, AMD, and soon Intel, VDI vendors optimize their software. Therefore, the performance of virtual stations is practically not inferior to physical ones. However, such projects usually do not provide savings.
The use of VDI technology (in the case of virtualization of workstations) implies the replacement of a workstation is replaced by a thin client. All workload from workstations is transferred to several servers. The user's work environment is deployed in a virtual infrastructure, and the user's workstation will be a VM.
The price of the issue on the hardware of the solution is reduced to the cost of thin clients (plus a monitor, keyboard, mouse), virtual infrastructure (several servers are required per calculation - one server for 2-3 dozens of VMs, depending on software), a separate disk storage is required. To this is added the cost of software for virtualization (for example, VMware), Windows licenses, CAL client access licenses, VDI access licenses, CAD licenses or other special software.
As a result, the classical scheme is the cheapest. And virtualization of workstations actually remains technology expensive. That is why it makes sense to contact the VDI provider. This is not only a translation of CAPEX to OPEX, but also a significant savings on a number of the articles listed. So, according to different sources , VDI allows you to reduce administration costs by up to 70% and energy costs by 97%.
In particular, VDI "from the cloud" will not only provide an opportunity to abandon the use of powerful workstations and personal computers, but also significantly reduce the staff of technical support by switching to remote administration or IT outsourcing.
According to different sources, VDI allows you to reduce administration costs by up to 70% and energy costs by 97%.
The cost depends on the configuration and the number of users. Here is an approximate comparison chart for 50 employees.

Comparative cost of virtual and physical workstations for 50 users (according to the Efsol company).
IBS DataFort ExperienceAs a cloud provider providing a vGPU service, we in IBS DataFort distinguish several stages on the way to the formation of our service. - Cisco UCS HPE. GPU 2017 , - HPE WS460c Gen9 NVIDIA Tesla M6. , . : GPU- , , . , , , . 2018 , . GPU; , , NVIDIA, - VDI GPU . AMD FirePro S7150x2. NVIDIA 10, 40 V100. : , , ; , . , vGPU ( 1G 8/16G vGPU ). , , vmware Horizon, MS VDI Teamviewer. , MS VDI, , «» RDP-. — Teamviewer Horizon — , , . Horizon, vmware , Horizon. , AMD, ., NVIDIA. , NVIDIA , . , CUDA-, . , 2018 vmware Horizon + NVIDIA M10 40. V100 , .. big data data science — , .  IBS DataFort . rack- Cisco UCS ( , . ), NVIDIA . VDI , , . . , IBS DataFort NVIDIA T4, 2018 — 2019. , , ( PCI , 10 40). ( M10 40). , IBS DataFort T4 — , . |
Virtual workplaces are the centralization and protection of user data, the ability to quickly and cost-effectively connect new users, for example, when expanding the company, eliminating downtime in case of equipment failure (you can immediately resume working on another device without losing data. You can integrate and standardize business processes in remote branches, standardize and unify workplaces, improve the stability of work processes. The main thing is to choose a reliable provider with suitable tariff plans .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/457964/
All Articles