Self-made receiving part of the Qi standard
The wireless charging system could be made "stupid", but then it would not distinguish the receiving part from metal objects and heat them with eddy currents. Therefore, when there is no receiving part, the transmitter periodically sends short pulses. When the receiving part is brought in, it starts sending packets informing the transmitting part what power is required from it.
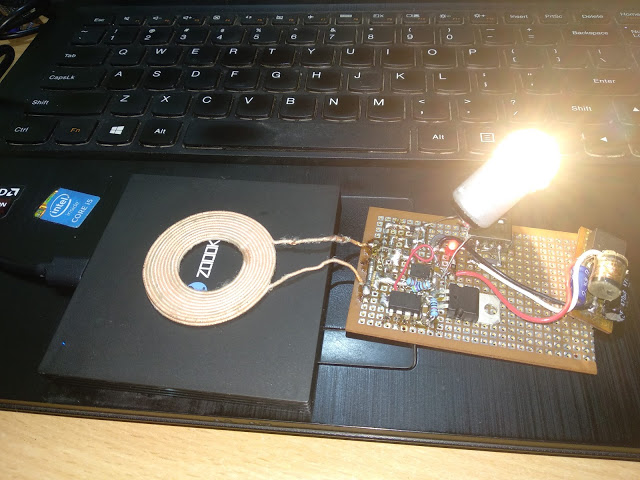
The transmitting part begins to generate oscillations continuously, while it adjusts the power, changing the frequency relative to the resonance as shown in the graph. The farther the frequency from the resonant, the lower the transmitted power.
')
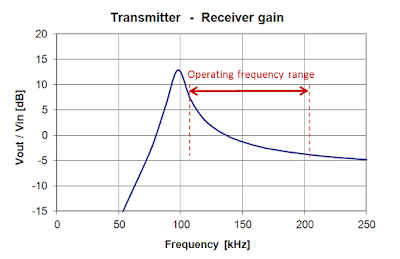
To transfer bits from the receiving part to the transmitter, two transistors are connected to the receiving circuit by small capacitors. The coding method for zeros and ones here is as follows:
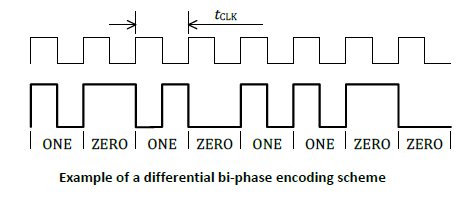
Priskulku with possible errors, they need correction. Each byte is transmitted by eleven bits, the first of them is the start bit, always equal to zero, then eight bits of the byte follow, then the parity bit (set to one if the byte contains an even number of ones), then a stop bit, always equal to one . If the parity bit does not match, the byte is considered received incorrectly.
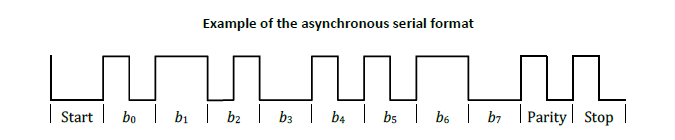
A package consists of an introduction, a header, a message and a checksum. Entry contains from 11 to 25 units. If the checksum does not match, the entire packet is considered incorrectly accepted.

A more detailed specification of the standard is here .
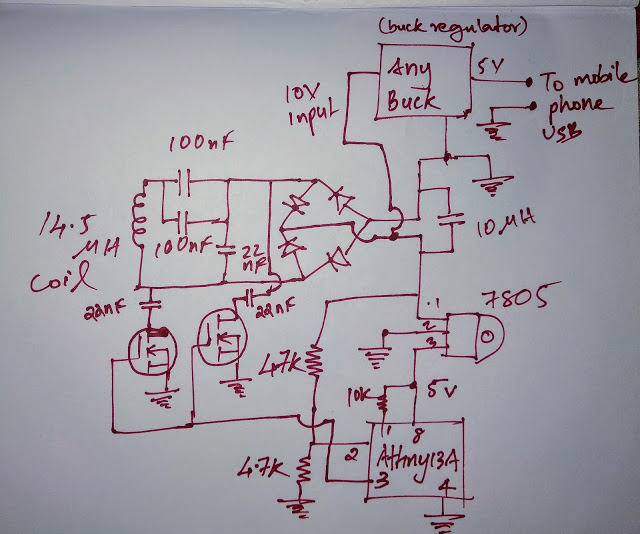
The self-made receiving part consists of a circuit (winding of 10 turns with an inductance of 14.5 μg, two capacitors of 100 nF and one for 22 nF), a rectifier, a filter (a capacitor of 10 μF), two transistors connecting capacitors of 22 nF to the circuit , two stabilizers - a pulse for the load (suitable and ready to charge the cigarette lighter on the MC34063) and linear for the microcontroller, a resistor divider to supply the voltage removed from the rectifier to the analog input of the microcontroller, as well as the microcontroller itself. The task of the program is to drive transistors and to send a command to the transmitting part, forcing it, despite load changes, to maintain such transmitted power so that the voltage at the output of the rectifier is 10 V.
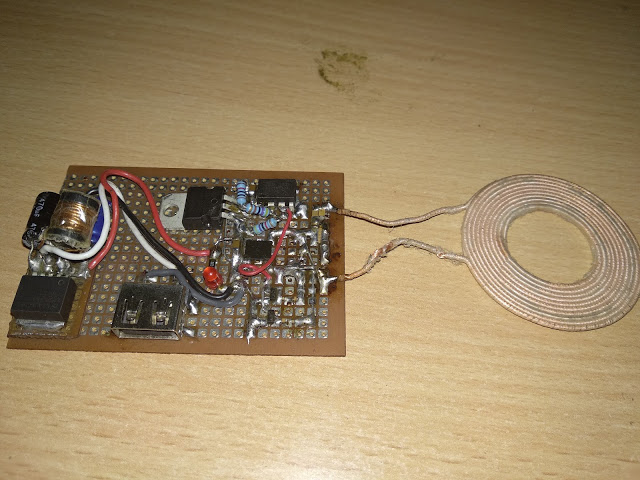
Appearance of the entire device and the board separately:

The firmware is here .
Video:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/450084/
All Articles