Details of the transition from paired (relative) exchange rates to absolute. Bug work

Introduction
This article describes the results of an experiment conducted in the framework of the Absolute Exchange Rates project. The protocol of the experiment can be seen by clicking on the link .
The project “ Absolute exchange rate ” is engaged in the analysis of paired exchange rates, the selection of absolute exchange rates from them and their analysis. Within the framework of the project, a method of converting from pair rates to absolute exchange rates was obtained. Absolute currency ABS is defined for this. Rates of all available currencies are expressed in relation to ABS.
A detailed description of the technology is given in the article “ From currency pairs to absolute exchange rates ”.
To date, several articles have already been published on the application of the absolute exchange rate method. I give the last two.
The article “ Study of connectedness of world currencies through the correlation of absolute exchange rates ” describes one of the applications of the absolute exchange rate technology. A formal method for calculating the relationship between different currencies is given.
The article “ The Markovits portfolio method with reference to the foreign exchange market ” describes the previously unavailable technology for optimizing the currency portfolio.
The following describes the method of conversion from paired (relative) exchange rates to absolute. The numerical parameters of the transformation and the method of their calculation are given.
In the source file, daily exchange rates are automatically loaded daily and absolute ones are calculated from them.
The transformation matrix was obtained in 2017. It was calculated on real pair exchange rates by minimizing the deviation error of the restored pair rates from the absolute ones. Since then, no error analysis has been performed on current data.
The unexpected test results described below forced us to develop a new method for obtaining a transformation matrix. In addition, an error was detected processing imported quotes.
Theoretical foundations
To obtain absolute exchange rates, you need to do the following conversion. For starters, paired courses are logarithmic. Next, multiply them by the inverse transform matrix. At the end we return back from the logarithmic scale using the exponent.
For the further transition to pair courses, absolute courses should be prologarithmic. Then multiply by the direct transformation matrix. We finish as before using the exhibitors.
The technology is described in more detail in the article “ From currency pairs to absolute rates of individual currencies ” (only this article in 2018 gives a transposed representation of transformation matrices in contrast to the presentation of this article).
The direct matrix is easily determined. The lines in it correspond to currencies, and the columns to currency pairs. The matrix is highly sparse and consists of zeros, ones, and minus ones.
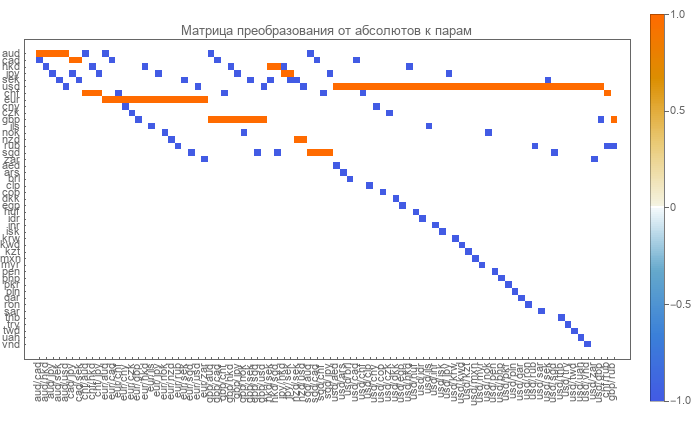
Zeros indicate the absence of such a pair and currency. The unit corresponds to the currency in the pair numerator. Minus one denotes the currency in the denominator of the pair.
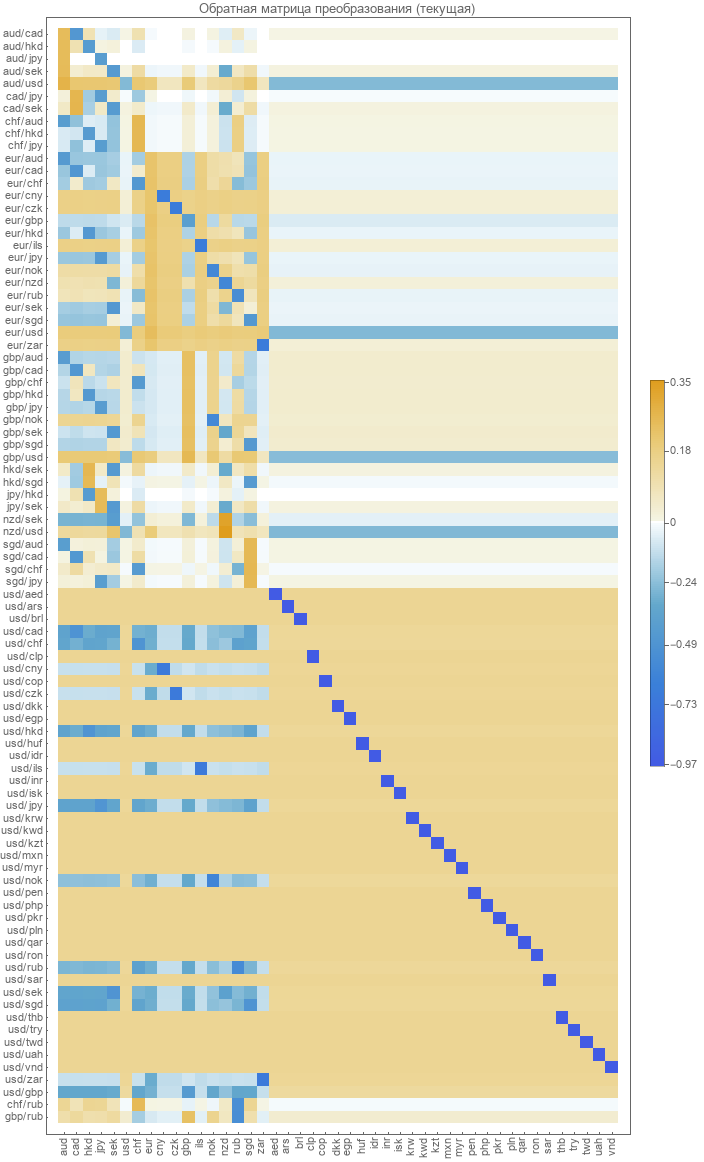
The inverse transformation matrix from pairs to absolute courses is not defined. It is necessary to calculate. The most obvious method is to minimize the recovery error of paired courses. What was done to calculate this matrix in 2017. Here is a graphical representation of this matrix.
Check the accuracy of the existing model
For the current matrix were obtained absolute and restored paired exchange rates. There were sharp differences between the original and reconstructed paired courses.

Further, the calculation of recovery errors for all pairs was made.
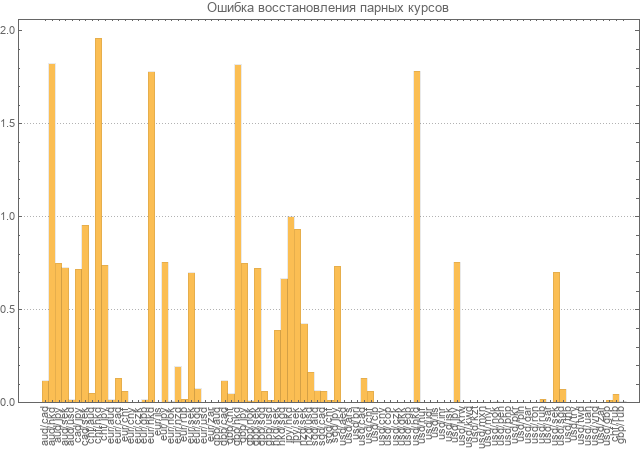
The error was considered as the average of the relative deviations taken in absolute value. As you can see in the diagram, the errors for many pairs are almost twice as many as the values themselves.
Of course, this level of error does not allow us to consider the model consistent and requires recalculation.
Pseudoinverse matrix from a straight line
The first thing we will try is to calculate just the inverse matrix for the direct transformation matrix. In view of the fact that the matrix is non-square, we will have to use a pseudoinverse transformation . The result is as follows.
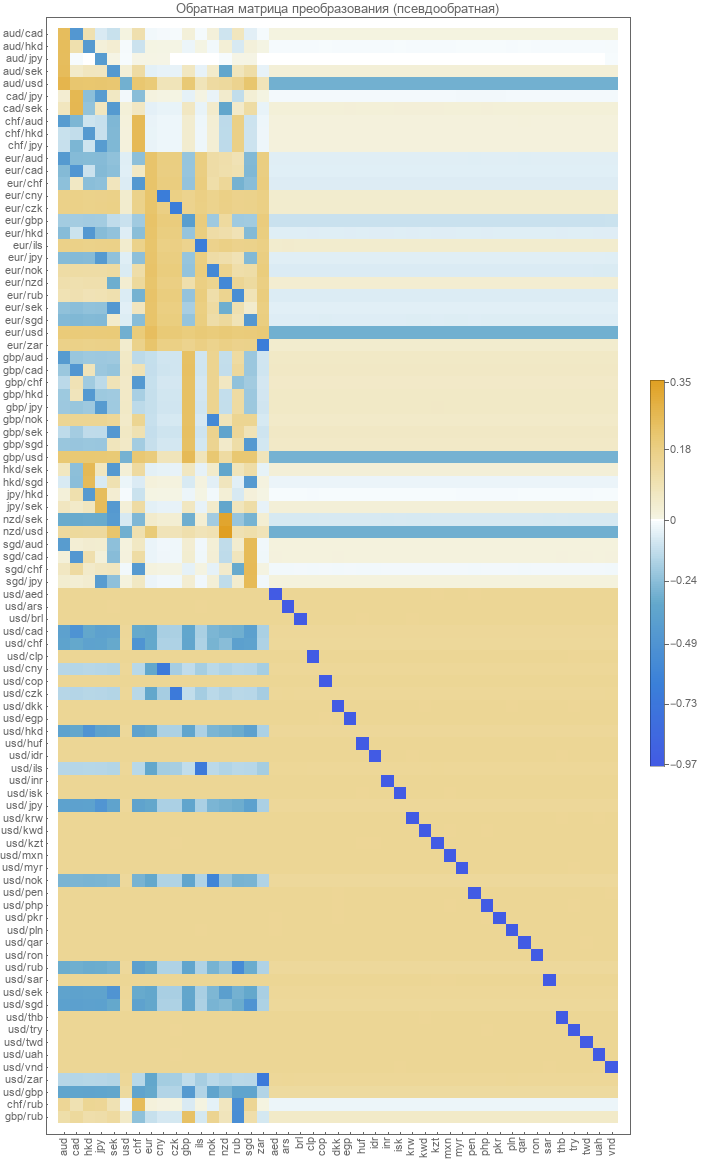
It is very similar to what we got earlier using real pair rates for optimization.
Calculate absolute rates. Then we restore pair courses from absolute ones. The error chart was the following.

Errors also turned out big as in the assessment above. This model also can not arrange us.
Calculation of the inverse matrix through linearly independent components
If we analyze in detail the direct transformation matrix, we can find that it has a degenerate appearance (the rank of the matrix is less than the number of currency rows). In other words, there are linearly dependent rows in the direct matrix. And therefore we will not be able to get an acceptable inverse matrix.
To resolve the current situation, the following solution was proposed. When moving from absolute courses to paired, you must first move to linearly independent components. And only then go to the pairs. The transition matrices from absolute courses to components and from components to pair courses will be non-degenerate and it will be possible to obtain inverse matrices.
To search for linearly independent components, it is necessary to attach a unit pair-pairing matrix to the direct transformation matrix. Thus, we obtain two matrices of transition from absolute courses to paired ones and an attached matrix of transitions from paired to paired.

Now we will produce standard transformations to a stepwise view of the upper part of this combined matrix (in fact, the standard tools of the Wolfram Mathematica mathematical package lead further to the diagonal form ). As a result, it was possible to obtain the following transformed matrix.

Now in the columns of this matrix we have linearly independent components. And we can move to them from both absolute courses (the upper part of the matrix) and from paired courses (the lower part of the combined transformed matrix).
We distinguish these transition matrices for linearly independent components. Here is the transition matrix for components from absolute courses.
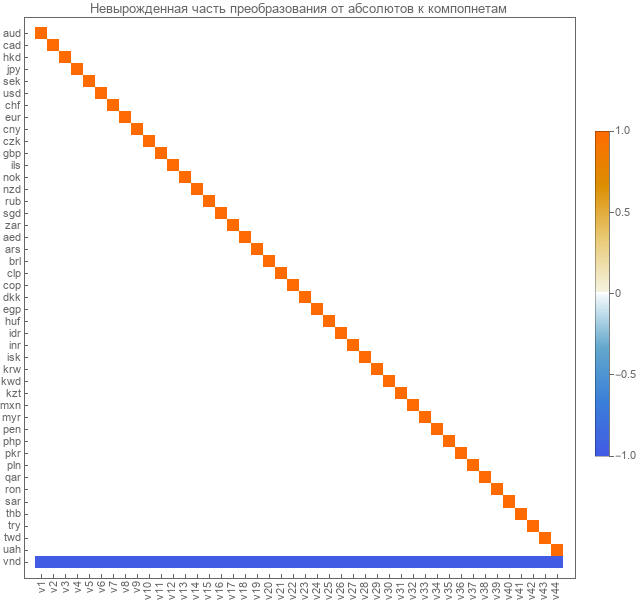
Here is the transition matrix from paired courses to linearly independent components.

The transition from absolutes to components occurs through the matrix calculated above. The inverse transformation from components to absolutes is done through the inverse matrix. Since it will be nondegenerate, a good inverse matrix can be obtained. We will receive as pseudo-inverse. Here is her view.

Now you can get the complete inverse transform matrix from pairs to absolutes. To do this, multiply the transformation matrix from pairs to components by the inverse transformation matrix from components to absolutes. She looks like this.

Although we have already seen the above, but the matrix is different. We investigate the results that it gives. We calculate the absolute rates, and of them we will restore the steam rooms. The recovery error was the following.

On all pairs except two, almost zero errors. Find out what's with these couples.
It turns out that in two currency pairs incorrect data is accepted. For jpy / hkd and jpy / sek, the data is sent in lots of 10,000 and 100 pcs. It is necessary to correct and re-check.
After correcting the input pair courses (getting rid of lots) and recalculating the absolute and restored pair courses, we look at the recovery error.

Received an error in the range of 0.3%. It is an acceptable level of error.
Here is an example of an absolute course graph.
Here is an example of the original and restored paired exchange rates.

Once the new inverse transformation matrix has been recalculated, we again present the data on the latest absolute rates of all participating currencies.
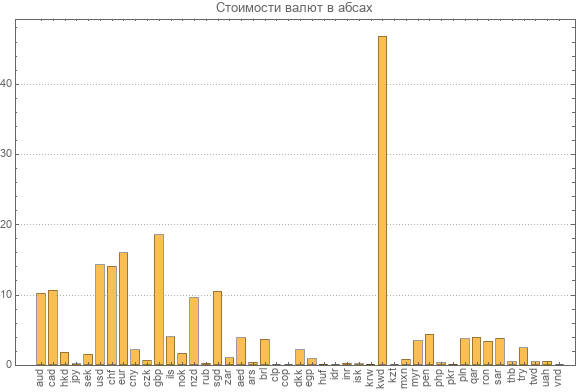
You can see the most expensive currency. This is a Kuwaiti dinar worth almost 47 abs. The smallest absolute value of the Vietnamese dong is 0.003 abs.
findings
As a result of the research, it was found that the existing method of calculating absolute rates gives a significant error. In addition, an error was detected in the source data.
The inverse transformation matrix from pairs to absolutes was obtained only using the transformation method to a smaller number of linearly independent components with a non-degenerate transformation matrix.
The method of obtaining the inverse transformation matrix did not use data from pairs of courses. And therefore independent of them.
Verification of conversion on real courses showed a low level of error. From which the conclusion was drawn about the applicability of the found matrix of the inverse transformation from pair exchange rates to absolute ones.
The method does not claim to be completed and mathematically verified, but as an acceptable solution it will be used for further research of its absolute exchange rates.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/448866/
All Articles