Introduction to MS Dynamics CRM
Hi Habr! In this article I would like to talk about some of the standard features of Dynamics CRM (to understand what it is all about), its core business processes and means of expanding the functionality right out of the box.

To begin with, let's go over some facts about Microsoft's CRM system:
For developers it is useful to know that:
')
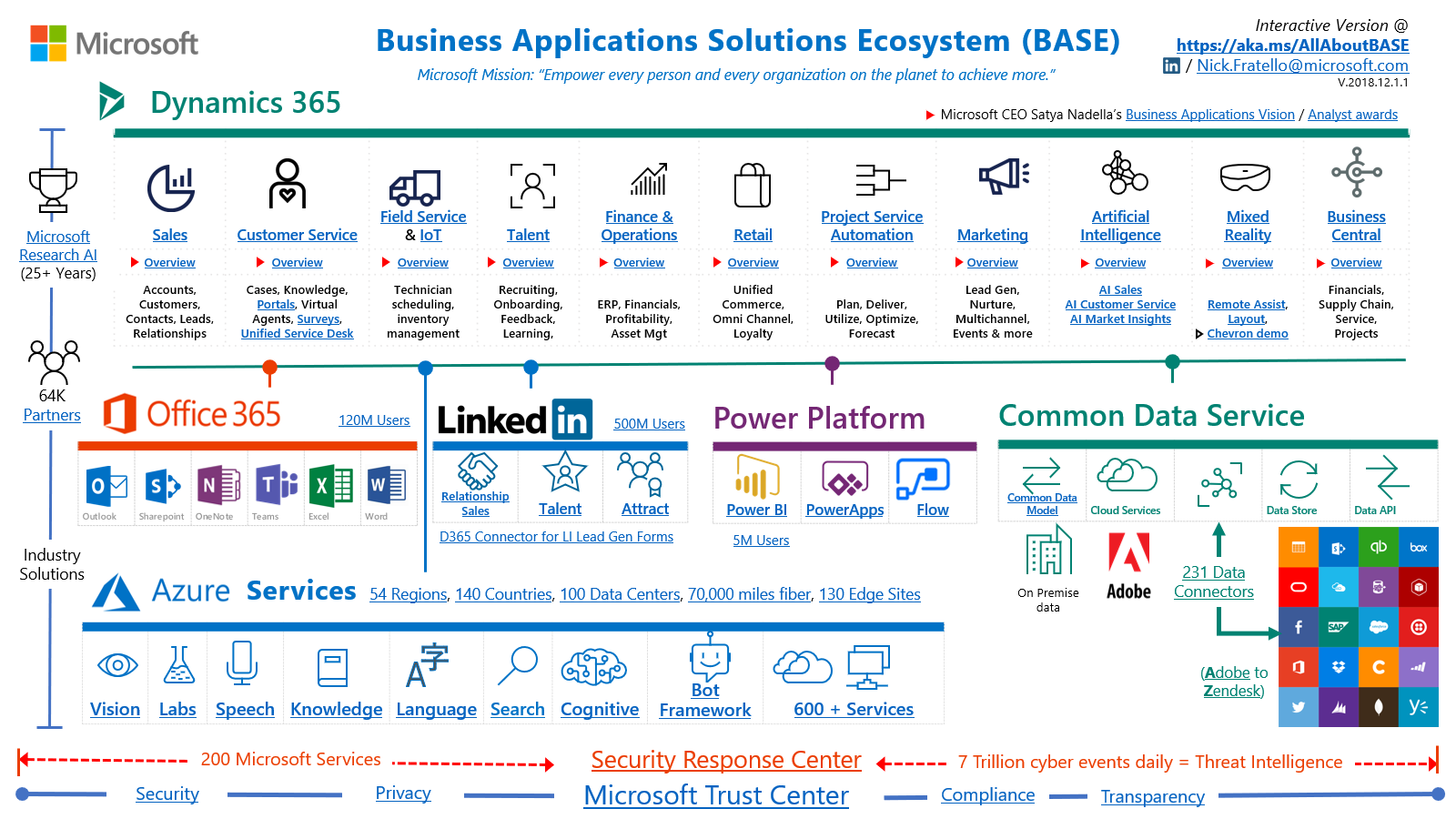
Also let's take a look at what place CRM (Sales) occupies in the ecosystem of Microsoft solutions.
From the user's point of view, everything is simple. We get the url address and go there using your favorite browser.
Until recently, Microsoft recommended using only Internet Explorer, but nothing lasts forever, and now you can work with a clear conscience through Chrome.
When you go to the address, you will have to enter your username and password account (CRM uses ADFS to authenticate users), and get to the home page.
Let's imagine you are a sales manager.
Our company carried out an advertising campaign a week ago, and the marketing director brought it to the lead system (Lead or Potential Client) and assigned them to us.
What is a lead? Well, there is some kind of company that seems to be interested in our services, and we have the opportunity to offer them something, but they still don’t know what they really need.
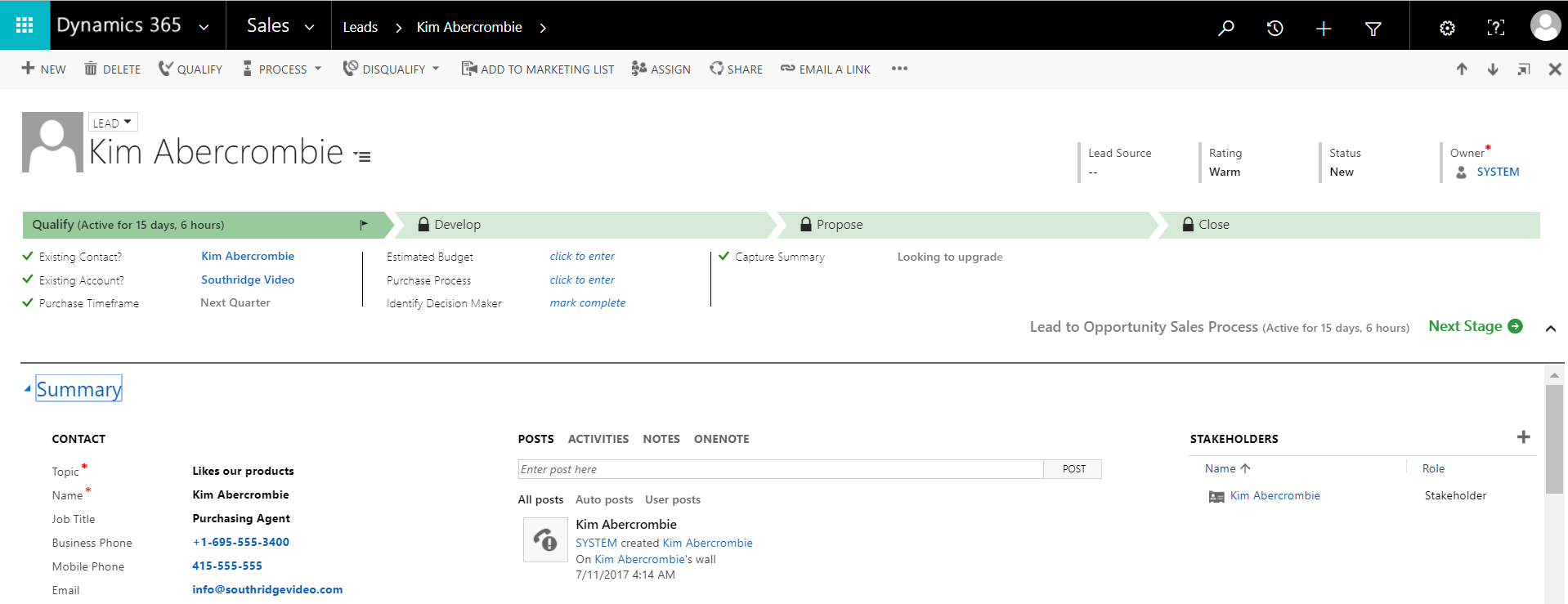
Lida's form looks like this:
We call them and find out what needs to be done, they seem to agree with the proposal and are ready to discuss further. Fine! This means that we can qualify (Qualify) a lead, and CRM will automatically create from one record as many as 3: Contact (Contact), Organization (Account) and Opportunity.
The next stage after Lida - Possible Transaction. At this stage, there is an active clarification of the client's needs, we will start filling in the Products of the Possible Transaction, which are taken from the Products catalog.
Standard Fields for Possible Transaction:
Additionally, you can fill in the Competitors table. Helps to analyze competition in general, keeps a history of winnings and losses for each company of rivals.
Table (Sub-Grid) The Sales Team allows you to have a list of people working on a transaction.
When adding Products to the Possible Transaction, the expected profit is automatically calculated. Developers have the opportunity to override it, if you need to add new fields to the calculation formula. Do you want to immediately include in the profit calculation possible rollback? No problem.
It is important to note that the transaction can be closed as lost. CRM will ask the reason and put it in the client’s story as an action.
The next step is the creation of a commercial offer (Quote).
Commercial Offer has its own life cycle. It is created from the Possible Transaction in the Draft status with the pull-up of its own products. User can change products and their price. As soon as he has reached the point where he is ready to send an offer to the client, the record goes into Active (Active) status and the record becomes unedited.
If the client agrees with the proposal, then it closes with the status of Win (Won) and we go to the Order stage. If it is necessary to change something, then we choose Revise, and a new Commercial Proposal will be created, with products pulled up again.
An order is essentially an approved commercial offer. It contains information about the products or services that the customer ordered. From it, you can create an Invoice (Invoice), which can be closed with the status Paid or Canceled.
Further in the course should come integration with other systems. For example, MS NAV. Microsoft provides a ready solution for this connector.
With such a customer story, you can build the most important chart in CRM - the Sales Funnel:
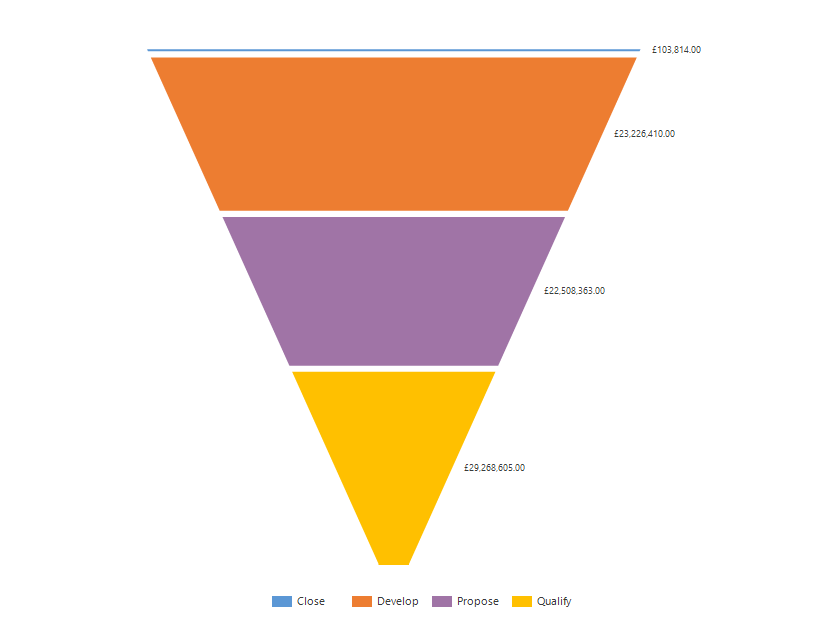
It allows you to analyze the dynamics of sales in various stages, starting with the lead and ending with the order. For example, you can find the bottlenecks in which most customers are lost, and try to fix them. Also, the director of sales can estimate future profits, depending on the number of leads at the moment.
Contains Incidents (Cases), which are created by the support service, automatically via emails or via integration with third-party systems. Incidents store information about the client’s problem. They can be added to special queues, which allows you to more effectively distribute the load on the support service.
Dynamics CRM has a Knowledge Base functionality (Knowledge Base) to help solve problems. The database contains articles that are grouped by topic.
It is also possible to monitor KPI (Key Performance Indicator) using customizable SLAs (Service Level Agreement). SLAs are customized based on work hours, work days, and schedule on weekends. When creating an Incident, these SLAs are taken and the time it takes to solve the problem is calculated.
For the user, this can be seen as a timer on the main form of the Incident. Reverse move can be stopped if, for example, the user is waiting for a response from the client.
Marketing lists are a convenient way to group Contacts, Organizations and Leads into groups by any criterion or manually. They can be both static and dynamic (obviously, for those created by a predetermined criterion). Ultimately, these lists are used for any kind of marketing actions: sending news messages, promotional materials, etc.

Campaigns in Dynamics CRM are represented by regular campaigns (Campaings) and quick campaigns (Quick Campaigns). In general, they are created to control actions for each of them, as well as for a convenient ROI (Return on investemnts).
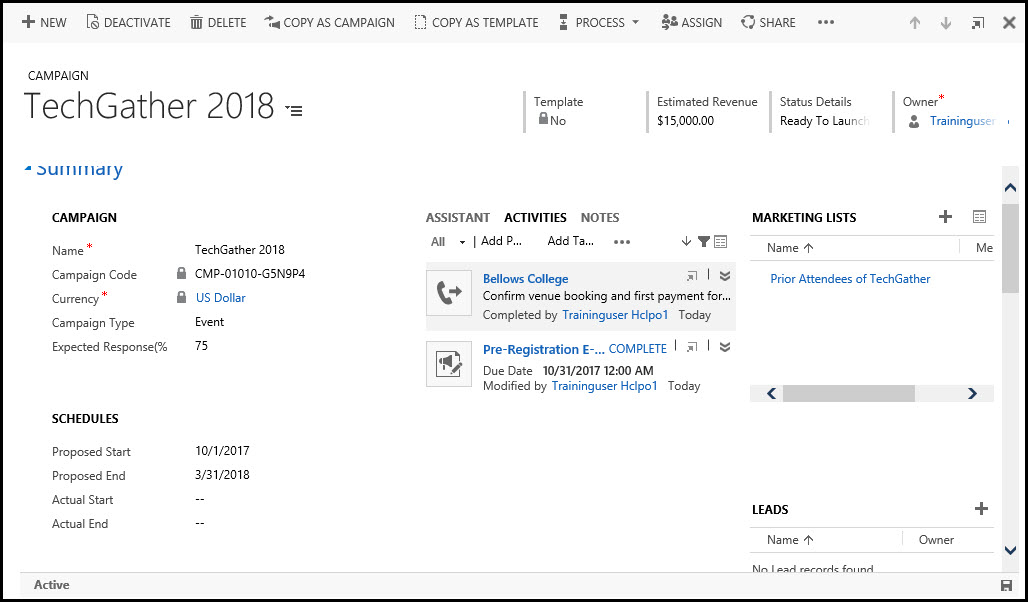
Campaigns have a list of responses (Campaign Responses), which is created to understand its success. Responses can be made both manually and automatically using incoming emails.
What are the differences between Campaign and Quick Campaign?
A quick campaign can have only one type of activity, one list of clients, does not have built-in metrics, cannot be created from campaign templates, it assumes quick execution. As an example, the email campaign is before Thanksgiving sale. Generated a mailing list, produced it, got feedback, counted the number of generated leads and ROI based on the conversion of Lida to Possible Transaction, closed the campaign.
Finally, you can go to what I started all this.
There are many ways to extend the functionality of CRM. In this article I will describe elementary things, such as the creation of new Entities, Fields, Forms, Views.
Solutions

To begin with, it is necessary to tell about Solutions (Solutions). These are packages containing the complete or partial state of any object added there. They are used to transfer components from one system to another, as well as to develop new components. You can get to the list of Solutions by going to Settings / Solutions in the menu.
Before us is the form of the newly created Solution.
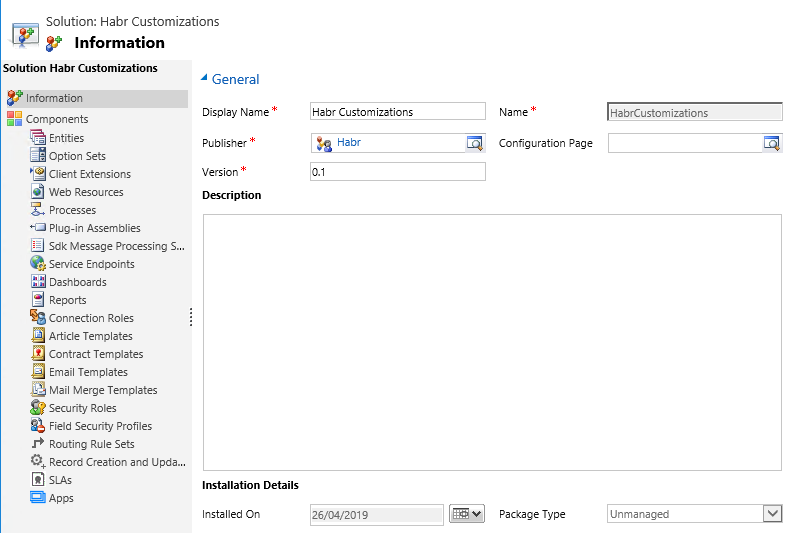
Note the Publisher field. It stores the Name and Component Developer Prefix. Depending on the solution in which the component will be created, it will have such a prefix. For example, the Publisher has the prefix habr, respectively, the new User entity will have a system name like habr_user.
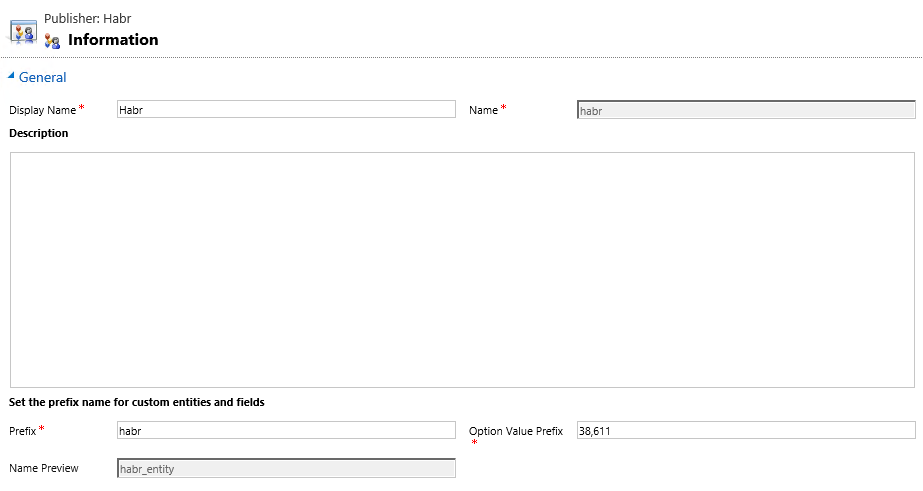
Solutions can be exported or imported. When exporting, you can choose how it should be. Managed or Unmanaged.
Solutions are divided into 3 types.
In order for the changes to take effect, they must be published (Publish). To do this, simply click on the necessary button by selecting the necessary Solution.
Entities
Or Entities. With their help, you can determine the types of records. The closest analogy is the database table.
Let's create our first Entity. Go to the Entities section and click New.
A new form for creating an entity will open.
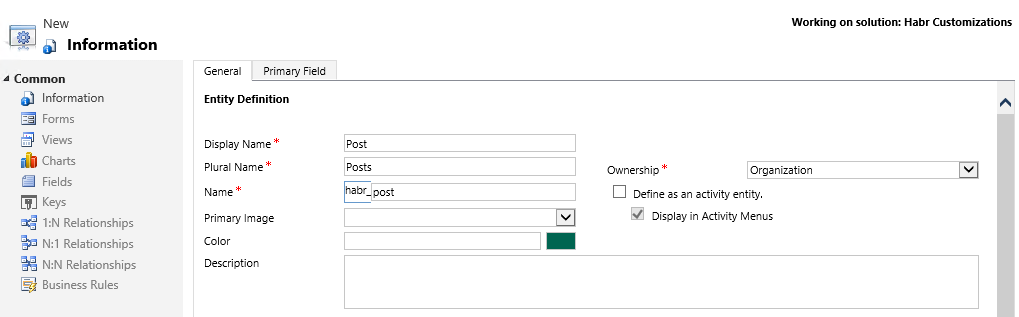
Ownership Type - allows you to select the owner of the record. By default, this is Organization, ie the owner is not as such. If you select User or Group, then the entity will have an Owner field. In the future, depending on the type of property, you can flexibly customize user access to records and their visibility in divisions.
If you select Define as an activity entity, then the entity will become an action. Actions are entries that can be displayed on a calendar. For such an entity, the Start Time, End Time, Duration fields will be automatically added. The action can be Undo or Execute. Only the User or Group can be the owner of such an entity.
In the Primary Field tab, you can set the parameters of the Main Field, which will be mandatory.
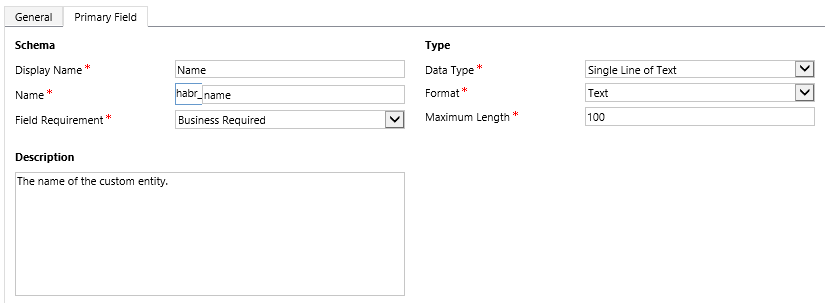
If you wish, you can change the name or type to something else. In this case, I recommend to make sure that it is filled for each record, and is unique. The value of this field is used as the Lookup field designation. As an example, lookup the Publisher field on the Solution form. (PS field types will be lower)

There is also a fairly large list of settings that can be set. Let's go over the most frequently used ones.


Entity visibility zones (Areas that display this entity) - you can set the tabs of the main menu, in which the entity will be available.
Allow quick create — by default, a new entry is created in a new window. When this function is activated, it becomes possible to create a record from the active window, with only the required fields entered.
Duplicate detection (Duplicate detection) - allows you to prevent the creation of identical records using rules.
Auditing - you can select entity fields for which the entire history of changes will be stored. With this setting you need to be careful, you can get a significant increase in the volume of the database.
Fields
Or Fields. Used to define individual data elements.
After creating an entity, CRM will automatically create base fields.
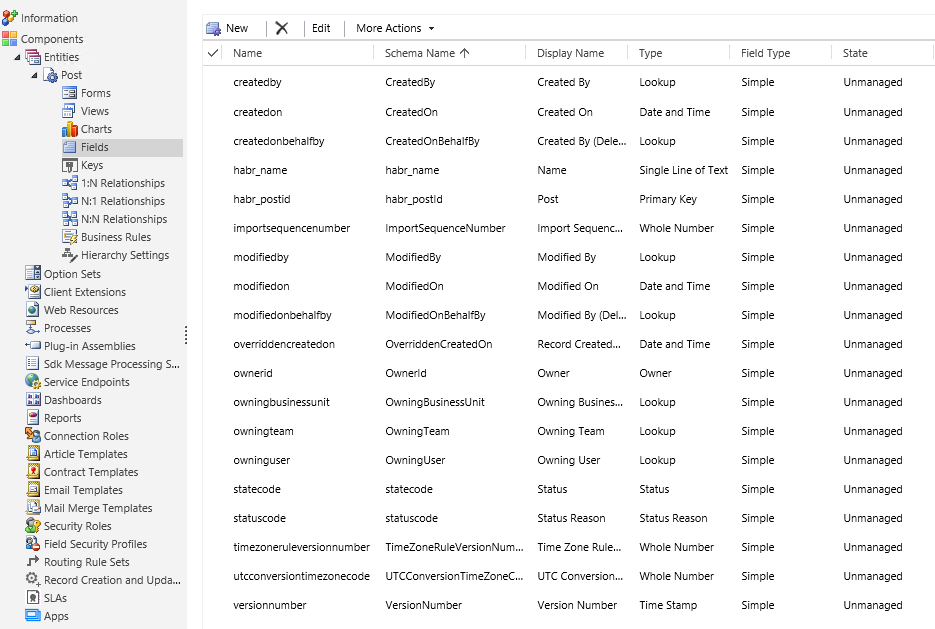
Let's add essence to ours. Click New and see the form to create a new field.
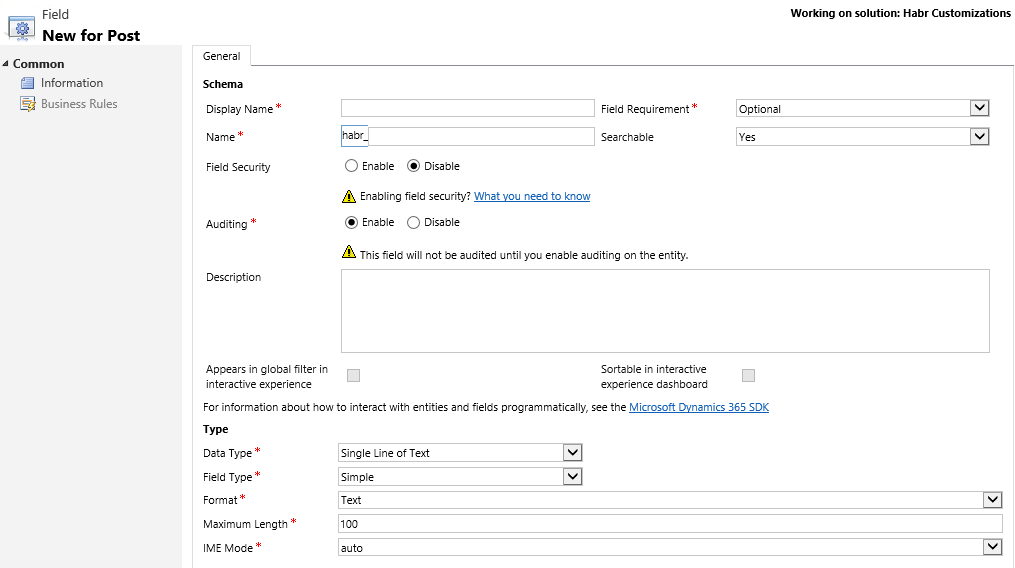
Display Name - the name that will be displayed on the entry form.
Field Requirement - sets the required field. In total there are 3 types. Optional - allows you to create an entry without filling the field; Business recommended - is similar to the optional one, but there will be an asterisk next to the field as a recommendation about filling; Required - you can not create a record without filling this field.
Name - the system name of the field.
Searchable - allows you to use the field to search for records by its value.
Field Security - allows you to further customize to whom this field is displayed.
Auditing - allows you to enable field auditing. (There will be a history of changes)
Data Type - the data type of the field. There are a total of 12 data types.
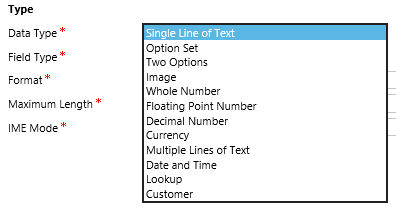
Single Line of Text - a line of text. May contain up to 4000 characters, but can be limited to a smaller number.
Option Set - Name-Value List
Two Options - the usual Boolean
Image - picture
Whole Number - An integer between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647.
Floating Point Number - a number in the range from -100,000,000,000 to 100,000,000,000, which can contain up to 5 decimal places.
Decimal Number - a number in the range from -100,000,000,000 to 100,000,000,000, which can contain up to 10 decimal places.
Currency - monetary values in the range from -922 337 203 685 477 to 922 337 203 685 477
Multiple Lines of Text - multiple lines of text. It can contain up to 1,048,576 characters, but can be limited to a smaller number.
Date and Time - date and time. In the database, this field is stored in UTC; the field can be configured to display UTC or the user's local time. You can also show the date and time, or just the date.
Lookup - is a link to the record of any entity. It stores 3 values at once (Record name, GUID and entity type). According to the rule of good tone at the end of the name is written 'id', as the designation of the field lookup. A small digression: a reference book from Microsoft translates the name of this field as Search. However, everyone calls him simply Lucap.
Customer - in fact it is a multi Lookup, which can refer only to 2 entities - Contact or Account.
There are 3 types of fields. Not every data type can have all 3 field types.
Forms
Each entity contains its own Forms. They allow you to customize the display of fields for different cases.
There are 4 types of forms:
Main - the form that will be displayed when opening a record through the browser.
Mobile - this form will open on a mobile device.
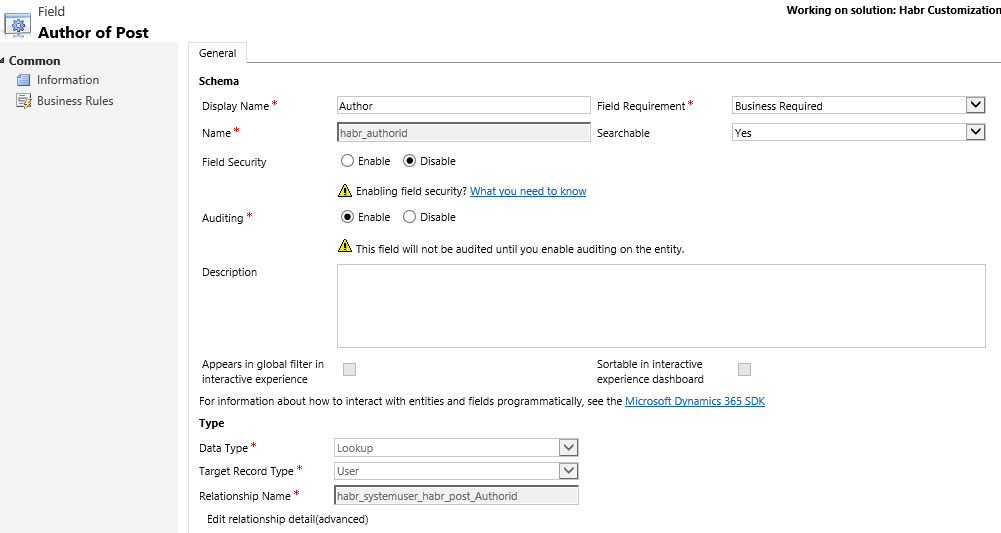
Quick View - allows you to embed this form in the form of other entities. For example, the Main form of the Post entity contains the Author field (which refers to the User entity), and we display additional User data through its Quick View form.

Quick Create - a form for quick record creation (Without opening a new browser window)
Customize Forms
Dynamics CRM allows you to flexibly customize the look and functionality of Forms.
Main features of the form editor:
This is what the form editor will look like for our Post entity.
In our case, we have only 1 Tab named General (circled in blue frame), inside of which there is one Section also named General.
Home tab
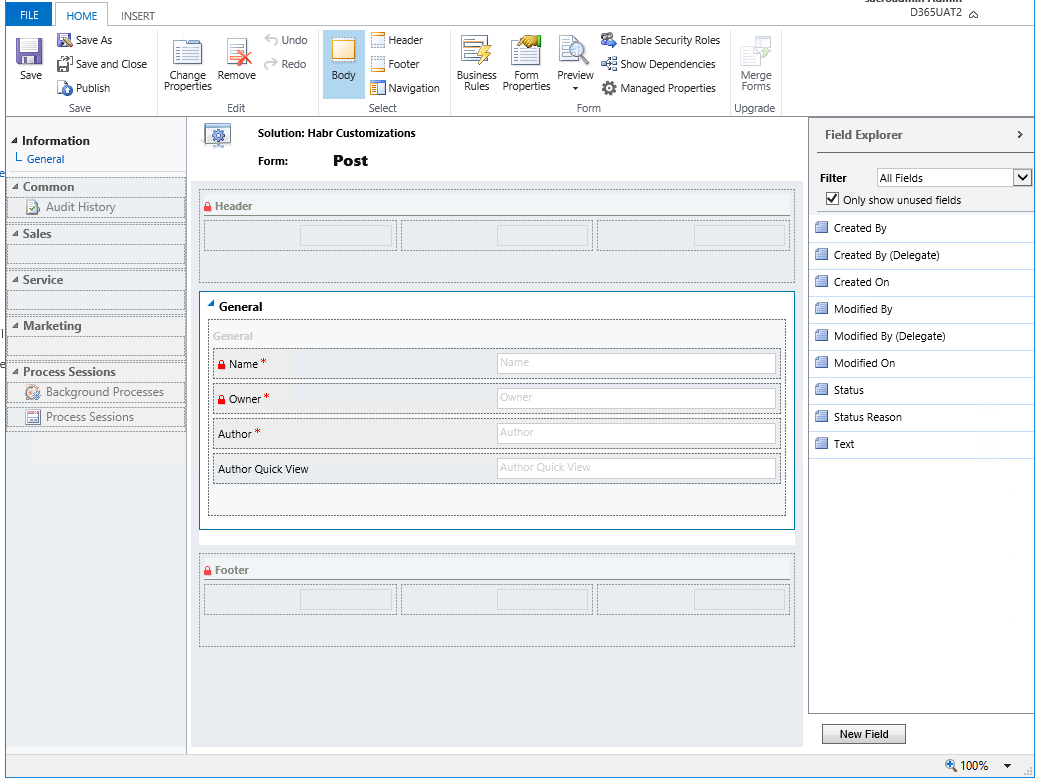
In general, Main forms consist of 4 parts: Header, Body, Footer, and Navigation on the left.
In order to choose what you currently want to edit, you will have to use the Select group on the ribbon ribbon.
Fields are added by double clicking or dragging.
Delete the same button Remove. Required fields (which are with a red asterisk), so simply remove from the form will not work. You must first change their type to Optional.
The Form Properties button allows you to add JS files to a form, and register their functions for form and field events.
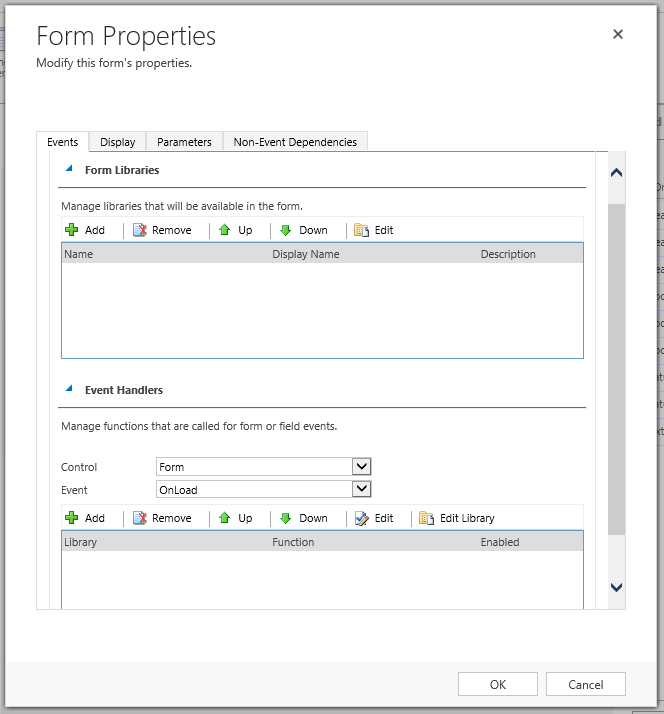
Insert tab
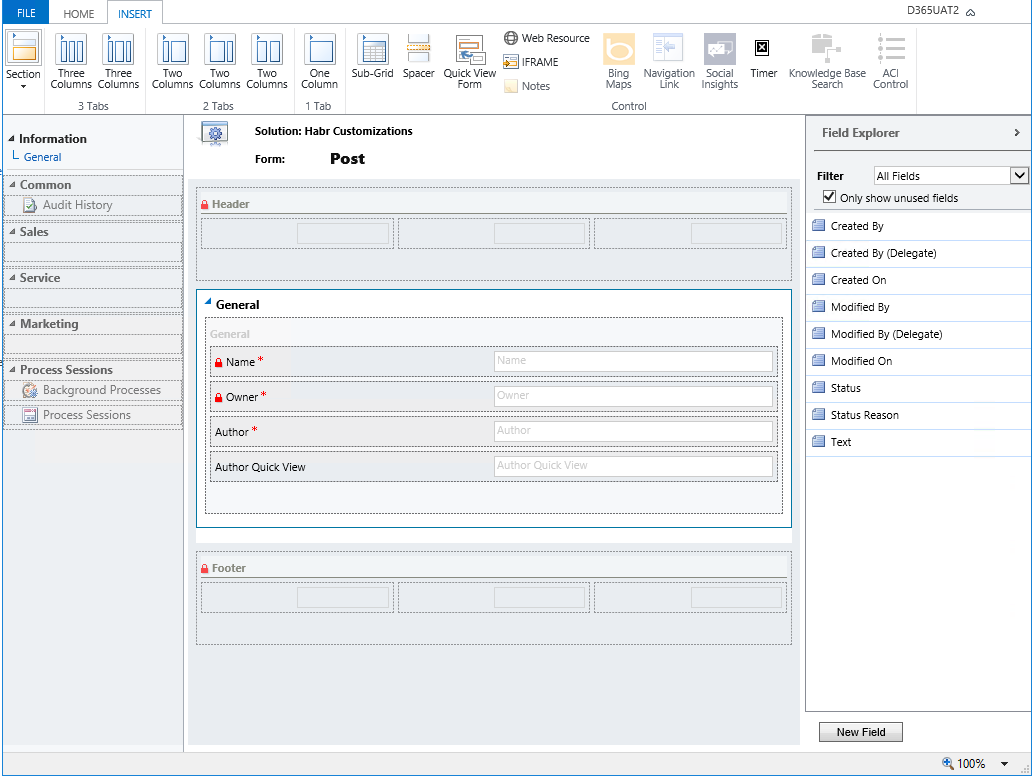
In the Insert tab, we work only with the form body. Here we change its markup.
Ribbon ribbon commands in this case:
Section - adds a section to the selected tab. May contain 1-4 columns.
Tabs (Tabs) - many options add a tab with the number of sections 1-3 of different widths.
Here is an example tab with three sections. One section has three columns, two others one by one. Each column is the potential location of the field.

Sub-Grid - adds a list of related (or not) entity records to the form.
Briefly about what it is.
For example, Habr added the donation feature for articles. Create a Donations entity that contains a lookup on Post. At the same time, when creating a field, an N: 1 relationship is created.
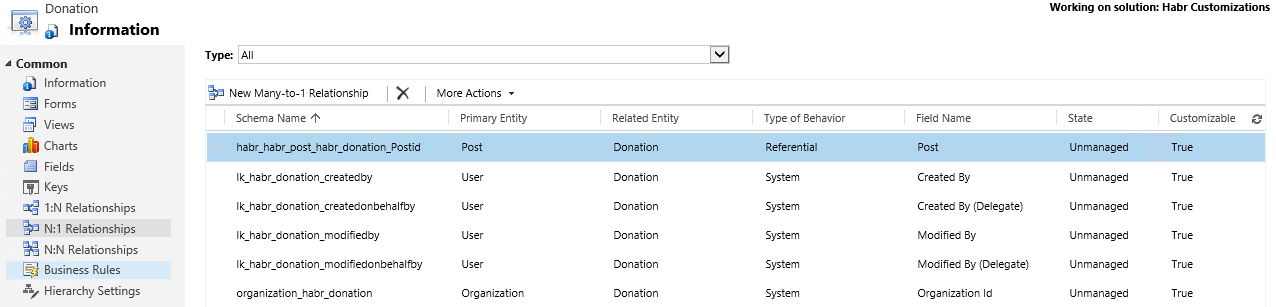
Everything, now we can add a Sub-Grid showing donations. The Sub-Grid configuration window looks like this:
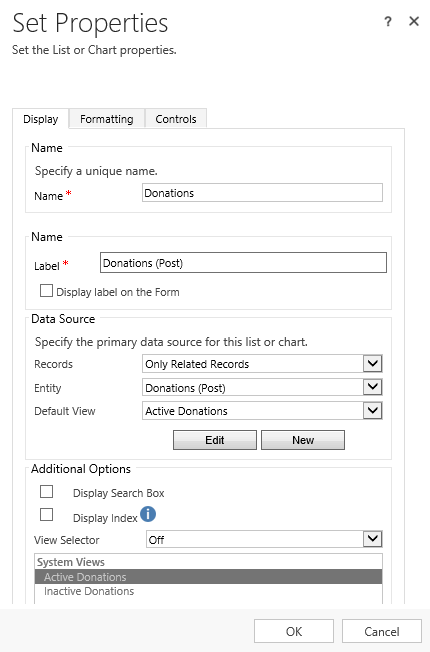
And our form will look like this:
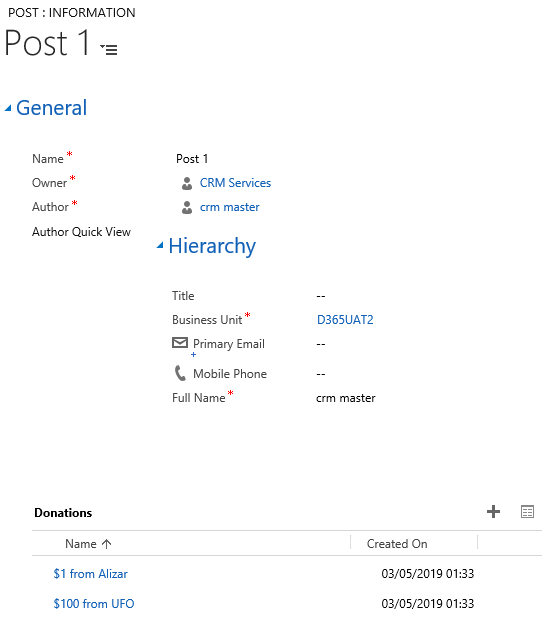
Spacer - creates empty space.
Quick View Form - adds a quick view form. We have already done this for the author.
Web Resource - adds a web resource to the form. For example, an interactive html page or a Silverlight application.
IFrame - you can add them too
Notes - Adds a panel for creating notes.
Views
Or Views, used to display lists of entries.
You can set the displayed fields, their width, as well as filters and sorting.
Here is an example that shows only active posts.
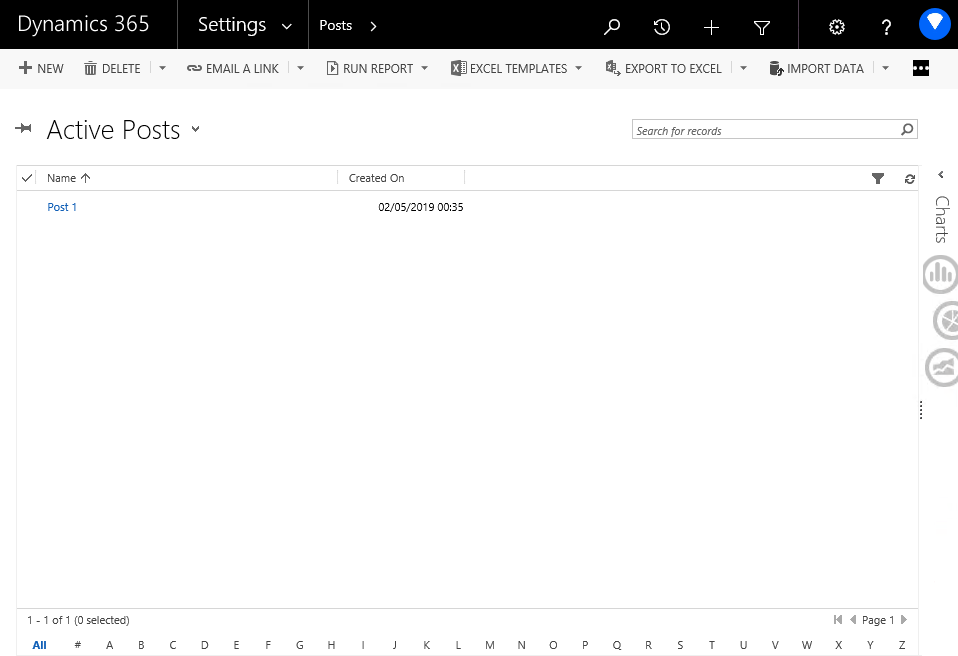
Submissions are:
General - views available to all users. When creating a new entity, Active and Inactive views are automatically created.
Personal - belong to individual users. Can be created by the administrator, and then separately assigned to another.
System - are not directly available for selection from the list of views, but exist as add-ons that extend the functionality of individual interface elements. For example, quick search, advanced search
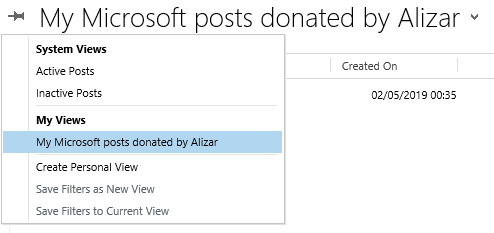
Create your personal presentation?
Click on the list of views and select Create Personal View.
A new window opens to customize the view. You can take an existing view as a basis by selecting it in Use Saved View.
Edit Columns allows you to select which fields to display.
Results allows you to check which records will be displayed after applying the filter.
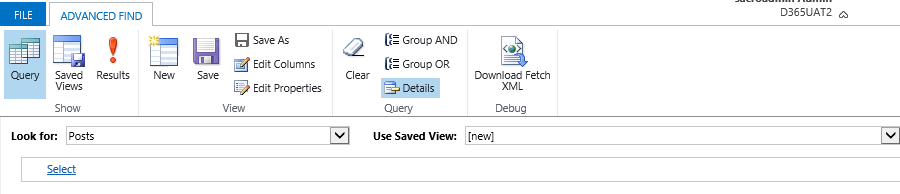
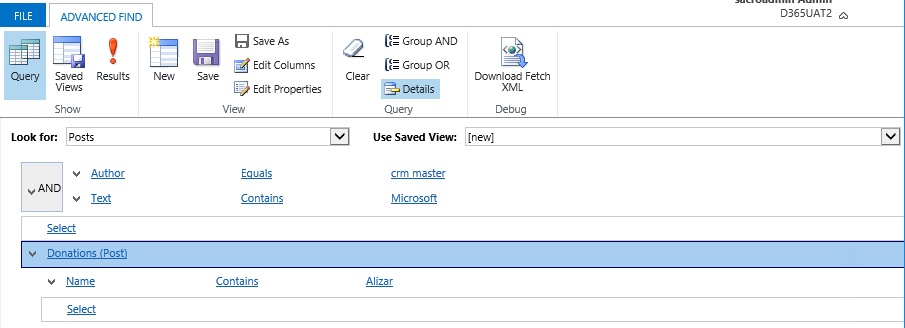
The filter is constructed by adding conditions using Select and grouping them through AND / OR.

Here is the finished filter. Save it along the way giving the name, and we get a finished personal presentation.
In this article, I gave information for a great start in the development for Dynamics CRM. In the following articles we will deal with the rest of the available customizations, the official SDK, must have applications, write plugins and workflows.
I would be grateful for the feedback and thank you for reading the article.

To begin with, let's go over some facts about Microsoft's CRM system:
- Currently included in the top 5 CRM systems in the world. The number of customers is gradually increasing from year to year.
- New customers can start working only as a cloud - online version. Before that, the version on a private server, on-premise, was available, old clients continue to use it.
- Available to work through a browser, Outlook plug-in, mobile applications, and through a special application Unified Interface.
- In the latest rethinking marketers became known under the new names Dynamics 365 for Sales and Dynamics 365 for Customer Engagement. The people continues to be called Dynamics CRM.
- Out of the box, the customer receives sales management, a catalog of products and services, and action tracking. Marketing campaign management and incident management are also available.
For developers it is useful to know that:
')
- The average sn in the US market: Junior - $ 87163, Middle - $ 127614, Senior - $ 151321
- For the selection of consultants and programmers there are entire agencies, for example Nigel Frank.
Also let's take a look at what place CRM (Sales) occupies in the ecosystem of Microsoft solutions.

Start using
From the user's point of view, everything is simple. We get the url address and go there using your favorite browser.
Until recently, Microsoft recommended using only Internet Explorer, but nothing lasts forever, and now you can work with a clear conscience through Chrome.
When you go to the address, you will have to enter your username and password account (CRM uses ADFS to authenticate users), and get to the home page.

Sales module
Let's imagine you are a sales manager.
Our company carried out an advertising campaign a week ago, and the marketing director brought it to the lead system (Lead or Potential Client) and assigned them to us.
What is a lead? Well, there is some kind of company that seems to be interested in our services, and we have the opportunity to offer them something, but they still don’t know what they really need.
Lida's form looks like this:

We call them and find out what needs to be done, they seem to agree with the proposal and are ready to discuss further. Fine! This means that we can qualify (Qualify) a lead, and CRM will automatically create from one record as many as 3: Contact (Contact), Organization (Account) and Opportunity.
The next stage after Lida - Possible Transaction. At this stage, there is an active clarification of the client's needs, we will start filling in the Products of the Possible Transaction, which are taken from the Products catalog.
Standard Fields for Possible Transaction:
- Potential Client - can be both Contact and Organization. This link allows you to track the entire history of working with the client.
- Expected closing date - shows the time of completion of the order. It can be used for an approximate calculation of the receipt of funds or for the preparation of labor for the project.
Additionally, you can fill in the Competitors table. Helps to analyze competition in general, keeps a history of winnings and losses for each company of rivals.
Table (Sub-Grid) The Sales Team allows you to have a list of people working on a transaction.
When adding Products to the Possible Transaction, the expected profit is automatically calculated. Developers have the opportunity to override it, if you need to add new fields to the calculation formula. Do you want to immediately include in the profit calculation possible rollback? No problem.
It is important to note that the transaction can be closed as lost. CRM will ask the reason and put it in the client’s story as an action.
The next step is the creation of a commercial offer (Quote).
Commercial Offer has its own life cycle. It is created from the Possible Transaction in the Draft status with the pull-up of its own products. User can change products and their price. As soon as he has reached the point where he is ready to send an offer to the client, the record goes into Active (Active) status and the record becomes unedited.
If the client agrees with the proposal, then it closes with the status of Win (Won) and we go to the Order stage. If it is necessary to change something, then we choose Revise, and a new Commercial Proposal will be created, with products pulled up again.
An order is essentially an approved commercial offer. It contains information about the products or services that the customer ordered. From it, you can create an Invoice (Invoice), which can be closed with the status Paid or Canceled.
Further in the course should come integration with other systems. For example, MS NAV. Microsoft provides a ready solution for this connector.
With such a customer story, you can build the most important chart in CRM - the Sales Funnel:

It allows you to analyze the dynamics of sales in various stages, starting with the lead and ending with the order. For example, you can find the bottlenecks in which most customers are lost, and try to fix them. Also, the director of sales can estimate future profits, depending on the number of leads at the moment.
Customer Service Management Module
Contains Incidents (Cases), which are created by the support service, automatically via emails or via integration with third-party systems. Incidents store information about the client’s problem. They can be added to special queues, which allows you to more effectively distribute the load on the support service.
Dynamics CRM has a Knowledge Base functionality (Knowledge Base) to help solve problems. The database contains articles that are grouped by topic.
It is also possible to monitor KPI (Key Performance Indicator) using customizable SLAs (Service Level Agreement). SLAs are customized based on work hours, work days, and schedule on weekends. When creating an Incident, these SLAs are taken and the time it takes to solve the problem is calculated.
For the user, this can be seen as a timer on the main form of the Incident. Reverse move can be stopped if, for example, the user is waiting for a response from the client.
Marketing module
Marketing lists are a convenient way to group Contacts, Organizations and Leads into groups by any criterion or manually. They can be both static and dynamic (obviously, for those created by a predetermined criterion). Ultimately, these lists are used for any kind of marketing actions: sending news messages, promotional materials, etc.

Campaigns in Dynamics CRM are represented by regular campaigns (Campaings) and quick campaigns (Quick Campaigns). In general, they are created to control actions for each of them, as well as for a convenient ROI (Return on investemnts).

Campaigns have a list of responses (Campaign Responses), which is created to understand its success. Responses can be made both manually and automatically using incoming emails.
What are the differences between Campaign and Quick Campaign?
A quick campaign can have only one type of activity, one list of clients, does not have built-in metrics, cannot be created from campaign templates, it assumes quick execution. As an example, the email campaign is before Thanksgiving sale. Generated a mailing list, produced it, got feedback, counted the number of generated leads and ROI based on the conversion of Lida to Possible Transaction, closed the campaign.
Means of functional expansion
Finally, you can go to what I started all this.
There are many ways to extend the functionality of CRM. In this article I will describe elementary things, such as the creation of new Entities, Fields, Forms, Views.
Solutions

To begin with, it is necessary to tell about Solutions (Solutions). These are packages containing the complete or partial state of any object added there. They are used to transfer components from one system to another, as well as to develop new components. You can get to the list of Solutions by going to Settings / Solutions in the menu.
Before us is the form of the newly created Solution.

Note the Publisher field. It stores the Name and Component Developer Prefix. Depending on the solution in which the component will be created, it will have such a prefix. For example, the Publisher has the prefix habr, respectively, the new User entity will have a system name like habr_user.

Solutions can be exported or imported. When exporting, you can choose how it should be. Managed or Unmanaged.
Solutions are divided into 3 types.
- Default Solution - The default solution or global solution. Each CRM system has one default Solution. It contains everything that is in the current system.
- Managed Solution - can be created during the export of an unmanaged solution by selecting the appropriate parameter. Anything inside this solution cannot be changed further. Typically, this type is used to distribute the finished product for CRM systems of several clients.
- Unmanaged Solution - everything inside this solution can be deleted or changed, new customizations can also be added to it. If you customize CRM individually (for each client - their own changes), then you will most likely use only this type of solutions.
In order for the changes to take effect, they must be published (Publish). To do this, simply click on the necessary button by selecting the necessary Solution.
Entities
Or Entities. With their help, you can determine the types of records. The closest analogy is the database table.
Let's create our first Entity. Go to the Entities section and click New.

A new form for creating an entity will open.

Ownership Type - allows you to select the owner of the record. By default, this is Organization, ie the owner is not as such. If you select User or Group, then the entity will have an Owner field. In the future, depending on the type of property, you can flexibly customize user access to records and their visibility in divisions.
If you select Define as an activity entity, then the entity will become an action. Actions are entries that can be displayed on a calendar. For such an entity, the Start Time, End Time, Duration fields will be automatically added. The action can be Undo or Execute. Only the User or Group can be the owner of such an entity.
In the Primary Field tab, you can set the parameters of the Main Field, which will be mandatory.

If you wish, you can change the name or type to something else. In this case, I recommend to make sure that it is filled for each record, and is unique. The value of this field is used as the Lookup field designation. As an example, lookup the Publisher field on the Solution form. (PS field types will be lower)

There is also a fairly large list of settings that can be set. Let's go over the most frequently used ones.


Entity visibility zones (Areas that display this entity) - you can set the tabs of the main menu, in which the entity will be available.
Allow quick create — by default, a new entry is created in a new window. When this function is activated, it becomes possible to create a record from the active window, with only the required fields entered.
Duplicate detection (Duplicate detection) - allows you to prevent the creation of identical records using rules.
Auditing - you can select entity fields for which the entire history of changes will be stored. With this setting you need to be careful, you can get a significant increase in the volume of the database.
Fields
Or Fields. Used to define individual data elements.
After creating an entity, CRM will automatically create base fields.

Let's add essence to ours. Click New and see the form to create a new field.

Display Name - the name that will be displayed on the entry form.
Field Requirement - sets the required field. In total there are 3 types. Optional - allows you to create an entry without filling the field; Business recommended - is similar to the optional one, but there will be an asterisk next to the field as a recommendation about filling; Required - you can not create a record without filling this field.
Name - the system name of the field.
Searchable - allows you to use the field to search for records by its value.
Field Security - allows you to further customize to whom this field is displayed.
Auditing - allows you to enable field auditing. (There will be a history of changes)
Data Type - the data type of the field. There are a total of 12 data types.

Single Line of Text - a line of text. May contain up to 4000 characters, but can be limited to a smaller number.
Option Set - Name-Value List
Two Options - the usual Boolean
Image - picture
Whole Number - An integer between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647.
Floating Point Number - a number in the range from -100,000,000,000 to 100,000,000,000, which can contain up to 5 decimal places.
Decimal Number - a number in the range from -100,000,000,000 to 100,000,000,000, which can contain up to 10 decimal places.
Currency - monetary values in the range from -922 337 203 685 477 to 922 337 203 685 477
Multiple Lines of Text - multiple lines of text. It can contain up to 1,048,576 characters, but can be limited to a smaller number.
Date and Time - date and time. In the database, this field is stored in UTC; the field can be configured to display UTC or the user's local time. You can also show the date and time, or just the date.
Lookup - is a link to the record of any entity. It stores 3 values at once (Record name, GUID and entity type). According to the rule of good tone at the end of the name is written 'id', as the designation of the field lookup. A small digression: a reference book from Microsoft translates the name of this field as Search. However, everyone calls him simply Lucap.

Customer - in fact it is a multi Lookup, which can refer only to 2 entities - Contact or Account.
There are 3 types of fields. Not every data type can have all 3 field types.
- Simple - ordinary field
- - Calculated - the content can be customized using the editor. Example:
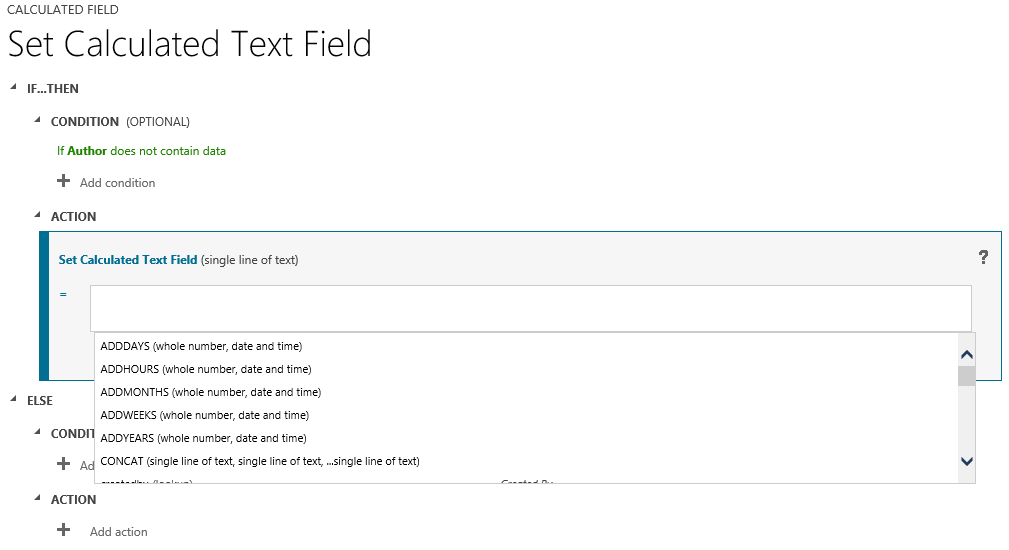
- Rollup - contains an aggregated value calculated by child records. Configured with the editor. An example of such a field is the total amount of all transactions for a manager.
Forms
Each entity contains its own Forms. They allow you to customize the display of fields for different cases.
There are 4 types of forms:
Main - the form that will be displayed when opening a record through the browser.
Mobile - this form will open on a mobile device.
Quick View - allows you to embed this form in the form of other entities. For example, the Main form of the Post entity contains the Author field (which refers to the User entity), and we display additional User data through its Quick View form.

Quick Create - a form for quick record creation (Without opening a new browser window)

Customize Forms
Dynamics CRM allows you to flexibly customize the look and functionality of Forms.
Main features of the form editor:
- Adding a field
- Deleting a field
- Hiding the field
- Adding Business Rules
- Changing shape markup
- Adding JS scripts and registering them on form events
This is what the form editor will look like for our Post entity.
In our case, we have only 1 Tab named General (circled in blue frame), inside of which there is one Section also named General.
Home tab

In general, Main forms consist of 4 parts: Header, Body, Footer, and Navigation on the left.
In order to choose what you currently want to edit, you will have to use the Select group on the ribbon ribbon.
Fields are added by double clicking or dragging.
Delete the same button Remove. Required fields (which are with a red asterisk), so simply remove from the form will not work. You must first change their type to Optional.
The Form Properties button allows you to add JS files to a form, and register their functions for form and field events.

Insert tab

In the Insert tab, we work only with the form body. Here we change its markup.
Ribbon ribbon commands in this case:
Section - adds a section to the selected tab. May contain 1-4 columns.
Tabs (Tabs) - many options add a tab with the number of sections 1-3 of different widths.
Here is an example tab with three sections. One section has three columns, two others one by one. Each column is the potential location of the field.

Sub-Grid - adds a list of related (or not) entity records to the form.
Briefly about what it is.
For example, Habr added the donation feature for articles. Create a Donations entity that contains a lookup on Post. At the same time, when creating a field, an N: 1 relationship is created.

Everything, now we can add a Sub-Grid showing donations. The Sub-Grid configuration window looks like this:

And our form will look like this:

Spacer - creates empty space.
Quick View Form - adds a quick view form. We have already done this for the author.
Web Resource - adds a web resource to the form. For example, an interactive html page or a Silverlight application.
IFrame - you can add them too
Notes - Adds a panel for creating notes.
Views
Or Views, used to display lists of entries.
You can set the displayed fields, their width, as well as filters and sorting.
Here is an example that shows only active posts.

Submissions are:
General - views available to all users. When creating a new entity, Active and Inactive views are automatically created.
Personal - belong to individual users. Can be created by the administrator, and then separately assigned to another.
System - are not directly available for selection from the list of views, but exist as add-ons that extend the functionality of individual interface elements. For example, quick search, advanced search
Create your personal presentation?
Click on the list of views and select Create Personal View.

A new window opens to customize the view. You can take an existing view as a basis by selecting it in Use Saved View.
Edit Columns allows you to select which fields to display.
Results allows you to check which records will be displayed after applying the filter.

The filter is constructed by adding conditions using Select and grouping them through AND / OR.

Here is the finished filter. Save it along the way giving the name, and we get a finished personal presentation.


Conclusion
In this article, I gave information for a great start in the development for Dynamics CRM. In the following articles we will deal with the rest of the available customizations, the official SDK, must have applications, write plugins and workflows.
I would be grateful for the feedback and thank you for reading the article.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/451056/
All Articles