5G - where and who needs it?
Even without really understanding the generations of mobile communication standards, anyone will most likely answer that 5G is cooler than 4G / LTE. In fact, everything is not so simple. Let's see what is 5G better / worse and which cases of its use are the most promising considering the current state.
So what does the 5G technology promise us?
All this is achieved by:
')
5G will improve 4G in traditional areas, whether it's an instant movie download, or a seamless mobile application connection with the cloud. So, it will be possible to refuse the delivery of the Internet to our apartments and offices by cable?
5G will provide a universal connection to everything with everything, combining broadband, energy-intensive protocols with narrowband, energy-saving. This will open new, inaccessible for 4G directions: machine-to-machine communication on the ground and in the air, Industry 4.0, Internet of Things. The 5G business is expected to earn $ 3.5T by 2035 and create 22 million jobs.
Or not?..

(Image source - Reuters)
Who knows how 5G works - skip this section.
So, at the expense of what we can achieve such a fast data transfer in 5G, as described above? After all, this is not some kind of magic?
The increase in speed will occur due to the transition to a higher frequency range - previously untapped. For example, the frequency of home WiFi is 2.4 or 5 GHz, the frequency of existing mobile networks within 2.6 GHz. But when we talk about 5G, then here we are talking about dozens of gigahertz. It's simple: increase the frequency, reduce the wavelength - and the data transfer rate becomes many times larger. And the network as a whole is unloaded.
Here's a visual comic, how it was and how it will be. It was:
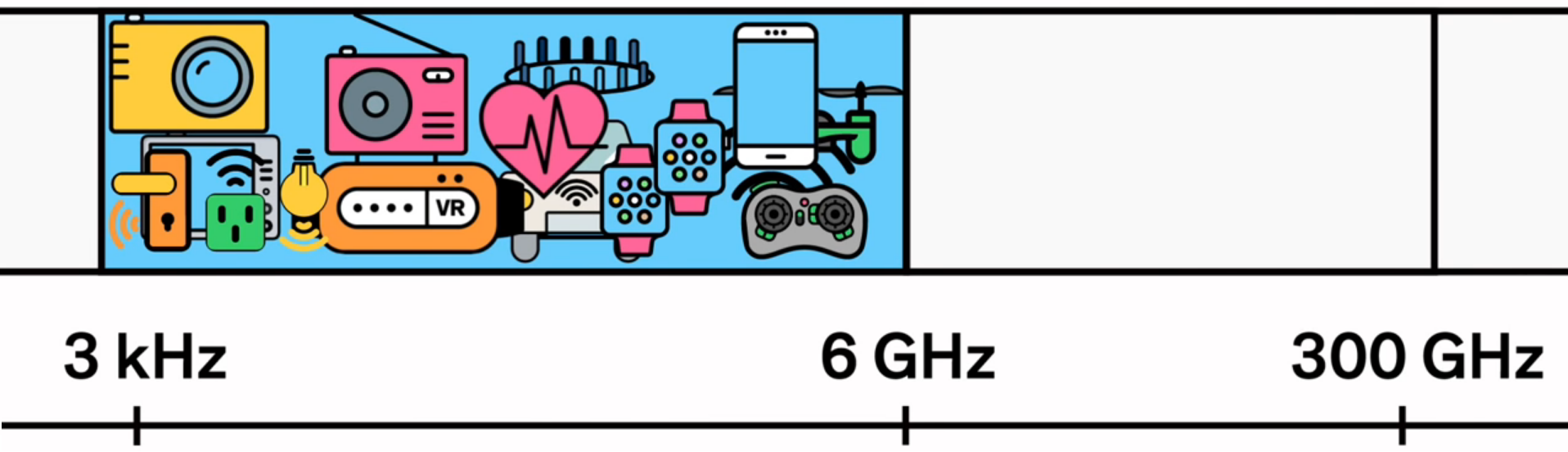
Will be:
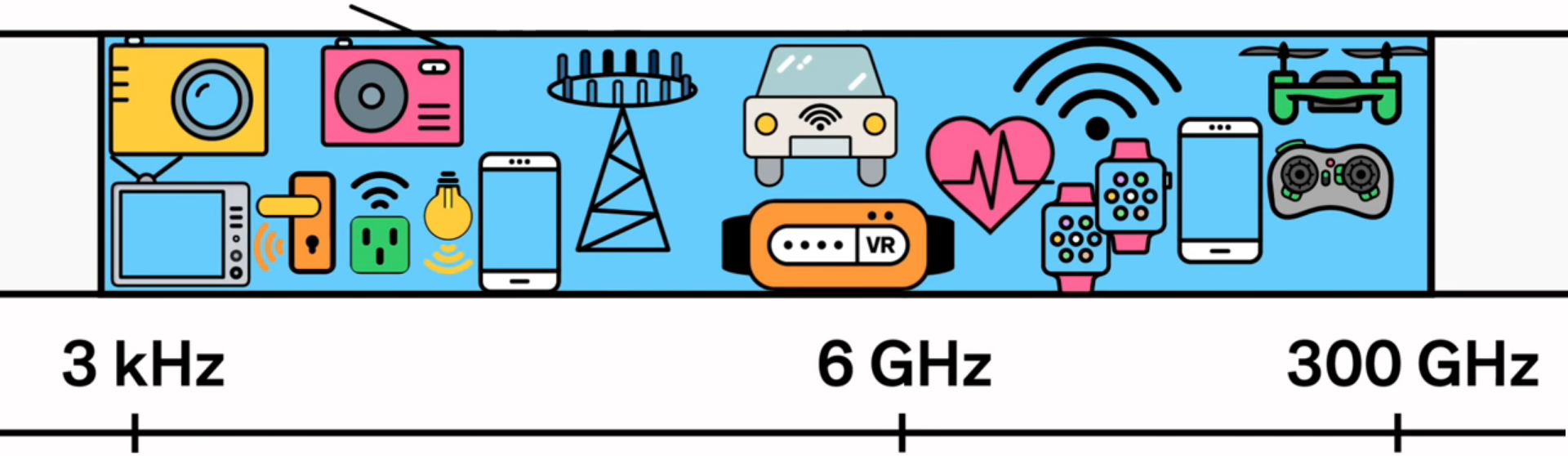
(Source: IEEE Spectrum, 5G )
The frequency has increased tenfold, so in 5G we are dealing with much shorter millimeter waves. They pass badly through obstacles. And in connection with this, the network architecture is changing. If earlier communication was provided to us by large powerful towers that provided communication at large distances, then now it will be necessary to place many compact low-power towers everywhere. And keep in mind that in large cities the stations will require a lot, due to the overlap of the signal by high-rise buildings. So, for surely equipping New York with 5G networks, you need to increase the number of base stations by 500 (!) Times.
According to Russian operators, switching to 5G will cost approximately 150 billion rubles for them - a cost comparable to previous costs of deploying a 4G network, even though the cost of a 5G station is lower than the existing ones (but they need a lot).
To reduce power consumption and increase the range, beamforming technology is used - dynamic formation of a radio beam for a specific subscriber. How is this done? The base station remembers where the signal came from and how much (it comes not only from your phone, but also as a reflection from obstacles), and using triangulation methods calculates your approximate location, and then builds the optimal signal path.

Source: Analysys Mason
However, the need to track the position of the receiver leads to a slight difference for fixed and mobile use cases, and this is reflected in different use cases (more on this in the “Consumer Market” section).
There is no adopted 5G standard. Technology is too complex and too many players with conflicting interests.
The 5G NR ( New Radio ) standard from the 3GPP ( 3rd Generation Partnership Project ) organization, which developed the previous 3G and 4G standards, is in the stage of offering a high degree of development. 5G uses two radio frequency bands ( Frequency Range , or simply FR ). FR1 offers frequencies below 6 GHz. FR2 - above 24 GHz, so-called. millimeter waves. The standard supports fixed and moving receivers and is a further development of the 5GTF standard from the American telecom giant Verizon, which supports only fixed receivers (this type of service is called fixed wireless access networks).
The 5G NR standard provides for three use cases:
Or briefly, the same thing in the picture:
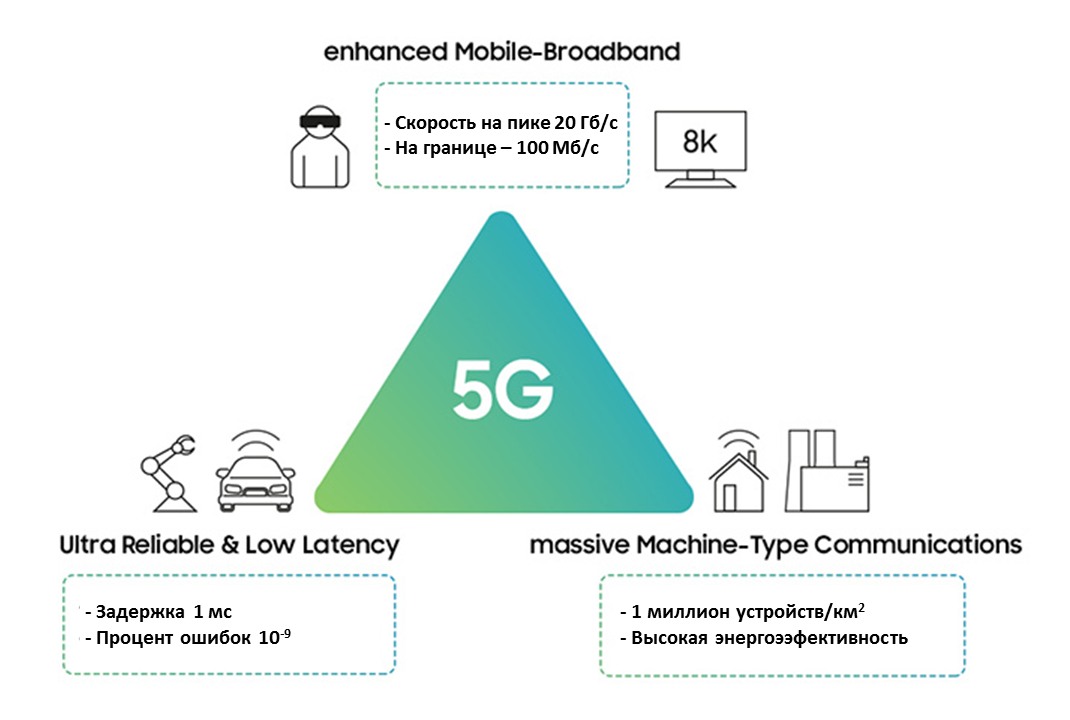
It is important to understand that the industry will first focus on the implementation of eMBB, as a more understandable scenario with existing cash flows.
From 2018, extensive testing is conducted, for example, at the Winter Olympics in South Korea. In 2018, all Russian operators of the Big Four conducted tests. MTS tested the new technology in conjunction with Samsung - they tested using video calls, transferring high-resolution video, online games.
In South Korea, for the first time in the world, 5G service was offered at the end of 2018. Worldwide commercial introduction is expected in the next, 2020th year. At the initial stage, the FR1 range will be used as an add-on to existing 4G networks. According to the plans of the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media, in Russia 5G will begin to appear in million-plus cities from 2020 onwards. In practice, large-scale deployment will be determined by the possibility of monetization, and this aspect of 5G is not yet clear.
What is the problem with monetization? The fact is that telecom operators do not yet see any weighty reasons for modernization: the existing networks do quite well with the load. And now 5G is viewed by them rather in the plane of marketing: the 5G icon on the phone screen will definitely be a plus in the eyes of telecom operator subscribers. The anecdotal incident with the AT & T operator , who placed the 5G icon in the absence of a real network, is indicative, for which competitors sued him for fraud.

If you take a good look, you can see that the icon is actually “5GE” - it stands for 5G Evolution, and suddenly this is not 5G, which we are thinking about, but just a label invented by marketers for the existing LTE network with some improvements.
Microelectronic companies have already invested many billions of dollars in 5G. Microcircuits for 5G NR cellular modems are offered by Samsung ( Exynos Modem 5100 ), Qualcomm ( Snapdragon X55 modem ), Huawei ( Balong 5000 ). Modems from Intel, a new player in this market, are expected by the end of 2019. The Samsung modem is made using 10nm FinFET technology, and is compatible with the old standards starting from 2G. In the frequency range up to 6 GHz, it provides a download speed of up to 2 Gb / s, while using the millimeter range, the speed increases to 6 Gb / s.
Almost all Android phone manufacturers have announced plans to introduce 5G. Samsung unveiled the flagship Galaxy S10 in the 5G version at Mobile World Congress at the end of February 2019. Already on April 5, it was released in Korea. In the US, the novelty appeared on May 16, and there the connection takes place with the network of the telecom operator Verizon. Other operators are catching up: AT & T announces plans to release a second smartphone with Samsung in the 2nd half of 2019.
During the year, 5G-smartphones from different manufacturers, mainly of premium class, will arrive at the store shelves. By some estimates, the new technology will increase the cost of devices by $ 200-300 and subscription fee by 10%.
Fixed wireless access 5G networks will become an alternative to the wired internet in our apartments. If before the Internet came to our apartment by cable, then in the future - from 5G-tower, and then the router will distribute it through the usual home WiFi. The main player companies have finished their training, synchronizing the release of routers for sale with the deployment of 5G networks. A typical 5G router costs $ 700-900, and provides download speeds of 2-3 Gbit / s. In this way, operators will solve the “last mile” problem for themselves and reduce the cost of wiring. And one should not be afraid that the existing backbone networks will not cope with the increased traffic that will come from 5G networks: studies are being conducted on the use of the existing reserve of fiber networks - the so-called “black fiber” (dark fiber).
How new will this scenario be for users? Already, in some countries, they are no longer using traditional home wired Internet, and are switching to LTE: it turns out to be faster and cheaper to use mobile communication in all situations, provided there are convenient rates. This situation, for example, has developed in Korea. And she illustrated here in this comic:
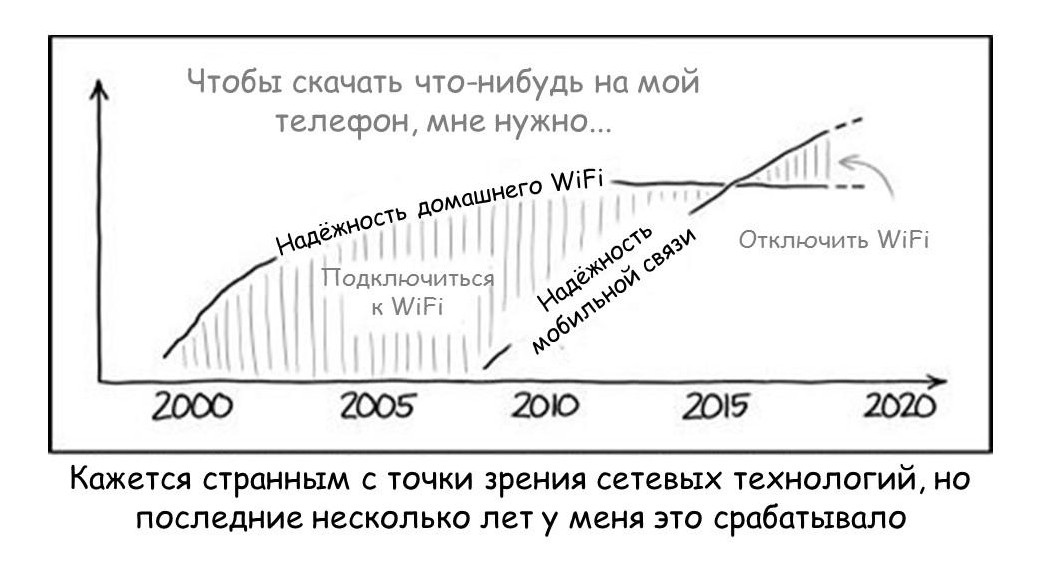
Surely everyone has been in such an unpleasant situation: come to the exhibition or the stadium, and mobile communication is lost. And this is exactly the moment when you want to post a photo or write on the social network.
Samsung conducted a test together with the Japanese telecom operator KDDI at the 30,000 baseball stadium. Using test 5G tablets, we were able to demonstrate streaming 4K video simultaneously on several tablets.
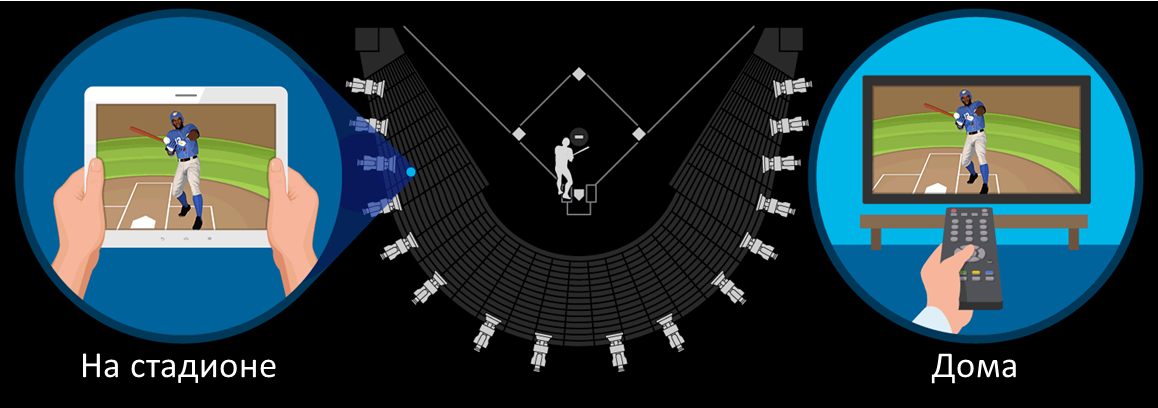
The stadium is one of three scenarios that are illustrated in a demo zone called 5G City located in Suwon (Samsung headquarters). Other scenarios include the urban environment (connecting video cameras, sensors and information boards) and a high-speed access point for delivering HD video to a moving bus: while it passes the point, it has time to download the movie.

The company Niantic - the creator of the world famous geolocation game Pokemon Go - has high hopes for 5G. And this is why: not so long ago group events appeared in the game - raids. In raids, you need to coordinate with other players in order to work together to defeat a particularly strong Pokemon, and this creates interesting situations in real life. So, the main legendary location of the game with the rarest pokemon Mewtwo is located on Times Square in New York - you can imagine what a crowd there is, consisting not only of Pokemon hunters, but also just tourists.

Augmented reality is also considered as the “killer app” for 5G. In this video you can see the concept of magical fights in real time, which are now being developed by Niantic in the new game based on "Harry Potter". Niantic has already entered into a partnership with Samsung and operators Deutsche Telecom and SK Telecom.

Finally, an interesting case with trains. There was an idea to provide the railway with 5G communications for entertainment and passenger comfort. A study by the University of Bristol showed that in order to achieve high-speed seamless communication, it is necessary to equip the railway with access points at a distance of 800 meters from each other!
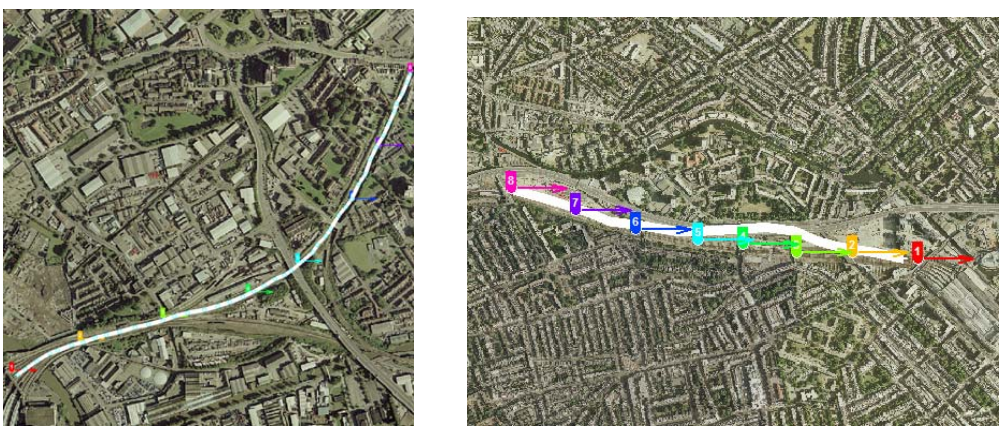
An example of how to arrange access points along the railway
Tests were successfully carried out on a train plying near Tokyo - they were conducted by Samsung and KDDI, the telecom operator. During the tests, a speed of 1.7 Gbps was achieved, and during the test, 8K-video was downloaded and 4K-video was downloaded from the camera.
But all this is more a solution to the problems we are already familiar with. And what fundamentally new can offer us 5G?
The main advantage is a small latency, allowing the machines to communicate with each other at speeds up to 500 km / h. Unlike people-drivers, cars will finally be able to agree among themselves or with fixed infrastructure about maneuvers, making the road safer. Interestingly, the system will take into account the weather conditions: everyone knows that in slippery weather the stopping distance is longer, therefore the rules in such a system should change.
The European Association of 5GAA (Automotive Association) already unites more than 100 major telecom and automakers around the world to accelerate the deployment of the C-V2X (Cellular Vehicle-To-Everything) system. The main objectives of the association are comprehensive road safety and traffic efficiency. Cyclists and pedestrians with 5G smartphones can also count on safety. Participants of the movement at distances of up to 1 km will be able to communicate directly, for longer distances they will need a 5G coverage. The system will ensure the creation of corridors for police and ambulance, provide for the exchange of sensorics between cars, remote driving and other wonders. After launching the C-V2X, the association plans to apply the experience gained in 5G V2X, where it will threaten industry 4.0, smart cities and everything thatmoves uses 5G.
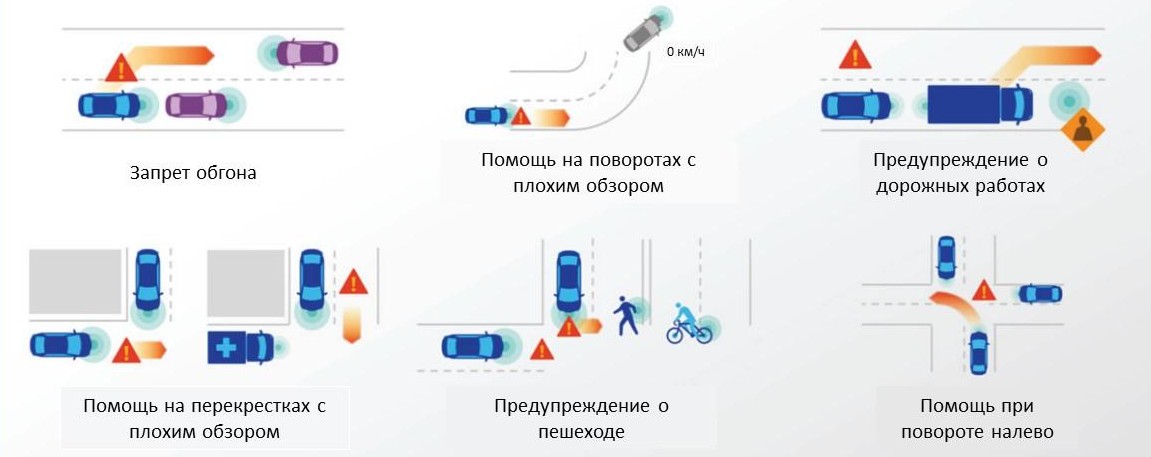
Examples of situations that can be resolved with Connected Car. Source: Qualcomm.
5G will allow to communicate not only ground vehicles, but also aircraft. This year, Samsung, together with Orange, a Spanish Internet provider, demonstrated how a remote pilot drove a drone’s flight using a 5G network and receiving a high-resolution video stream in real time. The American provider Verizon bought operator Skyward drone operators in 2017 promises millions of 5G-connected flights. Drones of the company are already connected to the running 4G-network of Verizon.
In general, the expression “Industrie 4.0” was invented in Germany for its industrial modernization program. The 5G-ACIA Association (5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation), headquartered in Germany, has, since 2018, united manufacturing companies interested in using 5G. The greatest demands on latency and reliability are made by controlling the movement of industrial robots, where the response time cannot exceed tens of microseconds. Now this is solved using Industrial Ethernet (for example, the EtherCAT standard). It is likely that 5G will compete for this niche!
Other applications, such as communication between industrial controllers or with a human operator, sensor networks are less demanding. Now most of these networks use cable, so wireless 5G seems to be an economically viable solution, in addition to allowing fast reconfiguration of production.
In practice, economic feasibility will lead to the introduction of 5G in the most expensive areas related to the payment of human labor, for example, forklift drivers in factories and warehouses. So, the European engineering company Acciona demonstrated the autonomous MIR200 rotor cart . A dolly transmits 360 high-resolution video; a remote operator will help her get out of an unforeseen situation. The cart uses Cisco and Samsung 5G technologies.

Remote collaboration technologies will go further. This year, it was demonstrated how an expert surgeon in real time monitors the progress of oncological surgery, which takes place many miles away, and shows his colleagues how best to perform the operation. As technology progresses, he will be able to take a more active part, already directly managing surgical instruments.
First of all, 5G will solve the problem with the numerous and poorly supported communication standards of the Internet of Things, which now, in our opinion, limits the development of this direction.
Here 5G can offer the following:
But it seems that big business is interested in other scenarios other than the Internet of Things. A quick search on the Internet did not find demonstrations by key players of the benefits of 5G for the Internet of things.
Concluding this topic, we turn our attention to the next interesting opportunity. Now dependence on the outlet or the need to replace the batteries limits the choice of "things". Low-frequency inductive wireless charging works only a few centimeters away. 5G and its directional millimeter waves will allow effective charging at distances of several meters. Although the existing standards do not stipulate this, we have no doubt that engineers will soon find ways to take advantage of this opportunity!
If you are interested in the topic, then where to go next?
Connections You will be able to personally meet 5G players at the upcoming Russian conferences of Skolkovo Startup Village 2019 May 29-30, Wireless Russia Forum: 4G, 5G & Beyond 2019 May 30-31, CEBIT Russia 2019 June 25-27, Smart Cars & Roads 2019 24 October
From academic contacts, it should be noted Moscow Telecommunication Seminar held at the Institute for Information Transmission Problems.
Funding . Key players hold contests to use 5G in various areas. In the US, Verizon recently announced the “Built on 5G Challenge” competition for Industry 4.0, immersive consumer applications (VR / AR), and breakthrough ideas (changing our way of life and work). The competition is open to a small business registered in the USA, applications are accepted until July 15. The prize fund is $ 1M. Winners will be announced in October of this year.
Employment . In addition to the mobile operators of the big four, in Russia there are several companies planning to use 5G in the near future. The business model of the leading content delivery provider in Russia and the CIS, CDNVideo, is a payment for the amount of traffic received. Using 5G, potentially reducing this price, will allow the company to reduce costs. PlayKey company promotes games in the cloud, it is not surprising that it plans to use 5G.
Open Source is likely to play a key role in the infrastructure. The US Open Networking Foundation supports 5G. The European OpenAirInterface Software Alliance unites those who want to circumvent the proprietary components of the 5G infrastructure. Strategic directions include support for 5G modems and software-defined systems, heterogeneous networks and the Internet of things. O-RAN Alliance virtualizes radio access networks (Radio Access Networks). Network core implementation is available from Open5GCore .
The authors:
So what does the 5G technology promise us?
- Increasing the speed tenfold to 10 Gb / s
- Delay reduction (latency) is dozens of times up to 1 ms,
- Increase the reliability of the connection ( packet loss error rate ) hundreds of times,
- Increase the density (number) of connected devices (10 6 / km 2 ).
All this is achieved by:
')
- multi-channel (parallelism in frequencies and base stations)
- increase in radio carrier frequencies from units to tens of GHz (radio channel capacity)
5G will improve 4G in traditional areas, whether it's an instant movie download, or a seamless mobile application connection with the cloud. So, it will be possible to refuse the delivery of the Internet to our apartments and offices by cable?
5G will provide a universal connection to everything with everything, combining broadband, energy-intensive protocols with narrowband, energy-saving. This will open new, inaccessible for 4G directions: machine-to-machine communication on the ground and in the air, Industry 4.0, Internet of Things. The 5G business is expected to earn $ 3.5T by 2035 and create 22 million jobs.
Or not?..

(Image source - Reuters)
How it works
Who knows how 5G works - skip this section.
So, at the expense of what we can achieve such a fast data transfer in 5G, as described above? After all, this is not some kind of magic?
The increase in speed will occur due to the transition to a higher frequency range - previously untapped. For example, the frequency of home WiFi is 2.4 or 5 GHz, the frequency of existing mobile networks within 2.6 GHz. But when we talk about 5G, then here we are talking about dozens of gigahertz. It's simple: increase the frequency, reduce the wavelength - and the data transfer rate becomes many times larger. And the network as a whole is unloaded.
Here's a visual comic, how it was and how it will be. It was:

Will be:

(Source: IEEE Spectrum, 5G )
The frequency has increased tenfold, so in 5G we are dealing with much shorter millimeter waves. They pass badly through obstacles. And in connection with this, the network architecture is changing. If earlier communication was provided to us by large powerful towers that provided communication at large distances, then now it will be necessary to place many compact low-power towers everywhere. And keep in mind that in large cities the stations will require a lot, due to the overlap of the signal by high-rise buildings. So, for surely equipping New York with 5G networks, you need to increase the number of base stations by 500 (!) Times.
According to Russian operators, switching to 5G will cost approximately 150 billion rubles for them - a cost comparable to previous costs of deploying a 4G network, even though the cost of a 5G station is lower than the existing ones (but they need a lot).
Two network options: fixed and mobile
To reduce power consumption and increase the range, beamforming technology is used - dynamic formation of a radio beam for a specific subscriber. How is this done? The base station remembers where the signal came from and how much (it comes not only from your phone, but also as a reflection from obstacles), and using triangulation methods calculates your approximate location, and then builds the optimal signal path.

Source: Analysys Mason
However, the need to track the position of the receiver leads to a slight difference for fixed and mobile use cases, and this is reflected in different use cases (more on this in the “Consumer Market” section).
Status Quo
Standards
There is no adopted 5G standard. Technology is too complex and too many players with conflicting interests.
The 5G NR ( New Radio ) standard from the 3GPP ( 3rd Generation Partnership Project ) organization, which developed the previous 3G and 4G standards, is in the stage of offering a high degree of development. 5G uses two radio frequency bands ( Frequency Range , or simply FR ). FR1 offers frequencies below 6 GHz. FR2 - above 24 GHz, so-called. millimeter waves. The standard supports fixed and moving receivers and is a further development of the 5GTF standard from the American telecom giant Verizon, which supports only fixed receivers (this type of service is called fixed wireless access networks).
The 5G NR standard provides for three use cases:
- eMBB ( enhanced Mobile Broadband ) - defines the usual mobile Internet;
- URLLC ( Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications ) - high demands on response speed and reliability - for such tasks as autonomous transport or remote surgery;
- mMTC ( massive Machine Type Communications ) - support for a large number of devices that send data rarely - the case of the Internet of things, that is, meters and monitoring devices.
Or briefly, the same thing in the picture:

It is important to understand that the industry will first focus on the implementation of eMBB, as a more understandable scenario with existing cash flows.
Implementation
From 2018, extensive testing is conducted, for example, at the Winter Olympics in South Korea. In 2018, all Russian operators of the Big Four conducted tests. MTS tested the new technology in conjunction with Samsung - they tested using video calls, transferring high-resolution video, online games.
In South Korea, for the first time in the world, 5G service was offered at the end of 2018. Worldwide commercial introduction is expected in the next, 2020th year. At the initial stage, the FR1 range will be used as an add-on to existing 4G networks. According to the plans of the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media, in Russia 5G will begin to appear in million-plus cities from 2020 onwards. In practice, large-scale deployment will be determined by the possibility of monetization, and this aspect of 5G is not yet clear.
What is the problem with monetization? The fact is that telecom operators do not yet see any weighty reasons for modernization: the existing networks do quite well with the load. And now 5G is viewed by them rather in the plane of marketing: the 5G icon on the phone screen will definitely be a plus in the eyes of telecom operator subscribers. The anecdotal incident with the AT & T operator , who placed the 5G icon in the absence of a real network, is indicative, for which competitors sued him for fraud.

If you take a good look, you can see that the icon is actually “5GE” - it stands for 5G Evolution, and suddenly this is not 5G, which we are thinking about, but just a label invented by marketers for the existing LTE network with some improvements.
Chipsets
Microelectronic companies have already invested many billions of dollars in 5G. Microcircuits for 5G NR cellular modems are offered by Samsung ( Exynos Modem 5100 ), Qualcomm ( Snapdragon X55 modem ), Huawei ( Balong 5000 ). Modems from Intel, a new player in this market, are expected by the end of 2019. The Samsung modem is made using 10nm FinFET technology, and is compatible with the old standards starting from 2G. In the frequency range up to 6 GHz, it provides a download speed of up to 2 Gb / s, while using the millimeter range, the speed increases to 6 Gb / s.
Telephones
Almost all Android phone manufacturers have announced plans to introduce 5G. Samsung unveiled the flagship Galaxy S10 in the 5G version at Mobile World Congress at the end of February 2019. Already on April 5, it was released in Korea. In the US, the novelty appeared on May 16, and there the connection takes place with the network of the telecom operator Verizon. Other operators are catching up: AT & T announces plans to release a second smartphone with Samsung in the 2nd half of 2019.
During the year, 5G-smartphones from different manufacturers, mainly of premium class, will arrive at the store shelves. By some estimates, the new technology will increase the cost of devices by $ 200-300 and subscription fee by 10%.
Consumer market
Case 1. Home Internet
Fixed wireless access 5G networks will become an alternative to the wired internet in our apartments. If before the Internet came to our apartment by cable, then in the future - from 5G-tower, and then the router will distribute it through the usual home WiFi. The main player companies have finished their training, synchronizing the release of routers for sale with the deployment of 5G networks. A typical 5G router costs $ 700-900, and provides download speeds of 2-3 Gbit / s. In this way, operators will solve the “last mile” problem for themselves and reduce the cost of wiring. And one should not be afraid that the existing backbone networks will not cope with the increased traffic that will come from 5G networks: studies are being conducted on the use of the existing reserve of fiber networks - the so-called “black fiber” (dark fiber).
How new will this scenario be for users? Already, in some countries, they are no longer using traditional home wired Internet, and are switching to LTE: it turns out to be faster and cheaper to use mobile communication in all situations, provided there are convenient rates. This situation, for example, has developed in Korea. And she illustrated here in this comic:

Case 2. Mass congestions
Surely everyone has been in such an unpleasant situation: come to the exhibition or the stadium, and mobile communication is lost. And this is exactly the moment when you want to post a photo or write on the social network.
Stadiums
Samsung conducted a test together with the Japanese telecom operator KDDI at the 30,000 baseball stadium. Using test 5G tablets, we were able to demonstrate streaming 4K video simultaneously on several tablets.

The stadium is one of three scenarios that are illustrated in a demo zone called 5G City located in Suwon (Samsung headquarters). Other scenarios include the urban environment (connecting video cameras, sensors and information boards) and a high-speed access point for delivering HD video to a moving bus: while it passes the point, it has time to download the movie.

Games
The company Niantic - the creator of the world famous geolocation game Pokemon Go - has high hopes for 5G. And this is why: not so long ago group events appeared in the game - raids. In raids, you need to coordinate with other players in order to work together to defeat a particularly strong Pokemon, and this creates interesting situations in real life. So, the main legendary location of the game with the rarest pokemon Mewtwo is located on Times Square in New York - you can imagine what a crowd there is, consisting not only of Pokemon hunters, but also just tourists.

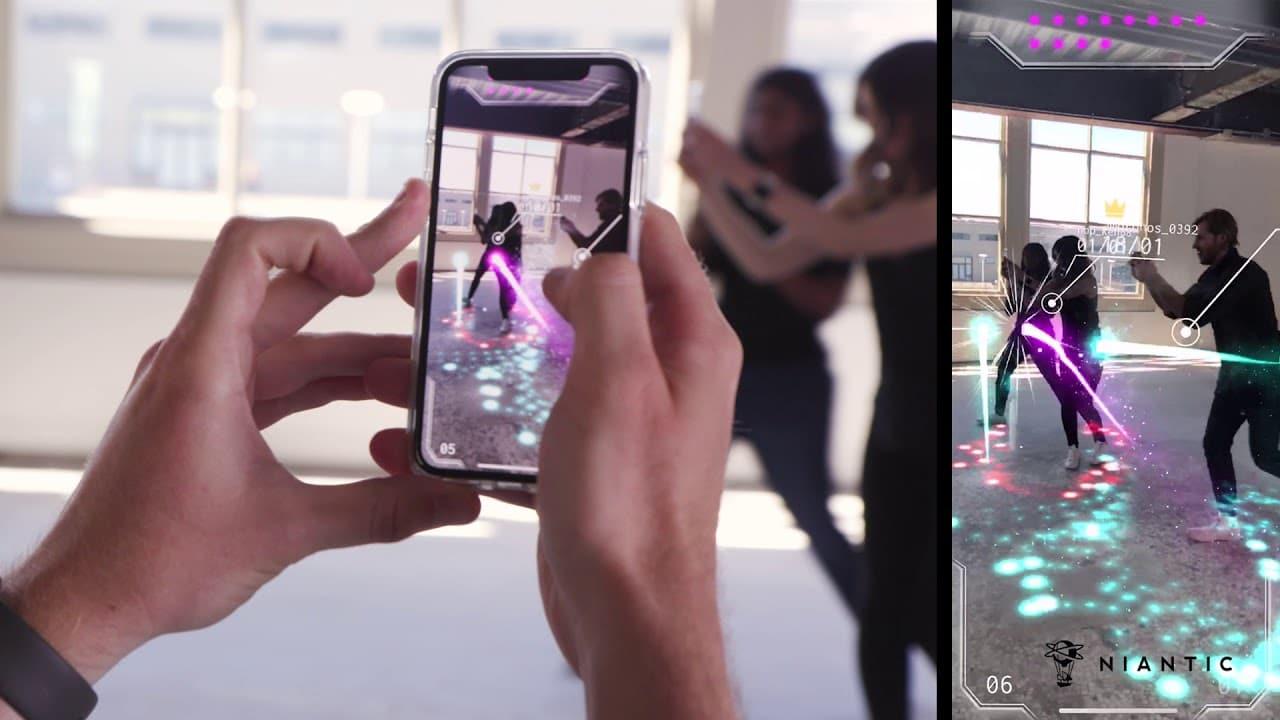
Augmented reality is also considered as the “killer app” for 5G. In this video you can see the concept of magical fights in real time, which are now being developed by Niantic in the new game based on "Harry Potter". Niantic has already entered into a partnership with Samsung and operators Deutsche Telecom and SK Telecom.

Transport
Finally, an interesting case with trains. There was an idea to provide the railway with 5G communications for entertainment and passenger comfort. A study by the University of Bristol showed that in order to achieve high-speed seamless communication, it is necessary to equip the railway with access points at a distance of 800 meters from each other!

An example of how to arrange access points along the railway
Tests were successfully carried out on a train plying near Tokyo - they were conducted by Samsung and KDDI, the telecom operator. During the tests, a speed of 1.7 Gbps was achieved, and during the test, 8K-video was downloaded and 4K-video was downloaded from the camera.
New usage scenarios
But all this is more a solution to the problems we are already familiar with. And what fundamentally new can offer us 5G?
Connected car
The main advantage is a small latency, allowing the machines to communicate with each other at speeds up to 500 km / h. Unlike people-drivers, cars will finally be able to agree among themselves or with fixed infrastructure about maneuvers, making the road safer. Interestingly, the system will take into account the weather conditions: everyone knows that in slippery weather the stopping distance is longer, therefore the rules in such a system should change.
The European Association of 5GAA (Automotive Association) already unites more than 100 major telecom and automakers around the world to accelerate the deployment of the C-V2X (Cellular Vehicle-To-Everything) system. The main objectives of the association are comprehensive road safety and traffic efficiency. Cyclists and pedestrians with 5G smartphones can also count on safety. Participants of the movement at distances of up to 1 km will be able to communicate directly, for longer distances they will need a 5G coverage. The system will ensure the creation of corridors for police and ambulance, provide for the exchange of sensorics between cars, remote driving and other wonders. After launching the C-V2X, the association plans to apply the experience gained in 5G V2X, where it will threaten industry 4.0, smart cities and everything that

Examples of situations that can be resolved with Connected Car. Source: Qualcomm.
5G will allow to communicate not only ground vehicles, but also aircraft. This year, Samsung, together with Orange, a Spanish Internet provider, demonstrated how a remote pilot drove a drone’s flight using a 5G network and receiving a high-resolution video stream in real time. The American provider Verizon bought operator Skyward drone operators in 2017 promises millions of 5G-connected flights. Drones of the company are already connected to the running 4G-network of Verizon.
Industry 4.0
In general, the expression “Industrie 4.0” was invented in Germany for its industrial modernization program. The 5G-ACIA Association (5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation), headquartered in Germany, has, since 2018, united manufacturing companies interested in using 5G. The greatest demands on latency and reliability are made by controlling the movement of industrial robots, where the response time cannot exceed tens of microseconds. Now this is solved using Industrial Ethernet (for example, the EtherCAT standard). It is likely that 5G will compete for this niche!
Other applications, such as communication between industrial controllers or with a human operator, sensor networks are less demanding. Now most of these networks use cable, so wireless 5G seems to be an economically viable solution, in addition to allowing fast reconfiguration of production.
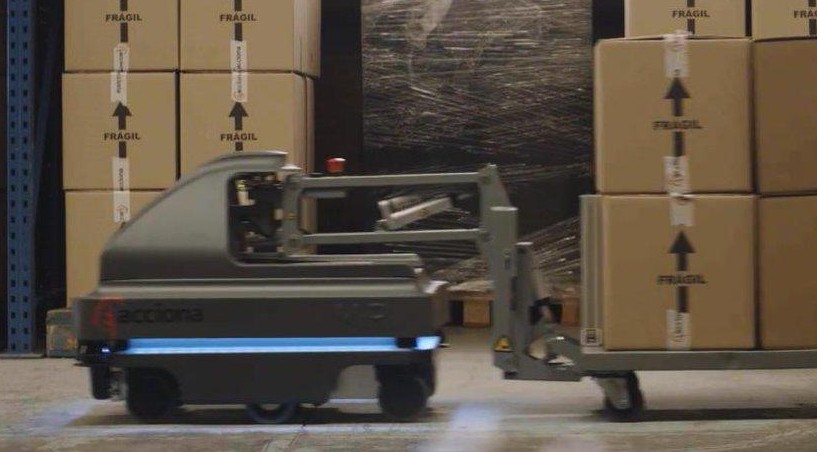
In practice, economic feasibility will lead to the introduction of 5G in the most expensive areas related to the payment of human labor, for example, forklift drivers in factories and warehouses. So, the European engineering company Acciona demonstrated the autonomous MIR200 rotor cart . A dolly transmits 360 high-resolution video; a remote operator will help her get out of an unforeseen situation. The cart uses Cisco and Samsung 5G technologies.

Remote collaboration technologies will go further. This year, it was demonstrated how an expert surgeon in real time monitors the progress of oncological surgery, which takes place many miles away, and shows his colleagues how best to perform the operation. As technology progresses, he will be able to take a more active part, already directly managing surgical instruments.
Internet of things
First of all, 5G will solve the problem with the numerous and poorly supported communication standards of the Internet of Things, which now, in our opinion, limits the development of this direction.
Here 5G can offer the following:
- Ad hoc network (without routers)
- High density connected devices
- Support narrowband, energy efficient (10+ years on one battery) communications
But it seems that big business is interested in other scenarios other than the Internet of Things. A quick search on the Internet did not find demonstrations by key players of the benefits of 5G for the Internet of things.
Concluding this topic, we turn our attention to the next interesting opportunity. Now dependence on the outlet or the need to replace the batteries limits the choice of "things". Low-frequency inductive wireless charging works only a few centimeters away. 5G and its directional millimeter waves will allow effective charging at distances of several meters. Although the existing standards do not stipulate this, we have no doubt that engineers will soon find ways to take advantage of this opportunity!
Developer Opportunities
If you are interested in the topic, then where to go next?
Connections You will be able to personally meet 5G players at the upcoming Russian conferences of Skolkovo Startup Village 2019 May 29-30, Wireless Russia Forum: 4G, 5G & Beyond 2019 May 30-31, CEBIT Russia 2019 June 25-27, Smart Cars & Roads 2019 24 October
From academic contacts, it should be noted Moscow Telecommunication Seminar held at the Institute for Information Transmission Problems.
Funding . Key players hold contests to use 5G in various areas. In the US, Verizon recently announced the “Built on 5G Challenge” competition for Industry 4.0, immersive consumer applications (VR / AR), and breakthrough ideas (changing our way of life and work). The competition is open to a small business registered in the USA, applications are accepted until July 15. The prize fund is $ 1M. Winners will be announced in October of this year.
Employment . In addition to the mobile operators of the big four, in Russia there are several companies planning to use 5G in the near future. The business model of the leading content delivery provider in Russia and the CIS, CDNVideo, is a payment for the amount of traffic received. Using 5G, potentially reducing this price, will allow the company to reduce costs. PlayKey company promotes games in the cloud, it is not surprising that it plans to use 5G.
Open Source is likely to play a key role in the infrastructure. The US Open Networking Foundation supports 5G. The European OpenAirInterface Software Alliance unites those who want to circumvent the proprietary components of the 5G infrastructure. Strategic directions include support for 5G modems and software-defined systems, heterogeneous networks and the Internet of things. O-RAN Alliance virtualizes radio access networks (Radio Access Networks). Network core implementation is available from Open5GCore .
The authors:

Stanislav Polonsky - Head of Advanced Research and Development of the Samsung Research Center

Tatyana Volkova - Author of the IoT project curriculum Samsung Academy, a specialist in corporate social responsibility programs at the Samsung Research Center
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/452344/
All Articles