How to avoid the bite of the bug kisser
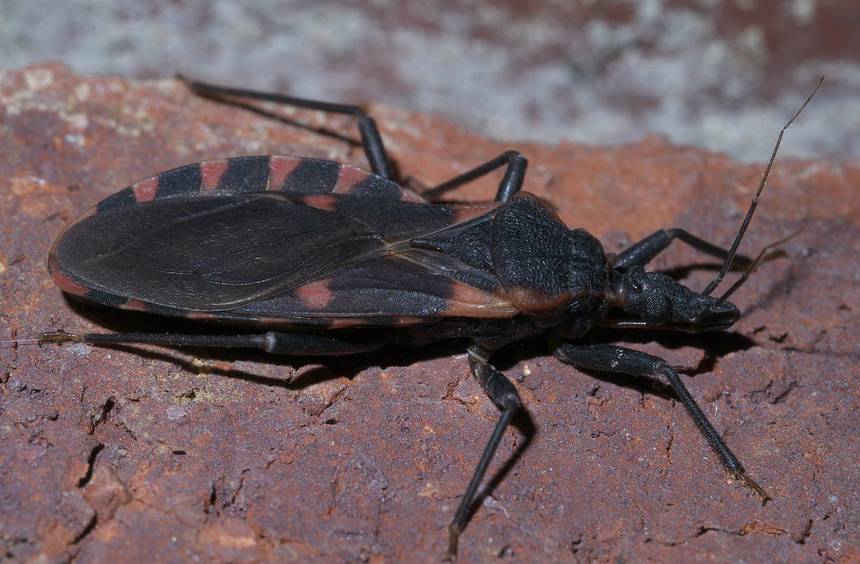

One of these days the holiday season opens. A forest tick is waiting for us in the woods. In the USA, a bug kisser is widespread, the bite of which is no better than the bite of "our" tick. How to prevent yourself from being bitten? Read the answers to these questions in this article. Calm dear readers: "kissing bug" in Russia has not yet been noticed.
Kisses bugs can carry parasites that cause Chagas disease, and now they are already in the United States. The bug kisser is an insect with a charming nickname and deadly habits. The bug kisser is a night-blooded bloodsucker carrying an inflammatory infectious disease to people.
They are also known as triatomine bugs, their kisses can spread the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which causes Chagas disease. Once found only in Latin America, this creepy “tracked robot” made its way north to the USA, where it can now be found in dozens of states. According to medical data, approximately 8 million people living in Mexico, Central America and South America suffer from Chagas disease, most of whom do not know that they are infected. If left untreated, the infection can remain in the human body for life and can be life-threatening.
')
The first (acute) phase of the disease can last from several weeks to several months and often has no symptoms, but can also be accompanied by fever, fatigue, body aches, headache, rash, loss of appetite, diarrhea and vomiting. In the chronic phase, which can last for decades, approximately 20-30 percent of infected people develop heart complications and / or gastrointestinal complications.
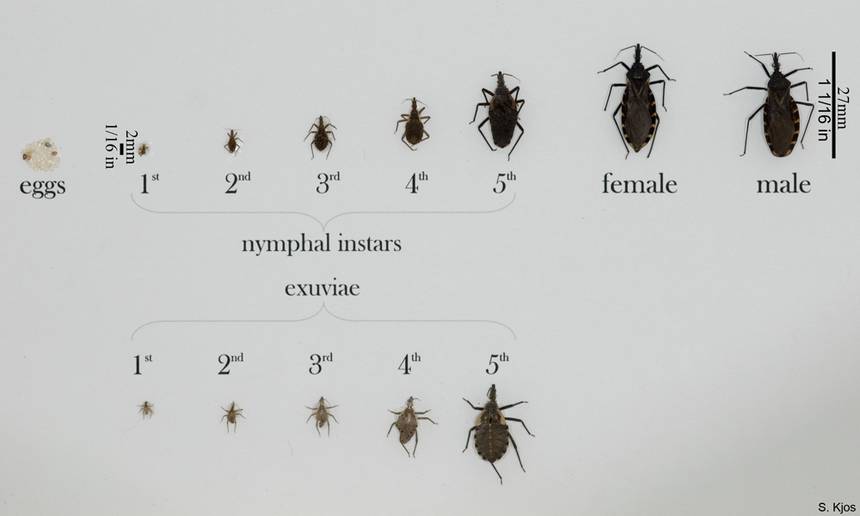

And although all this causes concern, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that the transmission of the T. cruzi parasite from a bug to a person is rather difficult.
It is important to note that not all triatomine bugs are infected with a parasite that causes Chagas disease. The likelihood of being infected with T Cruzi from triatomine is quite low in the United States.
However, children as well as people with weakened immune systems and pets are especially vulnerable. Therefore, to get bitten by you, take the precautions of the CDC.
The above-mentioned bug kisser has a tendency to bite the face, while he does not directly deliver the T. cruzi virus to his victim. The pathogen lives in the feces of the bug, and in order to infect a person, the bug must bite into the area of the damaged skin or through the mucosa.
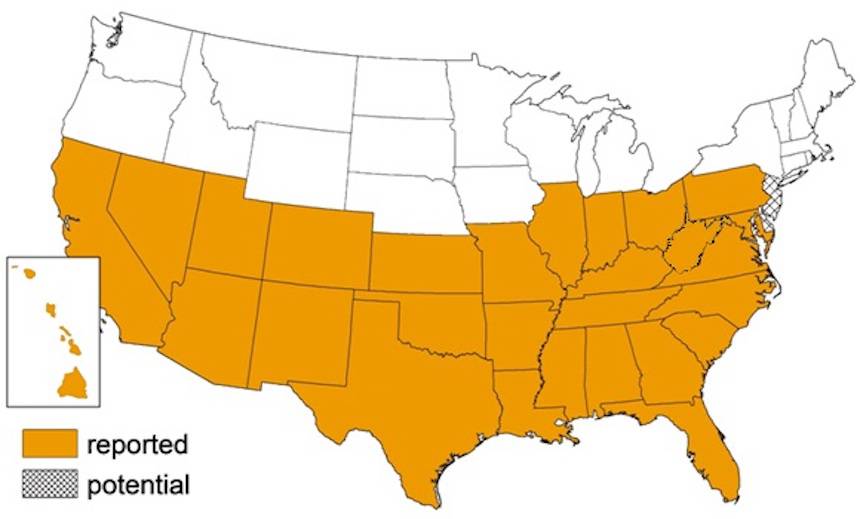
Where do they live?
Under the porches
Between rock structures
Under the concrete
In the rock, tree, bushes or under the bark
In rodent nests or animal burrows
In kennels or kennels
In chicken coops or homes
Near the places where your pets sleep
In places of infection with rodents
In and around beds and bedrooms, especially under or near mattresses or bedside tables
How to prevent infection
Make sure they cannot get into your home. As they bite at night, the bed is the most likely place where a person will be bitten.
Seal cracks and crevices around windows, walls, roofs and doors.
Remove trees and branches near your home.
Use meshes on doors and windows and eliminate any holes or gaps.
If possible, make sure that the lights are not near your house (lights can attract insects).
Seal holes and cracks leading to the attic.
Get pets to sleep indoors, especially at night.
Keep your home and any outdoor resting places for pets clean.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/449636/
All Articles