Salute from "Hayabusy-2"
A little more than a month ago, the Japanese apparatus "Hayabusa-2" fired its most spectacular shot at the asteroid Ryugu. The probe dropped the impactor with explosives (in simple terms, a bomb) and a special camera to look at the explosion from the side, while he hid behind the asteroid. The operation was successful - the camera took a shot of the explosion, and recently Hayabusa-2 dropped to the impactor's area and discovered a fresh crater there.
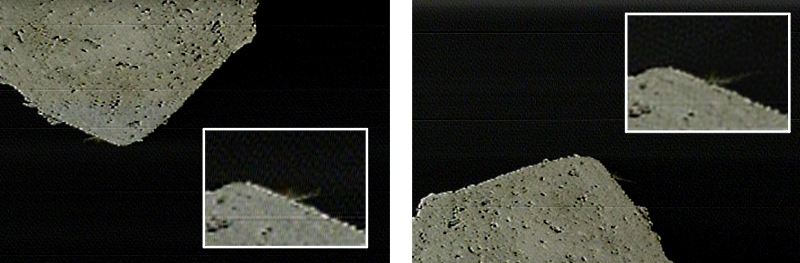
Photo 2 later (left) and 25 seconds after the explosion
The main characters are the Small Carry Impactor (Small carry-on impactor, SCI) and the detachable DCAM3 camera.
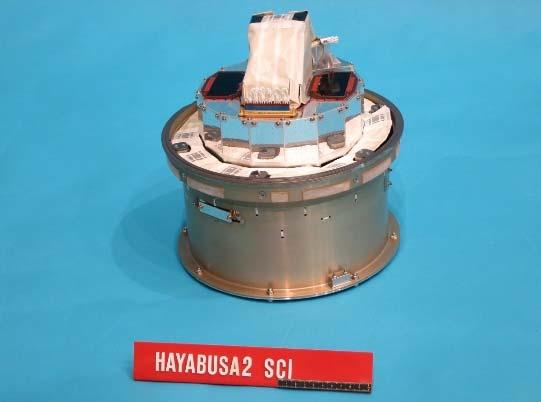

SCI, hereinafter images JAXA
')
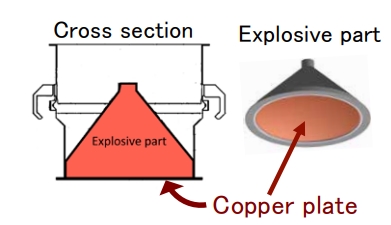
SCI is a small projectile or rather a bomb. Having a diameter of 30 cm, it weighs 14 kg and carries 9.5 kg of explosives in the form of a funnel, which gives a directional explosion. In the lower part there is a 2 mm copper sheet, which, in an explosion, became the main force forming the crater.
Explosive inside sci

The calculated form of the copper sheet in the first 500 microseconds after the explosion

DCAM3
DCAM3 is a detachable module, and not with one, but with two cameras, analog and digital. Analog transmits a signal in the worst quality, but in real time, digital provides the best picture quality, but with a delay. Each camera has its own equipment for processing and transmitting data.
"Hayabusa-2" moved to the path of descent, dropped the impactor, went aside, dropped the camera and went beyond the horizon of the asteroid, just in case.

Movement pattern
The target for the bombing was chosen S01 area near the equator and just west of the Kolobok crater. Selection criteria - a design slip of up to 200 meters does not allow working at high latitudes (risk of overshooting), the area must be even so that the crater is visible, and the probe can land.

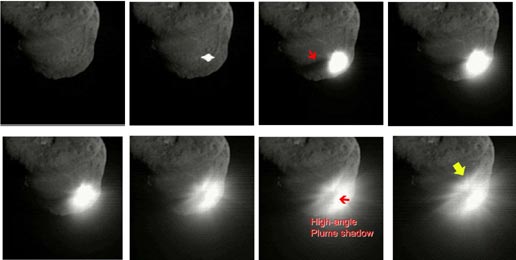
On April 5, the Hayabusy-2 side camera captured the last impactor's flight. Approximately 500 meters to the asteroid, time is greatly accelerated.

185 seconds before the explosion. See the SCIgopher in the photo on the left? And he is there!

At the very first photo at the top of the image from an analog camera. Digital quality will be better. 3 seconds after the explosion.
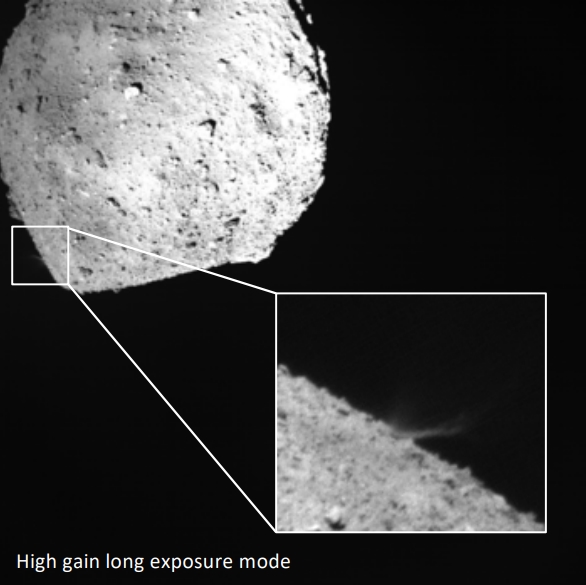

And on April 25, the probe dropped to 1.7 km to find traces of the explosion. In the photo before and after the crater is clearly visible.

The diameter of the crater was estimated at 20 meters, ahead of his study. For example, according to the data on the temperature change of the asteroid's surface depending on the local day, which the TIR-S infrared camera collects, it will be possible to draw conclusions about how porous the crater material is.
The earth apparatus made the first “bombardment” of the asteroid in 2005 — the Deep Impact probe dropped the impactor on Tempel 1 comet. Then the collision looked prettier — because of the relative speed of 10.6 km / s, the explosion energy was five tons in TNT.
Impactor Impactor Collision Results, NASA Photo
But the possibilities for studying the results were much smaller - the apparatus was on overlapping courses and, after taking a series of shots, flew away. Hayabusa-2 was the first probe to bomb an asteroid from its orbit. According to current plans, he will work with the asteroid until December 2019 and travel to Earth with collected samples, which will be delivered in December 2020.

Photo 2 later (left) and 25 seconds after the explosion
Members
The main characters are the Small Carry Impactor (Small carry-on impactor, SCI) and the detachable DCAM3 camera.

SCI, hereinafter images JAXA
')
SCI is a small projectile or rather a bomb. Having a diameter of 30 cm, it weighs 14 kg and carries 9.5 kg of explosives in the form of a funnel, which gives a directional explosion. In the lower part there is a 2 mm copper sheet, which, in an explosion, became the main force forming the crater.

Explosive inside sci

The calculated form of the copper sheet in the first 500 microseconds after the explosion

DCAM3
DCAM3 is a detachable module, and not with one, but with two cameras, analog and digital. Analog transmits a signal in the worst quality, but in real time, digital provides the best picture quality, but with a delay. Each camera has its own equipment for processing and transmitting data.
"Hayabusa-2" moved to the path of descent, dropped the impactor, went aside, dropped the camera and went beyond the horizon of the asteroid, just in case.

Movement pattern
The target for the bombing was chosen S01 area near the equator and just west of the Kolobok crater. Selection criteria - a design slip of up to 200 meters does not allow working at high latitudes (risk of overshooting), the area must be even so that the crater is visible, and the probe can land.

Salute
On April 5, the Hayabusy-2 side camera captured the last impactor's flight. Approximately 500 meters to the asteroid, time is greatly accelerated.

185 seconds before the explosion. See the SCI

At the very first photo at the top of the image from an analog camera. Digital quality will be better. 3 seconds after the explosion.

And on April 25, the probe dropped to 1.7 km to find traces of the explosion. In the photo before and after the crater is clearly visible.

The diameter of the crater was estimated at 20 meters, ahead of his study. For example, according to the data on the temperature change of the asteroid's surface depending on the local day, which the TIR-S infrared camera collects, it will be possible to draw conclusions about how porous the crater material is.
The earth apparatus made the first “bombardment” of the asteroid in 2005 — the Deep Impact probe dropped the impactor on Tempel 1 comet. Then the collision looked prettier — because of the relative speed of 10.6 km / s, the explosion energy was five tons in TNT.

Impactor Impactor Collision Results, NASA Photo
But the possibilities for studying the results were much smaller - the apparatus was on overlapping courses and, after taking a series of shots, flew away. Hayabusa-2 was the first probe to bomb an asteroid from its orbit. According to current plans, he will work with the asteroid until December 2019 and travel to Earth with collected samples, which will be delivered in December 2020.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/450624/
All Articles