Botnets in 2019: actual dangers and harm caused to small and medium businesses
About botnets on Habré have been written many times, which is not surprising - this is really a significant threat that has not disappeared anywhere. In our today's article we will talk about what botnets are relevant in 2019 and what damage they can cause to business - not large corporations, but small and medium-sized companies.
Who is the threat?
According to Securelist , financial organizations and services represent the maximum interest for botnet developers. They account for more than 70% of all attacks. These are online banking services, online stores, various payment aggregators, etc.
The second place (here only about 6% of all attacks) is occupied by social networks and large informational sites, plus search engines and social mail services. Here, the attackers are trying to capture as much of the personal data of users as possible for further attacks.
')
Third place with about 5% is occupied by resources offering different products and services, and these sites are not online stores. Hosting providers and some other organizations fall into this category. The intruders here are primarily interested in the personal data of the victim.

Also, the “botovody” sent their systems to various cryptocurrency services, including stock exchanges, wallets, etc.
It is clear that intruders, first of all, are interested in companies from rich countries, so services and websites based in the USA, Great Britain, Canada, European countries and China are being attacked.
How does botnet harm business?
Spamming from company IP addresses
A botnet may not be “sharpened” to conduct some kind of complex attacks, but work as a spam tool. And the more items in the botnet, the higher the effectiveness of this tool. If spam is sent from infected devices of a company, then its IP will automatically fall into the spam filters. And this means that after some time, all e-mails sent by employees of the company from local PCs will get into spam for clients, partners, and other contacts. It is not so easy to rectify this situation, and it can cause significant harm (you can imagine how the agreement is broken because important documents did not fall into the right hands in time).
DDoS from company IP addresses
Approximately the same as in the case above, only this time the botnet uses the infected computers of the company to conduct DDoS attacks. In this case, the IPs seen in the “dark matter” will be blacklisted by various providers and will be blocked. In the future, employees of the company whose PCs have suffered will experience difficulties with access to certain resources - requests will be blocked at the level of providers of various sizes.
In some cases, companies may turn off network access altogether if the attack was serious. And the absence of the Internet, even within a few hours, is a serious problem for a business.
Direct DDoS attack on a company
A large number of botnets are created for DDoS attacks. Their power is now very large, so that the average botnet can completely "put" the services and websites of a regular company. And this is a very expensive pleasure. According to experts, such a direct can cost businesses in amounts from $ 20,000 to $ 100,000 per hour .
Even if the services of the attacked company continue to work, it is much slower than usual. It threatens direct and indirect damages. And even in the case of a weak DDoS-attack, which did not affect the efficiency of the company, you can encounter "dirty logs" - when the analysis of the work of the company's services is impossible due to the huge number of third-party IP. Google Analytics in such cases becomes useless.
Theft of important information
The botnets that exist today are multifunctional and consist of a large number of modules. A botnet operator can turn a “sleeping” botnet into a corporate data hijacker (customer data, access to internal resources, access to a client-bank, etc.). at the click of a finger. And this is a much more sensitive threat to business than spam or DDoS.
Stealing data from a botnet can be done in various ways, including such a common one as keylogging. The keylogger can be “sharpened”, for example, to work with PayPal and be activated only when the user tries to log in to his account.
Proxy for attacks
A botnet can turn corporate machines into proxies that will serve as a “transit point” for attacks. And here everything is much worse than in the case of spam or DDoS - if the attack was serious and caused damage to someone, the company may face scrutiny from law enforcement agencies.
Expenditure of company resources
If the botnet behaves actively, then this may require significant computational resources. That is, corporate machines will be used by attackers, with the corresponding expenditure of energy and CPU time. If a company whose computers are infected works with demanding costs, it can affect the efficiency of workflows. One example is mining. A botnet can be activated as a miner and then infected PCs will give a significant part of their power to mining coins for intruders.
Reputational loss
All this may ultimately affect the company's reputation, since an organization whose IP addresses are seen in “dark deeds” will be a difficult situation. Bringing everything back to square can be not so easy.
How to calculate losses?
Better, of course, if there is no loss. But if there is a problem with the botnet, then it is possible to calculate the current and future costs that are required to eliminate the problem, according to the algorithm below. Sum up all the costly items and get the total amount.
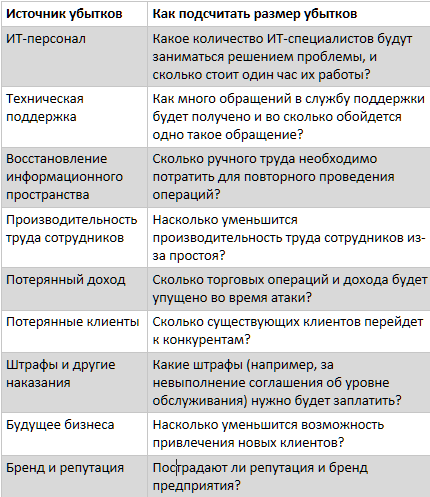
According to the Ponemon Institute, in difficult situations when a company stops working, losses can be huge and amount to thousands of dollars per minute. In the case of large companies, this is already hundreds of thousands. For small and medium businesses, the total amount of losses is not as large as that of corporations, but for a company itself even a couple of thousand dollars can be an unaffordable luxury, if we talk about the organization of a small size.
Botnet examples
There are a lot of botnets, both small and large-scale, with millions of elements in their network. As an example, those that were most active in 2018 (and they have not gone anywhere today).
BetaBot
The number of attacks made by this botnet is more than 13% of the total unique attacks in 2018. The malware worked in 42 countries, financial services, social networks and major portals were of the greatest interest to its creators.
Trickster (TrickBot)
Almost the same active botnet as the previous one. With his help, committed 12.85% of the total number of unique attacks. He worked in 65 countries, attacked financial and cryptocurrency services.
Panda
This botnet made 9.84% of the total number of unique attacks. He worked in 33 countries, attacked financial and cryptocurrency services.
Among the successful botnets should also indicate SpyEye and Ramnit.
The giant botnet Mirai stands apart, which at one time caused damage to hundreds of millions of US dollars. The new version of the botnet is already active and working, gradually starting to infect new devices around the world .
How to protect yourself from a botnet?
In principle, the methods of protection are no different from those used to prevent computers from being infected by any malware. This is, first of all, personal “IT hygiene”, that is, you need to be aware that clicking on the links in e-mail messages, opening files sent by known and unknown contacts, clicking on banners like “your PC is infected and its need to be treated "- all this is fraught with infection not only personal, but also corporate technology.
Companies need to regularly instruct employees on information security with a demonstration of various cases. People need to understand that following a link with funny cats, which personal contact sent, may threaten a business. The weakest link in the chain of business information protection is a person, not software or hardware.
But software and hardware protection should be. These are software antiviruses, firewalls or “iron” firewalls like the ZyWALL ATP500 , which provide multi-level Multi-Layer Protection protection. Such systems help to block not only known, but also unknown threats (zero-day threats), as well as prevent mid-level DDoS. Depending on the size of the enterprise network and its financial capabilities, you can use the Zyxel ATP200, ATP500 or ATP800 model.
In any company whose work largely depends on computers and software, including cloud services, there should be a detailed information protection strategy. And this is not just a piece of paper that hangs next to the evacuation plan. Elaboration of the strategy means that the proposed measures should be tested "in the field", you need to conduct trainings and workshops with employees. All this will not exclude, but will significantly reduce the information threats that are dangerous to the company's business.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/449186/
All Articles