Tests of the drifting stratostat. Launch of Rogozin and LoRa into the stratosphere
Recently, one can increasingly see launches of amateur latex meteo-probes, which have a heated box with a camera, a GPS beacon and a power source as their payload. The flight of such devices is usually limited to 2-3 hours, during which the device reaches the stratosphere and lands at 80-100 kilometers from the launch site.

Preparing to launch our drifting stratostat
Can a stratostatus fly longer, farther and more stable? Yes maybe. The stratostats of the Zero-Pressure and Super-Pressure categories come to the rescue. We chose Zero-Pressure as the first experience, because This technology is time-tested and fairly simple.
Flight technology
The essence of this technology is to maintain a “zero” pressure inside the gas envelope, while the Super-Pressure casings drift at the expense of an excess of gas pressure. When climbing, the gas expands. The meteorological probe at peak pressure is broken, and the Zero-Pressure shell releases excess pressure and remains to drift in the jet currents before the sun goes down. When the sun goes down, the air begins to cool and the machine is reduced. For flights lasting more than 1-2 days, a supply of ballast is needed; it compensates for the loss of gas lift (helium, hydrogen).

Image of Zero-Pressure and Super-Pressure Stratostatic Flight Profiles
Shell
For the first launch, we made a pumpkin-shaped shell with a volume of 170m3, a height of 5 meters and a diameter of 8 meters. Pumpkin form, because it optimally distributes the pressure inside the shell. We did not require a large payload and height from the first flight, the task was to obtain information about the moment of achieving neutral buoyancy and drift of the device in order to further increase the duration of flights and the shells volumes (fly Zero-Pressure from 2 to 55 days).
Model of pumpkin shell of eight segments
Technical part
The tasks of the stratostat were divided into two stages:
- First stage (returnable) - modular platform with parachute
- Second Stage (Drifting) - Zero-Pressure Shell with Radiosonde
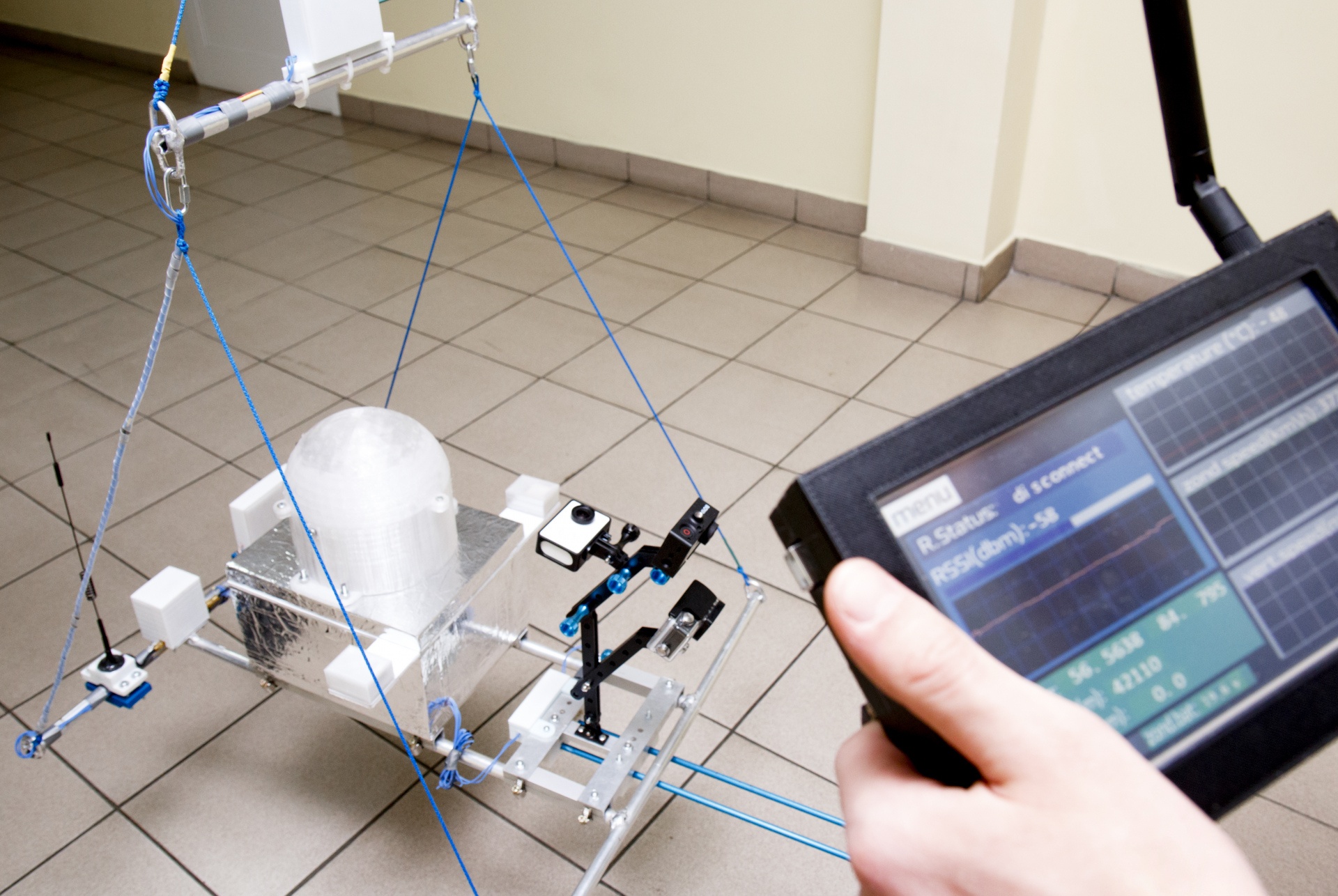

Modular platform with telemetry receiving tablet
First stage, modular platform
The first stage platform is an aluminum frame, which, in addition to its basic function (module fixing), is part of the antenna system and radiator for the Lawmate 1.2GHz video transmitter and a 433 MHz LoRa modem amplifier with a power of 1 and 2 watts.
It has the following communication channels:
- LoRa 433MHz, telemetry transmission
- Lawmate 1.2GHz, video broadcast with OSD
- GlobalStar, location information
- GSM, telemetry
- search beacons 433/868 MHz, search for the device in the landing area by signal level
The flight controller that collects and controls power relays and transistors is based on AtMega2560. To assist the flight controller, a LoRa-GSM modem is installed on the AtMega328p, which collects telemetry from the PC and transmits it to the ground.
Video is recorded on 2 shielded GoPro Hero 4 Black with a view of the horizon and Yi 2k with a view of the gas shell.
The power source are 2 batteries NiMH 12v 4500mah and LiPo 11.1v 2000mah.
Second stage, radiosonde
The second-stage radio probe performs a very important function - disconnecting the steps. Without undocking, the payload will fly to China, Mongolia or North Korea, which we certainly do not need.
To accomplish this task, the radiosonde detects the moment of achieving neutral buoyancy (drift), after which it waits 30 minutes and disconnects.
In addition to this task, if you are lucky with the cellular coverage, the radiosonde communicates via GSM and transmits the data recorded in the memory in the form of a flight path, profiles of temperature changes and battery charge.
The power source is a LiPo 11.1v battery with a capacity of 3800mah.
Payload
Since this test we could not launch a commercial payload, but it would also be wrong to leave the launch without a payload. The program of ADA launches by the Russian Ministry of Defense ended in 2013, and, since it was the only client on ADS in DKBA, since that time there were no ADA launches in Russia and the CIS. Our, albeit indirect, task was to draw attention to ADS. Through a survey in one of the cosmic communities of the social network Vkontakte, we determined the desired payload, which was the seven with Rogozin.

Rogozin as a first stage payload
Launch
4 days before launch, we submitted a flight plan to Rosaviatsia, after which on June 2 we received permission at 06:00 am (permission is given on launch day).
Preparations for the launch began with the sweep-filling of the shell and the installation of a relay station on the roof, a case with receiving equipment on the ground.
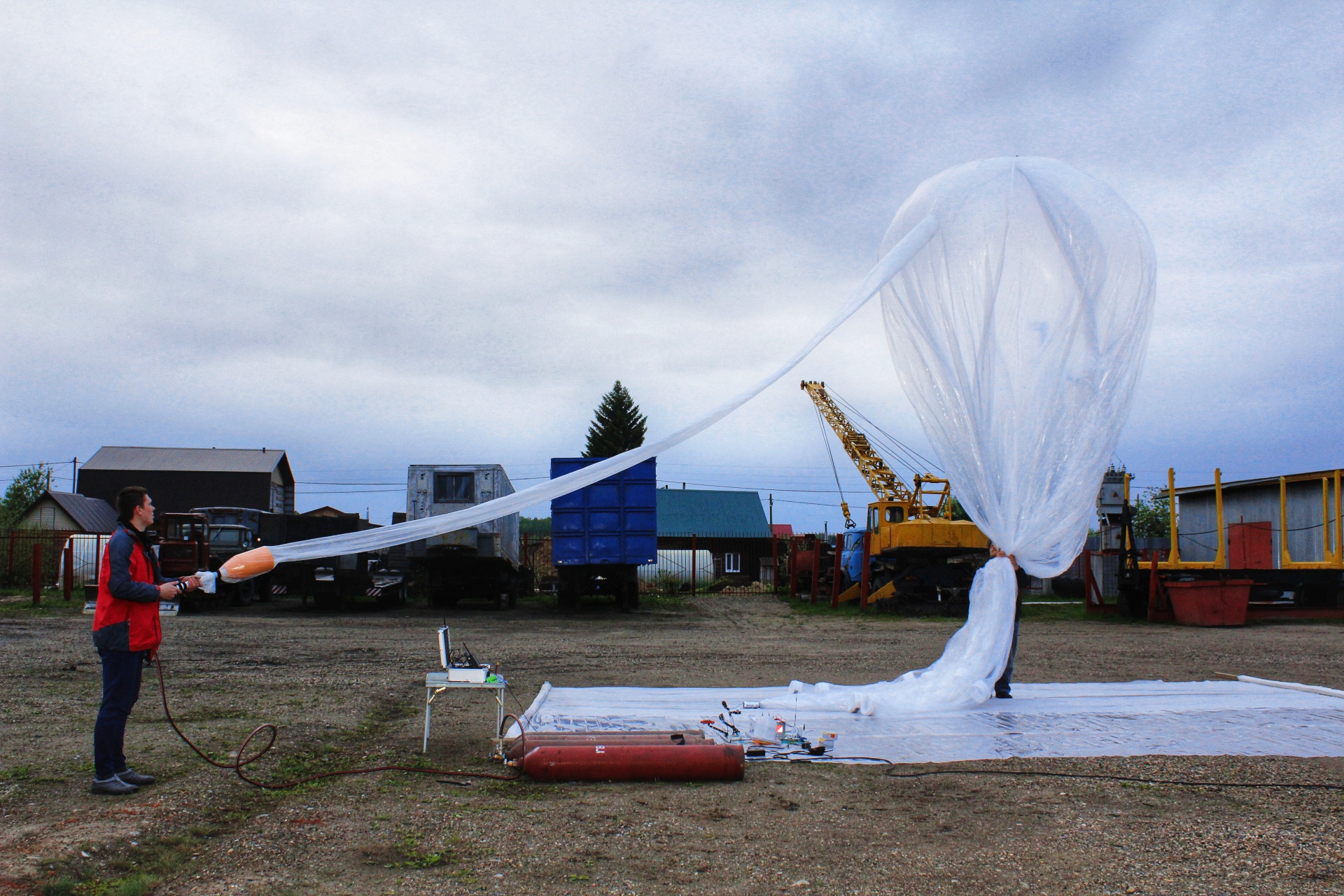

Filling the gas shell of the stratostat
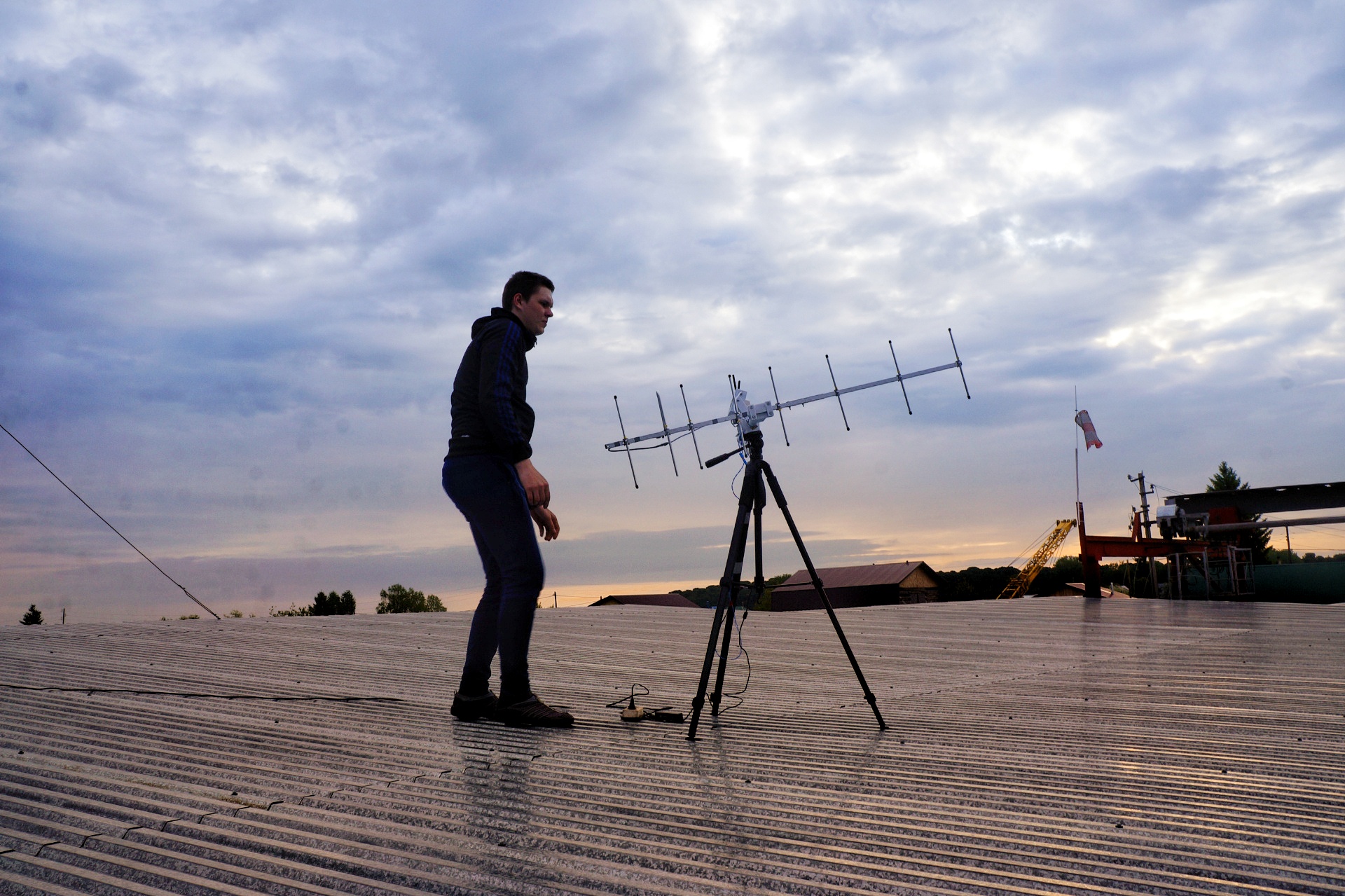

Relay station (LoRa, Lawmate)
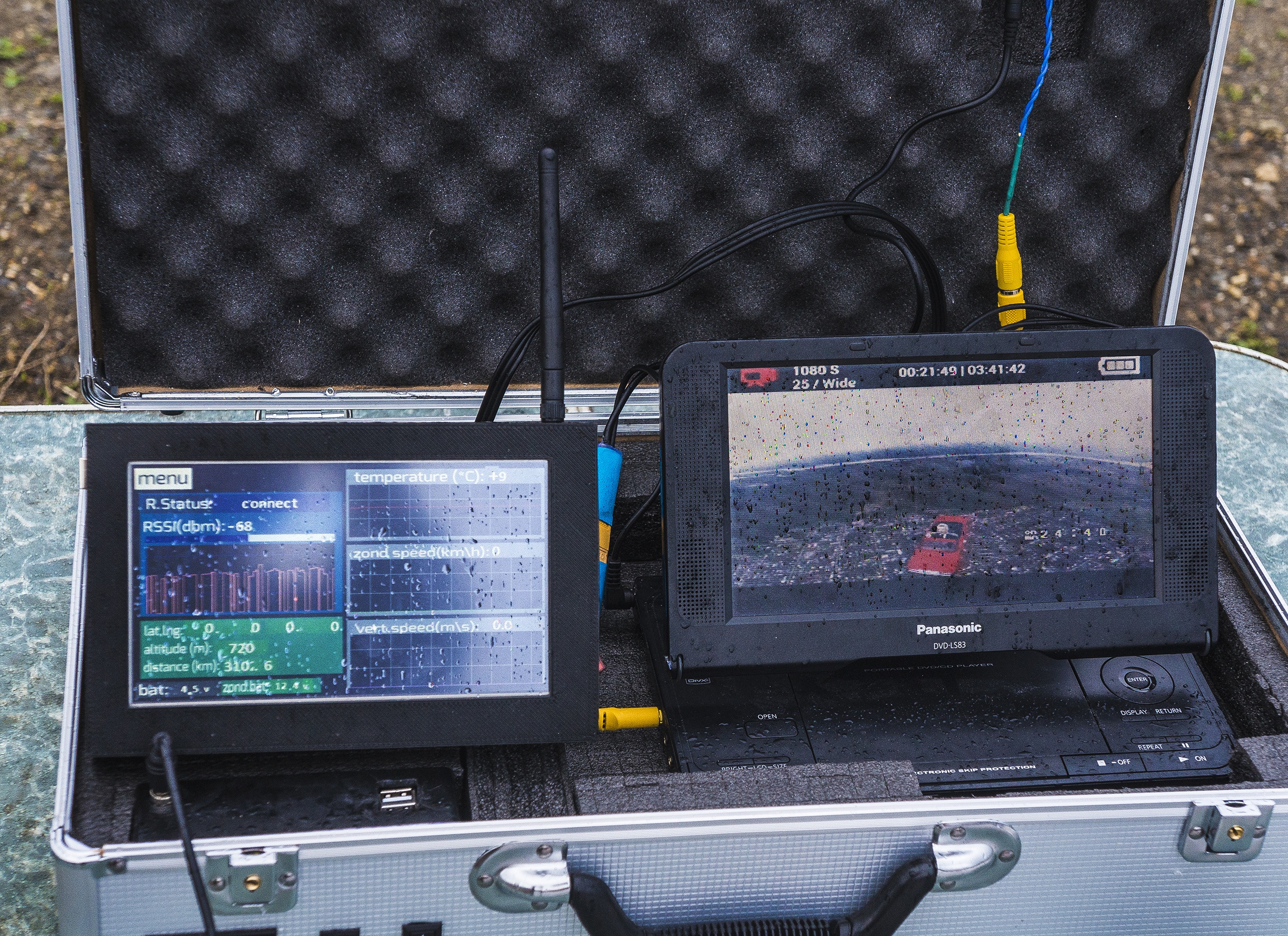

Case with receiving equipment
The filling of the shell took almost four 60-liter helium balloons, which provided a lifting force of 13 kilograms, which is enough to launch 9 kilograms of cargo with a lifting speed of 2.5 m / s.
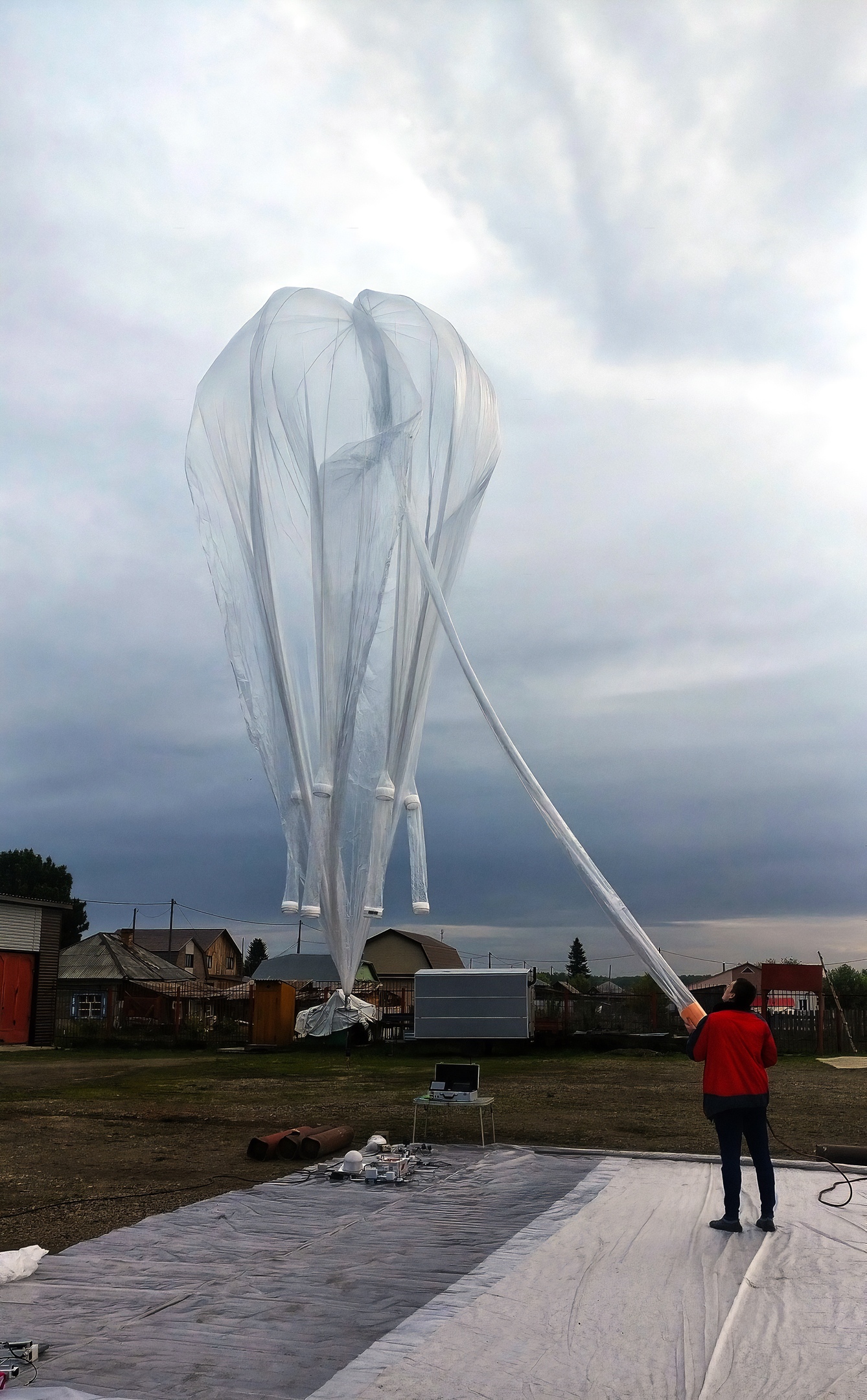

Helium Refill Shell
After filling the shell, we started the launch of the equipment and the stepwise assembly of the device, collected the first and second stages of the stratostat. The height of the shell at the start was 10 meters, the total height of the vehicle was 20 meters.
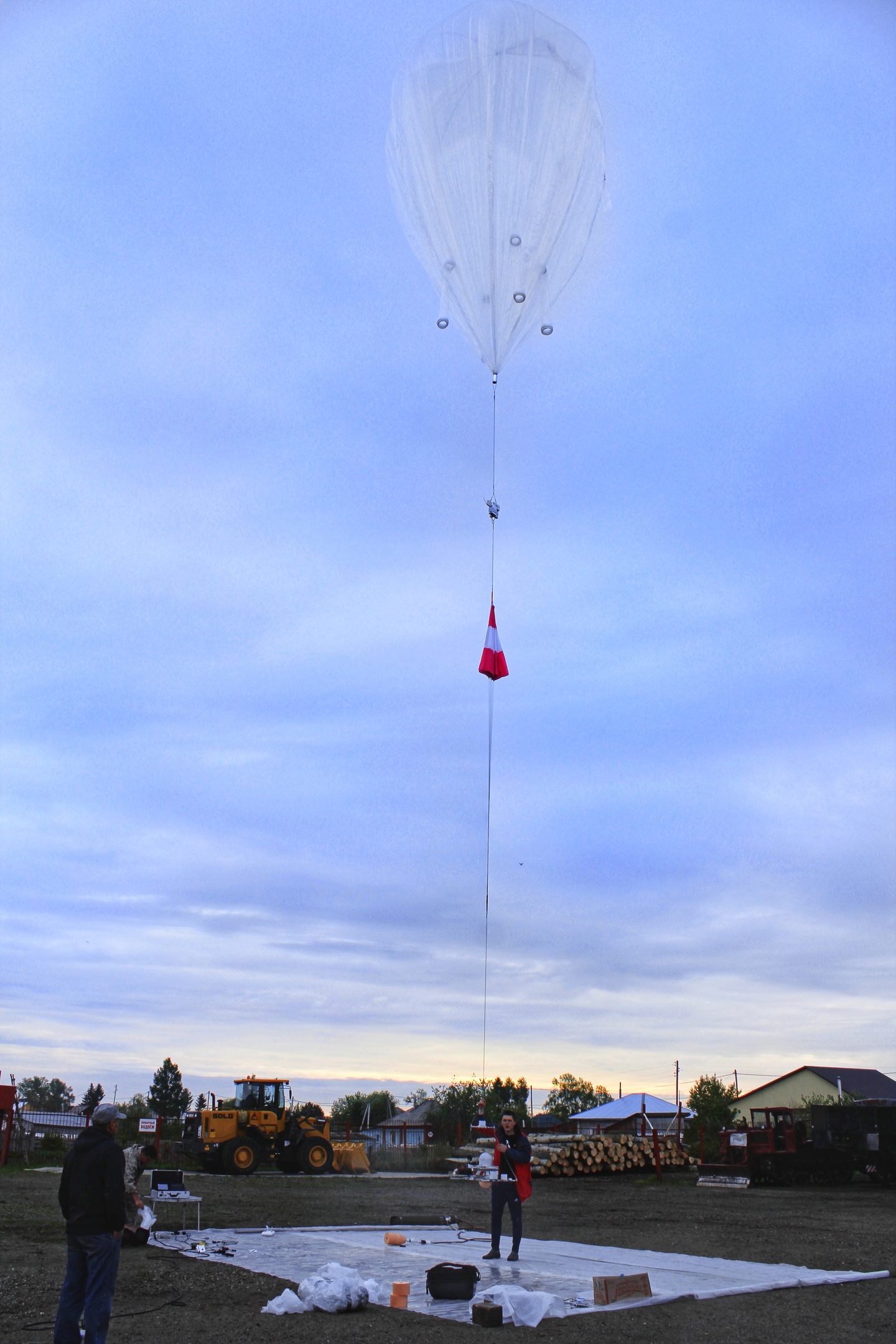

Stratostat 10 seconds before launch
Good windless weather (with the exception of light rain) allowed the stratostat to run almost unhindered.
The stratostat rose at a speed of 2.5 m / s, after 1 hour and 10 minutes, he strained the excess helium for 40 minutes, after which he undocked the first stage. The first step began parachute landing at a speed of 4-5m / s (which took 45 minutes), while the second step continued to climb, after which it drifted at altitudes of 18-20km for 10 hours and the accelerating decline began due to sunset .

Infographic of stratostat flight
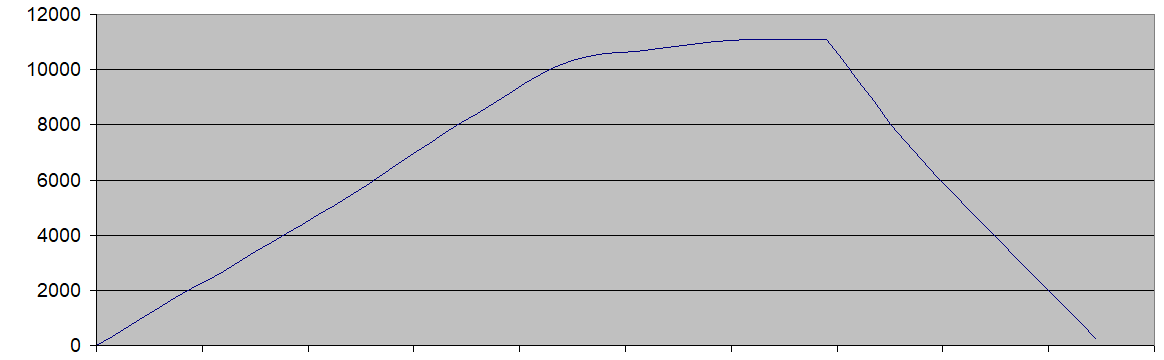
First step height profile
Despite the cloudy weather, LoRa showed itself very well when transmitting data at a distance of 120 kilometers. Video broadcasting on Lawmate 1.2GHz equipment was available at a distance of up to 60 kilometers, which is not bad in similar weather. The GlobalStar beacon worked steadily, transmitting location information every 2.5 minutes.
Startup Video
The second stage was a bit unlucky with the cellular coverage, during its flight it had a GSM connection five times available. Received information on overcoming the altitude of 18 kilometers and landing 16 hours after launch.
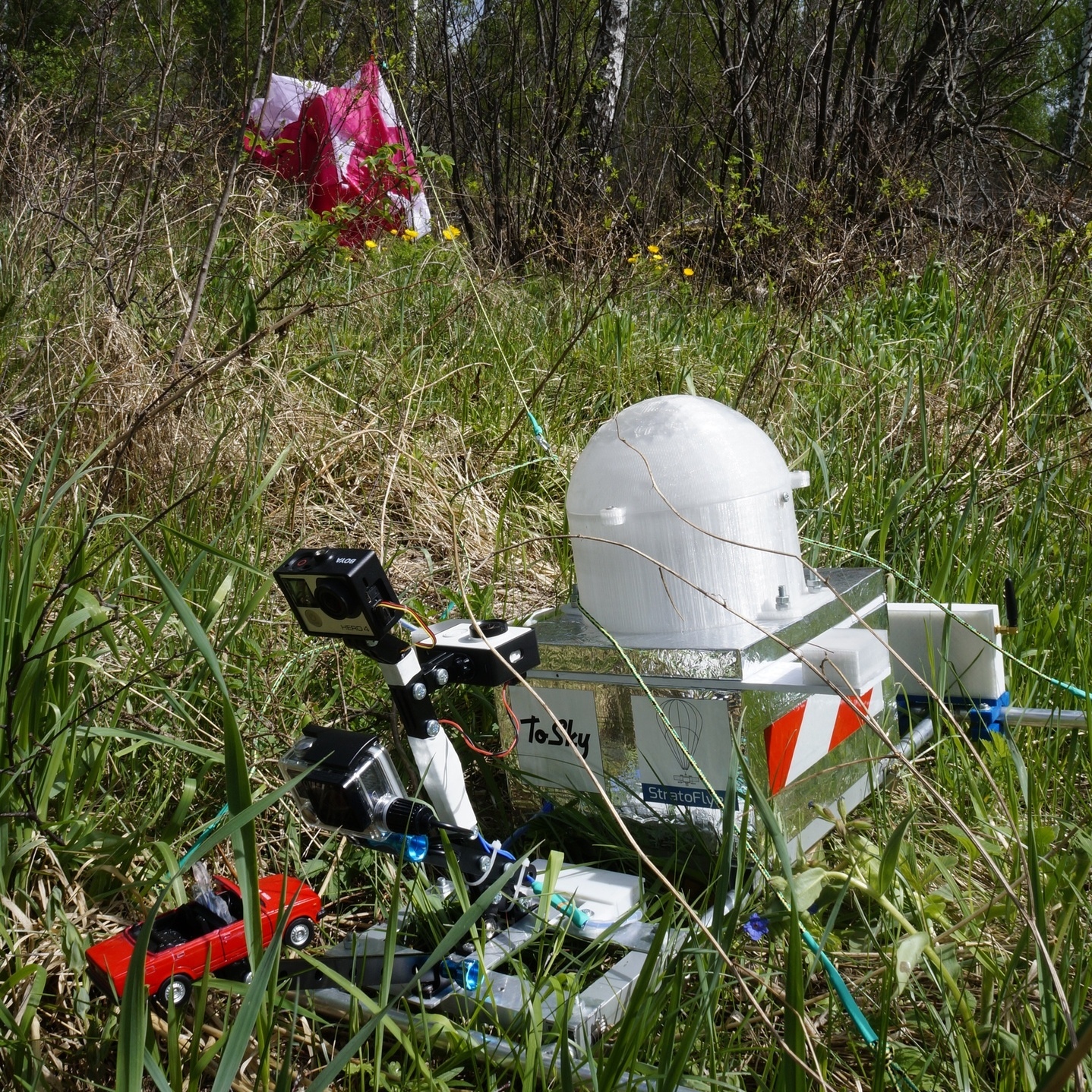

Landed first stage
In general, the mission was successful. The industry of automatic stratostats in Russia began its revival through private efforts. Gradually, the duration of flights will increase, one and a half to two weeks of stay in the jet streams of the stratosphere is enough to fly around the planet.
Planned flight duration of 2-3 days with testing AirMax, iridium communication channels. We will test the stratostat, as a means of organizing WISP networks with a coverage of more than 150 kilometers (check the project Loon and AirBus models).
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/455754/
All Articles