How to create an OS certified for I class of protection
A first-hand account of how it is created and then prepared for certification for working with data under the heading of "special importance" protected OS Astra Linux.


Astra is a domestic Linux distribution that combines components from the community, distributed under open licenses such as GPL, MPL, Xiph License, etc., and software developed by the same-name group of companies. The user functionality is closed for the most part by components of the open source software - standard Linux mechanisms are used to perform basic tasks, such as running applications, virtualization, supporting hardware, or the same Steam. The components of their own design basically solve two key tasks: ensuring security, as well as the interaction of the graphical interface of the operating system and the person.
')
From the point of view of licensing, a distribution kit is a complex object (a concept from part 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), i.e. composite work, so its distribution in general has some limitations. Although all components of open source software included in the product retain their free status.
Versions of Astra Linux exist for a wide variety of platforms. The name of the platform is “hidden” in the first digit of the version number:
It would seem that an unusual solution is to place the type of platform in the first position, having received a strange sequence of versions - 1.6, 2.12.13, 8.1, etc. But this is done consciously in order to simplify the life of technical support, since the visually graphical interface of the operating system looks the same on any hardware platform, regardless of the computer’s intended use: from the server to the smartphone. So in a conversation with the user can quickly understand what kind of platform in question.
By the way, the version for each platform has its own code name in honor of one of the cities-heroes of Russia. There are no guidelines here, we rely on the feeling of beauty.
Among the Astra versions being developed there are both normal distributions and protected ones (Special Edition), oriented to work with confidential data, certified according to the information security requirements of all Russian certification systems. From the point of view of the user feature set, the versions are almost the same. However, the protection system in them is built in different ways. Some components of the ad hoc version required to work with confidential data, although they are not necessarily redundant for regular users and businesses, are not included in the regular version, since regulatory and legal framework of the Russian Federation requires their mandatory certification.
The normal version of Astra Linux is targeted at corporate customers. For home users, when using for non-commercial purposes, the license is free - but in development we strive to meet the needs of the corporate segment. In the end, we are also a commercial company, and the home users segment is a very difficult one. There are various Linux distributions for them, including free ones.
The usual version of Astra Linux uses the discretionary access control model - users themselves determine to whom they can grant access rights to their files. Third-party programs (browsers, office suites, etc.) run in the same way as in other Linux distributions.
Like any other software, a regular version of Astra Linux can be downloaded or purchased (for organizations) in electronic form without any physical media. By the way, this version is also posted on the resource of the international community Linux, where there is a good external channel.
Following global trends, the version is actively developing towards the support of new equipment and technologies.
In addition to the usual versions, Astra Linux has the so-called special versions - Special Edition, which are developed with the expectation of certification by the FSTEC of Russia and other certification systems. From the point of view of the user functionality, the special version is practically no different from the usual one. However, it implements additional components to improve security (just self-written), in particular:
Of course, this is not a complete list. There are lots of other modules and components. All these tools work independently of each other, providing such separation of the security system. All the listed security functions are implemented on the basis of original domestic computer security developments without using the SELinux developed by the NSA.
At the same time, they are turned on and off independently of each other (by the system administrator). For some components there are different modes of operation. For example, for the EDS verification tool, you can turn on the learning mode, when files with the wrong EDS (or which do not have it) still run, but a warning is issued at the system level. All these mechanisms are configured by the administrator under the security policy defined by the management. At the same time, almost the entire setup is already carried out as in the graphic mode. Of course, administrators have access to a full range of console-based tools for automating tasks for configuring and configuring security subsystems.
The current version of Astra Linux Special Edition - Smolensk 1.6.
The special version develops like the regular one, but innovations only get into it after testing and running in a regular release.
Each security and system administrator in their own way prioritize information security issues. Ask them to create a project to protect a certain IT infrastructure, and each will offer their own solution, since they will see their own threats and accents. If we are talking about commercial companies, the decision about whose opinion to listen, takes the business - at your own peril and risk.
At the state level, any risk must be minimized, so we need general mechanisms for assessing the effectiveness of protection, or rather, confirmation that information systems can withstand a certain set of threats. To do this, certain security functions must be implemented in the systems (for example, password checking, access control functions, etc.), and on the other hand, the development process and the code of this system itself must meet certain trust requirements. The task of the certification system and the certifying authority is to check the specific product for compliance with all functional conditions as well as the requirements of trust.
Depending on the functionality of information systems, various departments deal with the issues of their certification for the possibility of using them in working with important data. For example, FSTEC of Russia is engaged in certification of information security tools. However, the FSB and the Ministry of Defense also have their own systems of certification of protection. By the way, Astra Linux Special Edition is the only OS that has all the certificates in our country.

With regard to data processing systems of limited access, the nature of this data plays an important role - it is information for free distribution, personal data, valuable medical information, state secrets, including information of particular importance. It is logical that for each degree of secrecy there is a list of functional requirements and criteria for evaluating the “power of attorney” of the information systems code - its own protection class, including the level of trust. The list of requirements for each subsequent level includes a list for the previous level, as well as some additional conditions. This practice exists in many countries. In addition, each insists on some of its own criteria, and even in its own way shares data by levels. Russia has adopted six classes, with the sixth one being the lowest, and the first one being the highest.
The lower classes - from the sixth to the fourth - are the requirements for the protection of personal data, as well as commercial and official secrets. In the Russian market, products corresponding to these classes are no longer uncommon. We will talk about certification for the highest classes - from the third to the first - with the “secret”, “top secret” and “special importance” stamps (living examples are the drawings of the new Sukhoi fighter or general data on the state of critical infrastructure in the country, not so long ago equivalent to state secrets). And here the most difficult thing is not even functional requirements (in the end, developing something is not a problem), but confirmation of trust in the OS. For this, a correct mathematical model of data access control and a justification of the compliance of a real software product with this mathematical model is necessary. Those. the procedure for developing a system focused on working with sensitive data is many times more complicated.
Here is an example of the system's reaction to the inclusion of the MLS (multi level security) policy in SELinux in the Fedora distribution:
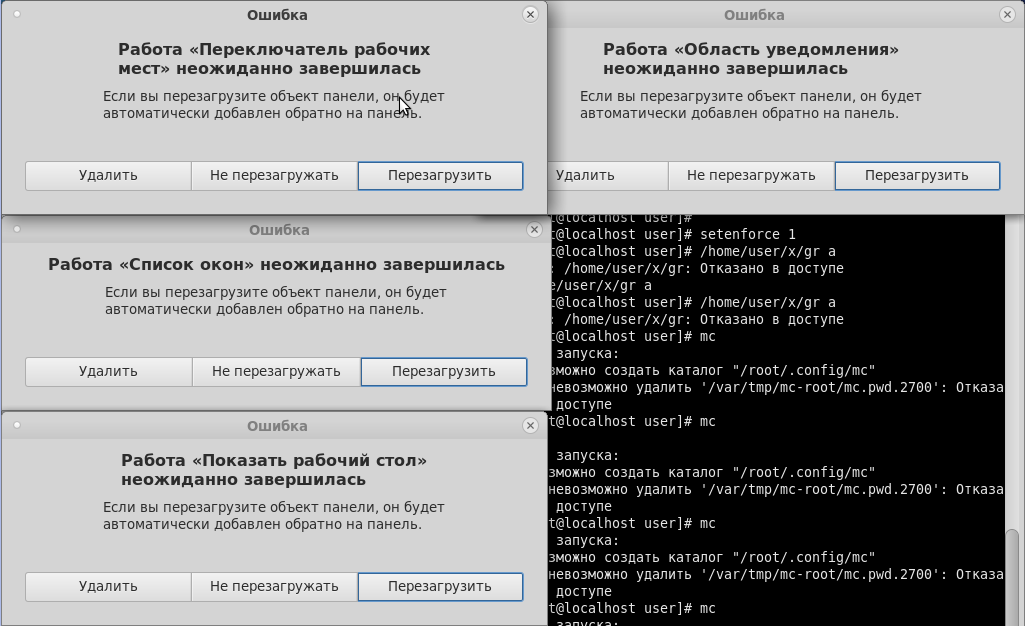
As we see, neither the graphical shell nor the console applications are able by default to correctly handle the situation when the system has a policy for working with several levels of secrecy. Accordingly, all this is necessary either to recycle or make your own, which is done in Astra Linux.
By the way, certification does not limit the freedom of system administrators in terms of enhancing protection. Passing certification reflects the satisfaction of the minimum requirements, but each company, government agency, and even each individual security officer can improve the system as they see fit. Certification only confirms the “necessary minimum” of the availability of information security functionality and the correctness of its work, as well as the vendor’s obligation to support this functionality throughout the life cycle, for example:
The certification procedure in practice is quite lengthy. However, the mentioned release was certified within just six months, which is quite fast, since this is the sixth version that has been tested. The previous five releases (and this is about ten years of development) Astra Linux went to getting certificates up to the second class, and without these developments it would not have been possible to debug all the protection mechanisms, adapt the code for verification, pass the necessary checks and “wipe” on first grade.
At the same time, it should be noted that at present, certification is not a freezing of the product, but a mandatory prompt elimination of identified vulnerabilities in a certified solution.
The most important thing that happened during these six months is that Astra Linux Special Edition has gone through a multi-level process of checking and analyzing the program code. In this case, different parts of the product were tested differently.
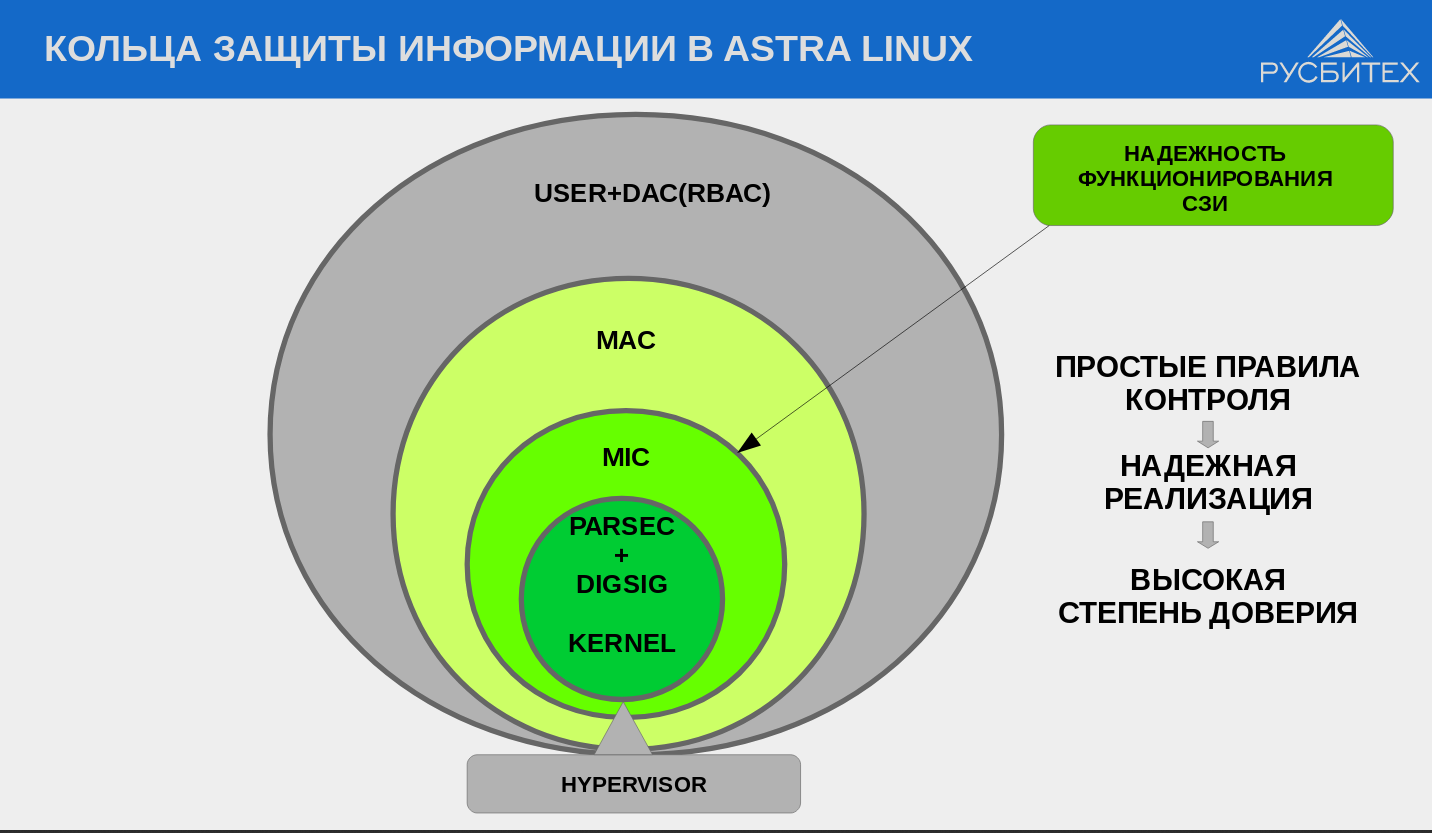
The most severely tested security system. In addition to the standard discretionary, it uses the mandatory role-based model of access control and integrity control, which maintains the secrecy of information existing in Russia - “secret”, “top secret”, etc. According to this model, each user account, process, file or directory is assigned a confidentiality label, by which the access rights are determined. For example, files created by the department of production of tanks of the “top secret” level are inaccessible to other departments with the access level “secret” or lower. In addition, all user accounts, processes, files, or directories are assigned an integrity label; as a result, for example, user low integrity processes will not be able to modify system high integrity files. Even if a user process gains system privileges as a result of exploiting a vulnerability, it will not be able to affect the performance of the system.
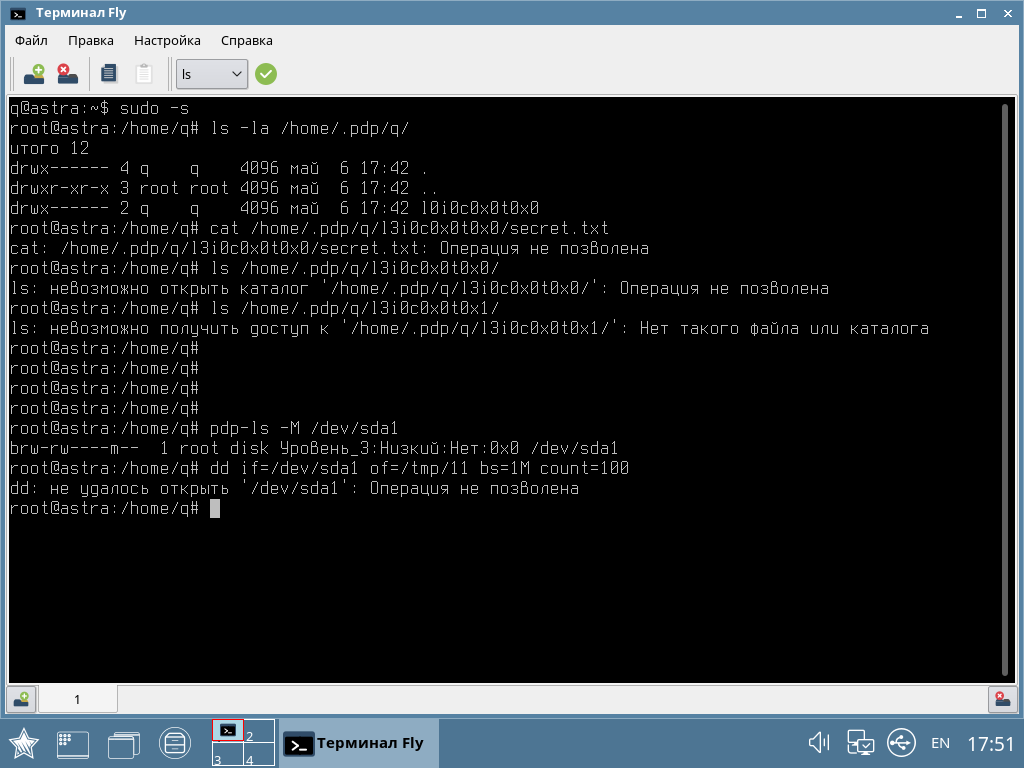
The screenshot shows an example of how a low-integrity user has received superuser rights, but cannot copy data.
To substantiate the security of such access, a mathematical model was built, which was tested for logical integrity, closure and correctness.
Further, the source codes of the security system were checked for compliance with the stated mathematical model. And this is a rather complicated and time-consuming procedure, which was performed jointly with the staff of the Institute for System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
It should be noted that now in Russia we can solve similar problems of checking the code for compliance with the mathematical model for components with a total complexity of up to 10 thousand lines. And the Astra Linux security system fits into these limits. But the Linux kernel is tens of millions of lines of code, and there are currently no tools for rigorous mathematical verification of a project of this size, not only in the company, but in the country as a whole. So, for them, other control mechanisms are used - with the help of static and dynamic code analysis tools from the same Institute of System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences or in-house development. The task of this stage is to check the code for errors, bookmarks or backdoors. Passing this check provides a high level of confidence in the code and, accordingly, the possibility of its certification for the first class of information protection.
Certification determines not only what the Astra Linux code looks like, but how the product (or rather its special version) is delivered to the user - it applies only to disks. This is connected both with the restrictions of the regulatory documents: to confirm that the program code has not been changed, and with the real objectives for the long-term storage of the original medium. Technically, this could be a flash drive, but they tend to break, while storage on an optical disc is more predictable (and there is a guarantee against overwriting).
At the moment, no one else can boast of certification for such a high level of protection.
But even if we assume that tomorrow there will be a competitor with a version of the OS that hypothetically could meet the conditions of certification, in the near future it will not be able to press Astra Linux. The barrier will be the very certification procedure, or rather its part concerning the verification of program code. According to our estimates, only the Institute of System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Astra Linux have the resources and scientific knowledge for this procedure.
If we evaluate the scientific and technical potential of companies, then theoretically certification in Russia could pass Microsoft products. The company has the necessary resources and competencies, they even talk about the importance of the task of verifying the code on YouTube. However, they are unlikely to open the source code. And even more so they will not refine their security model to Russian requirements (let me remind you, the United States has a different list of requirements for state certification).
Perhaps, Google and Kaspersky Lab could go the same way with their project protected by Kaspersky OS. However, we have no information about them. The company "Basalt" tried to go for certification in the second class. But it is not yet clear to us whether they have technical and scientific potential.
In fact, Astra Linux has a lot of clients, because the system was introduced before certification. And the potential market is large enough - these are the bodies of military and state administration, working with any information of limited access. In the absence of a certified OS, these organizations created their own information systems — they assembled existing solutions, modified them within individual projects, in order to be certified to work with data requiring protection. However, such solutions are expensive and not always optimal. Suppose there is no system that would allow access to the three levels of secret data within the same workplace - it means that you can use three different computers and issue the keys against a signature in the journal (i.e., you can solve the problem administratively, though not the easiest and most convenient). This does not correspond to the current level of IT development. And the development of such systems requires considerable time, because there is a need for an individual threat model (relevant specifically for this system), and additional protection components, and the certification procedure itself.
A serial product - in this case Astra Linux Special Edition - is cheaper, more logical, more modern, although it requires administrators to complete the training phase. Otherwise, it will be difficult to configure a security system that has no analogues in software for a wide range of users.
Astra Linux is suitable for deployment even at the highest levels of management. For example, the President’s Administration plans to switch to this product. The transition to Astra Linux was included in the plans for a long time, but at that time the system could not be implemented, because did not have integration with the required components. The operating system does not exist by itself, but is embedded in a certain ecosystem of software products - antiviruses, protection systems of communication channels, etc. Since then, a new version of Astra Linux has been released, under which certification of the necessary solutions, for example, Kaspersky Anti-Virus 10th version, has already begun. And work with manufacturers of other software products and protection systems continues.

What is Astra Linux?

Astra is a domestic Linux distribution that combines components from the community, distributed under open licenses such as GPL, MPL, Xiph License, etc., and software developed by the same-name group of companies. The user functionality is closed for the most part by components of the open source software - standard Linux mechanisms are used to perform basic tasks, such as running applications, virtualization, supporting hardware, or the same Steam. The components of their own design basically solve two key tasks: ensuring security, as well as the interaction of the graphical interface of the operating system and the person.
')
From the point of view of licensing, a distribution kit is a complex object (a concept from part 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), i.e. composite work, so its distribution in general has some limitations. Although all components of open source software included in the product retain their free status.





Versions of Astra Linux exist for a wide variety of platforms. The name of the platform is “hidden” in the first digit of the version number:
- 1 and 2 - Intel (versions Smolensk and Eagle);
- 3 - IBM System Z (Murmansk);
- 4 - ARM (Novorossiysk)
- 6 - MIPS processors (Sevastopol);
- 8 - Elbrus (Leningrad).
It would seem that an unusual solution is to place the type of platform in the first position, having received a strange sequence of versions - 1.6, 2.12.13, 8.1, etc. But this is done consciously in order to simplify the life of technical support, since the visually graphical interface of the operating system looks the same on any hardware platform, regardless of the computer’s intended use: from the server to the smartphone. So in a conversation with the user can quickly understand what kind of platform in question.
By the way, the version for each platform has its own code name in honor of one of the cities-heroes of Russia. There are no guidelines here, we rely on the feeling of beauty.
Among the Astra versions being developed there are both normal distributions and protected ones (Special Edition), oriented to work with confidential data, certified according to the information security requirements of all Russian certification systems. From the point of view of the user feature set, the versions are almost the same. However, the protection system in them is built in different ways. Some components of the ad hoc version required to work with confidential data, although they are not necessarily redundant for regular users and businesses, are not included in the regular version, since regulatory and legal framework of the Russian Federation requires their mandatory certification.
Basic version - what and for whom
The normal version of Astra Linux is targeted at corporate customers. For home users, when using for non-commercial purposes, the license is free - but in development we strive to meet the needs of the corporate segment. In the end, we are also a commercial company, and the home users segment is a very difficult one. There are various Linux distributions for them, including free ones.
The usual version of Astra Linux uses the discretionary access control model - users themselves determine to whom they can grant access rights to their files. Third-party programs (browsers, office suites, etc.) run in the same way as in other Linux distributions.

Like any other software, a regular version of Astra Linux can be downloaded or purchased (for organizations) in electronic form without any physical media. By the way, this version is also posted on the resource of the international community Linux, where there is a good external channel.
Following global trends, the version is actively developing towards the support of new equipment and technologies.
Special version
In addition to the usual versions, Astra Linux has the so-called special versions - Special Edition, which are developed with the expectation of certification by the FSTEC of Russia and other certification systems. From the point of view of the user functionality, the special version is practically no different from the usual one. However, it implements additional components to improve security (just self-written), in particular:
- Mandatory Model of Access Control (MAC) and Integrity Control (MIC), when all system components are hierarchically divided by degree of importance for its security from the most untrusted, user-defined (integrity level 0), to system administrative ones (default integrity level 63);
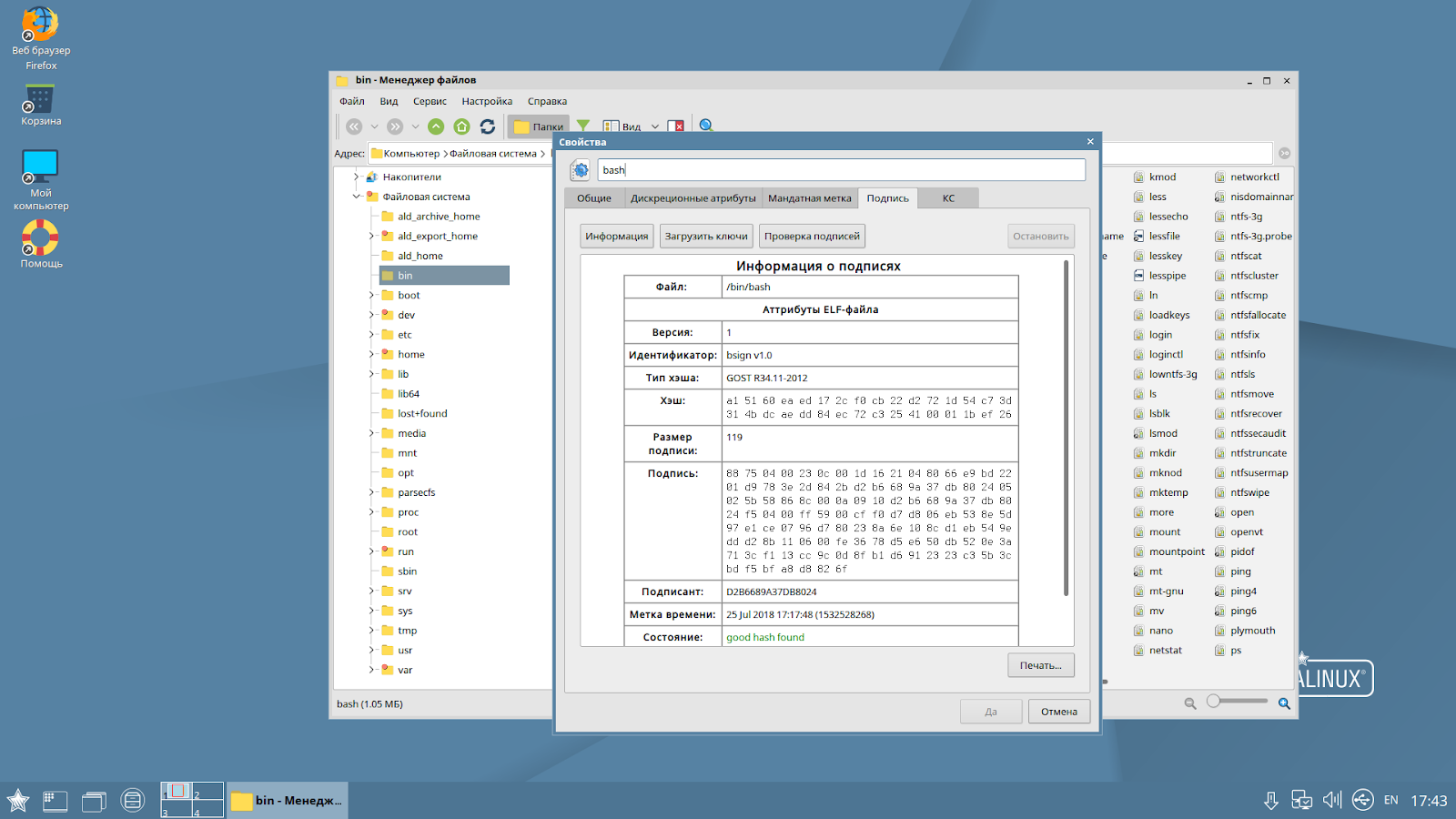
- Automatic verification of the digital signature of any file in the system to protect against unauthorized changes. In fact, the EDS mechanism can block not only individual files, but even scripts written in any text editor in languages like Python or Perl. When trying to start or open a file, the module hanging in memory checks the correctness of the digital signature on the fly and decides whether it can be started. In the case of scripts, EDS is not placed in the script itself, but in the extended attributes of the file system. Separately, I would like to note the use of the term "digital signature" in relation to the implemented security features. This name is intentionally taken from the national standard GOST R 34.10 and is used in our documentation and reference materials in order to clearly separate the security function implemented in Astra Linux from the task of ensuring the legal value of an electronic document, which is solved by appropriate means of creating and verifying an electronic signature;

- kiosk mode, at the kernel level allowing the launch of a well-defined set of applications;
- restriction of work with interpreted programming languages;
- restricting user access to the console;
- the possibility of overwriting files on the disk with sequences of zeros and ones in several passes;
- blocking the connection of "unfamiliar" external devices that prevents malware from entering the system through various tricks with flash drives. It is no secret that enterprise systems can be compromised by simply scattering cute flash drives with malware around the building with the expectation that one of the employees will pick up. In our case, this trick will not work.
Of course, this is not a complete list. There are lots of other modules and components. All these tools work independently of each other, providing such separation of the security system. All the listed security functions are implemented on the basis of original domestic computer security developments without using the SELinux developed by the NSA.

At the same time, they are turned on and off independently of each other (by the system administrator). For some components there are different modes of operation. For example, for the EDS verification tool, you can turn on the learning mode, when files with the wrong EDS (or which do not have it) still run, but a warning is issued at the system level. All these mechanisms are configured by the administrator under the security policy defined by the management. At the same time, almost the entire setup is already carried out as in the graphic mode. Of course, administrators have access to a full range of console-based tools for automating tasks for configuring and configuring security subsystems.


The current version of Astra Linux Special Edition - Smolensk 1.6.
The special version develops like the regular one, but innovations only get into it after testing and running in a regular release.
How we prepared a special version for certification
Each security and system administrator in their own way prioritize information security issues. Ask them to create a project to protect a certain IT infrastructure, and each will offer their own solution, since they will see their own threats and accents. If we are talking about commercial companies, the decision about whose opinion to listen, takes the business - at your own peril and risk.
At the state level, any risk must be minimized, so we need general mechanisms for assessing the effectiveness of protection, or rather, confirmation that information systems can withstand a certain set of threats. To do this, certain security functions must be implemented in the systems (for example, password checking, access control functions, etc.), and on the other hand, the development process and the code of this system itself must meet certain trust requirements. The task of the certification system and the certifying authority is to check the specific product for compliance with all functional conditions as well as the requirements of trust.
Depending on the functionality of information systems, various departments deal with the issues of their certification for the possibility of using them in working with important data. For example, FSTEC of Russia is engaged in certification of information security tools. However, the FSB and the Ministry of Defense also have their own systems of certification of protection. By the way, Astra Linux Special Edition is the only OS that has all the certificates in our country.



Degrees of secrecy
With regard to data processing systems of limited access, the nature of this data plays an important role - it is information for free distribution, personal data, valuable medical information, state secrets, including information of particular importance. It is logical that for each degree of secrecy there is a list of functional requirements and criteria for evaluating the “power of attorney” of the information systems code - its own protection class, including the level of trust. The list of requirements for each subsequent level includes a list for the previous level, as well as some additional conditions. This practice exists in many countries. In addition, each insists on some of its own criteria, and even in its own way shares data by levels. Russia has adopted six classes, with the sixth one being the lowest, and the first one being the highest.
The lower classes - from the sixth to the fourth - are the requirements for the protection of personal data, as well as commercial and official secrets. In the Russian market, products corresponding to these classes are no longer uncommon. We will talk about certification for the highest classes - from the third to the first - with the “secret”, “top secret” and “special importance” stamps (living examples are the drawings of the new Sukhoi fighter or general data on the state of critical infrastructure in the country, not so long ago equivalent to state secrets). And here the most difficult thing is not even functional requirements (in the end, developing something is not a problem), but confirmation of trust in the OS. For this, a correct mathematical model of data access control and a justification of the compliance of a real software product with this mathematical model is necessary. Those. the procedure for developing a system focused on working with sensitive data is many times more complicated.
Here is an example of the system's reaction to the inclusion of the MLS (multi level security) policy in SELinux in the Fedora distribution:

As we see, neither the graphical shell nor the console applications are able by default to correctly handle the situation when the system has a policy for working with several levels of secrecy. Accordingly, all this is necessary either to recycle or make your own, which is done in Astra Linux.
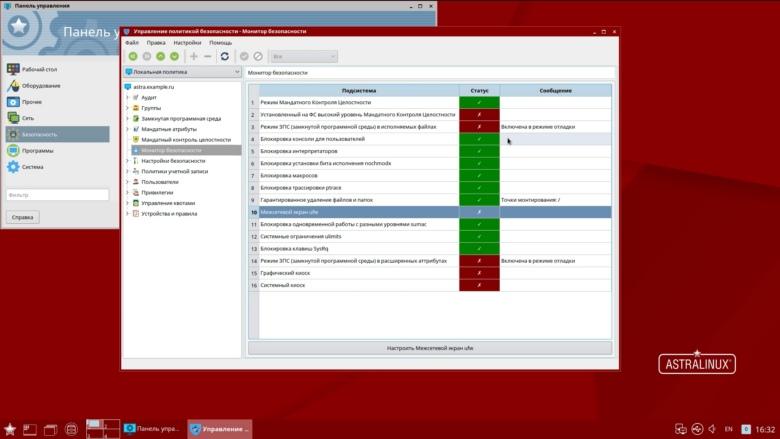
By the way, certification does not limit the freedom of system administrators in terms of enhancing protection. Passing certification reflects the satisfaction of the minimum requirements, but each company, government agency, and even each individual security officer can improve the system as they see fit. Certification only confirms the “necessary minimum” of the availability of information security functionality and the correctness of its work, as well as the vendor’s obligation to support this functionality throughout the life cycle, for example:
- identification and authentication;
- access control;
- security event logging;
- restriction of the software environment;
- process isolation;
- memory protection;
- integrity control;
- ensuring reliable operation;
- network flow filtering

Preparation for certification
The certification procedure in practice is quite lengthy. However, the mentioned release was certified within just six months, which is quite fast, since this is the sixth version that has been tested. The previous five releases (and this is about ten years of development) Astra Linux went to getting certificates up to the second class, and without these developments it would not have been possible to debug all the protection mechanisms, adapt the code for verification, pass the necessary checks and “wipe” on first grade.
At the same time, it should be noted that at present, certification is not a freezing of the product, but a mandatory prompt elimination of identified vulnerabilities in a certified solution.
The most important thing that happened during these six months is that Astra Linux Special Edition has gone through a multi-level process of checking and analyzing the program code. In this case, different parts of the product were tested differently.
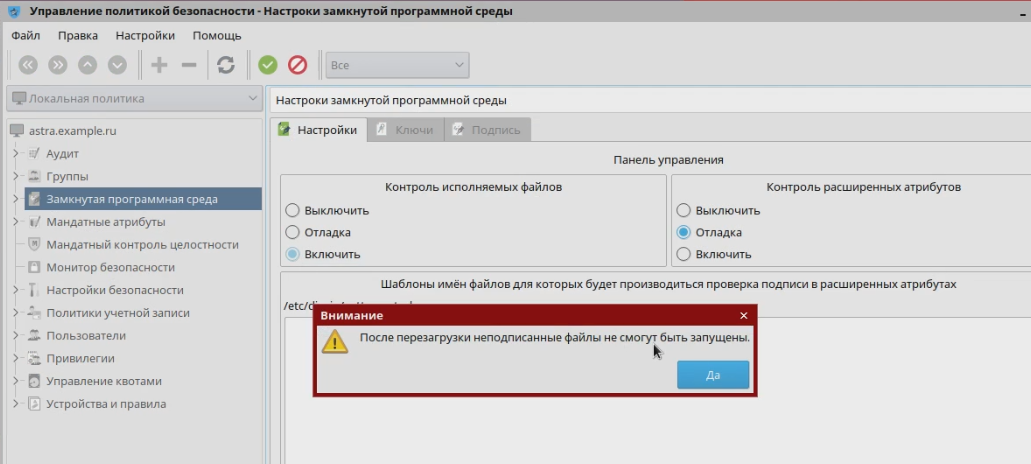
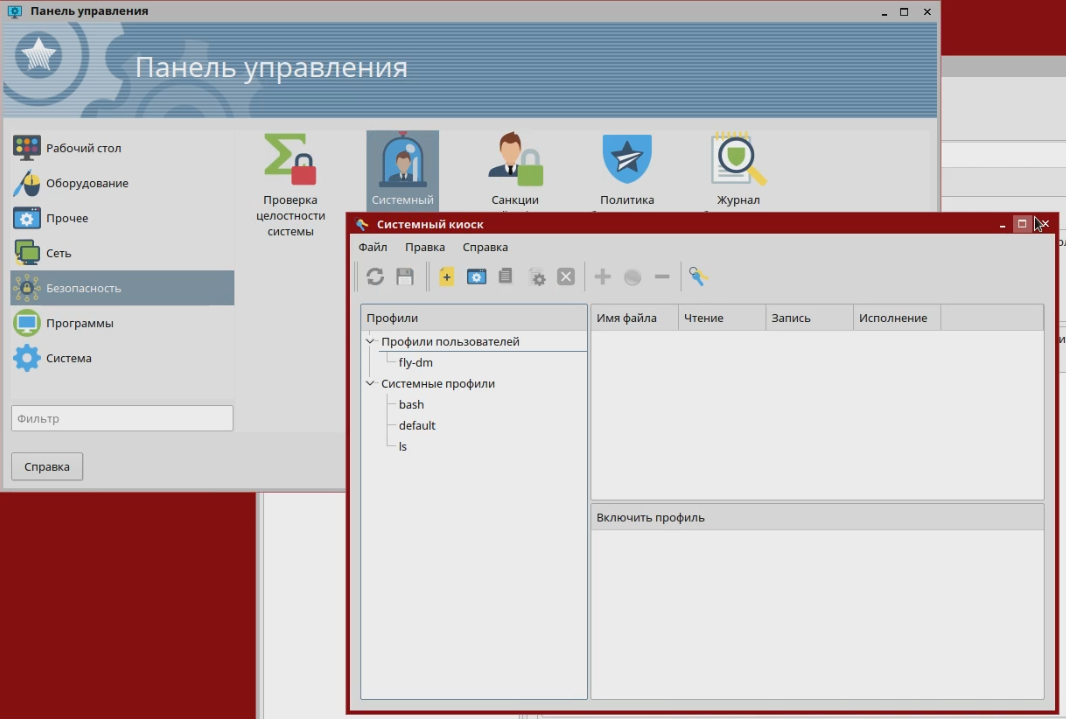
The most severely tested security system. In addition to the standard discretionary, it uses the mandatory role-based model of access control and integrity control, which maintains the secrecy of information existing in Russia - “secret”, “top secret”, etc. According to this model, each user account, process, file or directory is assigned a confidentiality label, by which the access rights are determined. For example, files created by the department of production of tanks of the “top secret” level are inaccessible to other departments with the access level “secret” or lower. In addition, all user accounts, processes, files, or directories are assigned an integrity label; as a result, for example, user low integrity processes will not be able to modify system high integrity files. Even if a user process gains system privileges as a result of exploiting a vulnerability, it will not be able to affect the performance of the system.

The screenshot shows an example of how a low-integrity user has received superuser rights, but cannot copy data.
To substantiate the security of such access, a mathematical model was built, which was tested for logical integrity, closure and correctness.
Further, the source codes of the security system were checked for compliance with the stated mathematical model. And this is a rather complicated and time-consuming procedure, which was performed jointly with the staff of the Institute for System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
It should be noted that now in Russia we can solve similar problems of checking the code for compliance with the mathematical model for components with a total complexity of up to 10 thousand lines. And the Astra Linux security system fits into these limits. But the Linux kernel is tens of millions of lines of code, and there are currently no tools for rigorous mathematical verification of a project of this size, not only in the company, but in the country as a whole. So, for them, other control mechanisms are used - with the help of static and dynamic code analysis tools from the same Institute of System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences or in-house development. The task of this stage is to check the code for errors, bookmarks or backdoors. Passing this check provides a high level of confidence in the code and, accordingly, the possibility of its certification for the first class of information protection.

Certification determines not only what the Astra Linux code looks like, but how the product (or rather its special version) is delivered to the user - it applies only to disks. This is connected both with the restrictions of the regulatory documents: to confirm that the program code has not been changed, and with the real objectives for the long-term storage of the original medium. Technically, this could be a flash drive, but they tend to break, while storage on an optical disc is more predictable (and there is a guarantee against overwriting).
What about competitors?
At the moment, no one else can boast of certification for such a high level of protection.
But even if we assume that tomorrow there will be a competitor with a version of the OS that hypothetically could meet the conditions of certification, in the near future it will not be able to press Astra Linux. The barrier will be the very certification procedure, or rather its part concerning the verification of program code. According to our estimates, only the Institute of System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Astra Linux have the resources and scientific knowledge for this procedure.
If we evaluate the scientific and technical potential of companies, then theoretically certification in Russia could pass Microsoft products. The company has the necessary resources and competencies, they even talk about the importance of the task of verifying the code on YouTube. However, they are unlikely to open the source code. And even more so they will not refine their security model to Russian requirements (let me remind you, the United States has a different list of requirements for state certification).
Perhaps, Google and Kaspersky Lab could go the same way with their project protected by Kaspersky OS. However, we have no information about them. The company "Basalt" tried to go for certification in the second class. But it is not yet clear to us whether they have technical and scientific potential.
Who uses Astra?
In fact, Astra Linux has a lot of clients, because the system was introduced before certification. And the potential market is large enough - these are the bodies of military and state administration, working with any information of limited access. In the absence of a certified OS, these organizations created their own information systems — they assembled existing solutions, modified them within individual projects, in order to be certified to work with data requiring protection. However, such solutions are expensive and not always optimal. Suppose there is no system that would allow access to the three levels of secret data within the same workplace - it means that you can use three different computers and issue the keys against a signature in the journal (i.e., you can solve the problem administratively, though not the easiest and most convenient). This does not correspond to the current level of IT development. And the development of such systems requires considerable time, because there is a need for an individual threat model (relevant specifically for this system), and additional protection components, and the certification procedure itself.
A serial product - in this case Astra Linux Special Edition - is cheaper, more logical, more modern, although it requires administrators to complete the training phase. Otherwise, it will be difficult to configure a security system that has no analogues in software for a wide range of users.
Astra Linux is suitable for deployment even at the highest levels of management. For example, the President’s Administration plans to switch to this product. The transition to Astra Linux was included in the plans for a long time, but at that time the system could not be implemented, because did not have integration with the required components. The operating system does not exist by itself, but is embedded in a certain ecosystem of software products - antiviruses, protection systems of communication channels, etc. Since then, a new version of Astra Linux has been released, under which certification of the necessary solutions, for example, Kaspersky Anti-Virus 10th version, has already begun. And work with manufacturers of other software products and protection systems continues.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/456622/
All Articles