Cable TV networks for the smallest. Part 7: Optical Receivers

The boundary between the optical medium and the coaxial cable is an optical receiver. In this article we consider their design and configuration.
Content of a series of articles
- Part 1: The overall architecture of the CATV network
- Part 2: Composition and waveform
- Part 3: Analog Signal Component
- Part 4: The digital component of the signal
- Part 5: Coaxial distribution network
- Part 6: RF Amplifiers
- Part 7: Optical Receivers
- Part 8: Optical Trunk Network
- Part 9: Head Station
- Part 10: Troubleshooting on a CATV network
The task of an optical receiver is the transfer of a signal from an optical medium to an electrical one. In its simplest form, this can be done with the help of a passive device, which bribes its simplicity:

')
However, this engineering miracle provides very mediocre signal parameters: with the optical signal level of -1 - -2 dBm, the output parameters barely fit into the GOST, and overestimation of the signal leads to a significant increase in noise.
To be sure of the quality of the delivered signal, the FTTB architecture requires the use of more complex devices:
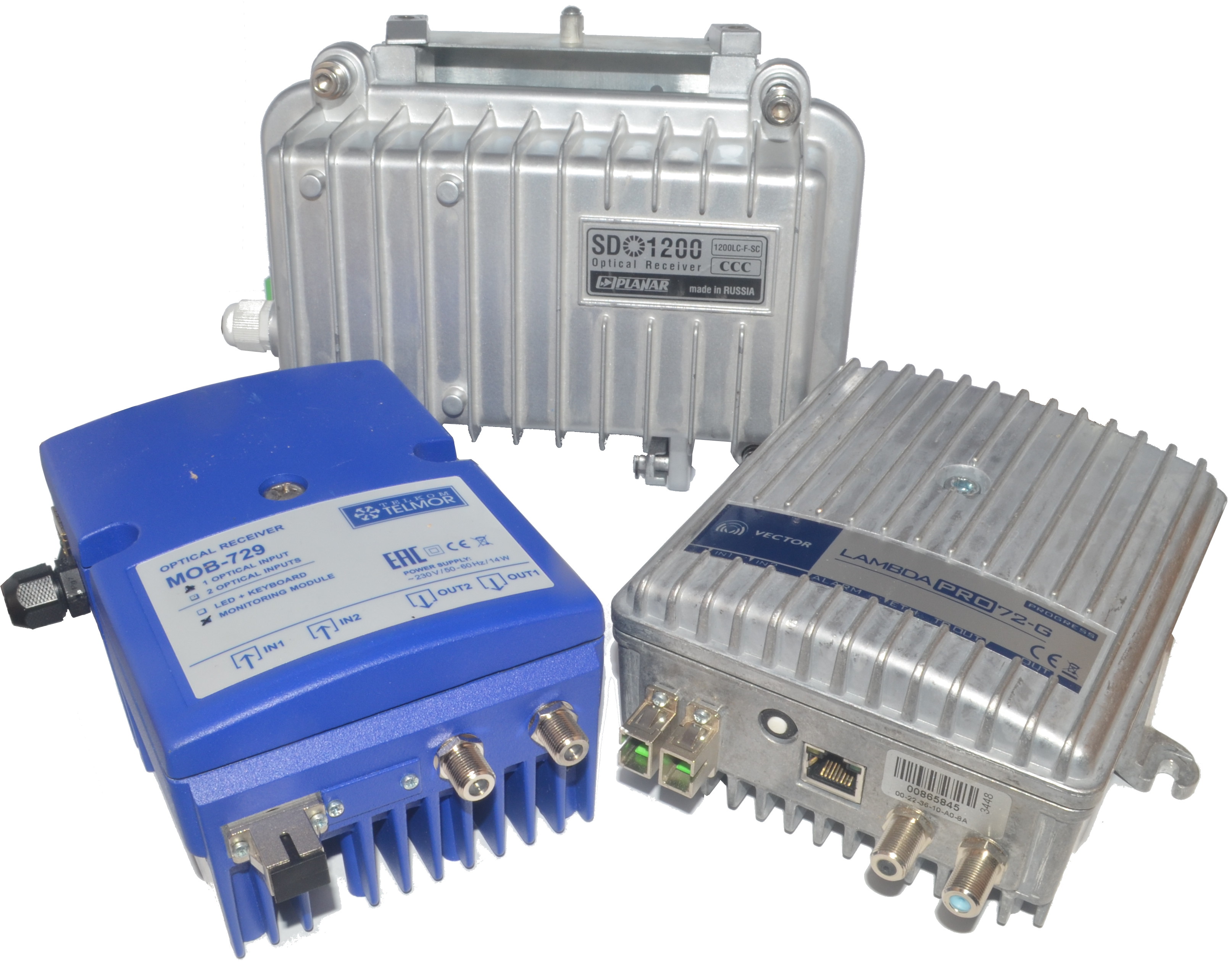

Receivers found in our network: Vector Lambda, Telmor MOB and domestic Planar.
They all differ from their passive younger brother in more complex circuitry, including filters and amplifiers, so that one can be quiet for the signal reaching the subscriber. Consider them closer:
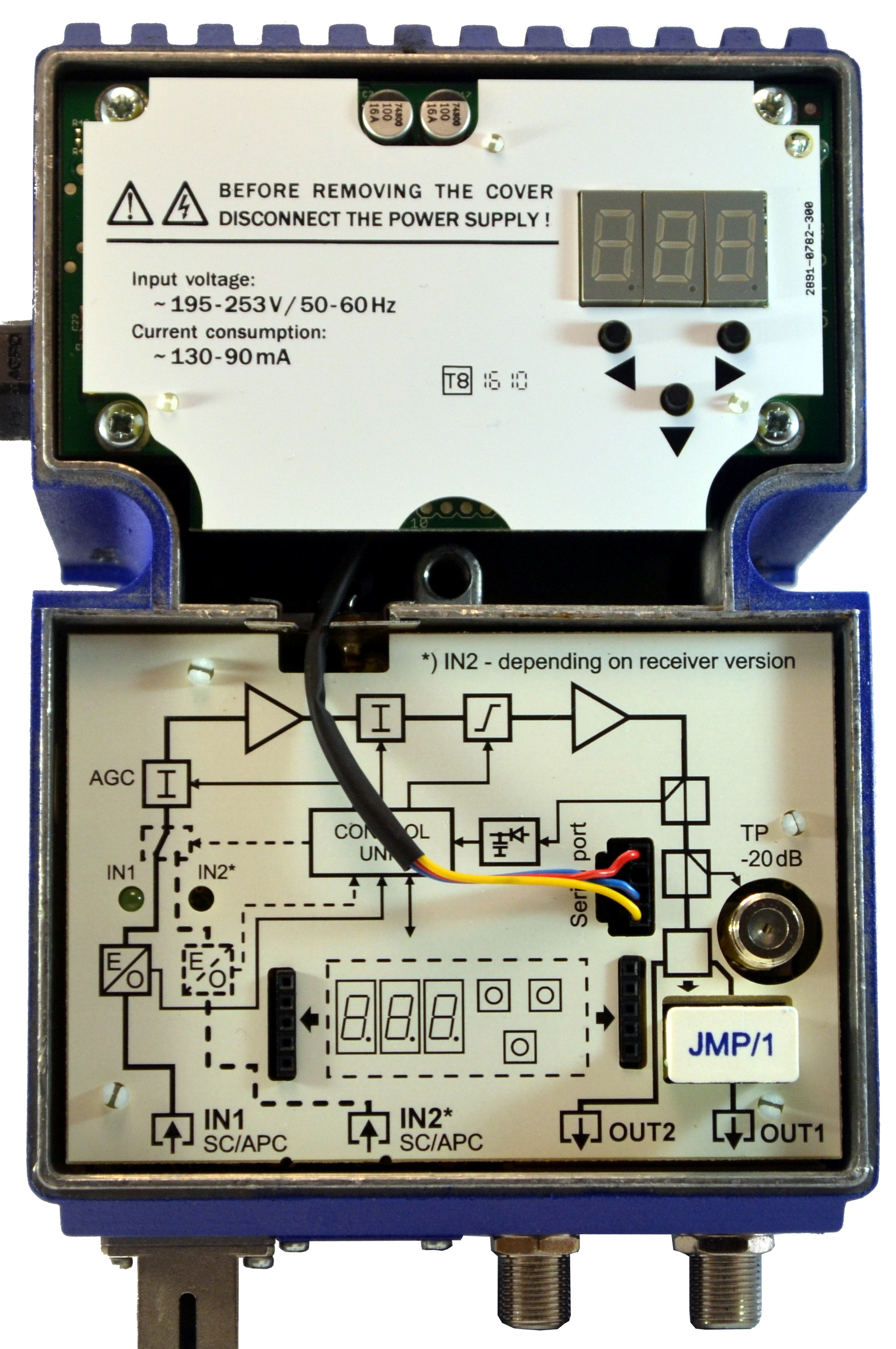
The optical receiver Telmor has inside the panel with the image of the structural scheme. Such a scheme is typical for OP.
The required optical signal level is usually from -10 to +3 dBm, during design and commissioning the optimal value is -1 dBm: this is a decent margin in case of transmission line degradation and at the same time a low level creates less noise when passing equipment circuits.
The AGC ( AGC ) circuit built into the optical receiver is precisely responsible for the fact that, by controlling the level of the incoming signal, it keeps the output in specified parameters. This means that if for any reason the optical signal suddenly changes significantly, but remains in the AGC operating range (approximately from 0 to -7 dBm), the receiver will regularly send a signal to the coaxial network with the level that was set at . For especially important cases, there are devices with two optical inputs, each of which is monitored and can be operated both manually and automatically.
All active ODs contain an amplifier stage, which also provides the ability to control the slope and level of the output signal.
Optical receiver control
To adjust the parameters of the signal, as well as changes and controls built-in service functions within the receivers themselves, there are usually simple controls. In MOBa, shown in the photo above is a separate fee, which is optionally installed in the case. Also, as an alternative, it is proposed to use a quick-detachable card, which is installed only for the time of configuration in the ports on the main board. In practice, this is not very convenient, of course.
The control panel allows you to set the values of the input attenuator (as you increase the output signal decreases, respectively, to the gain), enable or disable (and also set fixed values) AGC, set the slope parameters and configure the ethernet interface.
Chelyabinsk OP Planar has a clear indicator of the level of the optical signal, and the settings are carried out in a simple way: with a twister and a change of inserts that change the characteristics of the amplifier cascade. In the flip cover is the power supply.

And made in the design of "technoporn" OP Vector Lambda has a two-digit screen and only three buttons.

To distinguish between positive and negative values, this RO displays negative values with all segments, and a positive zero and +1 indicate half the height of the screen. For values greater than +1.9, it simply writes “HI”.
Such controls are convenient for quick configuration at the facility, but to enable remote monitoring and control, almost all receivers have an ethernet port. The web interface allows monitoring and changing parameters, and for integration with monitoring systems, SNMP polling is supported.
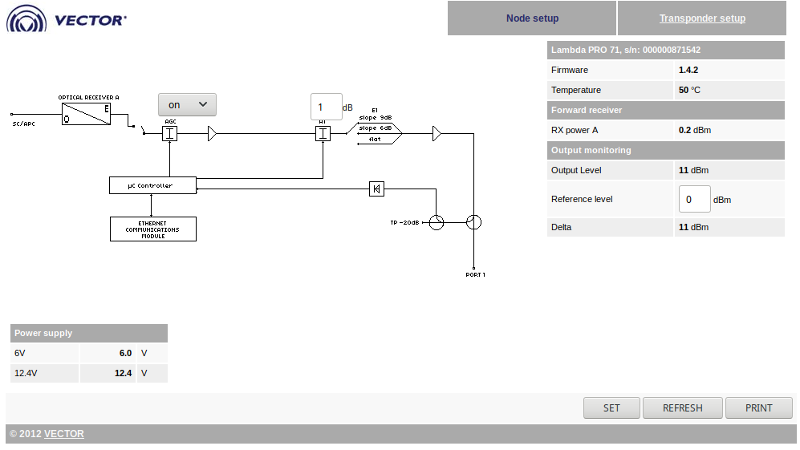
Here we see the same typical block diagram of the OP, on which there is the possibility of changing the parameters of the AGC and attenuator. But the slope of this OP is set only by jumpers on the board and has three fixed positions.

Next to the circuit, the parameters that are important for monitoring are displayed: the levels of the incoming and outgoing signals, as well as the values of voltages received from the built-in power supply unit. 99% of the failure of such OP occur after the deterioration of these voltages, so they should be monitored to prevent accidents.
The word Transponder here means the IP interface and this tab contains the settings of the address, mask and gateway - nothing interesting.
Bonus: terrestrial TV reception
This does not apply to the theme of the series, but I will only briefly tell you about the on-air TV reception. Why now? Yes, simply if we consider the network of an apartment building, then it depends on the source of the signal in the coaxial distribution network whether the network is cable or terrestrial.
If there is no fiber with a CATV signal, instead of an OP, an on-air broadcast receiver can be installed, for example, Terra MA201:

Several antennas (usually three) are connected to the input ports of the receiver, each of which provides reception of its own frequency range.

, , .For each of the antennas, you can adjust the sensitivity to reduce noise, as well as, if necessary, apply remote power to the amplifier built into the antenna. Further, the signal passes the amplifying stage and is summed up. The ability to adjust the output level is reduced to turning off the cascade steps, and the tilt adjustment is not provided at all: you can get the desired shape of the spectrum by adjusting the sensitivity of each antenna individually. And if kilometers of coaxial cable lie behind such a receiver, then the attenuation in it is already fought by installing and configuring amplifiers, such as on a cable network.
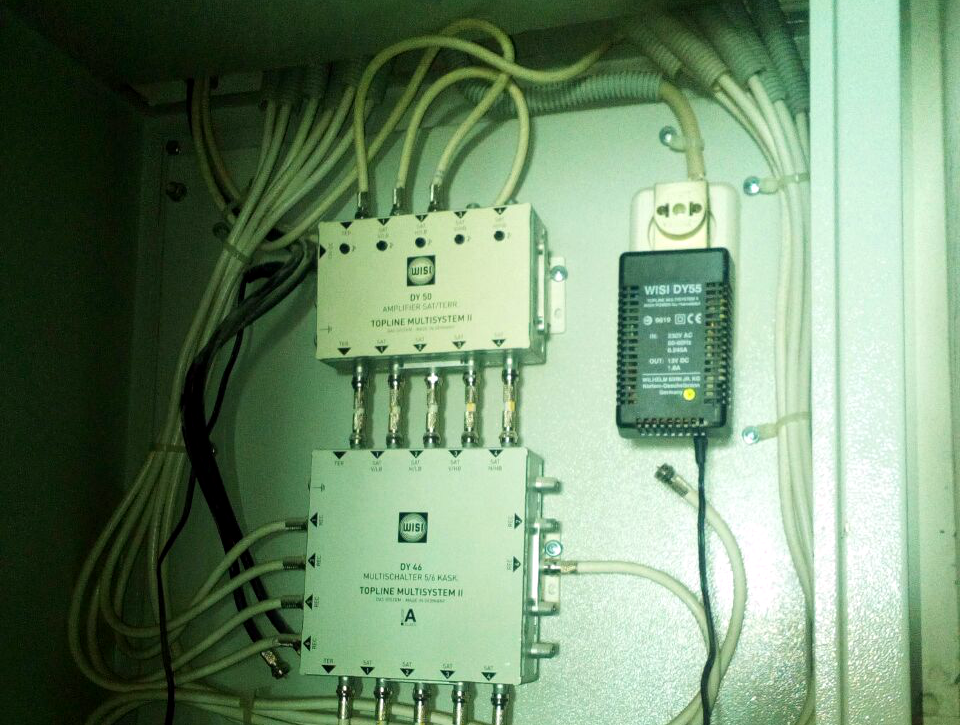
If desired, you can combine signal sources: gather in one network and cable, and terrestrial, and at the same time also a satellite signal. This is done with the help of multiswitches - devices that allow to summarize and distribute signals from different sources.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/454542/
All Articles