Found the place of the fall of the apparatus "Bereshit" on the moon

One and a half weeks after the fatal accident, the lunar orbital probe LRO recorded the appearance of the landing procedure of the Bereshit apparatus and recorded the appearance of new damage on the lunar surface in the area of the supposed fall.
Launched by NASA on June 18, 2009, the lunar orbital probe (LRO) continues to be used to obtain a large amount of valuable scientific information.
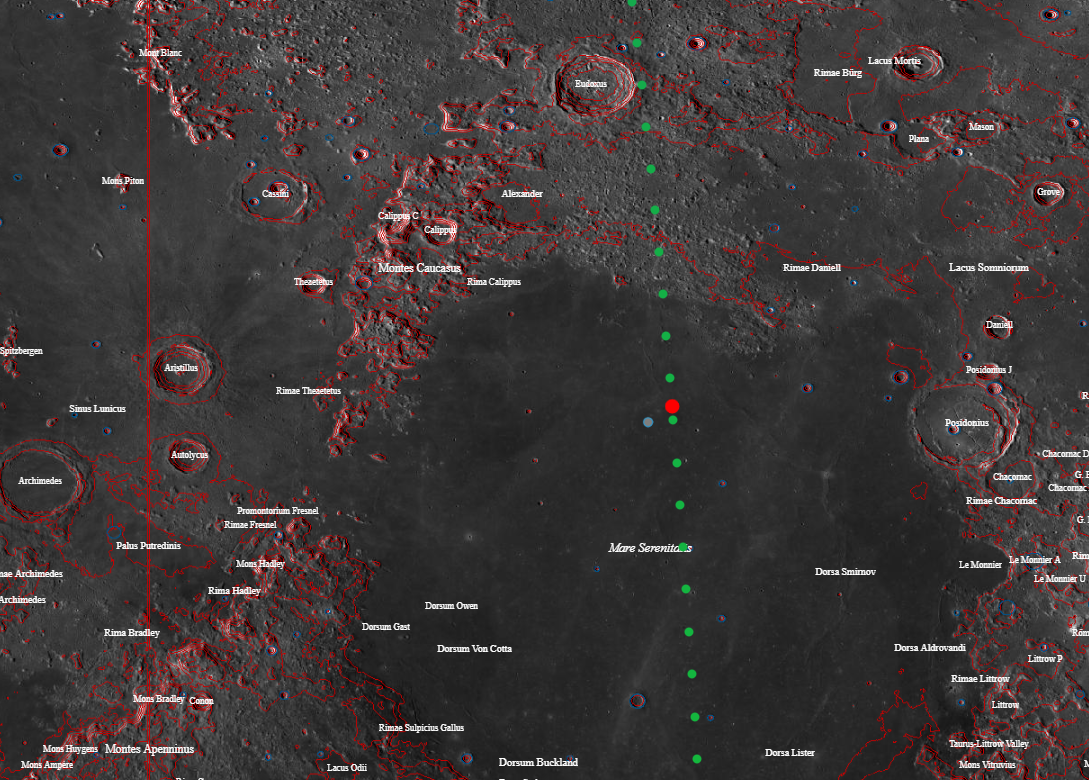
The trajectory of the probe LRO, when it turned out to detect new traces on the moon:
')
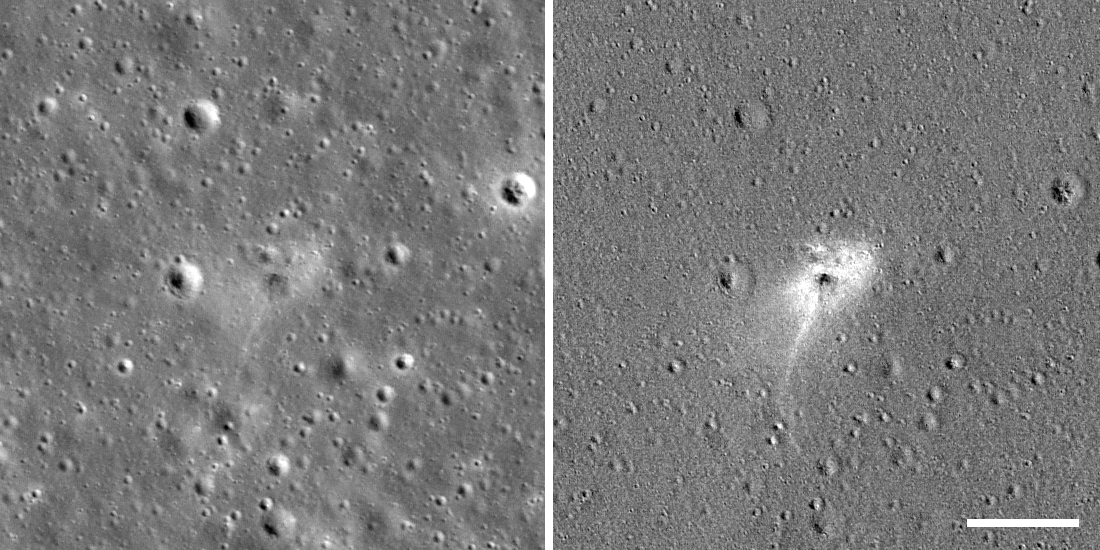
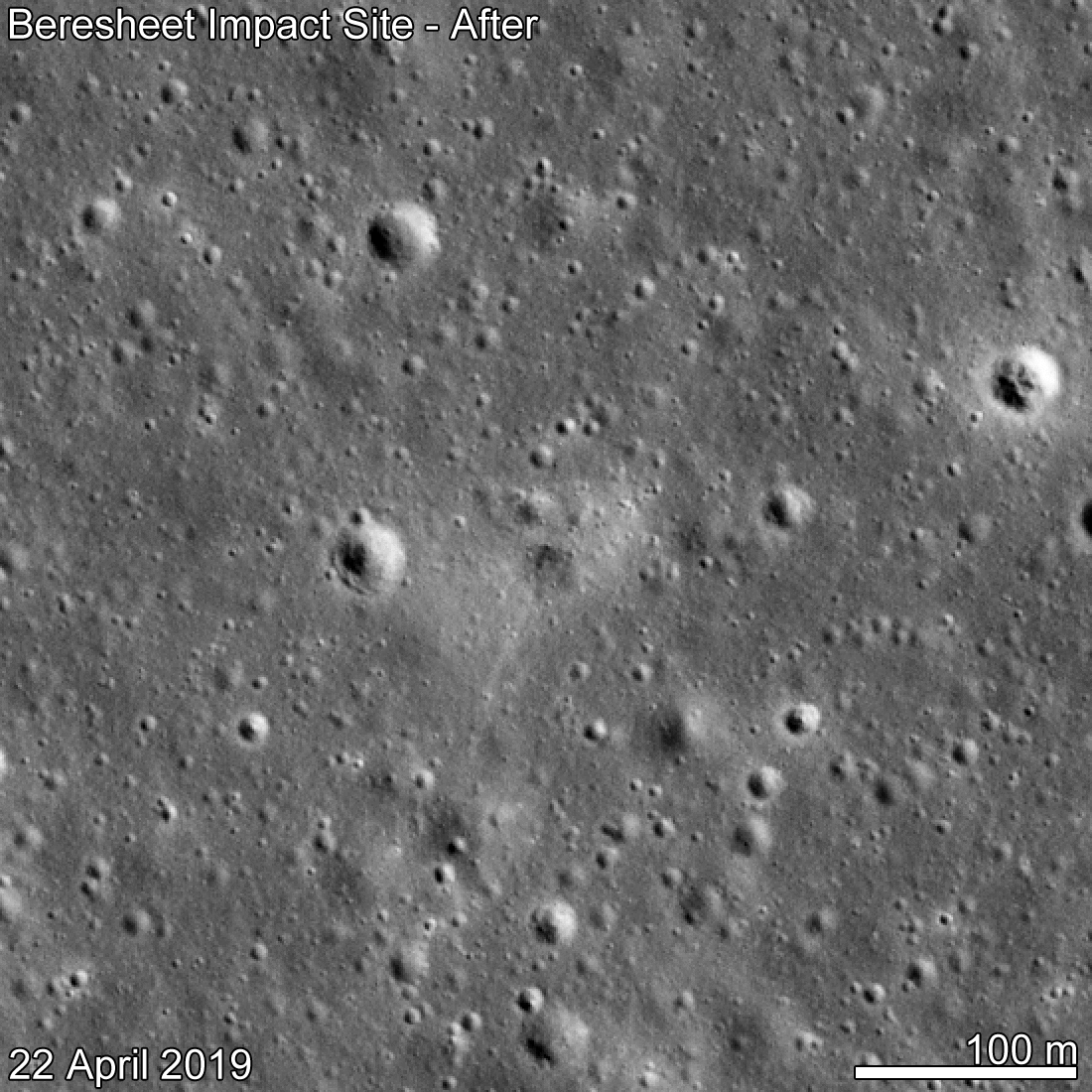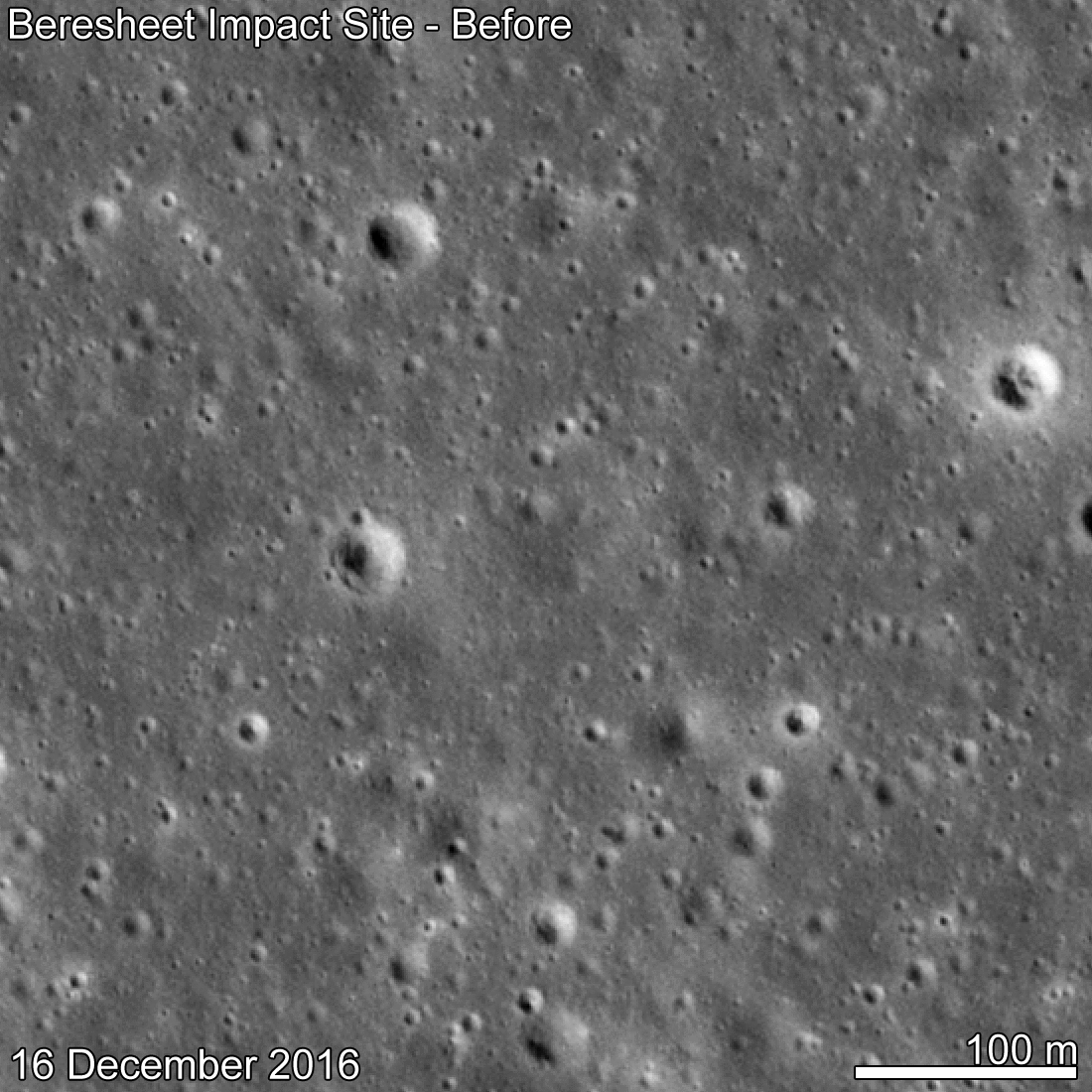
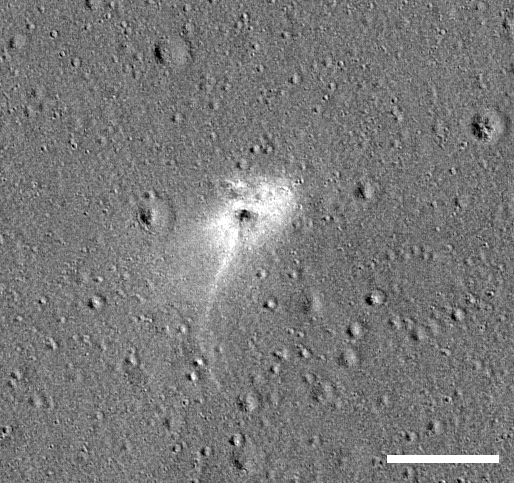
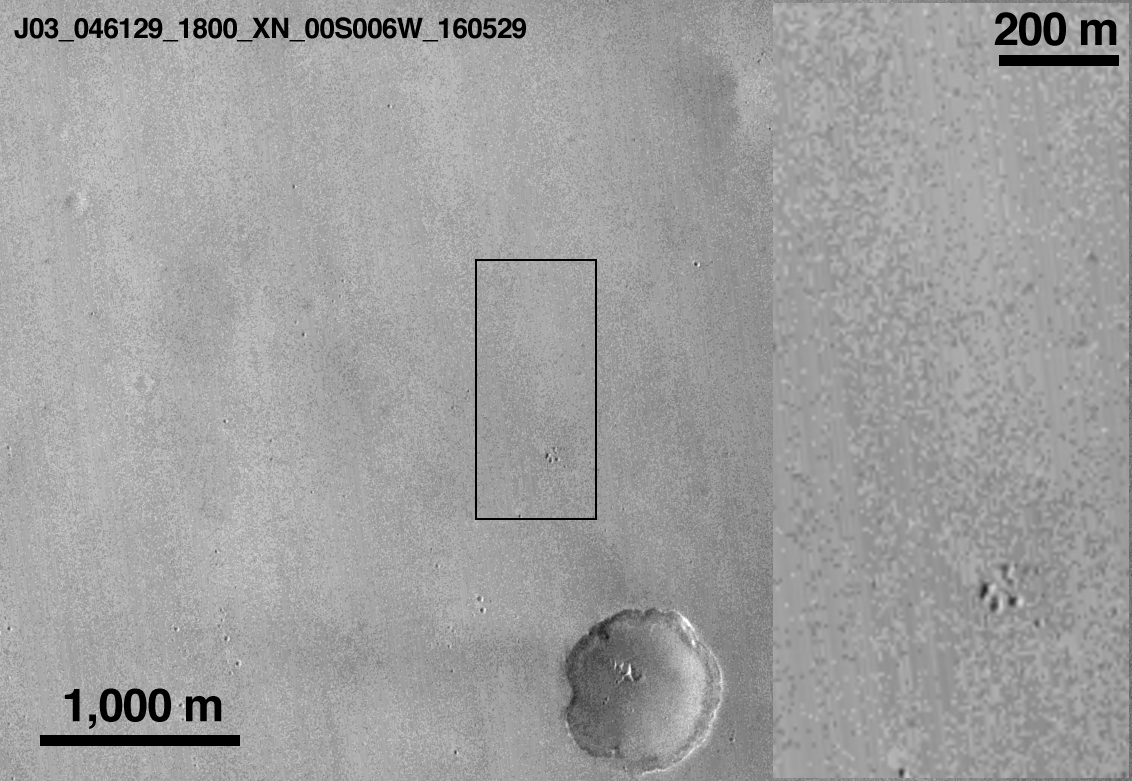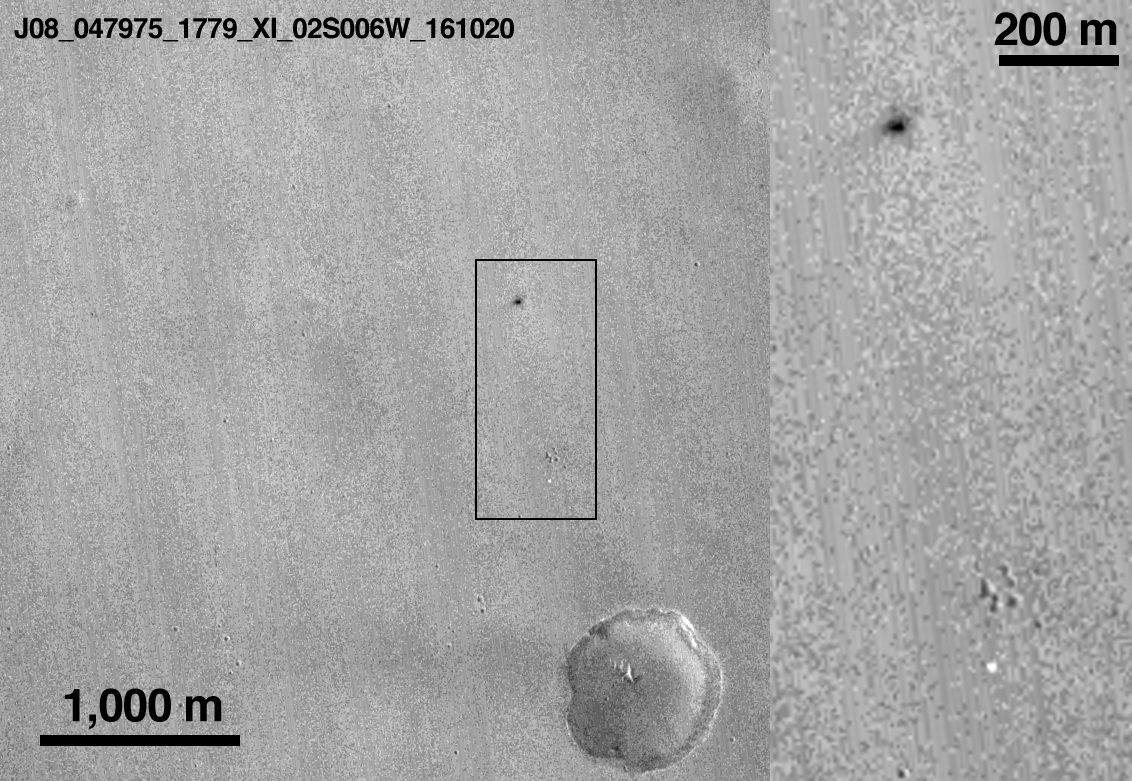
So on April 22, 2019, the LRO probe made an interesting photograph in the intended area of the Bereshit apparatus's fall, which revealed the secret of the place of its accident.
The LRO probe earlier on December 16, 2018 already flew over this place and it became possible to see how the surface of the Moon was transformed after the fall of the Bereshit vehicle.
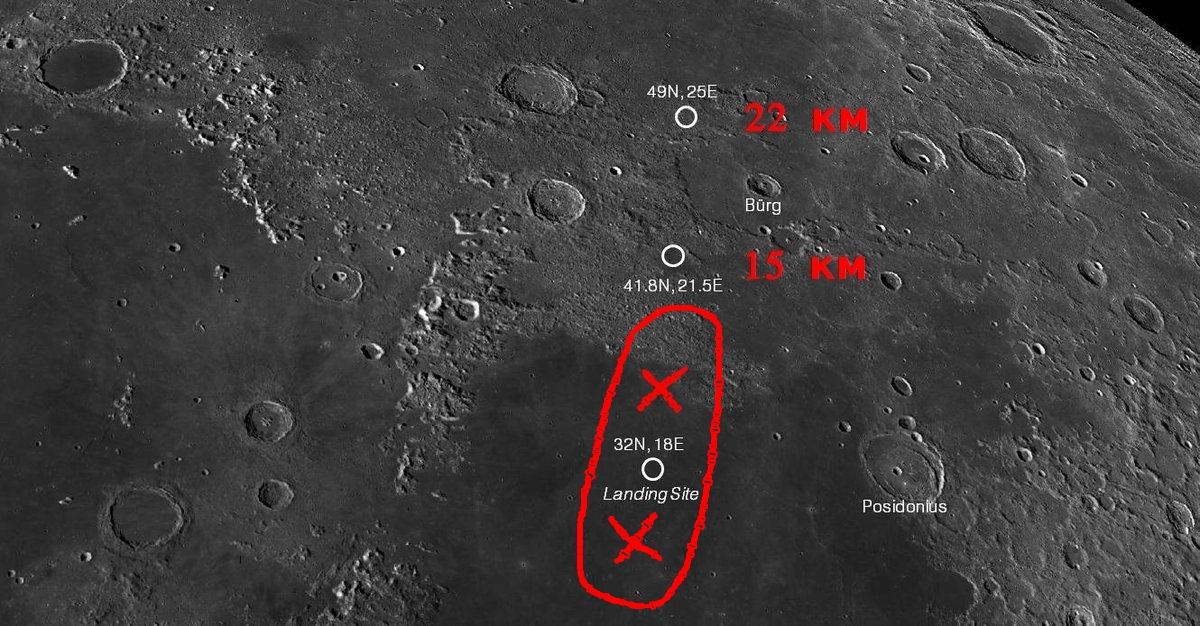
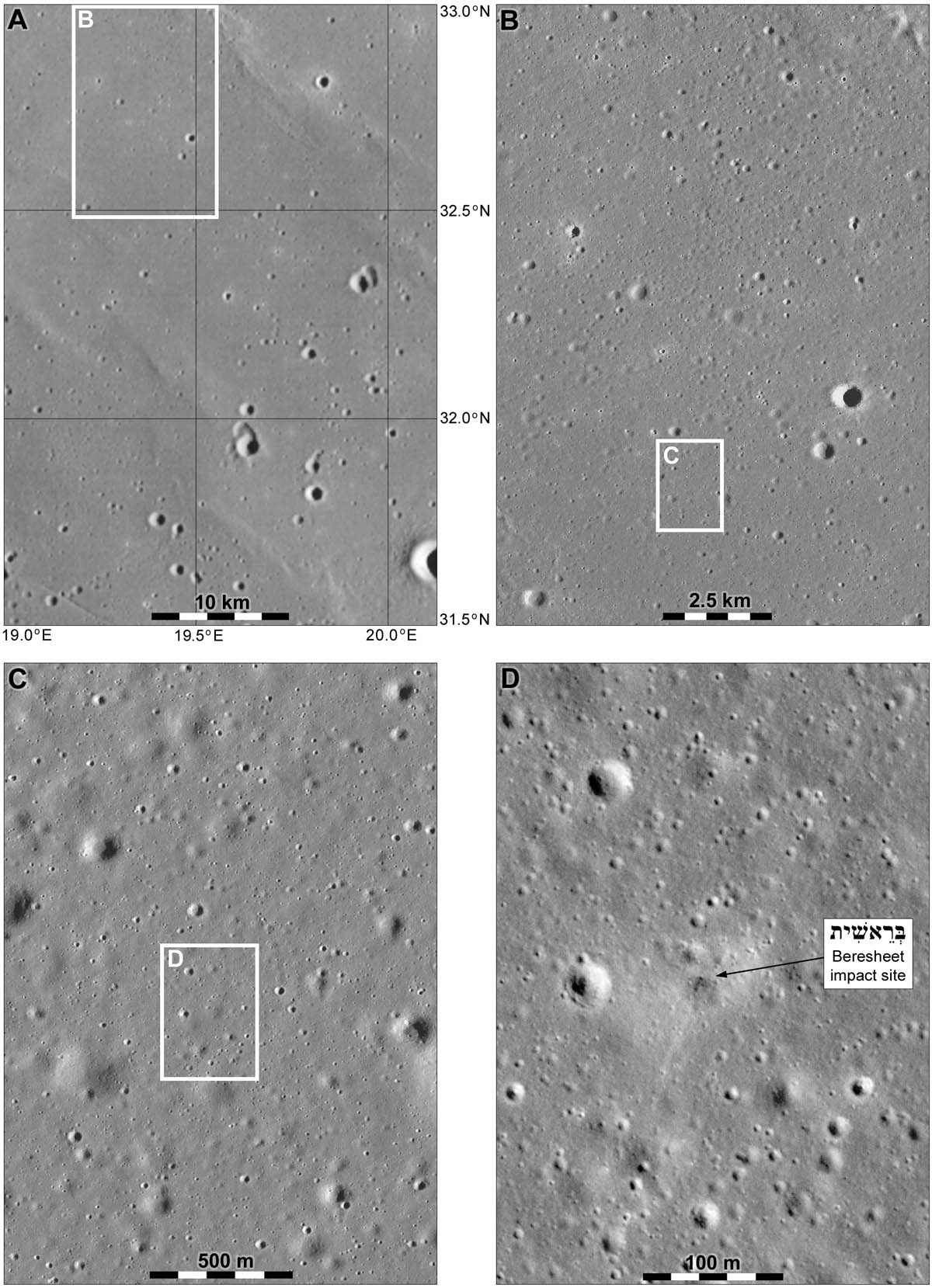
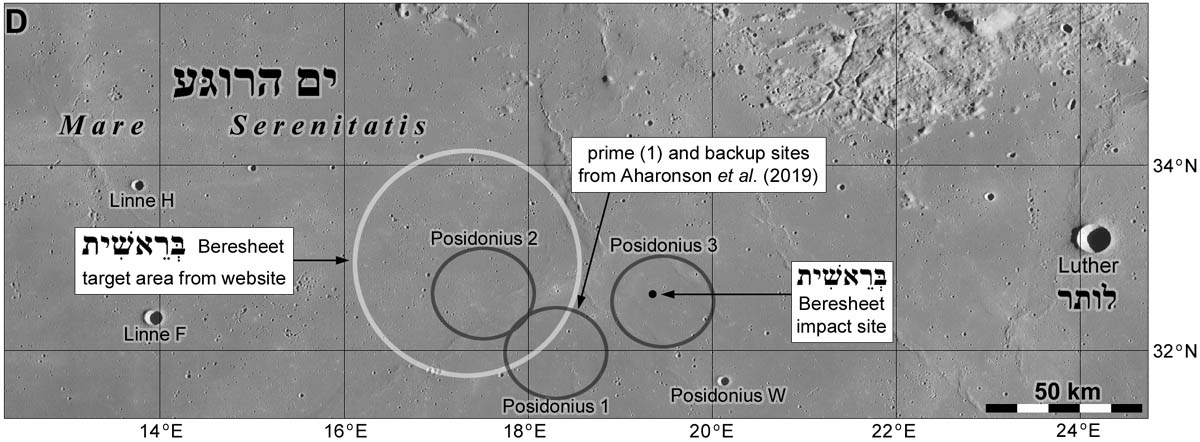
According to preliminary calculations, the Bereshit unit flew 16-20 km further than the estimated landing site. And the place of his fall had to be searched in a zone with a diameter of 140 km in the area of the lunar surface planned for landing earlier in the Sea of Clarity.
Red numbers are the height of the Bereshit apparatus over the surface of the Moon at two fixed points from which photographs of the lunar surface were sent to them.

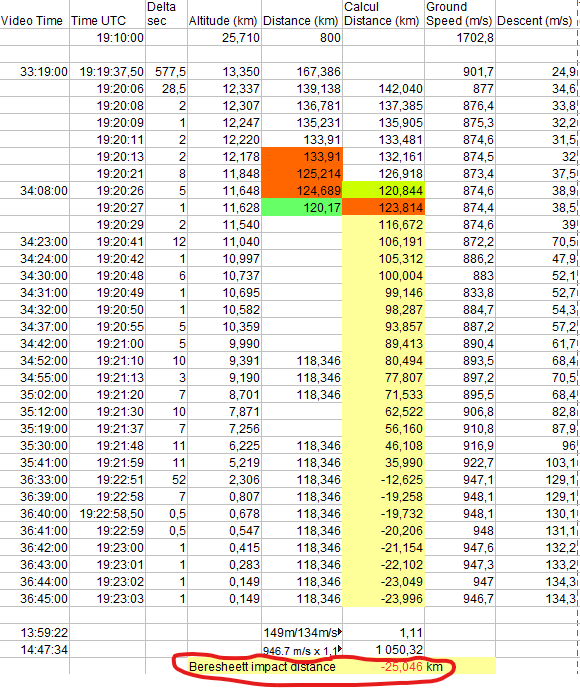
The latest data from the SpaceIL MCC at the time of landing:

The total mass of the Bereshit apparatus when it strikes the lunar surface: 150 kg (the apparatus itself) +76 kg (remaining fuel) = 226 kg.
The last 4 seconds of the life of the device according to the data center (from 678 to 149 meters reduction):
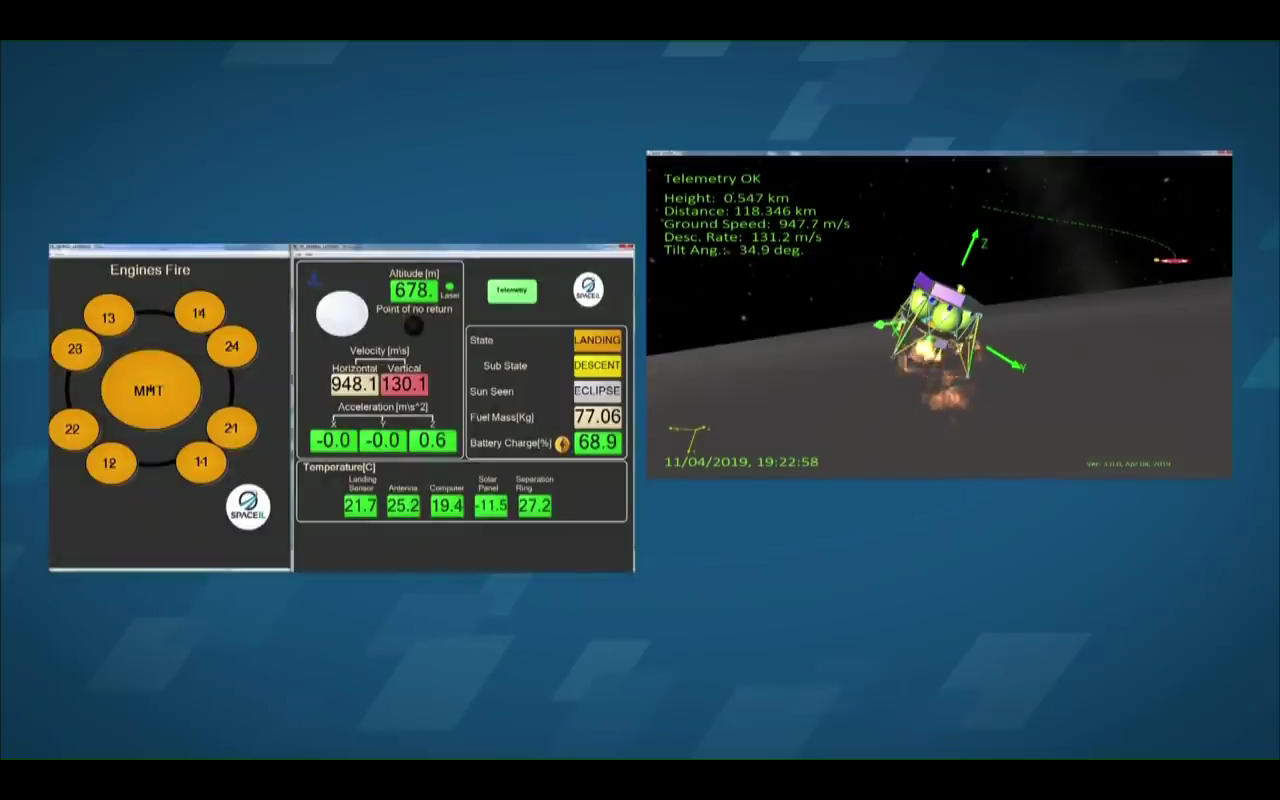
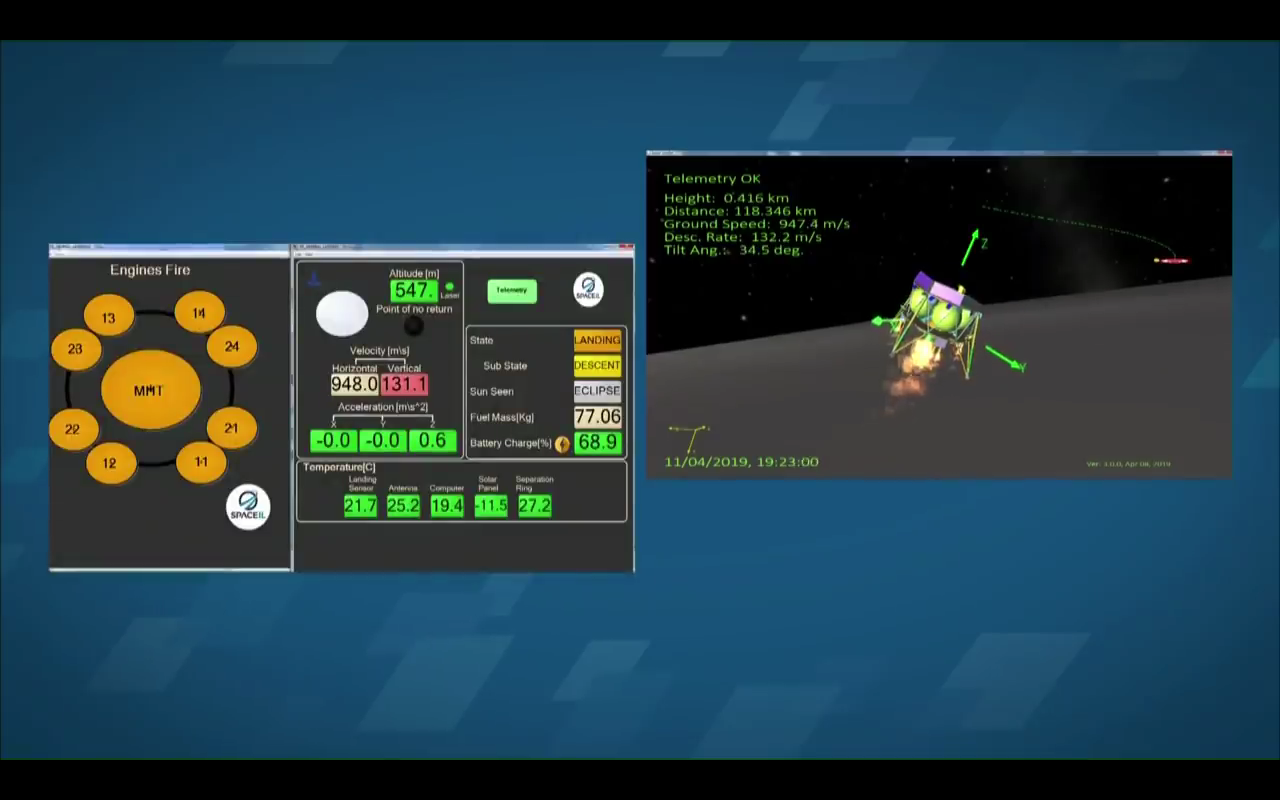
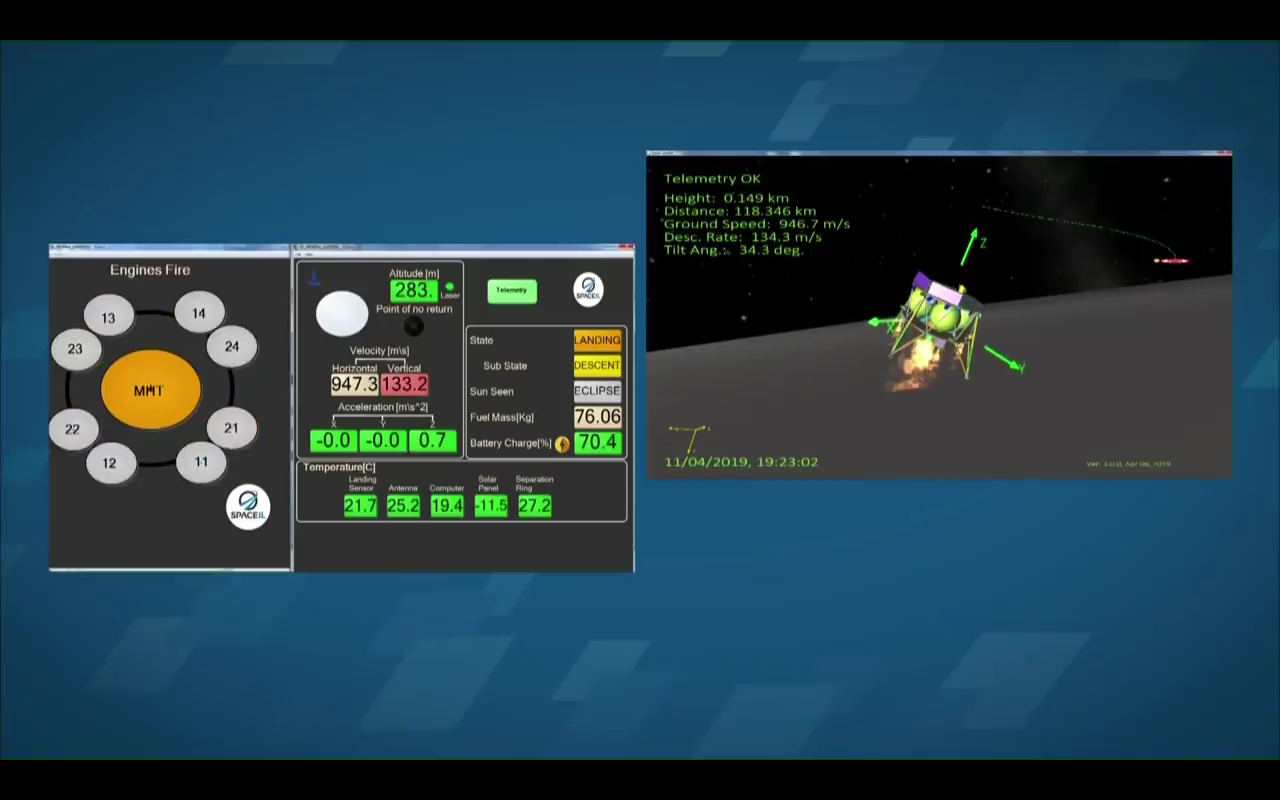

An enthusiast from Slovakia created, according to online video broadcasting data, an attempt to land just such a table with telemetry data and time:
And what happened on the lunar surface in the Sea of Clarity - a new crater and a big boom - a completely destroyed apparatus.
As expected, the diameter of the shallow crater formed after the fall of the device is about 7-8 meters. The Bereshit device crashed into the surface of the Moon at a small angle (~ 8 °), the crater turned out to be elongated.
Data from LRO.
The coordinates of the darkest pixel in the center in the right figure are 32.5956 ° N, 19.3496 ° E.

The main characteristics of the mission and lunar apparatus "Bereshit":
- the beginning of the mission: February 22, 2019;
- end of the mission: an accident occurred (falling to the moon) while attempting to perform the final landing procedures on April 11, 2019, a complete loss of communication with the device at an altitude of 149 meters;
- trajectory of motion to the moon (in fact, the maximum of the possible): complex, changeable by performing a series of maneuvers (turning on the engines for a few seconds or even minutes) to increase the apogee of its elliptical orbit after each orbit around the Earth, then go to the lunar orbit with subsequent landing;
- the height of the Bereshit apparatus is about 1.5 meters, the diameter is 2 meters (2.3 meters between the landing supports);
- weight 530 kilograms with fuel (mass of fuel (hydrazine) - 380 kg), 150 kg without fuel;
- scientific instruments: a magnetometer (sent some scientific data while the device was in orbit of the Moon and in the process of landing), an array of laser corner reflectors (an LRO probe will look for them).
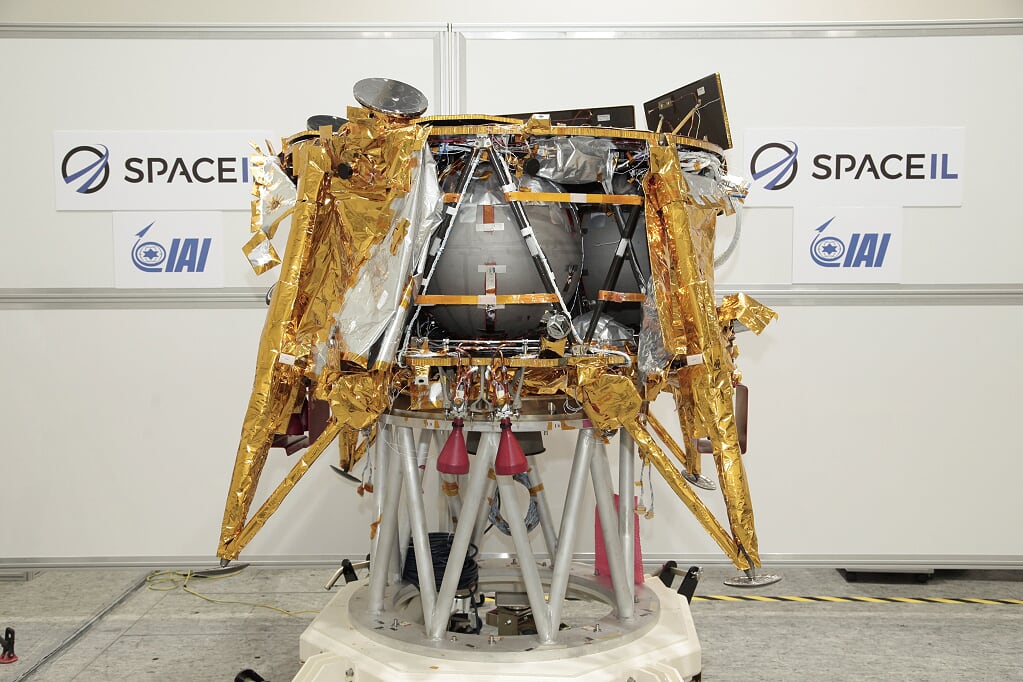
How to assemble the unit "Bereshit":
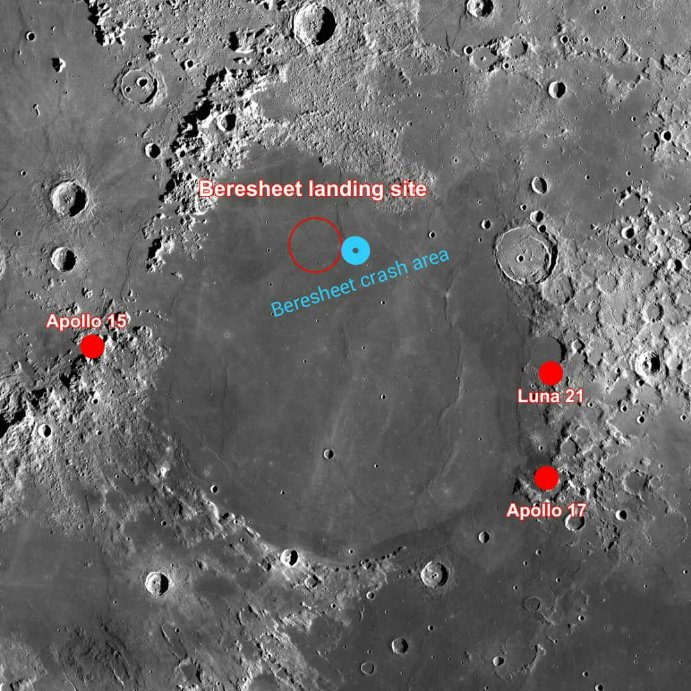
The Bereshit apparatus was to land on April 11, 2019 on a dark lava plain, known as the Sea of Clarity, not far from the region in which the astronauts of the Apollo 17 mission leaped on December 11, 1972.

The Bereshit spacecraft in orbit of the moon and during landing used a magnetometer and transmitted to the MCC some of the scientific data on the magnetic field of the moon.
Unfortunately, due to a software error in the operation of the onboard computer and the engines of the Bereshit apparatus, an abnormal situation occurred during a landing, which led to the main engine disconnecting and an uncontrolled fall at high speed onto the lunar surface.
And so the space voyage of the first private lunar apparatus ended.
Eight (8!) Years of development, project cost $ 100 million, 200 volunteers, scientists and engineers, 47 days of flight and more than 6.5 million kilometers overcome, at the start 380 kilograms of fuel, the forced engine "LEROS 2b", 6 onboard chambers, magnetometer, an array of laser corner reflectors, and 1 landing attempt, in which a 150-kilogram apparatus with 76 kilograms of fuel (hydrazine) in tanks at high speed fell to the surface of the moon.
The total mass of the Bereshit device when hitting the lunar surface: 150 kg (the device itself) +76 kg (remaining fuel) = 226 kg, speed over 940 m / s, the kinetic energy of the Bereshit device at the moment of collision was at least 103 MJ that is equivalent to an explosion of 25 kg of TNT (trinitrotoluene).
In the picture below, the white bar is 100 meters.

Comparison of the location of the apparatus and the planned areas for landing:

By the way, after the fall of the Bereshit apparatus, dark spots were formed on the surface of the Moon from hydrazine emissions upon impact, as well as at the site of the fall of the Schiaparelli apparatus on Mars (the European Schiaparelli probe crashed to Mars at a speed of 300 km / h).
Space lunar spacecraft around the crash site:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/452004/
All Articles