How do smart cities come about?
According to the UN , for 2018, 55.3% of the world's population live in cities. By 2030, 60% of people around the world will live in cities with a population of at least 0.5 million people. A growth of 5% in 12 years is evidence of the ongoing process of urbanization. Therefore, it is now important to understand how to make cities safe and ensure their sustainable development.
In the past, I wrote about the “rusty belt” and single-industry towns , as well as successful case studies from urban development institutes . Today we will talk about how technologies help to make cities safe and ensure their sustainable development, about how “smart cities” arise, where ideas for them come from and how projects are implemented. Consider these questions on the example of Chicago and Barcelona, let's talk about the various formats of work with residents - "open government", competitions and hackathons and other initiatives aimed at the development of cities.

Cities account for 80% of gross domestic product due to lower transaction costs. That is, in the cities there are lower costs, which are not related to the production of products, but to the indirect costs associated with this - collecting and searching for information necessary for the activity, concluding transactions, contracts, and so on. The second component of the success of the city is the concentration of high-quality human capital. Therefore, cities are the drivers of the development of the world economy.
')
In the process of development, the city goes through several stages of evolution:
In the process of evolution problems may arise. For example, production in the city leads to a deterioration of the environmental situation. Later, during the transition to the services sector and the development of small and medium-sized businesses, there may be a “rusty belt” - unused production areas that hinder the movement around the city and the efficient use of space. But these problems simultaneously open up different opportunities for improving the city.
Chicago is today one of the most populated cities in the United States: 2.7 million people live in it, and the agglomeration has more than 9 million inhabitants.
It is worth looking at the history of this city in order to understand how it developed and how it influenced the cities of the whole world.
One of the factors in the development of Chicago is its location. At the site of the future city in 1674, a missionary post was organized for wintering, which by 1833 turned into a village with 350 inhabitants, and after only four years received city status. In 1840, 4,000 people lived here.
The location between the west and east of the country made Chicago become one of the key transportation hubs in the United States. Trade contributed to the railroad and the opening of the Michigan Canal. The city traded grain, meat, in the 1960s it opened an exchange where they traded futures for frozen pork and cattle, and later for agricultural products and world currencies. The city became not only a commercial, but also an industrial center - in the early 1960s metallurgical and woodworking plants appeared here.
The appearance of Chicago was influenced by the tragedy - the Great Chicago fire, which in 1871 claimed the lives of several hundred people and destroyed most of the city - buildings on an area of about 8 square kilometers. The need to rebuild this city and the support of people from all over the country who helped with money, clothes, furniture and food, led to the fact that Chicago became one of the most interesting cities in terms of architecture.
The best architects from around the world were called into the city after a fire. In 1885, the first skyscraper in the world was built in Chicago - the 42-meter-high Home Insurance Building, in which the steel frame was used. The city overtook New York, where a 40-meter-high building already stood, which did not have such a framework and, accordingly, did not belong to skyscrapers. And the city continued to grow "up" and in the next century - 1973 built the Willis Tower, a 108-story skyscraper, which for almost 25 years was the tallest building in the world.
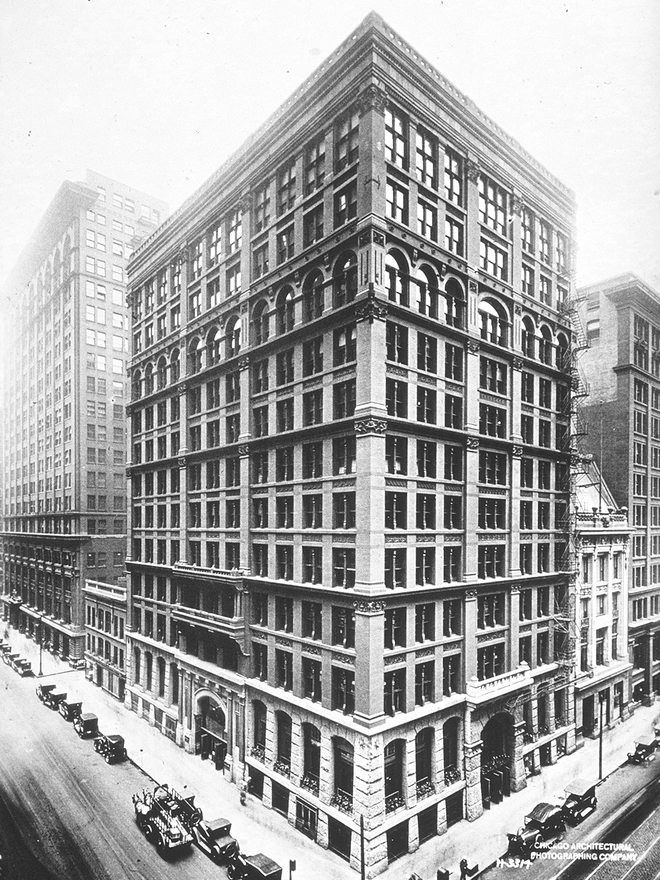

Home Insurance Building
Another event that has become an incentive for development is the World Exhibition of 1893. By that time, more than a million people lived in the city, and the exhibition received 27 million visitors in six months.
This exhibition once again shows how various events can influence the development of cities. The Westinghouse Company, with which Nikola Tesla worked, won the tender for the coverage of the World Fair. The project was another step towards electric street lighting, which today has become commonplace for us, and then it was something completely new, advanced. The exhibition town in Chicago in the number of lanterns was ahead of any other city in America.

Electric lighting at the 1893 World's Fair in Chicago
From 2000 to 2010, he lost 7.1% of jobs - this is the worst result among the ten largest cities in the United States. The city budget deficit reached $ 600 million. The budget deficit of urban schools in 2011 was $ 720 million , and half of the students did not complete the training. Crime grew again. And there was no one to fight it - there were 2,000 open vacancies in the city police.
At the same time, the city remained one of the important transport hubs of North America, there are two major airports and a railway hub. And there were 2.7 million inhabitants in it - and people are the main value in the era of digital transformation.
Transformation into a “smart city” began with the Transition Plan , released by Mayor Emanuel Ram, elected in 2011. In 2012, he issued a decree on open data in the city , in which such posts in city authorities as the Chief data officer and Chief information officer, and definitions such as the City of Chicago data portal and Data, were prescribed. According to the decree, DOIT was organized in the city - the Department of Innovation and Technology , which became the central organization for ensuring the implementation of innovations.
The smart city initiative in Chicago was aimed at identifying and solving city problems. At the same time, the use of new technologies and the involvement of residents in these processes are important. The goal was to create a “city-platform”, flexible and changeable ecosystem, allowing to introduce new solutions, launch new projects. And for this the city began to work in three directions.
XXI century - the time of high-speed Internet. With the help of the Broadband project , the digital infrastructure has been updated. Universities and organizations, parks and public places were equipped with Internet access, increased availability of Internet services in residential areas of the city.
But the Internet will not help if you do not have computer skills. The Sustainable Broadband Adoption program was dedicated to addressing this issue: computer centers in 5 disadvantaged areas allow 11,000 city residents and 500 small businesses to be trained.
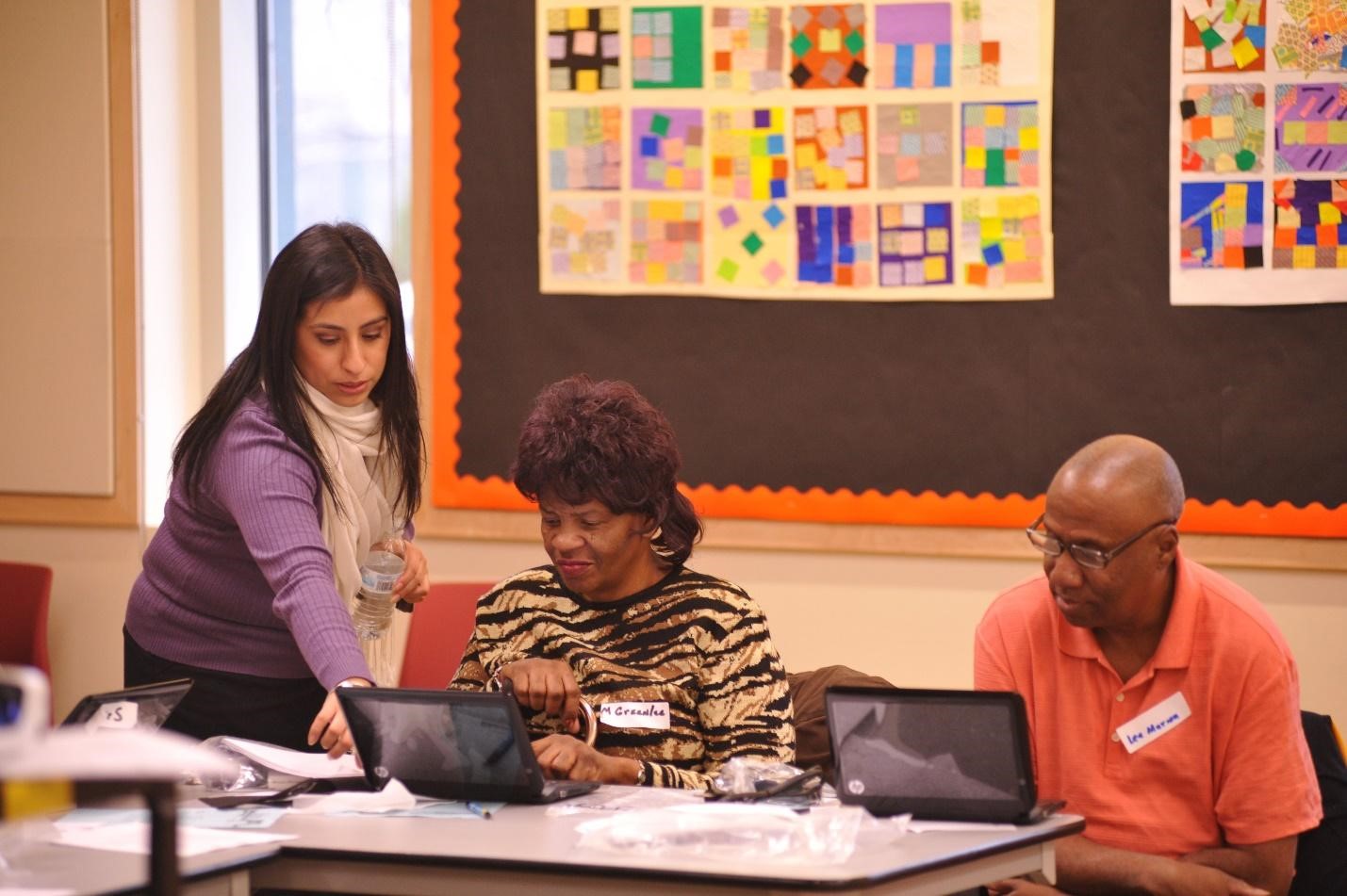

One of the digital skills training centers in Chicago
“Open data”, around which the Smart city initiative in Chicago was built from the very beginning, is also needed in order to deploy new businesses and applications on the existing platform. It turns out something like a marketplace, but across the city.
In order to provide access to data, several projects were launched in Chicago. The Chicago Hearth Atlas site aggregates data from medical organizations in the city, and surveys and research results to better understand the health status of city residents. For example, here you can find out the race, gender, number of people who have been vaccinated against HPV.
The geolocation platform OpenGrid collects real-time data from urban services. Here you can find out about the companies that are opening up, requests from residents to municipal services - for example, about where graffiti is being painted over or where animal pests are found. This platform allowed to optimize the interaction between services.
What is important is not the data, but how they are used. As part of the Illinois Open Technology Challenge competition , new problem-solving tools were developed. The goal of the program is to involve the authorities, local universities, non-profit organizations and entrepreneurs in the development of the city.
The prerequisites for this step were laid before the election of Rama. In 2007, a report was presented on the City of NetWorks: Transforming Society and the Economy through Digital Excellence . It contained recommendations for the development of the city. Among them - the search for leaders who can organize a partnership of residents and authorities for the effective implementation of digital opportunities. This idea was embodied in the Smart Chicago Collaborative initiative, now called City Tech .
In order to train residents in the field of digital competence, they launched the projects Digital Skills and Connect Chicago in the city. They coordinate educational processes and provide a network of computer-equipped places where residents can access the Internet and computer and receive free training.
None of the technologies that are used in Chicago is decisive. And while many of them could be implemented separately from others. But the main value of the "city-platform" is the ability to quickly implement them. Therefore, the City Tech initiative declared the city a “cradle” for new solutions and is now ready to help other cities in development.
Chicago was the first city in which they launched Array of Things (“an array of things”). The project is called the "fitness tracker" for the city. Devices mounted on lampposts collect information on air cleanliness, climate, traffic — automobile, bicycle and pedestrian, atmospheric pressure, sounds. The project was developed jointly by the University of Chicago, the Argonne National Laboratory and city authorities - all in order to better understand, maintain and improve Chicago.
This is an interesting example of cooperation between universities, city and business: the communication partner of the project is AT & T, technological support is provided by Cisco, Microsoft, Schneider Electric, Intel, Motorola Solutions and Zebra Technologies. Also part of the project was to attract residents of the city - a number of local events were held in which citizens talked about their problems, and teachers taught the Internet of things to share this experience with schoolchildren.

The city uses predictive analytics for pest control. The system predicts where trash cans will be filled. According to the city authorities, the effectiveness of the fight against rats has increased by 20%. Sensors installed on the bridges inform the services of freezing. Sensors also detect the pollution of Lake Michigan.
To save the citizens from parking problems, they launched ParqEx project in the city. Property owners - both shopping centers or offices, and private homes - add the available parking spaces to the service, and car owners book them. It turns out something like Airbnb for cars.
To ensure safety, cameras are placed all over the city that find crowds of people. In the command center for live broadcasts from the cameras, it is determined whether the police officers should be sent to the scene.
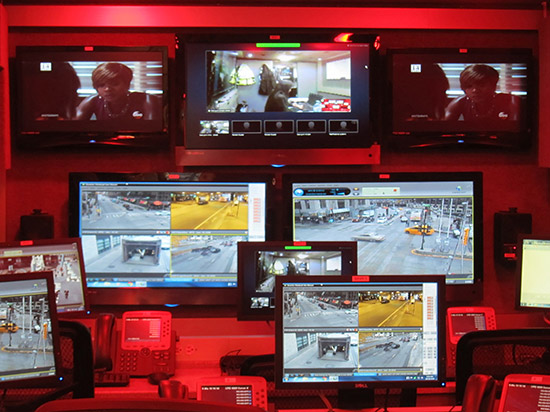

Chicago Police Headquarters
The project of modernization of lighting Chicago Smart Lighting involves the replacement of 270 thousand obsolete lamps to modern LED. According to Mayor Emanuel Ram, this project will simultaneously become the largest lighting upgrade in the country and will decide the main reason why citizens call the city’s non-emergency number. Such coverage will save the city 17.8 million kWh, this electricity will be enough for 1990 homes.

Chicago street after installing smart lighting
Since 2006, the Spanish city of Barcelona has been holding one of the largest exhibitions in the mobile industry - Mobile World Congress. This city is the largest industrial and commercial center of Spain. Its population is over 1.6 million people. Barcelona is the second most populous city in Spain after Madrid and the tenth in the European Union.
The history of Barcelona has more than two thousand years, and there are many episodes in it connected with the cultural development of the city. The volume of this text is not enough for a detailed description, so we start with the second industrial revolution.
Barcelona is one of the first areas of continental Europe in which industrialization began. By the middle of the XIX century, the city with the population became an important center of the textile industry and mechanical engineering.
In 1888 the World Fair took place in Barcelona. It was visited by 2.3 million people. Thanks to the event, many new infrastructure facilities appeared in the city: parks were opened, Columbus Avenue was built, a 4-storey hotel with 2,000 beds was built in the port for 53 days (though it was demolished after the exhibition), and the Palace of Fine Arts built for the exhibition was held until 1942 exhibitions and concerts, at the site of the ruined fortress appeared Citadel Park, which still functions today. The city was held the first street electric lighting. This exhibition is considered successful in the field of economic development of the city.
In 1929, the World Exhibition again takes place in Barcelona, the site occupied 118 hectares, and 20 countries took part in it. The exhibition has become a test platform for new architectural styles.
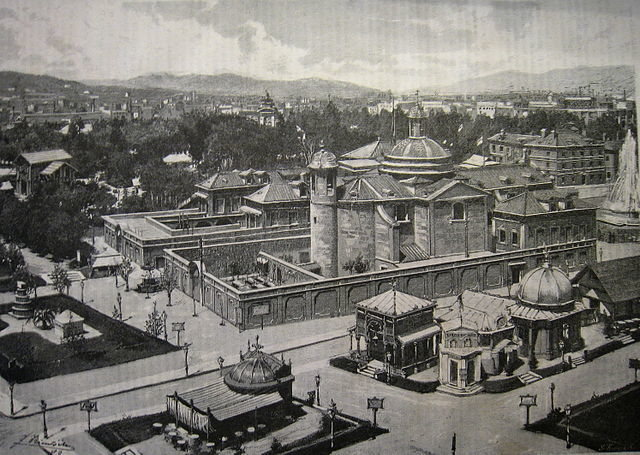

World Exhibition in 1888 in Barcelona
In 1992, Barcelona hosted the 25th Summer Olympic Games , which also influenced the appearance of the city. During preparation, the city got rid of the “rusty belt” , the legacy of the industrial revolution - the old port, the industrial zone and the railway line. The city has equipped beaches with a total area of 18 hectares, built a walking boulevard, buildings to accommodate guests, as well as many entertainment facilities.

Mary Ellen Clark on the background of Barcelona at the 1992 Olympics
Now it is a city with a port on the Mediterranean Sea, 120 km from the border of France, the largest industrial and commercial center of Spain, attracting many tourists. Here are car assembly plants SEAT, Renault, Peugeot, Ford. Redevelopment during the preparation for the Olympic Games helped the city, but it was not enough to build facilities - you need to use them wisely. In addition, you need to work as efficiently as possible with the residents of the city and attract new employers to solve the problem of unemployment.
In 2000, the Barcelona City Council launched Project 22 @ - Innovation District . One of the areas decided to make the center of knowledge. Within ten years, the population of this area grew by 23%. By 2010, 90 thousand people in 7 thousand companies were already working in the innovation district. The authorities engaged in attracting 22 @ companies in several clusters: media, energy, IT-technologies, biomedicine and design. Among the companies that are operating this quarter is Amazon - it has placed a small and medium business service office for companies from Italy and France.

In 2012, the elected mayor, Xavier Trias, decided to concentrate all initiatives in the field of a smart city in one strategy. After that, the city launched several new services. Urban Habitats is responsible for planning the development of Barcelona and resolves issues with resources - energy, water, human resources, and also deals with the environment. The Smart City PMO team is responsible for the projects of the “smart city”.
In 2013, at the level of the authorities, the task was set to make Barcelona the first real “smart city” in the country, which would be as autonomous as possible and have zero emissions. To achieve this, the city must work with the infrastructure, solve economic issues, involve the best talents and communities as much as possible, and take care of the environment. All projects in the field of "smart city" in Barcelona can be divided into cross-cutting and vertical.
It is worth noting that by 2014 the city created 47 thousand new jobs to implement the initiatives of the “smart city”. It saves 42.5 million euros annually on efficient water use and earns 36.5 million euros on smart parking lots.
Cross-cutting projects are projects that affect the entire city. Thanks to them, it develops. One of the important steps was the upgrade of the telecommunications infrastructure. The communication speed in the city was increased, public places were equipped with Wi-Fi, and all sensors were combined on the Urban Platform platform.
As in Chicago, which collects data from utilities and other services on the same site, and all health information on another, in Barcelona data sets are collected in various directions on the Open Data BCN . Here you can learn a lot about the population of the city, about administrative resources, about the territory. For example, you can find out where new bicycle stations open, learn about cleanliness in the city and how and where cars park. This open data can be used to create new services and solutions.
Vertical projects include specific issues. For example, in the city they introduced new “smart” lighting, installed charges for electric transport, work with “smart” parking, and simplified the receipt of public services by the population. Since Barcelona attracts many tourists every year, a special application has been made for them in the city.
The city is helped to formulate current issues and implement initiatives of the Citizens Advisory Council of the Barcelona City Office for Transparency and Best Practices for Using Technologies The organization of Xnet activists as part of this council in 2017 in Barcelona launched an anti-corruption platform based on Tor . With its help, city residents can write anonymous complaints without the risk that the data about them will go somewhere else.
The goal of the DECODE project, which started in 2017 in Barcelona and Amsterdam, is to give people the opportunity to control their own personal data, which they create, use and store in the process of working on the network.
One of the key initiatives in the field of “smart city” is smart lighting . First, the city uses LED lights that need less energy than traditional lamps. Secondly, the lamps are equipped with sensors that measure environmental data - temperature, air pollution, noise, and people. The lamps communicate with the central unit on this street, which is responsible not only for the lighting, but also for other services — for example, Wi-Fi, fiber optics stretched into homes, or the charging station for electric vehicles. All data is transmitted to the central control center, it allows you to track what is happening anywhere in the city.
Lighting varies with the time of day and the presence of people. The city thanks to this approach saves $ 37 million per year .

In order for tourists to feel comfortable in the city, Barcelona launched a number of applications . These are audio guides, travel guides, an app with the best restaurants in the city and the “Official Guide of Barcelona”.
The same approach to citizens. For them, there are Points of Interest apps for identifying places of interest nearby, Map Barcelona + Sustainable, which shows the city’s environmental initiatives, Apparkb for finding legal parking places.
Russia's national projects, including the Digital Economy and Electronic Government , imply the use of modern technologies to ensure the transparency of government activities and the convenient access to services for citizens. Simply put, everything is aimed at improving the quality of life.
Changes in recent years have been noticeable. Ten years ago, in order to receive documents on property inherited, I had to stand in line at the BTI from six in the morning, writing down my name in the notebook of the person who spent the night at this BTI. Now, the solution of such a question will take several times less time. Moreover, most of it is solved online. The same is true, for example, with a tax deduction: you do not need to fill out any papers, just go to your personal account on nalog.ru and send an electronic application.
In the cities in 2007 multifunctional centers began to appear - MFC. Various services are provided on the principle of “one window”. They were renamed “My Documents” in order not to scare off citizens with a complex name. Similar projects for cities are launched “from above”, but there are other ways - when the city itself or individual companies solve problems in this area.
So, for example, “Yandex” works, with the help of which you can find out the duration of a trip on the subway, the condition of traffic jams, or Tutu - these enthusiasts did the impossible by allowing people across Russia to find out the train schedule.
Moscow today is one of the most intelligent cities in the world. 5G networks are already piloting in the city. One of the first industries for this technology will be health care - talking about remote operations and telemedicine. Now the city has prepared the Strategy "Smart City - 2030" . The business community got involved in working with the strategy, specific proposals were collected on various issues.
Prior to this, a number of “open government” initiatives were implemented. Portal "Our City" is designed to send complaints about the posting of ads in the wrong places, uncleared snowdrifts and other urban problems. For a while, officials tried to solve these problems with the help of Photoshop , but after several loud cases, it passed. The portal registered 1.39 million people. During the operation of the portal, he solved 3.2 million problems.
Portal "Active Citizen" is designed to involve citizens in the management of the city - it carries out polls on various topics related to the development and improvement of the city. Now among the polls, for example, there is a question about new services for metro passengers. 2.2 million people registered on the portal, at the moment he held 3.9 thousand votes.
The recording system in the Moscow city clinics Emias.info helped to reduce the queues in clinics. Since 2013, doctors have been registered more than 40 million times. The technology customary for commercial clinics, thus applied to the state. In December 2014, the number of people who could not get to the precinct office today or tomorrow was more than 90 thousand. In 2017, this figure dropped to several thousand people.
The city occupies one of the world's leading positions on Wi-Fi. In 2016, the number of points with free internet access within the Garden Ring reached 300 . Also, access to the network is in the subway and public transport. The Wireless Broadband Alliance Association in 2015 recognized the Wi-Fi project in the Moscow metro as the world's best public network . The Department of Information Technologies is responsible for the development and use of urban information systems and tools of an open government in Moscow.
Nizhny Novgorod should also become one of the “smart cities”. To catalyze this idea, it was decided to use the hackathon format. The city will be the first in Russia to host Global City Hackaton, an initiative of one of the Councils of the World Economic Forum.
First of all, with the help of city experts a list of topical social problems was formulated. Representatives of non-profit and public organizations were divided into groups, compiled a list and set priorities in the field of health problems and well-being of city residents, the economy and society, city infrastructure and ecology, city strategy and interaction with residents.
The second session was aimed at selecting priority technologies for solving this list of tasks. It was attended by experts from technology companies. As it turned out, nothing supernatural to solve problems is needed.
The next stage is the hackathon itself on April 19-21.Participants will receive a list of problems and a list of proposed technologies in order to solve these problems. First of all, developers and IT entrepreneurs are waiting here .
The city needs to be comfortable for residents, competitive, in order to attract and retain people. People become valuable for the city not only by telling the authorities and business about their needs, but also by creating new urban products and services.
Also, the city should attract entrepreneurs and companies that open new jobs. For example, Barcelona, thanks to its policy of attracting innovative business, in 2016 reached a decrease in the number of unemployed in the city to 13.4%, whereas in the whole of Spain at that time the average was over 20%. In the city, the number of entrepreneurs reached 7.54% , which is higher than the European average of 6.9%.
Business is capable of helping city administrations make life more convenient. For example, the EMIAS portal in Moscow is a commercial project, but it aggregated the ability to write to Moscow clinics on one site and through an application. Yandex. Traffic jams make the city "smarter", even if they are not a state project.
In the age of “high technology”, one of the most effective solutions is “smart” lighting. Re-equipment of lampposts with modern lamps, as a rule, shows an instant effect on the city economy. This suggests that technologies for solving problems should not be fantastic - it is important to find new ways to use what is available to any city today.
In the past, I wrote about the “rusty belt” and single-industry towns , as well as successful case studies from urban development institutes . Today we will talk about how technologies help to make cities safe and ensure their sustainable development, about how “smart cities” arise, where ideas for them come from and how projects are implemented. Consider these questions on the example of Chicago and Barcelona, let's talk about the various formats of work with residents - "open government", competitions and hackathons and other initiatives aimed at the development of cities.

A moment of theory: the evolution of cities
Cities account for 80% of gross domestic product due to lower transaction costs. That is, in the cities there are lower costs, which are not related to the production of products, but to the indirect costs associated with this - collecting and searching for information necessary for the activity, concluding transactions, contracts, and so on. The second component of the success of the city is the concentration of high-quality human capital. Therefore, cities are the drivers of the development of the world economy.
')
In the process of development, the city goes through several stages of evolution:
- City 1.0 is an industrial city in which industry is developed, large enterprises are located.
- Cities 2.0 - the city moves to a greater extent to the services sector, the development of small medium-sized businesses.
- City 3.0 is a post-industrial city that is a center for education, technology and knowledge.
In the process of evolution problems may arise. For example, production in the city leads to a deterioration of the environmental situation. Later, during the transition to the services sector and the development of small and medium-sized businesses, there may be a “rusty belt” - unused production areas that hinder the movement around the city and the efficient use of space. But these problems simultaneously open up different opportunities for improving the city.
Chicago - the city of winds
Chicago is today one of the most populated cities in the United States: 2.7 million people live in it, and the agglomeration has more than 9 million inhabitants.
It is worth looking at the history of this city in order to understand how it developed and how it influenced the cities of the whole world.
One of the factors in the development of Chicago is its location. At the site of the future city in 1674, a missionary post was organized for wintering, which by 1833 turned into a village with 350 inhabitants, and after only four years received city status. In 1840, 4,000 people lived here.
The location between the west and east of the country made Chicago become one of the key transportation hubs in the United States. Trade contributed to the railroad and the opening of the Michigan Canal. The city traded grain, meat, in the 1960s it opened an exchange where they traded futures for frozen pork and cattle, and later for agricultural products and world currencies. The city became not only a commercial, but also an industrial center - in the early 1960s metallurgical and woodworking plants appeared here.
The appearance of Chicago was influenced by the tragedy - the Great Chicago fire, which in 1871 claimed the lives of several hundred people and destroyed most of the city - buildings on an area of about 8 square kilometers. The need to rebuild this city and the support of people from all over the country who helped with money, clothes, furniture and food, led to the fact that Chicago became one of the most interesting cities in terms of architecture.
The best architects from around the world were called into the city after a fire. In 1885, the first skyscraper in the world was built in Chicago - the 42-meter-high Home Insurance Building, in which the steel frame was used. The city overtook New York, where a 40-meter-high building already stood, which did not have such a framework and, accordingly, did not belong to skyscrapers. And the city continued to grow "up" and in the next century - 1973 built the Willis Tower, a 108-story skyscraper, which for almost 25 years was the tallest building in the world.

Home Insurance Building
Another event that has become an incentive for development is the World Exhibition of 1893. By that time, more than a million people lived in the city, and the exhibition received 27 million visitors in six months.
This exhibition once again shows how various events can influence the development of cities. The Westinghouse Company, with which Nikola Tesla worked, won the tender for the coverage of the World Fair. The project was another step towards electric street lighting, which today has become commonplace for us, and then it was something completely new, advanced. The exhibition town in Chicago in the number of lanterns was ahead of any other city in America.

Electric lighting at the 1893 World's Fair in Chicago
With what did the city eventually enter the XXI century?
From 2000 to 2010, he lost 7.1% of jobs - this is the worst result among the ten largest cities in the United States. The city budget deficit reached $ 600 million. The budget deficit of urban schools in 2011 was $ 720 million , and half of the students did not complete the training. Crime grew again. And there was no one to fight it - there were 2,000 open vacancies in the city police.
At the same time, the city remained one of the important transport hubs of North America, there are two major airports and a railway hub. And there were 2.7 million inhabitants in it - and people are the main value in the era of digital transformation.
Transformation into a “smart city” began with the Transition Plan , released by Mayor Emanuel Ram, elected in 2011. In 2012, he issued a decree on open data in the city , in which such posts in city authorities as the Chief data officer and Chief information officer, and definitions such as the City of Chicago data portal and Data, were prescribed. According to the decree, DOIT was organized in the city - the Department of Innovation and Technology , which became the central organization for ensuring the implementation of innovations.
The smart city initiative in Chicago was aimed at identifying and solving city problems. At the same time, the use of new technologies and the involvement of residents in these processes are important. The goal was to create a “city-platform”, flexible and changeable ecosystem, allowing to introduce new solutions, launch new projects. And for this the city began to work in three directions.
Infrastructure
XXI century - the time of high-speed Internet. With the help of the Broadband project , the digital infrastructure has been updated. Universities and organizations, parks and public places were equipped with Internet access, increased availability of Internet services in residential areas of the city.
But the Internet will not help if you do not have computer skills. The Sustainable Broadband Adoption program was dedicated to addressing this issue: computer centers in 5 disadvantaged areas allow 11,000 city residents and 500 small businesses to be trained.

One of the digital skills training centers in Chicago
Economic development
“Open data”, around which the Smart city initiative in Chicago was built from the very beginning, is also needed in order to deploy new businesses and applications on the existing platform. It turns out something like a marketplace, but across the city.
In order to provide access to data, several projects were launched in Chicago. The Chicago Hearth Atlas site aggregates data from medical organizations in the city, and surveys and research results to better understand the health status of city residents. For example, here you can find out the race, gender, number of people who have been vaccinated against HPV.
The geolocation platform OpenGrid collects real-time data from urban services. Here you can find out about the companies that are opening up, requests from residents to municipal services - for example, about where graffiti is being painted over or where animal pests are found. This platform allowed to optimize the interaction between services.
What is important is not the data, but how they are used. As part of the Illinois Open Technology Challenge competition , new problem-solving tools were developed. The goal of the program is to involve the authorities, local universities, non-profit organizations and entrepreneurs in the development of the city.
Residents involvement
The prerequisites for this step were laid before the election of Rama. In 2007, a report was presented on the City of NetWorks: Transforming Society and the Economy through Digital Excellence . It contained recommendations for the development of the city. Among them - the search for leaders who can organize a partnership of residents and authorities for the effective implementation of digital opportunities. This idea was embodied in the Smart Chicago Collaborative initiative, now called City Tech .
In order to train residents in the field of digital competence, they launched the projects Digital Skills and Connect Chicago in the city. They coordinate educational processes and provide a network of computer-equipped places where residents can access the Internet and computer and receive free training.
Technologies of the city
None of the technologies that are used in Chicago is decisive. And while many of them could be implemented separately from others. But the main value of the "city-platform" is the ability to quickly implement them. Therefore, the City Tech initiative declared the city a “cradle” for new solutions and is now ready to help other cities in development.
Chicago was the first city in which they launched Array of Things (“an array of things”). The project is called the "fitness tracker" for the city. Devices mounted on lampposts collect information on air cleanliness, climate, traffic — automobile, bicycle and pedestrian, atmospheric pressure, sounds. The project was developed jointly by the University of Chicago, the Argonne National Laboratory and city authorities - all in order to better understand, maintain and improve Chicago.
This is an interesting example of cooperation between universities, city and business: the communication partner of the project is AT & T, technological support is provided by Cisco, Microsoft, Schneider Electric, Intel, Motorola Solutions and Zebra Technologies. Also part of the project was to attract residents of the city - a number of local events were held in which citizens talked about their problems, and teachers taught the Internet of things to share this experience with schoolchildren.

The city uses predictive analytics for pest control. The system predicts where trash cans will be filled. According to the city authorities, the effectiveness of the fight against rats has increased by 20%. Sensors installed on the bridges inform the services of freezing. Sensors also detect the pollution of Lake Michigan.
To save the citizens from parking problems, they launched ParqEx project in the city. Property owners - both shopping centers or offices, and private homes - add the available parking spaces to the service, and car owners book them. It turns out something like Airbnb for cars.
To ensure safety, cameras are placed all over the city that find crowds of people. In the command center for live broadcasts from the cameras, it is determined whether the police officers should be sent to the scene.

Chicago Police Headquarters
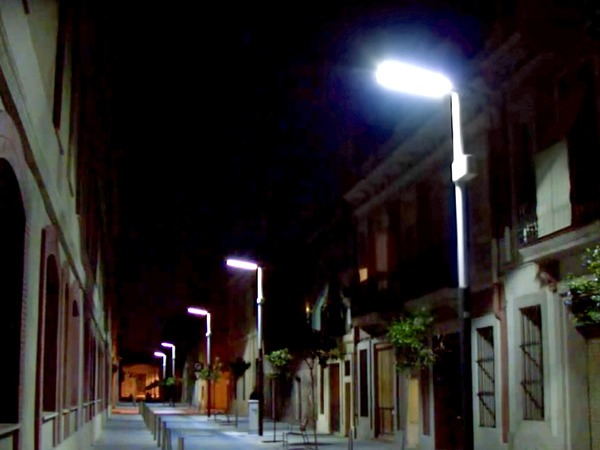
The project of modernization of lighting Chicago Smart Lighting involves the replacement of 270 thousand obsolete lamps to modern LED. According to Mayor Emanuel Ram, this project will simultaneously become the largest lighting upgrade in the country and will decide the main reason why citizens call the city’s non-emergency number. Such coverage will save the city 17.8 million kWh, this electricity will be enough for 1990 homes.

Chicago street after installing smart lighting
Barcelona
Since 2006, the Spanish city of Barcelona has been holding one of the largest exhibitions in the mobile industry - Mobile World Congress. This city is the largest industrial and commercial center of Spain. Its population is over 1.6 million people. Barcelona is the second most populous city in Spain after Madrid and the tenth in the European Union.
The history of Barcelona has more than two thousand years, and there are many episodes in it connected with the cultural development of the city. The volume of this text is not enough for a detailed description, so we start with the second industrial revolution.
Barcelona is one of the first areas of continental Europe in which industrialization began. By the middle of the XIX century, the city with the population became an important center of the textile industry and mechanical engineering.
In 1888 the World Fair took place in Barcelona. It was visited by 2.3 million people. Thanks to the event, many new infrastructure facilities appeared in the city: parks were opened, Columbus Avenue was built, a 4-storey hotel with 2,000 beds was built in the port for 53 days (though it was demolished after the exhibition), and the Palace of Fine Arts built for the exhibition was held until 1942 exhibitions and concerts, at the site of the ruined fortress appeared Citadel Park, which still functions today. The city was held the first street electric lighting. This exhibition is considered successful in the field of economic development of the city.
In 1929, the World Exhibition again takes place in Barcelona, the site occupied 118 hectares, and 20 countries took part in it. The exhibition has become a test platform for new architectural styles.

World Exhibition in 1888 in Barcelona
In 1992, Barcelona hosted the 25th Summer Olympic Games , which also influenced the appearance of the city. During preparation, the city got rid of the “rusty belt” , the legacy of the industrial revolution - the old port, the industrial zone and the railway line. The city has equipped beaches with a total area of 18 hectares, built a walking boulevard, buildings to accommodate guests, as well as many entertainment facilities.

Mary Ellen Clark on the background of Barcelona at the 1992 Olympics
The baggage of the past in the XXI century
Now it is a city with a port on the Mediterranean Sea, 120 km from the border of France, the largest industrial and commercial center of Spain, attracting many tourists. Here are car assembly plants SEAT, Renault, Peugeot, Ford. Redevelopment during the preparation for the Olympic Games helped the city, but it was not enough to build facilities - you need to use them wisely. In addition, you need to work as efficiently as possible with the residents of the city and attract new employers to solve the problem of unemployment.
In 2000, the Barcelona City Council launched Project 22 @ - Innovation District . One of the areas decided to make the center of knowledge. Within ten years, the population of this area grew by 23%. By 2010, 90 thousand people in 7 thousand companies were already working in the innovation district. The authorities engaged in attracting 22 @ companies in several clusters: media, energy, IT-technologies, biomedicine and design. Among the companies that are operating this quarter is Amazon - it has placed a small and medium business service office for companies from Italy and France.

In 2012, the elected mayor, Xavier Trias, decided to concentrate all initiatives in the field of a smart city in one strategy. After that, the city launched several new services. Urban Habitats is responsible for planning the development of Barcelona and resolves issues with resources - energy, water, human resources, and also deals with the environment. The Smart City PMO team is responsible for the projects of the “smart city”.
In 2013, at the level of the authorities, the task was set to make Barcelona the first real “smart city” in the country, which would be as autonomous as possible and have zero emissions. To achieve this, the city must work with the infrastructure, solve economic issues, involve the best talents and communities as much as possible, and take care of the environment. All projects in the field of "smart city" in Barcelona can be divided into cross-cutting and vertical.
It is worth noting that by 2014 the city created 47 thousand new jobs to implement the initiatives of the “smart city”. It saves 42.5 million euros annually on efficient water use and earns 36.5 million euros on smart parking lots.
Cross-cutting projects
Cross-cutting projects are projects that affect the entire city. Thanks to them, it develops. One of the important steps was the upgrade of the telecommunications infrastructure. The communication speed in the city was increased, public places were equipped with Wi-Fi, and all sensors were combined on the Urban Platform platform.
As in Chicago, which collects data from utilities and other services on the same site, and all health information on another, in Barcelona data sets are collected in various directions on the Open Data BCN . Here you can learn a lot about the population of the city, about administrative resources, about the territory. For example, you can find out where new bicycle stations open, learn about cleanliness in the city and how and where cars park. This open data can be used to create new services and solutions.
Vertical Designs
Vertical projects include specific issues. For example, in the city they introduced new “smart” lighting, installed charges for electric transport, work with “smart” parking, and simplified the receipt of public services by the population. Since Barcelona attracts many tourists every year, a special application has been made for them in the city.
Technology "smart" Barcelona
The city is helped to formulate current issues and implement initiatives of the Citizens Advisory Council of the Barcelona City Office for Transparency and Best Practices for Using Technologies The organization of Xnet activists as part of this council in 2017 in Barcelona launched an anti-corruption platform based on Tor . With its help, city residents can write anonymous complaints without the risk that the data about them will go somewhere else.
The goal of the DECODE project, which started in 2017 in Barcelona and Amsterdam, is to give people the opportunity to control their own personal data, which they create, use and store in the process of working on the network.
One of the key initiatives in the field of “smart city” is smart lighting . First, the city uses LED lights that need less energy than traditional lamps. Secondly, the lamps are equipped with sensors that measure environmental data - temperature, air pollution, noise, and people. The lamps communicate with the central unit on this street, which is responsible not only for the lighting, but also for other services — for example, Wi-Fi, fiber optics stretched into homes, or the charging station for electric vehicles. All data is transmitted to the central control center, it allows you to track what is happening anywhere in the city.
Lighting varies with the time of day and the presence of people. The city thanks to this approach saves $ 37 million per year .

In order for tourists to feel comfortable in the city, Barcelona launched a number of applications . These are audio guides, travel guides, an app with the best restaurants in the city and the “Official Guide of Barcelona”.
The same approach to citizens. For them, there are Points of Interest apps for identifying places of interest nearby, Map Barcelona + Sustainable, which shows the city’s environmental initiatives, Apparkb for finding legal parking places.


Smart cities in Russia
Russia's national projects, including the Digital Economy and Electronic Government , imply the use of modern technologies to ensure the transparency of government activities and the convenient access to services for citizens. Simply put, everything is aimed at improving the quality of life.
Changes in recent years have been noticeable. Ten years ago, in order to receive documents on property inherited, I had to stand in line at the BTI from six in the morning, writing down my name in the notebook of the person who spent the night at this BTI. Now, the solution of such a question will take several times less time. Moreover, most of it is solved online. The same is true, for example, with a tax deduction: you do not need to fill out any papers, just go to your personal account on nalog.ru and send an electronic application.
In the cities in 2007 multifunctional centers began to appear - MFC. Various services are provided on the principle of “one window”. They were renamed “My Documents” in order not to scare off citizens with a complex name. Similar projects for cities are launched “from above”, but there are other ways - when the city itself or individual companies solve problems in this area.
So, for example, “Yandex” works, with the help of which you can find out the duration of a trip on the subway, the condition of traffic jams, or Tutu - these enthusiasts did the impossible by allowing people across Russia to find out the train schedule.
Moscow
Moscow today is one of the most intelligent cities in the world. 5G networks are already piloting in the city. One of the first industries for this technology will be health care - talking about remote operations and telemedicine. Now the city has prepared the Strategy "Smart City - 2030" . The business community got involved in working with the strategy, specific proposals were collected on various issues.
Prior to this, a number of “open government” initiatives were implemented. Portal "Our City" is designed to send complaints about the posting of ads in the wrong places, uncleared snowdrifts and other urban problems. For a while, officials tried to solve these problems with the help of Photoshop , but after several loud cases, it passed. The portal registered 1.39 million people. During the operation of the portal, he solved 3.2 million problems.
Portal "Active Citizen" is designed to involve citizens in the management of the city - it carries out polls on various topics related to the development and improvement of the city. Now among the polls, for example, there is a question about new services for metro passengers. 2.2 million people registered on the portal, at the moment he held 3.9 thousand votes.
The recording system in the Moscow city clinics Emias.info helped to reduce the queues in clinics. Since 2013, doctors have been registered more than 40 million times. The technology customary for commercial clinics, thus applied to the state. In December 2014, the number of people who could not get to the precinct office today or tomorrow was more than 90 thousand. In 2017, this figure dropped to several thousand people.
The city occupies one of the world's leading positions on Wi-Fi. In 2016, the number of points with free internet access within the Garden Ring reached 300 . Also, access to the network is in the subway and public transport. The Wireless Broadband Alliance Association in 2015 recognized the Wi-Fi project in the Moscow metro as the world's best public network . The Department of Information Technologies is responsible for the development and use of urban information systems and tools of an open government in Moscow.
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod should also become one of the “smart cities”. To catalyze this idea, it was decided to use the hackathon format. The city will be the first in Russia to host Global City Hackaton, an initiative of one of the Councils of the World Economic Forum.
First of all, with the help of city experts a list of topical social problems was formulated. Representatives of non-profit and public organizations were divided into groups, compiled a list and set priorities in the field of health problems and well-being of city residents, the economy and society, city infrastructure and ecology, city strategy and interaction with residents.
The second session was aimed at selecting priority technologies for solving this list of tasks. It was attended by experts from technology companies. As it turned out, nothing supernatural to solve problems is needed.
The next stage is the hackathon itself on April 19-21.Participants will receive a list of problems and a list of proposed technologies in order to solve these problems. First of all, developers and IT entrepreneurs are waiting here .
Do we need "smart cities"?
The city needs to be comfortable for residents, competitive, in order to attract and retain people. People become valuable for the city not only by telling the authorities and business about their needs, but also by creating new urban products and services.
Also, the city should attract entrepreneurs and companies that open new jobs. For example, Barcelona, thanks to its policy of attracting innovative business, in 2016 reached a decrease in the number of unemployed in the city to 13.4%, whereas in the whole of Spain at that time the average was over 20%. In the city, the number of entrepreneurs reached 7.54% , which is higher than the European average of 6.9%.
Business is capable of helping city administrations make life more convenient. For example, the EMIAS portal in Moscow is a commercial project, but it aggregated the ability to write to Moscow clinics on one site and through an application. Yandex. Traffic jams make the city "smarter", even if they are not a state project.
In the age of “high technology”, one of the most effective solutions is “smart” lighting. Re-equipment of lampposts with modern lamps, as a rule, shows an instant effect on the city economy. This suggests that technologies for solving problems should not be fantastic - it is important to find new ways to use what is available to any city today.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447724/
All Articles