MS SQL backup: a couple of useful Commvault functions that not everyone knows about

Today I’ll tell you about two Commvault possibilities for MS SQL backup, which are unfairly avoided: granular recovery and the Commvault plugin for SQL Management Studio. The basic moments of the settings will not be considered. The post is more likely for those who already know how to install an agent, set up a schedule, policies, etc. On how Commvault works and what it can do, I told in this post .
Granular restoration
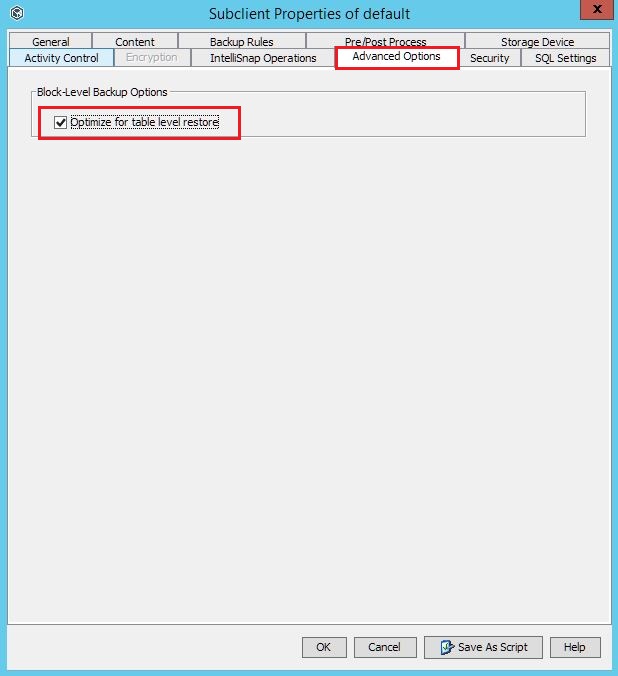
The table level restore option has appeared in the Subclient properties relatively recently. It allows you to enable the ability to restore tables from the database, while not restoring the entire database from the backup. This is useful when you know exactly where the error or data loss is. At the same time, the base itself is large and it will take a lot of time to restore it.
')
This option has limitations:
- Tables cannot be restored to the original database, only to another.
- All tables are restored to the dbo schema. The table cannot be restored to the user schema.
- Only local SQL Server account with system administrator rights is supported.
- The target server to restore the table should work on Windows.
- On the target server, in addition to the SQL Agent, the Media Agent and Java Runtime Environment must be installed.
- The database must use the Recovery model in Full mode.
- If the granular database recovery option is enabled, the ability to run differential backup jobs is lost.
The table-level-restore option is disabled.

The table-level-restore option is disabled.
In my practice there was a case when the client for the SQL server was configured with the following schedule: one full backup once a week and 6 differential backups on weekdays. He enabled the table-level-restore function, and the tasks for the differential backup were performed with an error.
Let's see what the recovery will look like.
1. We start recovery on the necessary agent.
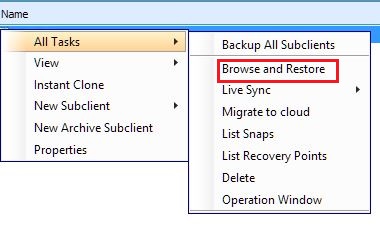
2. In the window that appears, go to the Advanced Options tab. Select SQL Granular Browse - View Content.
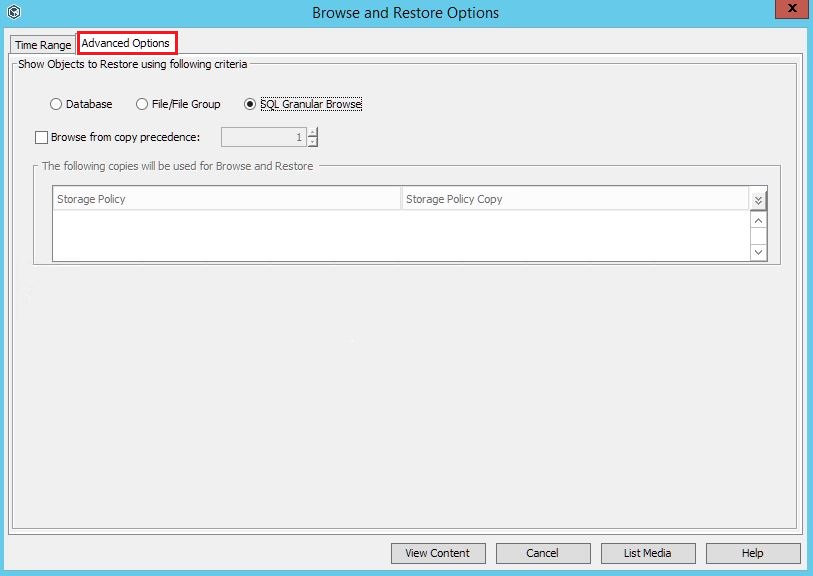
3. In the list that opens, select the database from which we will restore the table, and click Restore Granular .
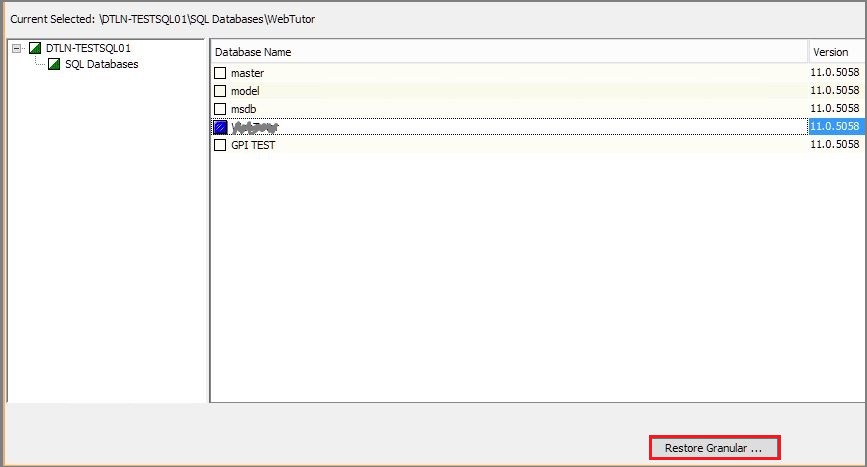
4. In the dialog box, set up a database mount point from backup files (something like Instant Recovery technology).
Specify:
- name for the temporary database;
- how long to keep this recovery point in days;
- server where we will mount the database. Only servers that fulfill all the necessary conditions mentioned above will be available in the list: with the Windows operating system, the installed Media Agent and the Java Runtime Environment, etc.
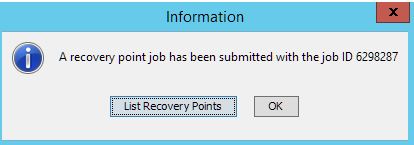
Click OK.

5. In the new window, click on List Recovery Points.
6. A list of mounted recovery points will open. If the database is large, you will have to wait. Then click Browse . A window will appear to view the tables from the selected database.
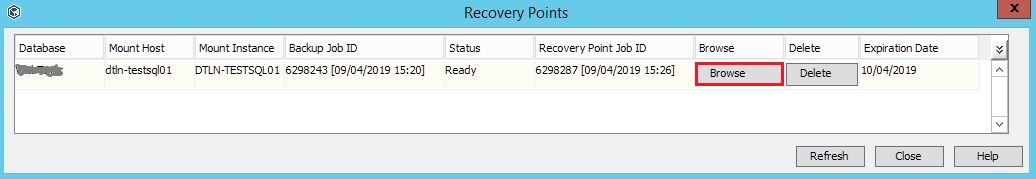
While the list is being formed, often the Recovery Points dialog box is closed, and then they cannot return there again. It's simple: right-click on the instance of the SQL server where the restore point mount process was started. Go to All Tasks and select List Recovery Points.

7. If there are many tables, it will take some time to display them. For example, for a 40 GB database, the list is formed in about ten minutes. Select the desired table, click Recover All Selected.
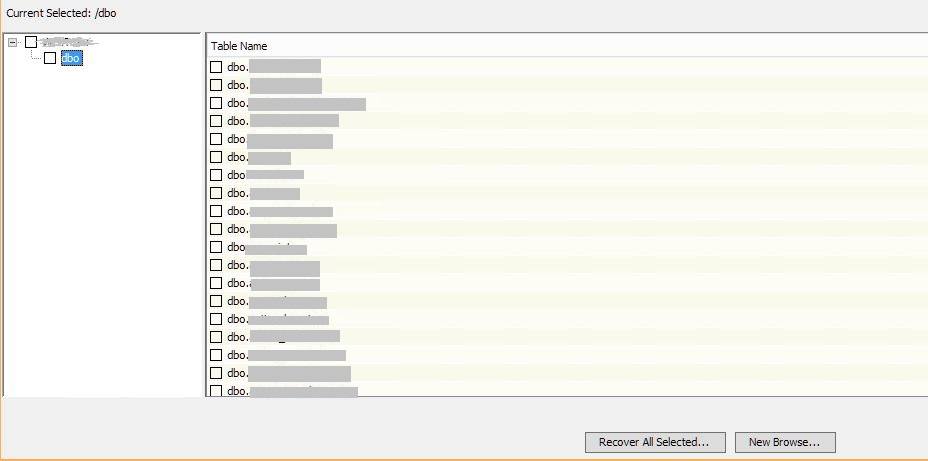
8. In the new window, select the database where we will restore the table (s). In our case, this is the base GPI TEST.
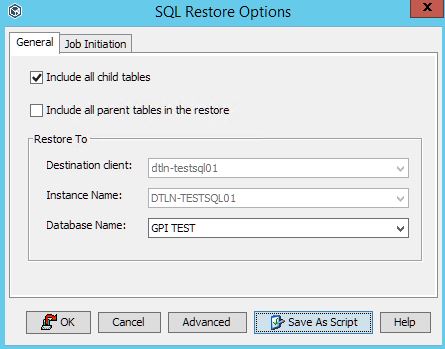
9. After the recovery is completed, the selected tables will appear in the GPI TEST database.
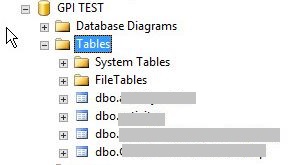
After the table is restored to a temporary database, it can be transferred to the original database using Management Studio.
Commvault Plug-in for SQL Management Studio
Database administrators do not always have access to the backup system (RMS). Sometimes you need to do something urgently, but the administrator of the RMS is not in place. Using the Commvault plugin for SQL Management Studio, the DBA will be able to perform basic backup and restore operations.
| QL Management Studio Version | Command |
| SQL 2008 R2 | CvSQLAddInConfig.exe / i 10 / r |
| SQL 2012 | CvSQLAddInConfig.exe / i 11 / r |
| SQL 2014 | CvSQLAddInConfig.exe / i 12 / r |
| SQL 2016 | CvSQLAddInConfig.exe / i 13 / r |
| SQL 2017 | CvSQLAddInConfig.exe / i 14 / r |
Versions of SQL servers that support Commvault Plug-in and commands that activate the plug-in. The plugin is supported only on the 64-bit version of Windows.
1. Execute the command that corresponds to our version of SQL server:

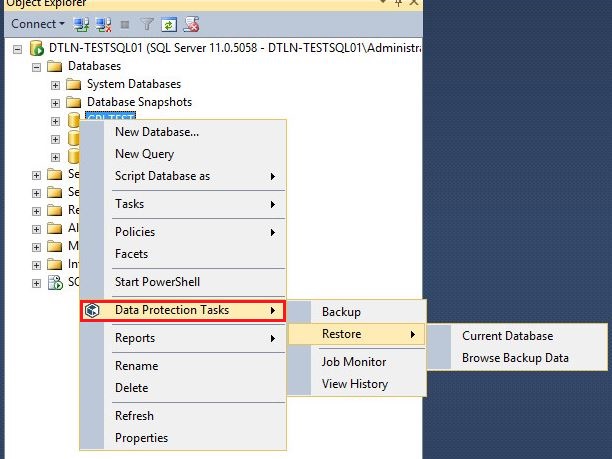
2. Now backup and restore options are available in Management Studio. To do this, right-click on the desired database.
Thus, the administrator has the opportunity to directly interact with the backup copies of this database without the Commvault console and calls to the administrator of the RMS.
3. When starting any of the available functions of this menu, a window will appear asking for the login and password. To connect to CommServe, use SSO or any other account from the Security section of Commserve (Commcell login).

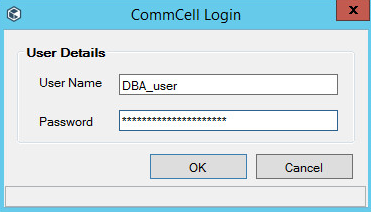
4. If the credentials have been entered correctly and access rights are sufficient, the DBA may:
- run an extraordinary backup (Backup);
- restore the database from the backup (Restore);
- view the history of completed tasks (View History) and the progress of tasks in the process of execution (Job monitor).
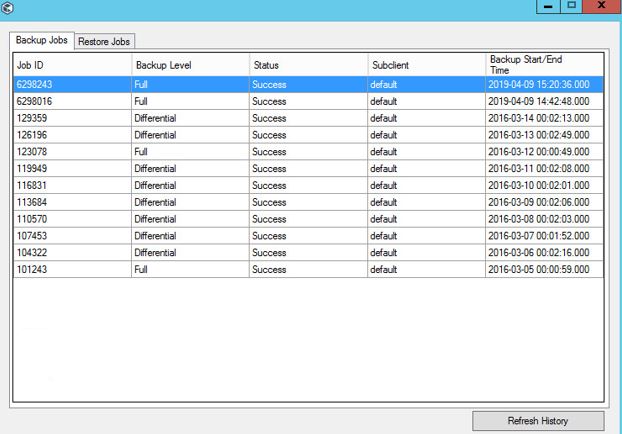
This is how the history of completed backup tasks for the selected database looks in Management Studio.
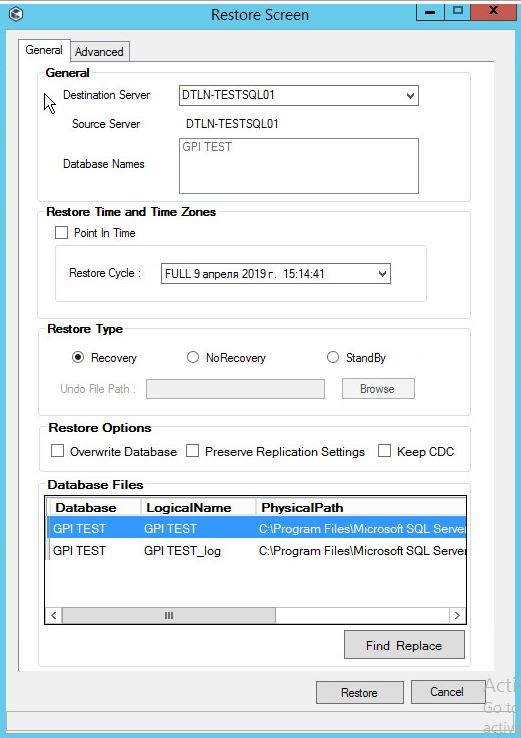
Menu to restore the database. It does not even differ from the console menu.
That's all about these two features of the SQL Agent from Commvault. I will add that backing up with Commvault means will be more suitable for those who have dozens of servers serviced, with several instances and databases, all this is possible at different sites and requires setting different schedules, depths, etc. If you have a couple of servers, then there is enough backup and regular MS SQL tools.
A source
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447666/
All Articles