EDR technology as an element of the SOC nuclear triad
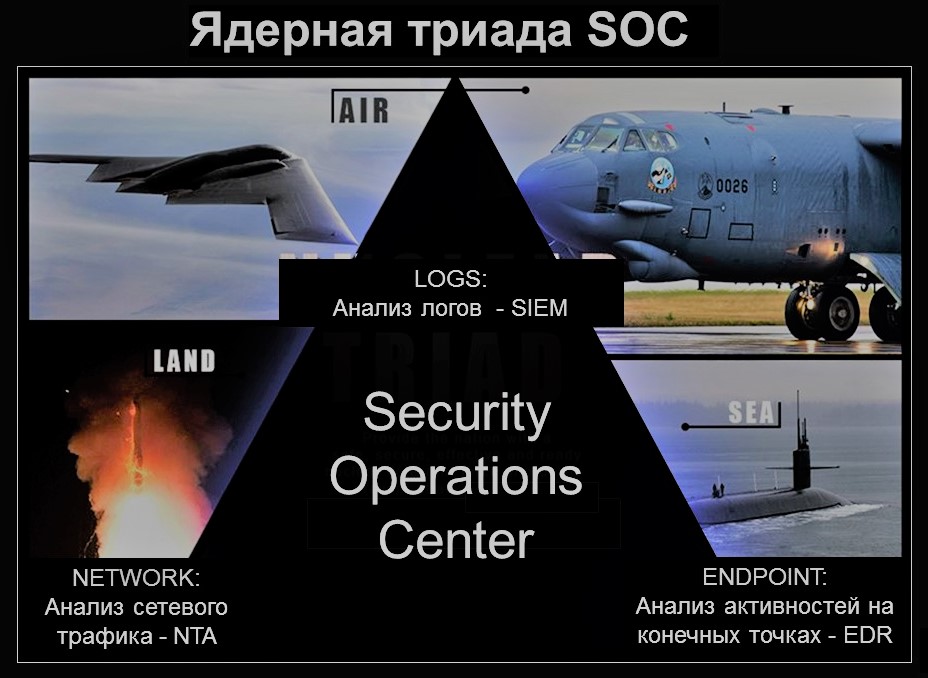
To begin with, let us recall what a nuclear triad is. This term refers to the strategic armed forces of a state equipped with nuclear weapons. The triad consists of three components: air - strategic aviation, land - intercontinental ballistic missiles, sea - nuclear submarines.
Dear Gartner drew an analogy between the state’s strategic armed forces and the incident monitoring and response center (SOC), highlighting the following elements of the SOC triad: Security information and event management (SIEM), Network Traffic Analysis (NTA), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). Looking at this analogy, it becomes obvious that a SOC can be as effective as possible only if it is equipped with all the components of protection: in the “air”, on the “ground” and in the “sea”.
Unfortunately, today most organizations use only “strategic aviation” - SIEM systems. Rarely enough, “intercontinental ballistic missiles” are NTA, replacing a full-fledged analysis of network traffic only by collecting logs from standard network defenses. And very often the “nuclear-powered submarine rocket carriers” - EDR.
')
In my today's note, according to the precepts of Gartner, I want to highlight the main reasons for the importance of incorporating EDR technology, as one of the elements of a modern monitoring and response center for incidents.
In the world of information security, EDR technology is much more than just advanced protection of workstations and servers against complex threats. From year to year, workplaces remain the key target of attackers and the most common entry points into the infrastructure of organizations, which requires proper attention and adequate protection. And telemetry is valuable information necessary for high-quality investigation of incidents, the importance of access to which increases even more with the advent of the TLS 1.3 encryption protocol and its active distribution.
EDR is rapidly becoming the driving force for increasing the maturity and efficiency of modern SOC.
Let's see why?
Additional visibility
First of all, the EDR technology is able to provide the SOC team with visibility where most organizations are blind today, since most of them are focused on monitoring activities in the network. Such companies, as part of the operation of a monitoring center and rapid response to incidents, rarely or only partially connect endpoints as sources of events in a SIEM system. This is due to the high cost of collecting and processing logs from all endpoints, as well as due to the generation of a huge number of events for parsing at a sufficiently high level of false positives, which often leads to an overload of specialists and inefficient use of expensive resources in general.
Special tool for detecting complex threats on hosts
Complicated threats and targeted attacks using unknown malicious code, compromised accounts, fileless methods, legitimate applications and actions that do not bear anything suspicious require a multi-level approach to detection using advanced technologies. Depending on a particular vendor, EDR can usually include various detection technologies that operate in automatic, semi-automatic mode, and built-in tools that require manual setting of tasks, involving highly qualified personnel. For example, it could be: antivirus, behavioral analysis engine, sandbox, search for compromise indicators (IoC), work with IoA attack indicators, comparison with MITER ATT & CK techniques, as well as automatic interaction with Threat Intelligence and manual queries to the global threat database, retrospective analysis, the ability to proactively search for threats (Threat Hunting). EDR is an additional SOC analytics tool with an intuitive interface for real-time threat hunting that allows you to create complex queries for searching for suspicious activities and malicious actions, taking into account the features of the protected infrastructure.
All of the above allows organizations to detect complex threats aimed at bypassing traditional means of protection on hosts, such as regular antiviruses, NGAV, or EPP (Endpoint protection platform) class solutions. The latter today interact very closely with EDR solutions and most manufacturers of this class of products provide EPP and EDR functionality within a single agent, without overloading the machine and at the same time providing an integrated approach to protecting endpoints from complex threats, ranging from automatic blocking of simpler threats, ending the detection and response to more complex incidents. The advanced detection mechanisms used in the EDR allow teams to quickly identify a threat and respond quickly, preventing possible damage to the business.
Additional context
The data from the EDR about events on the hosts are a significant addition to the information generated by other security elements and business applications of the protected infrastructure, which are mapped by the SIEM system in the center of monitoring and rapid response to incidents. EDR provides quick access to already enriched additional context data from the endpoint infrastructure, which allows, on the one hand, to quickly identify false positives, on the other hand, to use this data as precious, pre-processed material when investigating complex attacks, that is, EDR provides relevant logs to correlate with events from other sources, thereby improving the quality of the global SOC investigations.
Additional automation
For organizations that do not have an EDR, detecting complex threats on the infrastructure of the endpoints, which includes: collecting, storing and analyzing data, as well as carrying out various actions at the stages of investigation and response to complex incidents, is a rather laborious task without the use of automation tools.
Today, many analysts spend a lot of time on routine operations that are necessary and important, but can be automated. Automating these routine manual tasks will allow organizations not only to save the analyst’s expensive work time, but also reduce their workload and allow them to focus on analyzing and responding to really complex incidents. EDRs provide fully automated incident management workflow, from threat detection to analysis and response. This allows the SOC team to perform more efficiently daily tasks without wasting time on manual work, thereby reducing the cost of analyzing unnecessary logs.
Quick access to data and their visual presentation of information
In order to obtain the data needed for an investigation, organizations may face some difficulties, such as the inability to quickly access workstations and servers with a distributed infrastructure or the inability to obtain contextual information from specific machines due to their destruction or data encryption by attackers. This of course leads to the impossibility of obtaining the necessary data for an effective investigation process and further response to incidents. When the incident has already occurred, the use of EDR technology, which includes continuous and centralized recording, eliminates guesswork and saves analysts time.
The attacker often destroys his tracks, but the EDR, as already mentioned, records every attacker's action. The entire chain of events is fixed and securely stored for future use. When a warning of any nature is triggered, the EDR provides convenient tools by which SOC analysts can quickly request information to check for threats, eliminate false positives, and also make requests to rescan historical data to increase the effectiveness of the investigation and response.
All actions on the hosts are presented in the interface as a tree of events, thereby helping analysts to see the whole picture of the attack, as well as to find the information they need to investigate and take prompt measures to prevent the threat.
The centralized storage of telemetry, objects and previously formed verdicts allows analysts to work with historical data as part of investigating threats, including attacks that are extended over time. EDR today is a source of valuable data for modern SOC.
Centralized response
When an incident is detected, the EDR provides enhanced options for taking action at various stages of its investigation: for example, quarantining a file, executing arbitrary commands on a host, deleting an object, network isolation of hosts, and other actions. EDR allows you to immediately respond to incidents through a visual presentation of information and centralized setting of tasks, which does not require trips to the crime scene to search for evidence and take response measures. EDR is a tool for optimizing SOC labor costs. Organizations significantly reduce the number of routine manual operations, save analysts SOC time and reduce the response time from hours to minutes.
Conclusion
EDR serves as an invaluable data source for SOCs, providing powerful threat detection and centralized response to incidents, while maximally automating the processes of collecting, analyzing and responding to detected threats.
Using EDR within SOC will allow organizations to:
- Increase the efficiency of processing complex incidents due to the additional visibility of the endpoint level, the ability to proactively search for threats and visual presentation of information about detected events on hosts;
- to enrich the SOC with pre-processed relevant data from workstations and servers, for comparison with logs provided by other sources for effective investigation;
- Significantly reduce the number of hours spent by analysts on tedious but necessary tasks associated with analyzing data from workstations and servers, as well as responding to incidents.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/457838/
All Articles