Make go GraphQL API
1. Add Graphiql client to go project

Graphiql is an interactive client working in GraphQL browser.
To use in a go project, you need to add an html page with several dependencies.
If you need to have the latest versions, it will help install the node and packages. The project will grow greatly. There is an option to collect HTML into one go file and pull up dependencies with cdn at startup.
My version is go-graphiql .
To work you need to add only:
http.HandleFunc("/cli", graphiql.ServeGraphiQL) The result is:
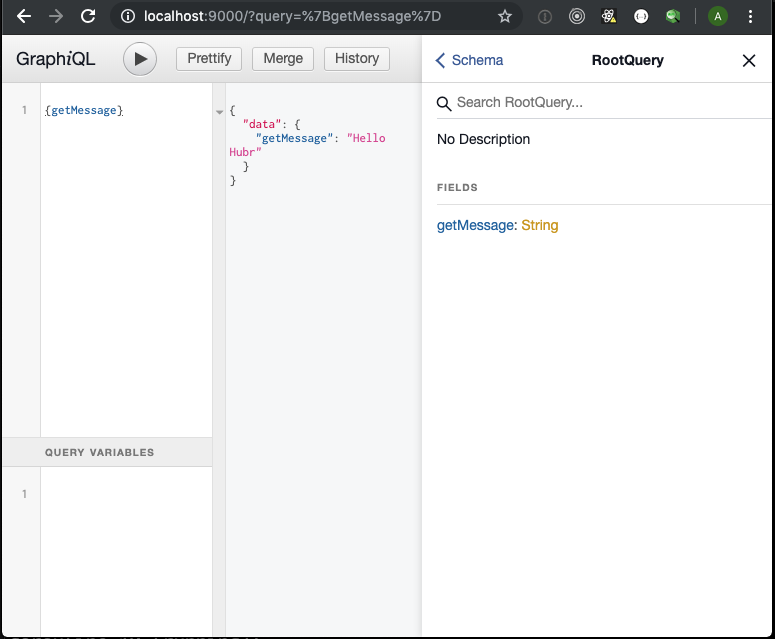
2. Let's see how the API works in terms of the browser.
In the browser, open the developer console and add the js code:
let q=`{getMessage}` let v={} let options = (query, variables={}) =>{ return { method: 'POST', headers: { Accept: 'application/json', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, body: JSON.stringify({ query, variables }), } }; let o = options(q, v) console.log(o) fetch("http://localhost:9000/graphql",o) .then(response=>response.json()) .then(console.log) Result of performance:
There is an error in the API. Need to change the message text.
q=`mutation { setMessage(msg: "Hello Habr") } ` v={} o = options(q, v) console.log(o) fetch("http://localhost:9000/graphql",o) .then(response=>response.json()) .then(console.log) Result of performance: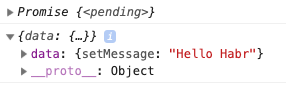
3. Let's see how it works from the point of view of the server.
The scheme of work describes the object:
schema, err := graphql.NewSchema(graphql.SchemaConfig{ Query: types.RootQuery, Mutation: types.RootMutation, }) Query
Data retrieval
var RootQuery = graphql.NewObject(graphql.ObjectConfig{ Name: "RootQuery", Fields: graphql.Fields{ "getMessage": &graphql.Field{ Type: graphql.String, Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) { msg := logic.GetMessage() return msg, nil }, }, }, }) The Resolve function gets data for us. Data can be from any source from the Database to the micro controller
Mutation
Data mutation
var RootMutation = graphql.NewObject(graphql.ObjectConfig{ Name: "RootMutation", Fields: graphql.Fields{ "setMessage": &graphql.Field{ Type: graphql.String, Args: graphql.FieldConfigArgument{ "msg": &graphql.ArgumentConfig{Type: graphql.NewNonNull(graphql.String)}, }, Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) { msg := p.Args["msg"].(string) logic.SetMessage(msg) return msg, nil }, }, }, }) Edit data is also using the Resolve function.
Resolve can also trigger light events or regulate temperature.
An interesting point is that the type of the returned data can also have graphql.Fields, which will also have their own Resolve functions.
4. Typed languages?
There are some limitations (features) of data exchange.
Variables have default values in go
Int is 0, String = ""
In graphql, there may be a situation when a variable is not set.
Therefore, for such parameters, we use the variable reference
In continuation,
I will write how to make graphql api to the registry of open data.
Because programmers are the laziest people on the planet. We will do the API so as to do something smaller.
TODO:
Api starter kit
schema
There is an interesting project that creates a scheme for the text.
func main() { s := ` schema { query: Query } type Query { hello: String! } ` schema := graphql.MustParseSchema(s, &query{}) http.Handle("/query", &relay.Handler{Schema: schema}) log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)) } github.com/graph-gophers/graphql-go
resolv
I will make the generator for fields on structures
query
did not think up how to construct requests the generator
Waiting for suggestions.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/449286/
All Articles