Microbiota What bacteria live in the intestines of Russians
In the first article , Atlas and I told what the intestinal microbiota is, how the colon is arranged, where bacteria appear from and why we need them. And this time we are sharing what kind of bacteria live in the intestines of Russians according to the statistics of our users, what they eat and what functions they perform.

Illustration by Rentonorama
As the entire population of the Earth can be divided into countries and populations, so all the intestinal bacteria can be divided into families and genera. The bacteria family combines genera similar in structure, but different in function. And departments unite different families.
Most of the genera of microbiota bacteria belong to two divisions: Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes. In the first section, the genera Bacteroides and Prevotella are most common, and in the second, Faecalibacterium, Ruminococcus, Eubacterium, Blautia, Roseburia, Coprococcus. There is also a genus of bacteria Akkermansia, the presence of which is considered a marker of health. In the human intestine, it is the only representative of the Verrucomicrobia department.
')
A number of studies mention the relationship of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes. In some works, it is noted that Firmicutes is more full of people, and in others - the opposite. In fact, all the more confusing. The bacterial genus Bacteroides is associated with a Western diet, which rather promotes weight gain, and Firmicutes are the main producers of an energy-intensive substance that helps our body stay healthy. Therefore, it remains unclear why the prevalence of Firmicutes according to research results may be a sign of obesity.
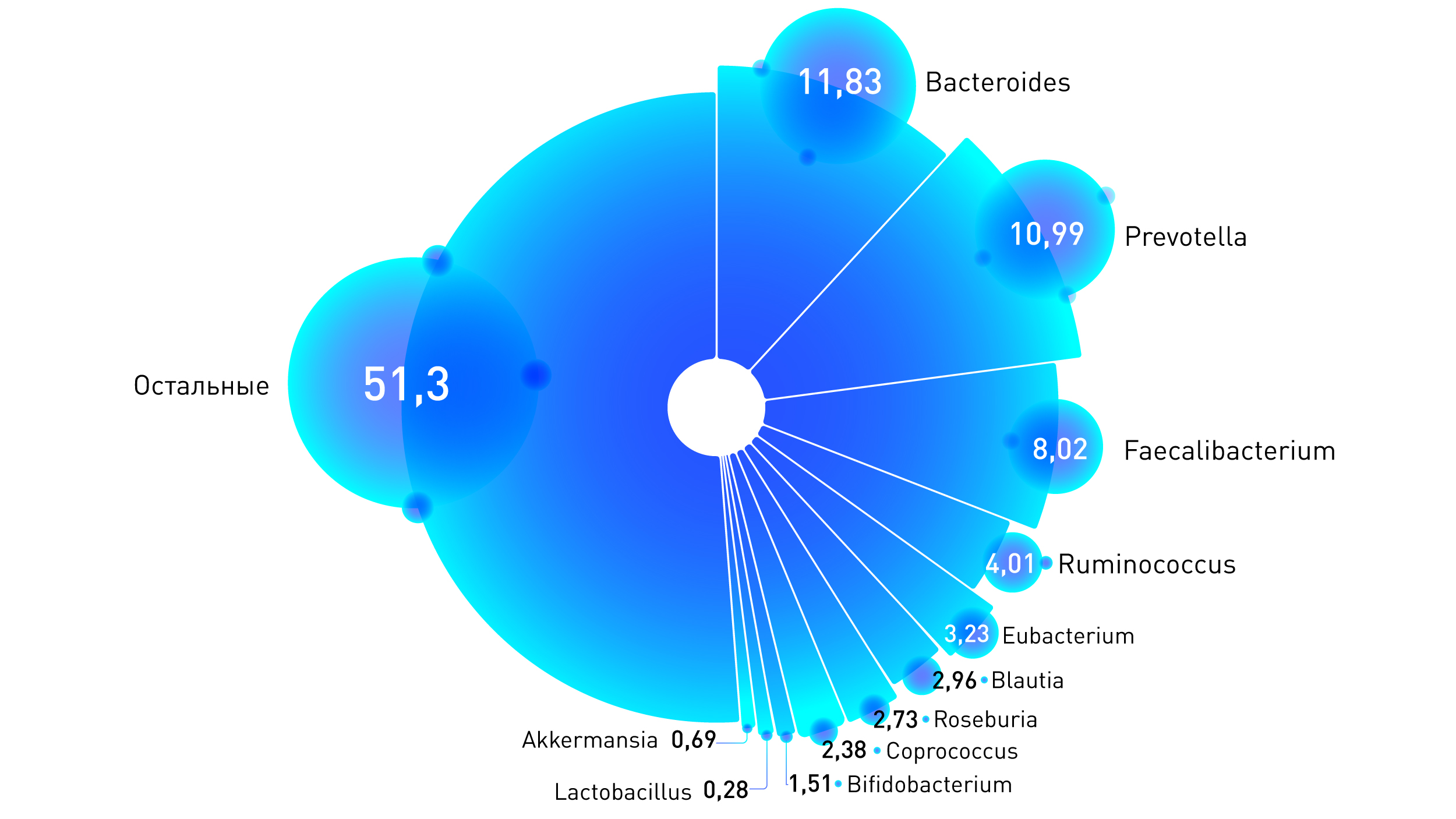
Below we present the average statistics on users of the “Genetics of microbiota” test in Atlas. Note that most of the samples come to us from Moscow, so this ratio is more typical for residents of large cities.
The main role of Bacteroides is to break down and help a person absorb fiber. As we said in the first article, a person simply does not have genes that encode information about the breakdown of complex carbohydrates (except for starch and glycogen). We get this ability through the genome of bacteria.
Bacteroides are able to recognize and process more than a dozen fibers, and some species contain more than 260 genes for their metabolism. They also process sugars and proteins, so a large representation of this genus is associated with a Western diet rich in meat and sweet dishes.
Bacteroides care not only about their master, but also help their neighbors. They create a beneficial environment for other beneficial intestinal bacteria. For example, Bacteroides reduce oxygen levels, allowing anaerobic genera to grow.
A high value is considered to be 13.78%.
The genera Prevotella and Bacteroides belong to the same department, but the representation of Prevotella is associated with a vegetable diet and is more common among the tribes of Africa and Amazonia, to which the Western diet has not reached. In Western countries, the prevalence of Prevotella is found in vegetarians and adherents of the Mediterranean diet. At the same time, this genus is associated with a high content of not only complex carbohydrates, but also simple sugars. Therefore, the number of Prevotella is often higher in sweet teeth.
Those who have Prevotella representation higher than Bacteroides, were a little more fortunate. A study by the Swedish University of Gothenburg showed that an increased number of Prevotella in the microbiota normalizes glucose metabolism. In mice with the microbiota of people from the study, an elevated glycogen content in the liver was noted. This means that the hormone insulin in mice with such a microbiota correctly performs its work and transfers the incoming glucose to the liver, where it is stored as glycogen.
When insulin cannot tolerate glucose, resistance develops and the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes increases. Researchers note that a high-fiber diet may be the cause of a high level of Prevotella.
A high value is considered 16.87%
Faecalibacterium is a major producer of butyric acid. This short-chain fatty acid accounts for 90% of the nutrition of the cells lining the intestinal wall. When it is not enough, the cells perform their functions worse or die at all, which reduces the body's immune response and increases the risk of inflammation. Therefore, Faecalibacterium is considered a marker of health: the more, the better.
Faecalibacterium produces butyric acid by splitting complex carbohydrates. Therefore, this kind of more among lovers of vegetables, fruits and grains.
This type of bacteria is also associated with satisfaction with the quality of life. This is the conclusion reached by scientists from Belgium and the Netherlands. They evaluated the composition of the microbiota and asked the participants to fill out a questionnaire about the general perception of health, limitations related to physical or emotional problems, emotional well-being, physical pain, fatigue or the presence of forces. The researchers noted that many criteria related to satisfaction with quality of life were positively correlated with a large representation of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus. About the second kind we will describe below.
A high value is 11.64%.
Ruminococcus - lovers of resistant starch, which is found in green bananas, lentils, green peas, white beans, cooled pasta and potatoes. Unlike simple starch, stable does not break down to simple sugars and is not digested by the body, and therefore comes to the microbiota whole. Ruminococcus is also a genus of bacteria that is able to process cellulose, although most of it remains undigested and helps to form fecal masses that pass faster through the intestine and less in contact with the walls.
The connection between Ruminococcus and the development of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease is being actively studied. Several studies have shown that patients with inflammation of the intestines have a higher representativeness of a certain type of Ruminococcus.
3.7% is considered a high value.
Eubacterium, like Faecalibacterium, when digesting cellulose, synthesizes most of the butyric acid. The number of Eubacterium increases with the addition of whole grains and brown rice to the diet and decreases when the fiber in the diet becomes low. Eubacterium converts lactate in the intestine into butyric acid, which reduces acidity and helps stabilize the microbiota.
What is interesting, scientists compared the microbiota of young people of 70 years and long-livers, who lived more than 100 years. It turned out that the microbiota of young and 70-year-olds practically does not differ, and long-livers had mild chronic inflammation (inflammageing). Scientists have even identified the bacterium characteristic of such people - Eubacterium limosum. They have the number of this bacterium was increased more than 10 times.
Considered a high value of 3.25%
During the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, Blautia produces acetate, which, like butyric acid, is a short-chain fatty acid. It is absorbed by intestinal cells, passes the blood-brain barrier and enters the brain.
Acetate is an important source of power for glial cells that surround neurons and provide reliable transmission of pulses between them. According to a study from the journal Nature, when large amounts of fiber are used, acetate triggers a signal in the hypothalamus that suppresses appetite. This work sheds some light on how a fiber-rich diet protects a person from obesity.
Despite the advantages, an increased representation of Blautia is associated with type 2 diabetes. This was found out by comparing the microbiots of three groups: patients with diabetes, pre-diabetes and healthy people with normal glucose metabolism.
A high value is 2.23%.
Roseburia cleaves plant mannans. These substances are found in nuts, legumes, coconuts, tomatoes, coffee beans, and they are also widely used in the food industry as thickeners and gelling agents. Mannans can increase in volume up to 200 times, which reduces appetite and gives a feeling of fullness.
Several studies have shown that Roseburia plays an important role in controlling the inflammatory processes in the intestines, protecting against atherosclerosis and in the body’s immune responses. Scientists suggest that these processes mainly occur due to the synthesis of butyric acid by using a sufficient amount of fiber. The study showed that the mice in which there are many Roseburia in the microbiome, but which do not receive enough fiber, are not protected from atherosclerosis.
Roseburia has a lower prevalence in people with inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer.
3.5% is considered a high value .
The same kind that, together with Faecalibacterium, is associated with satisfaction with the quality of life. In addition, it turned out that Coprococcus is associated with the development of depression. According to a study from Nature, the microbiota of depressed patients contains less Coprococcus and Dialister bacteria.
Coprococcus, like many other genera of the Firmicutes division, splits different types of fibers and produces butyric acid. Another representation of Coprococcus is associated with a low body mass index and a high diversity of microbiota.
Considered a high value of 2.74%
These genera begin to colonize our bodies since childhood, as they are contained in breast milk. With respect to other genera, Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in an adult are few and sometimes not at all, but this does not mean that they are useless. Even if these bacteria cannot settle in your microbiota and simply pass through the gastrointestinal tract, they still interact with other bacteria and are beneficial. However, those with whom they are represented in the microbiota are a bit more fortunate.
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are probiotic bacteria. They are able to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, strengthen the protective function of the intestinal walls and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines. Lactobacillus, like Coprococcus, is associated with low weight, while Bifidobacterium protects the intestines against inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer. Still Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus synthesize gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This neurotransmitter is responsible for attention, emotional and motor control. The relationship between taking probiotics with Lactobacillus and reducing the symptoms of depression and anxiety is being actively studied.
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are found in fermented foods, such as kefir or sourdough bread, kombucha, sauerkraut. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus microbiota feed on galacto-oligosaccharides found in Jerusalem artichoke, soybeans, garlic, tomatoes, onions, bananas, apples, asparagus and honey. A study on people with lactose intolerance has shown that this type of fiber helps these probiotic species grow.
0.5% High Bifidobacterium
0.16% is considered a high value of Lactobacillus
The high representation of this bacterium is considered a marker of human health, since a small percentage of Akkermansia often accompanies type 2 diabetes, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. A large percentage of this bacterium is associated with low weight and body mass index, as well as low fasting cholesterol and glucose levels.
Unlike other genera, Akkermansia feeds on the mucous layer of the intestine - mucin, therefore during periods of starvation, when other bacteria do not receive enough substances, its numbers increase significantly.
The bacterium not only consumes mucin, but also helps to produce it. Scientists suggest that Akkermansia synthesizes fatty acids that feed the producing cells of the intestinal mucosa. A study using intestinal epithelial cells showed that Akkermansia adheres to the cells and enhances protection, rather than destroying them, provoking inflammation.
A high value is 0.23%.
If you chose a bacterium for yourself and want to grow it - we are in a hurry to upset you. A healthy microbiota is characterized by a wide variety of very different types of bacteria, because it inhibits the growth of conditionally pathogenic species, synthesizes a sufficient amount of fatty acids and protects against inflammation. In addition, if there is no certain kind in the microbiota, then it is unlikely to settle it with a diet. It is possible to get a new kind only through microbiota transplantation, but in this case the composition of bacteria will completely change to the composition of the donor.
In the Genetics Microbiota test, we investigate which kinds of bacteria you have less in comparison with the average indicators of healthy people in the population, and give recommendations on products that are able to increase the number of certain bacteria.
In the next article we will describe how the microbiota affects the development of diseases.

Illustration by Rentonorama
What are bacterial genera and how do they relate to each other
As the entire population of the Earth can be divided into countries and populations, so all the intestinal bacteria can be divided into families and genera. The bacteria family combines genera similar in structure, but different in function. And departments unite different families.
Most of the genera of microbiota bacteria belong to two divisions: Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes. In the first section, the genera Bacteroides and Prevotella are most common, and in the second, Faecalibacterium, Ruminococcus, Eubacterium, Blautia, Roseburia, Coprococcus. There is also a genus of bacteria Akkermansia, the presence of which is considered a marker of health. In the human intestine, it is the only representative of the Verrucomicrobia department.
')
A number of studies mention the relationship of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes. In some works, it is noted that Firmicutes is more full of people, and in others - the opposite. In fact, all the more confusing. The bacterial genus Bacteroides is associated with a Western diet, which rather promotes weight gain, and Firmicutes are the main producers of an energy-intensive substance that helps our body stay healthy. Therefore, it remains unclear why the prevalence of Firmicutes according to research results may be a sign of obesity.
Below we present the average statistics on users of the “Genetics of microbiota” test in Atlas. Note that most of the samples come to us from Moscow, so this ratio is more typical for residents of large cities.

 Bacteroides
Bacteroides
The main role of Bacteroides is to break down and help a person absorb fiber. As we said in the first article, a person simply does not have genes that encode information about the breakdown of complex carbohydrates (except for starch and glycogen). We get this ability through the genome of bacteria.
Bacteroides are able to recognize and process more than a dozen fibers, and some species contain more than 260 genes for their metabolism. They also process sugars and proteins, so a large representation of this genus is associated with a Western diet rich in meat and sweet dishes.
Bacteroides care not only about their master, but also help their neighbors. They create a beneficial environment for other beneficial intestinal bacteria. For example, Bacteroides reduce oxygen levels, allowing anaerobic genera to grow.
A high value is considered to be 13.78%.
 Prevotella
Prevotella
The genera Prevotella and Bacteroides belong to the same department, but the representation of Prevotella is associated with a vegetable diet and is more common among the tribes of Africa and Amazonia, to which the Western diet has not reached. In Western countries, the prevalence of Prevotella is found in vegetarians and adherents of the Mediterranean diet. At the same time, this genus is associated with a high content of not only complex carbohydrates, but also simple sugars. Therefore, the number of Prevotella is often higher in sweet teeth.
Those who have Prevotella representation higher than Bacteroides, were a little more fortunate. A study by the Swedish University of Gothenburg showed that an increased number of Prevotella in the microbiota normalizes glucose metabolism. In mice with the microbiota of people from the study, an elevated glycogen content in the liver was noted. This means that the hormone insulin in mice with such a microbiota correctly performs its work and transfers the incoming glucose to the liver, where it is stored as glycogen.
When insulin cannot tolerate glucose, resistance develops and the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes increases. Researchers note that a high-fiber diet may be the cause of a high level of Prevotella.
A high value is considered 16.87%
 Faecalibacterium
Faecalibacterium
Faecalibacterium is a major producer of butyric acid. This short-chain fatty acid accounts for 90% of the nutrition of the cells lining the intestinal wall. When it is not enough, the cells perform their functions worse or die at all, which reduces the body's immune response and increases the risk of inflammation. Therefore, Faecalibacterium is considered a marker of health: the more, the better.
Faecalibacterium produces butyric acid by splitting complex carbohydrates. Therefore, this kind of more among lovers of vegetables, fruits and grains.
This type of bacteria is also associated with satisfaction with the quality of life. This is the conclusion reached by scientists from Belgium and the Netherlands. They evaluated the composition of the microbiota and asked the participants to fill out a questionnaire about the general perception of health, limitations related to physical or emotional problems, emotional well-being, physical pain, fatigue or the presence of forces. The researchers noted that many criteria related to satisfaction with quality of life were positively correlated with a large representation of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus. About the second kind we will describe below.
A high value is 11.64%.
 Rouminococcus
Rouminococcus
Ruminococcus - lovers of resistant starch, which is found in green bananas, lentils, green peas, white beans, cooled pasta and potatoes. Unlike simple starch, stable does not break down to simple sugars and is not digested by the body, and therefore comes to the microbiota whole. Ruminococcus is also a genus of bacteria that is able to process cellulose, although most of it remains undigested and helps to form fecal masses that pass faster through the intestine and less in contact with the walls.
The connection between Ruminococcus and the development of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease is being actively studied. Several studies have shown that patients with inflammation of the intestines have a higher representativeness of a certain type of Ruminococcus.
3.7% is considered a high value.
 Eubacterium
Eubacterium
Eubacterium, like Faecalibacterium, when digesting cellulose, synthesizes most of the butyric acid. The number of Eubacterium increases with the addition of whole grains and brown rice to the diet and decreases when the fiber in the diet becomes low. Eubacterium converts lactate in the intestine into butyric acid, which reduces acidity and helps stabilize the microbiota.
What is interesting, scientists compared the microbiota of young people of 70 years and long-livers, who lived more than 100 years. It turned out that the microbiota of young and 70-year-olds practically does not differ, and long-livers had mild chronic inflammation (inflammageing). Scientists have even identified the bacterium characteristic of such people - Eubacterium limosum. They have the number of this bacterium was increased more than 10 times.
Considered a high value of 3.25%
 Blautia
Blautia
During the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, Blautia produces acetate, which, like butyric acid, is a short-chain fatty acid. It is absorbed by intestinal cells, passes the blood-brain barrier and enters the brain.
Acetate is an important source of power for glial cells that surround neurons and provide reliable transmission of pulses between them. According to a study from the journal Nature, when large amounts of fiber are used, acetate triggers a signal in the hypothalamus that suppresses appetite. This work sheds some light on how a fiber-rich diet protects a person from obesity.
Despite the advantages, an increased representation of Blautia is associated with type 2 diabetes. This was found out by comparing the microbiots of three groups: patients with diabetes, pre-diabetes and healthy people with normal glucose metabolism.
A high value is 2.23%.
 Roseburia
Roseburia
Roseburia cleaves plant mannans. These substances are found in nuts, legumes, coconuts, tomatoes, coffee beans, and they are also widely used in the food industry as thickeners and gelling agents. Mannans can increase in volume up to 200 times, which reduces appetite and gives a feeling of fullness.
Several studies have shown that Roseburia plays an important role in controlling the inflammatory processes in the intestines, protecting against atherosclerosis and in the body’s immune responses. Scientists suggest that these processes mainly occur due to the synthesis of butyric acid by using a sufficient amount of fiber. The study showed that the mice in which there are many Roseburia in the microbiome, but which do not receive enough fiber, are not protected from atherosclerosis.
Roseburia has a lower prevalence in people with inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer.
3.5% is considered a high value .
 Coprococcus
Coprococcus
The same kind that, together with Faecalibacterium, is associated with satisfaction with the quality of life. In addition, it turned out that Coprococcus is associated with the development of depression. According to a study from Nature, the microbiota of depressed patients contains less Coprococcus and Dialister bacteria.
Coprococcus, like many other genera of the Firmicutes division, splits different types of fibers and produces butyric acid. Another representation of Coprococcus is associated with a low body mass index and a high diversity of microbiota.
Considered a high value of 2.74%
 Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus
These genera begin to colonize our bodies since childhood, as they are contained in breast milk. With respect to other genera, Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in an adult are few and sometimes not at all, but this does not mean that they are useless. Even if these bacteria cannot settle in your microbiota and simply pass through the gastrointestinal tract, they still interact with other bacteria and are beneficial. However, those with whom they are represented in the microbiota are a bit more fortunate.
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are probiotic bacteria. They are able to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, strengthen the protective function of the intestinal walls and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines. Lactobacillus, like Coprococcus, is associated with low weight, while Bifidobacterium protects the intestines against inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer. Still Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus synthesize gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This neurotransmitter is responsible for attention, emotional and motor control. The relationship between taking probiotics with Lactobacillus and reducing the symptoms of depression and anxiety is being actively studied.
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are found in fermented foods, such as kefir or sourdough bread, kombucha, sauerkraut. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus microbiota feed on galacto-oligosaccharides found in Jerusalem artichoke, soybeans, garlic, tomatoes, onions, bananas, apples, asparagus and honey. A study on people with lactose intolerance has shown that this type of fiber helps these probiotic species grow.
0.5% High Bifidobacterium
0.16% is considered a high value of Lactobacillus
 Akkermansia
Akkermansia
The high representation of this bacterium is considered a marker of human health, since a small percentage of Akkermansia often accompanies type 2 diabetes, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. A large percentage of this bacterium is associated with low weight and body mass index, as well as low fasting cholesterol and glucose levels.
Unlike other genera, Akkermansia feeds on the mucous layer of the intestine - mucin, therefore during periods of starvation, when other bacteria do not receive enough substances, its numbers increase significantly.
The bacterium not only consumes mucin, but also helps to produce it. Scientists suggest that Akkermansia synthesizes fatty acids that feed the producing cells of the intestinal mucosa. A study using intestinal epithelial cells showed that Akkermansia adheres to the cells and enhances protection, rather than destroying them, provoking inflammation.
A high value is 0.23%.
Disclaimer
If you chose a bacterium for yourself and want to grow it - we are in a hurry to upset you. A healthy microbiota is characterized by a wide variety of very different types of bacteria, because it inhibits the growth of conditionally pathogenic species, synthesizes a sufficient amount of fatty acids and protects against inflammation. In addition, if there is no certain kind in the microbiota, then it is unlikely to settle it with a diet. It is possible to get a new kind only through microbiota transplantation, but in this case the composition of bacteria will completely change to the composition of the donor.
In the Genetics Microbiota test, we investigate which kinds of bacteria you have less in comparison with the average indicators of healthy people in the population, and give recommendations on products that are able to increase the number of certain bacteria.
In the next article we will describe how the microbiota affects the development of diseases.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/449142/
All Articles