Radiation: the war with the invisible killer or a little more about radon
Hello again. In the comments to the previous article, I promised to write about protection against radon and its DPR. Well, I keep this promise.
As I said in the previous article, radon is a rather serious danger for people. It is especially great in some regions of the Earth, where radon from large depths is carried to the surface along tectonic faults. And in these places are vital measures to reduce its concentration in human housing.
Sources of radon in the bowels of the Earth are rocks such as granites, syenites, clays and shale rich in uranium and its “daughters”, including radium-226. Radon is allocated (or as they say - exhalated ) by rocks and building materials by two main mechanisms: diffusion and recoil. The radon atom formed inside a solid substance containing radium, before passing into the gaseous medium, must overcome the layer of solid matter, where it slowly migrates through the crystal lattice. Because of this, “radon-hazardous” is a rather thin layer of dense solid matter, which is millimeters, but this thickness significantly — up to meters — increases if the material is porous or cracked. An alternative to the diffusion path of radon release is the mechanism associated with the fact that the radon nucleus receives a significant impetus during the formation, due to which a thin layer of matter immediately overcomes. The thickness of this layer is very small, but the process of recoil, unlike diffusion, does not take time and does not depend on temperature. After the release of radon into the pore space of the soil or rock (regardless of the mechanism), it migrates relatively quickly and goes to the surface. The release of radon in this way creates vast patches of the earth’s surface with an elevated background of radon concentration, coinciding along the contours with the zones where these rocks are located shallowly from the surface.
')
As a rule, indoor concentration of radon is significantly higher than that observed outdoors. The main ways of its penetration into the room are the following:
Building materials are the main source of radon in high-rise buildings. The most "radon-hazardous" components of building materials are coal slag and alumina (bauxite), as well as phosphogypsum, used as a component of plaster mixes, drywall and other facing materials. Ordinary sand and clay can also be radioactive. It is known for its radioactivity and the release of radon granite, which is used both in the form of crushed stone for the preparation of concrete, and in the form of facing slabs and independent structural elements of buildings, for example, the foundation. Such popular building material as red brick is rich in radium-226. But porous and bulk materials are the most dangerous, since radon comes out of dense granite extremely reluctantly.
The total output of radon in a typical city apartment from the bowels of the Earth and from building materials reaches 60 kBq / day. With outside air, depending on the number of floors, comes from a negligible amount on the upper floors up to 10 kBq / day on the first floor. Water and natural gas are usually much smaller sources of radon - up to 3-4 kBq / day, but in poorly ventilated small rooms, kitchens and toilets can quickly create very significant levels of radon. Thus, the survey of houses in Finland gave the following values: with a tolerable level of radon in rooms 150-200 , in his kitchen his EROA reaches 3, and in the bathroom - up to 8.5 ! In the process of using a shower, the radon level increases tenfold.
With regard to the entry of radon with the outside air, then of course, it is only significant if there are no other sources of radon or they are insignificant - for example, in wooden houses. Because along with the intake of radon from the outside into the room, there is a reverse process - which contributes to the equalization of the external and internal EEDA of radon, and not to the accumulation of radon inside.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the radon concentration in the open air is insignificant; therefore, the simplest way to repeatedly reduce the EASA of radon is elementary ventilation. The external concentration of radon rarely exceeds one and the first tens and airing quickly reduces it to these values. A well-designed building ventilation system, the use of exhaust ventilation in kitchens and bathrooms is one of the most effective ways to solve a radon problem. Thus, in the kitchen, when using gas, the inclusion of an exhaust usually completely prevents an increase in the radon level, whereas in the absence of an exhaust, its level often increases rapidly.
In the seventies in Sweden began to actively combat the loss of heat from buildings, and in connection with this, the air exchange rate has more than halved. An unexpected and unpleasant consequence of this was an increase in radon levels by several times.
However, not always intensive ventilation is useful - sometimes a powerful extract, leading to a drop in pressure in the basement, contributes to the release of radon and dramatically increases its concentration in the basements. Therefore, ventilation should be organized in such a way that the exhaust hood is necessarily compensated by inflow. The organization of intensive ventilation of the space between the ground and the protected building significantly reduces the radon concentration in this zone and effectively prevents the penetration of radon from the soil into the building. The role of such a space can be performed by an uninhabited or rarely visited basement or an underground unit equipped in the basement.

These figures, like the one on the KDPV, are copied over many Russian-language sites.
I could not find the original source, but apparently, these are some official documents from the USA .
The next protective measure that is necessary to reduce the level of radon in the premises is the creation of an impenetrable barrier to prevent it from getting there. As such a barrier can serve as a standard foundation waterproofing. However, a polyethylene film often used as a waterproofing material is unexpectedly very radon-permeable material. However, if you remember that radon is perfectly soluble in saturated hydrocarbons, and the fact that polyethylene is actually a paraffin hydrocarbon with a very large molecular weight, the reason for this becomes clear. Polymer-bitumen mastics and rolled materials are effective against waterproofing radon materials. There should be two such barriers: one at the border between the ground and the building, and the other at the level of the basement floor. In combination with the ventilation of the volumes cut off by these barriers, this makes it possible to sharply reduce the penetration of radon into habitable rooms.
The release of radon from building materials is effectively prevented by painting, pasting walls with special wallpaper (even ordinary paper wallpapers reduce the emission of radon by 30%) by impregnating their surface with special compounds. An obstacle to the selection of radon is tile. By the way, porous and fractured materials are the most radon-hazardous, therefore preventing the formation of cracks (for example, in the basement material) not only reduces the penetration of radon through the thickness of concrete, but also drastically reduces the release of radon from the concrete itself. Of course, this also applies to materials with which walls and floors are laid, the reduction of porosity and fracturing of which effectively reduces their emanating ability.
A good way to reduce the radon content in water is its aeration. It can be carried out by bubbling air through a layer of water or vice versa, splashing water into the air, passing water and air in a countercurrent through a packed column and other methods. This measure reduces the radon concentration in water by at least an order of magnitude, and often more. As a rule, water undergoes this operation at water treatment plants - but it does not exist if water comes from a well for individual use. The radon content in such water can reach 500-1000 Bq / l at an acceptable level of 60 Bq / l. Further purification of water from radon is possible with the use of various adsorbents, for example, activated carbon, which is able to remove 99.7% of radon. The cleaning efficiency decreases with time due to the "aging" of coal, but the radon itself on the filter, of course, does not accumulate, as it quickly disintegrates. Radon removal is also a side effect of all sorts of ion-exchange and membrane filters. Specialized filtration plants are also available to remove radon - from small ones, to a single house or apartment, to those that can serve the whole city. Of course, an individual installation for cleaning water from radon should be installed outside the dwelling, and not directly in the kitchen under the sink, because otherwise the entire radon will end up in the air.
Mainly, the purpose of cleaning water from radon is to prevent it from entering the room. As for the use of water with radon inside, then boiling it in an open dish instantly reduces the concentration of radon in it to almost zero, so do not drink raw tap water.
The simplest and most effective way to reduce the radon content in natural gas is exposure. A month of exposure in a gas storage facility almost completely destroys radon in gas. The problem with radon occurs either when gas is supplied to the network from the production site directly, or when radon enters the storage facility itself, in addition to gas.
All the above measures are good when the house is being built. But in the existing housing there is little that can be done, except for forced ventilation of the basement. But maybe you can try to organize air cleaning? After all, as we have already seen, radon is readily sorbed.
Yes, there is such an option. And first of all, it is advisable to remove from the air, not radon itself, but its much more harmful DPR. They are present in the form of active plaque on aerosol particles and beta decay gives these particles a positive charge. This is what we use.
The first option is to use HEPA filters or the so-called Petryanov tissue. This material is a matted polymer fibers, prone to accumulate a negative charge, and this electrification is due to the fact that such a filter with high efficiency picks up the smallest aerosol particles whose dimensions are many times smaller than the pores of the filter (there are other mechanisms, but this one is important to us) . And the positive charge of aerosol particles coated with active bloom contributes to electrostatic sticking to the filter fibers. In order to effectively capture radon, the performance of the filtration plant must be such that the time during which the filter pumps the air volume equal to the volume of the room exceeds the time of complete air exchange in the room.
The second option is electric precipitators. As in the method of trapping the DPR of radon to the “trap” that I described in the previous article, when I spoke about home methods for estimating the level of radon in a room, active deposition of radar DPR occurs on a negatively charged electrode. A prerequisite for the successful operation of an electrostatic precipitator is the potential of the trapping electrode, which is within certain limits — about 1000–5000 V. A lower voltage is inefficient, a higher voltage leads to the recharging of dust particles and their repulsion from the electrode. This, by the way, we observe by the example of the Chizhevsky chandelier, the ceiling above which is covered with a layer of stubborn dust. By the way, fans of the Chizhevsky chandelier love to mention that it cleans the air from radon. So no, it does not clear.
I will give an interesting description of a successful experiment on air purification from radon by an electrostatic method conducted by begin_end .
In conclusion, I would add that the effectiveness of such cleaning should increase significantly with the introduction of a "flow booster" - a fan that pumps air through the trapping electrode.
ERAA of radon in rooms usually noticeably exceeds that in the open air. Since a person spends most of his life on the premises, it is advisable, and in many cases it is also vital, to take measures to reduce the level of air pollution with radon and its DPR.
The degree of complexity and effectiveness of these measures is different, but there is one quick and worthless method - to open the window.

As I said in the previous article, radon is a rather serious danger for people. It is especially great in some regions of the Earth, where radon from large depths is carried to the surface along tectonic faults. And in these places are vital measures to reduce its concentration in human housing.
Ways radon in the room
Sources of radon in the bowels of the Earth are rocks such as granites, syenites, clays and shale rich in uranium and its “daughters”, including radium-226. Radon is allocated (or as they say - exhalated ) by rocks and building materials by two main mechanisms: diffusion and recoil. The radon atom formed inside a solid substance containing radium, before passing into the gaseous medium, must overcome the layer of solid matter, where it slowly migrates through the crystal lattice. Because of this, “radon-hazardous” is a rather thin layer of dense solid matter, which is millimeters, but this thickness significantly — up to meters — increases if the material is porous or cracked. An alternative to the diffusion path of radon release is the mechanism associated with the fact that the radon nucleus receives a significant impetus during the formation, due to which a thin layer of matter immediately overcomes. The thickness of this layer is very small, but the process of recoil, unlike diffusion, does not take time and does not depend on temperature. After the release of radon into the pore space of the soil or rock (regardless of the mechanism), it migrates relatively quickly and goes to the surface. The release of radon in this way creates vast patches of the earth’s surface with an elevated background of radon concentration, coinciding along the contours with the zones where these rocks are located shallowly from the surface.
Thus, in the Leningrad region, in a narrow strip of land 3–15 km wide, stretching from the town of Kingisepp to the Syas River, there are exits of the so-called dictationaean shales of the Koporskaya suite (lower Ordovician — shown on the map below in dark green). These slates are characterized by an abnormally high (up to 0.17%) uranium content, which accounts for the active release of radon in this area. The concentration of radon in the soil air here reaches in separate points 136 and higher. Uranium-bearing dictatehem schists are also found in other places of the Leningrad Region, as well as in Estonia.At the same time, there are also local radon outlets in tectonically active zones, marking faults, karst channels and other “radon” structures. Above such “hot spots”, the radon concentration can sometimes exceed the background by hundreds and thousands of times, reaching dozens of kilobackers in a cubic meter.
')
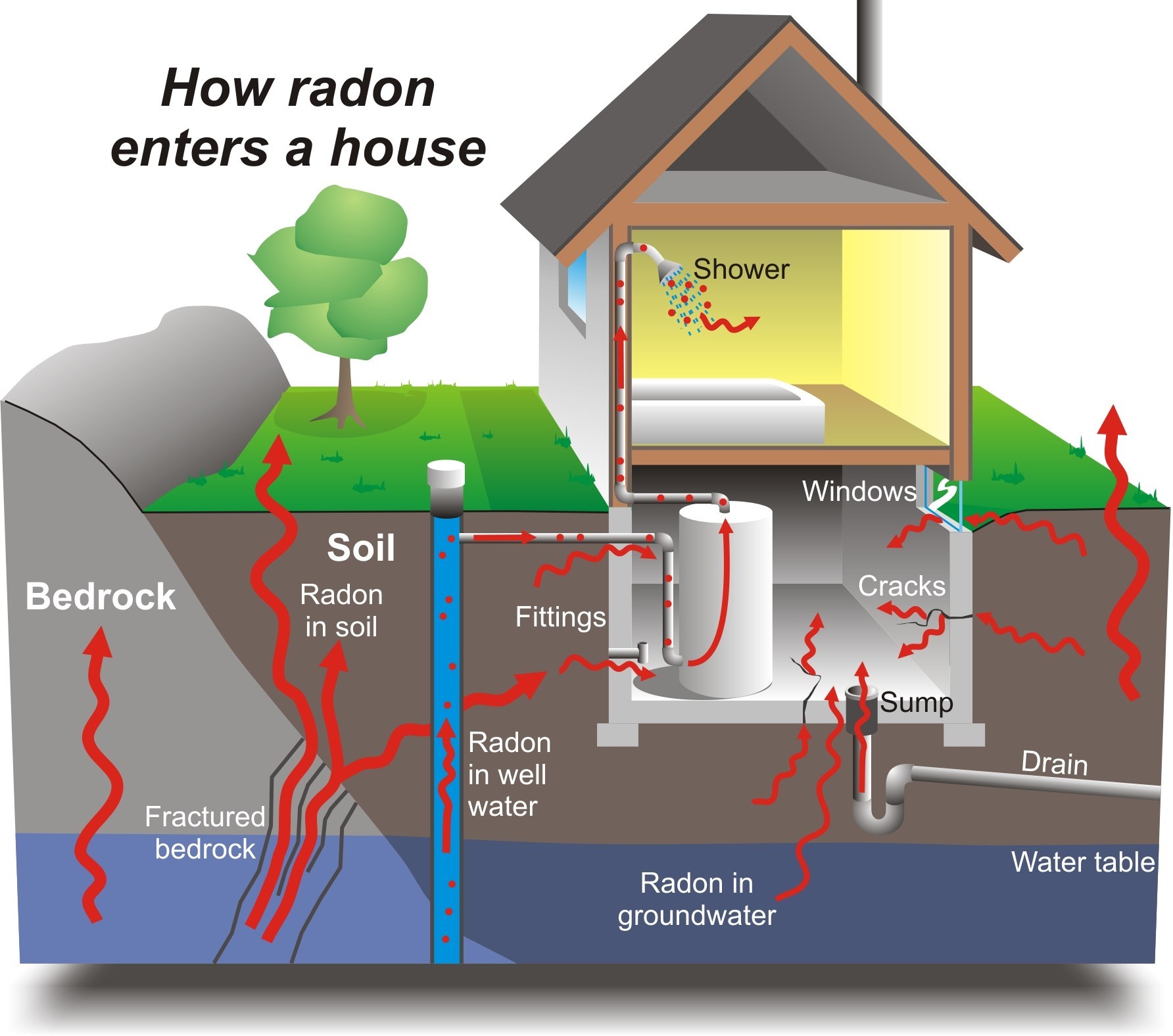
As a rule, indoor concentration of radon is significantly higher than that observed outdoors. The main ways of its penetration into the room are the following:
- direct ascending diffusion of radon from the Earth’s interior through microcracks and pores of the basement;
- penetration through underground utilities, including water and natural gas, as well as the combustion of solid fuels (coal, wood);
- the release of radon by building and facing materials of the house itself, and sometimes by objects in the house containing radium and thorium;
- the entry of radon with outside air through the open windows of the lower floors, the airways of the basements, the surface air “sucked in” with radon enriched.
Building materials are the main source of radon in high-rise buildings. The most "radon-hazardous" components of building materials are coal slag and alumina (bauxite), as well as phosphogypsum, used as a component of plaster mixes, drywall and other facing materials. Ordinary sand and clay can also be radioactive. It is known for its radioactivity and the release of radon granite, which is used both in the form of crushed stone for the preparation of concrete, and in the form of facing slabs and independent structural elements of buildings, for example, the foundation. Such popular building material as red brick is rich in radium-226. But porous and bulk materials are the most dangerous, since radon comes out of dense granite extremely reluctantly.
The total output of radon in a typical city apartment from the bowels of the Earth and from building materials reaches 60 kBq / day. With outside air, depending on the number of floors, comes from a negligible amount on the upper floors up to 10 kBq / day on the first floor. Water and natural gas are usually much smaller sources of radon - up to 3-4 kBq / day, but in poorly ventilated small rooms, kitchens and toilets can quickly create very significant levels of radon. Thus, the survey of houses in Finland gave the following values: with a tolerable level of radon in rooms 150-200 , in his kitchen his EROA reaches 3, and in the bathroom - up to 8.5 ! In the process of using a shower, the radon level increases tenfold.
With regard to the entry of radon with the outside air, then of course, it is only significant if there are no other sources of radon or they are insignificant - for example, in wooden houses. Because along with the intake of radon from the outside into the room, there is a reverse process - which contributes to the equalization of the external and internal EEDA of radon, and not to the accumulation of radon inside.
The benefits of fresh air
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the radon concentration in the open air is insignificant; therefore, the simplest way to repeatedly reduce the EASA of radon is elementary ventilation. The external concentration of radon rarely exceeds one and the first tens and airing quickly reduces it to these values. A well-designed building ventilation system, the use of exhaust ventilation in kitchens and bathrooms is one of the most effective ways to solve a radon problem. Thus, in the kitchen, when using gas, the inclusion of an exhaust usually completely prevents an increase in the radon level, whereas in the absence of an exhaust, its level often increases rapidly.
In the seventies in Sweden began to actively combat the loss of heat from buildings, and in connection with this, the air exchange rate has more than halved. An unexpected and unpleasant consequence of this was an increase in radon levels by several times.
However, not always intensive ventilation is useful - sometimes a powerful extract, leading to a drop in pressure in the basement, contributes to the release of radon and dramatically increases its concentration in the basements. Therefore, ventilation should be organized in such a way that the exhaust hood is necessarily compensated by inflow. The organization of intensive ventilation of the space between the ground and the protected building significantly reduces the radon concentration in this zone and effectively prevents the penetration of radon from the soil into the building. The role of such a space can be performed by an uninhabited or rarely visited basement or an underground unit equipped in the basement.


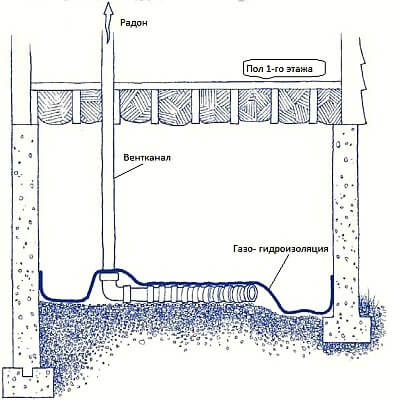
These figures, like the one on the KDPV, are copied over many Russian-language sites.
I could not find the original source, but apparently, these are some official documents from the USA .
Barrier against radon
The next protective measure that is necessary to reduce the level of radon in the premises is the creation of an impenetrable barrier to prevent it from getting there. As such a barrier can serve as a standard foundation waterproofing. However, a polyethylene film often used as a waterproofing material is unexpectedly very radon-permeable material. However, if you remember that radon is perfectly soluble in saturated hydrocarbons, and the fact that polyethylene is actually a paraffin hydrocarbon with a very large molecular weight, the reason for this becomes clear. Polymer-bitumen mastics and rolled materials are effective against waterproofing radon materials. There should be two such barriers: one at the border between the ground and the building, and the other at the level of the basement floor. In combination with the ventilation of the volumes cut off by these barriers, this makes it possible to sharply reduce the penetration of radon into habitable rooms.
The release of radon from building materials is effectively prevented by painting, pasting walls with special wallpaper (even ordinary paper wallpapers reduce the emission of radon by 30%) by impregnating their surface with special compounds. An obstacle to the selection of radon is tile. By the way, porous and fractured materials are the most radon-hazardous, therefore preventing the formation of cracks (for example, in the basement material) not only reduces the penetration of radon through the thickness of concrete, but also drastically reduces the release of radon from the concrete itself. Of course, this also applies to materials with which walls and floors are laid, the reduction of porosity and fracturing of which effectively reduces their emanating ability.
Fighting radon in water and gas
A good way to reduce the radon content in water is its aeration. It can be carried out by bubbling air through a layer of water or vice versa, splashing water into the air, passing water and air in a countercurrent through a packed column and other methods. This measure reduces the radon concentration in water by at least an order of magnitude, and often more. As a rule, water undergoes this operation at water treatment plants - but it does not exist if water comes from a well for individual use. The radon content in such water can reach 500-1000 Bq / l at an acceptable level of 60 Bq / l. Further purification of water from radon is possible with the use of various adsorbents, for example, activated carbon, which is able to remove 99.7% of radon. The cleaning efficiency decreases with time due to the "aging" of coal, but the radon itself on the filter, of course, does not accumulate, as it quickly disintegrates. Radon removal is also a side effect of all sorts of ion-exchange and membrane filters. Specialized filtration plants are also available to remove radon - from small ones, to a single house or apartment, to those that can serve the whole city. Of course, an individual installation for cleaning water from radon should be installed outside the dwelling, and not directly in the kitchen under the sink, because otherwise the entire radon will end up in the air.
Mainly, the purpose of cleaning water from radon is to prevent it from entering the room. As for the use of water with radon inside, then boiling it in an open dish instantly reduces the concentration of radon in it to almost zero, so do not drink raw tap water.
The simplest and most effective way to reduce the radon content in natural gas is exposure. A month of exposure in a gas storage facility almost completely destroys radon in gas. The problem with radon occurs either when gas is supplied to the network from the production site directly, or when radon enters the storage facility itself, in addition to gas.
Air purification from radon and DPR
All the above measures are good when the house is being built. But in the existing housing there is little that can be done, except for forced ventilation of the basement. But maybe you can try to organize air cleaning? After all, as we have already seen, radon is readily sorbed.
Yes, there is such an option. And first of all, it is advisable to remove from the air, not radon itself, but its much more harmful DPR. They are present in the form of active plaque on aerosol particles and beta decay gives these particles a positive charge. This is what we use.
The first option is to use HEPA filters or the so-called Petryanov tissue. This material is a matted polymer fibers, prone to accumulate a negative charge, and this electrification is due to the fact that such a filter with high efficiency picks up the smallest aerosol particles whose dimensions are many times smaller than the pores of the filter (there are other mechanisms, but this one is important to us) . And the positive charge of aerosol particles coated with active bloom contributes to electrostatic sticking to the filter fibers. In order to effectively capture radon, the performance of the filtration plant must be such that the time during which the filter pumps the air volume equal to the volume of the room exceeds the time of complete air exchange in the room.
The second option is electric precipitators. As in the method of trapping the DPR of radon to the “trap” that I described in the previous article, when I spoke about home methods for estimating the level of radon in a room, active deposition of radar DPR occurs on a negatively charged electrode. A prerequisite for the successful operation of an electrostatic precipitator is the potential of the trapping electrode, which is within certain limits — about 1000–5000 V. A lower voltage is inefficient, a higher voltage leads to the recharging of dust particles and their repulsion from the electrode. This, by the way, we observe by the example of the Chizhevsky chandelier, the ceiling above which is covered with a layer of stubborn dust. By the way, fans of the Chizhevsky chandelier love to mention that it cleans the air from radon. So no, it does not clear.
I will give an interesting description of a successful experiment on air purification from radon by an electrostatic method conducted by begin_end .
We carried out studies of electrostatic filtration of DPR radon - namely, the Chizhevsky chandelier is not suitable, since the potential at such a plant is higher than 5kV. If the voltage is too high, dust particles are not deposited on the electrode, but on objects nearby.I will also refer to the begin_end post devoted to the problem of cleaning air from radon.
Electrostatic filter in the form of a -5 kV electrode with a tablet act. Coal reduces activity in a 200 l barrel from 1988 Bq / m3 to 67 Bq / m3 (almost 30 times) in 6 hours. Of course, the experience in the barrel is only a trial one, it has no high significance.
When tested in a 59m3 room (p. 317), the concentration of DPR was reduced from 89 Bq / m3 to 28 Bq / m3 in 8 hours (3.2 times, but 28 Bq / m3 is close to the lower limit of the definition of the PAA-10 device; the method is difficult to evaluate at such a low initial concentration, and a room with a high level in our area cannot be found).
In conclusion, I would add that the effectiveness of such cleaning should increase significantly with the introduction of a "flow booster" - a fan that pumps air through the trapping electrode.
* * *
ERAA of radon in rooms usually noticeably exceeds that in the open air. Since a person spends most of his life on the premises, it is advisable, and in many cases it is also vital, to take measures to reduce the level of air pollution with radon and its DPR.
The degree of complexity and effectiveness of these measures is different, but there is one quick and worthless method - to open the window.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447762/
All Articles
