Security Week 16: Digital Identity Theft
 Last week, Kaspersky Lab held a regular Security Analyst Summit conference. The event traditionally reveals information about the study of the most complex cyber attacks discovered by the specialists of “Laboratories” and other companies. Today we have a brief overview of the presentations, and we will start not with APT, but with financial fraud in cyberspace. The report of the GReAT team shows that the theft of money in the network is reaching a new level, and the attackers are trying to circumvent even the advanced anti-fraud systems.
Last week, Kaspersky Lab held a regular Security Analyst Summit conference. The event traditionally reveals information about the study of the most complex cyber attacks discovered by the specialists of “Laboratories” and other companies. Today we have a brief overview of the presentations, and we will start not with APT, but with financial fraud in cyberspace. The report of the GReAT team shows that the theft of money in the network is reaching a new level, and the attackers are trying to circumvent even the advanced anti-fraud systems.To block a suspicious transaction, when intruders already have access to the payment system, online banking or credit card data, you can, if you have a model of normal client behavior on the network: where does it come from, which computer, which browser does it use etc. In total, more than a hundred different indirect signs help to distinguish the real account holder from the cybercriminal, even if the correct payment information is entered. The logical consequence of the introduction of such systems was the appearance on the black market not of credit card numbers, but rather copies of the digital identity of the victims.
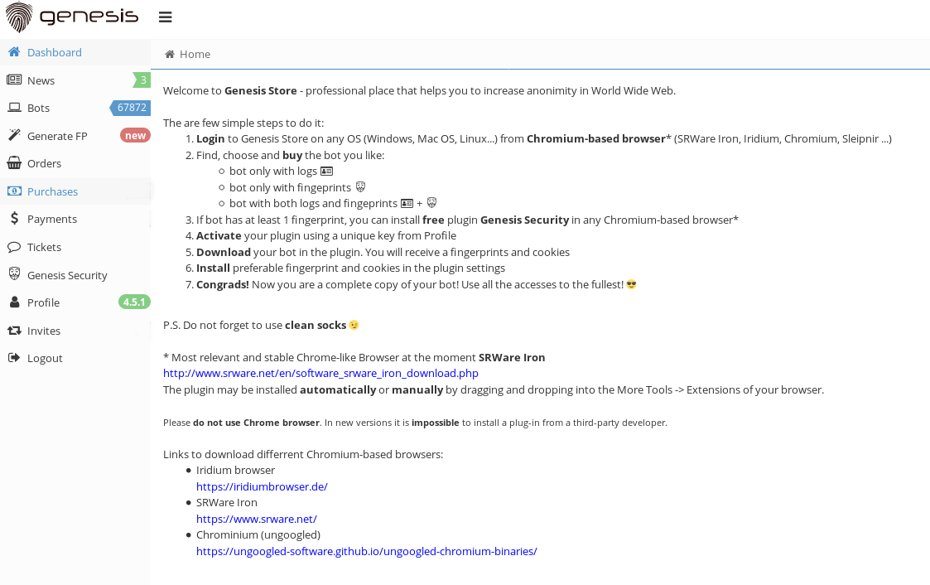
The study shows an example of the underground exchange Genesis Store. At the time of publication, over 60 thousand digital personalities were exhibited there. Examples of lots in the screenshot below:
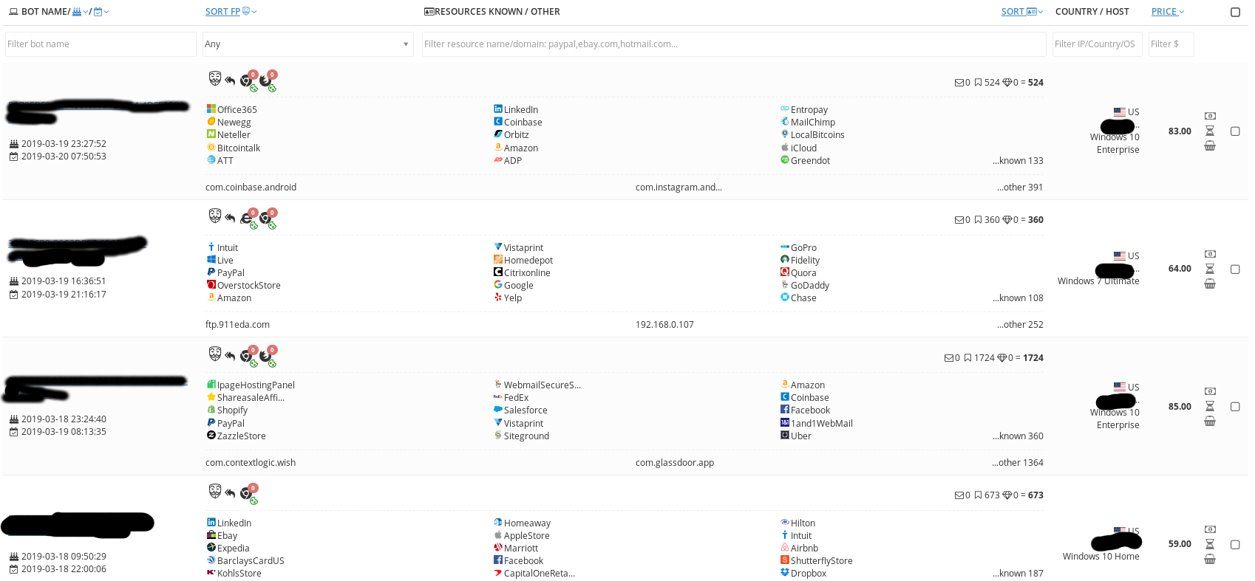
The cost of the lot is considered automatically; if there is a password to the online bank, the price will be more expensive. The average price tag - from 5 to 200 dollars. After purchasing a digital identity can be downloaded via the plugin for Chrome. If you obtain an IP address in the victim’s home region, making payments to the bank will not seem suspicious. For those who want to save, the same resource offers to download an artificial set of identifiers. The technology is quite simple, but it sounds impressive: it is not a password theft, it is, in fact, the cloning of people - so far only in the network and only in terms of systems to combat financial fraud.
')
Let's go to apt. The obvious tendency of modern targeted attacks is the reduction of the radius of destruction. A good example is the ShadowHammer attack, theoretically capable of hitting tens of thousands of laptops and computers with Asus hardware, but in fact active in only a limited list of several hundred MAC addresses.
The campaign TajMahal ( news , research ) operates with more than 80 malicious modules, but it was extremely difficult to detect. The researchers found only one confirmed sacrifice - a diplomatic mission in one of the countries of Central Asia. Among the features of the attack is the possibility of data theft from removable media, but only by a list of files of interest in the code. The more accurate the attack and the smaller the list of victims, the longer the tooling is able to live - before it is detected and blocked by defensive solutions.

Experts of Lookout told ( news , post in the company's blog) at the conference Kaspersky SAS about the spyware program Exodus. In early April, Security Without Borders told about this trojan: they discovered 25 versions of a spyware utility in the Google Play app store. In Lookout, we found a version of Exodus for iOS, signed with an official developer certificate.
The program (both in the version for Android and iOS) was distributed on phishing sites that mimic the pages of mobile operators in Italy and Turkmenistan. Users reported that the software is supposedly necessary to connect to Wi-Fi access points. In fact, the Trojan could send personal information from the phone to the remote server: contacts, photos, videos, GPS data. There was even the ability to remotely turn on the microphone.
An interesting study tells about the problems (friends in Russia) with the replacement of the SIM-card for subsequent access to network services and theft of money through online banking. For Brazil, even quoted are the prices on the black market for issuing a new SIM card - from $ 10 to $ 40, depending on the telecom operator (phones of famous people will cost more). In Mozambique, card substitution is usually done in order to access the very popular ($ 5 billion a year) M-Pesa electronic payment system, in addition to traditional online banking. They are fighting a similar cybercrime in a rather original way: all mobile operators exchange data with banks in real time. This allows you to automatically block all payments using the phone number for which the SIM card was recently replaced. The blocking time is small - up to two days, but long enough for the victim to detect the problem and regain access.
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this digest may not always coincide with the official position of Kaspersky Lab. Dear editors generally recommend to treat any opinions with healthy skepticism.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/448184/
All Articles