And who did this? We automate the audit of information security

A source
It is believed that there are three approaches to the diagnosis of information security: auditing, vulnerability assessment and penetration tests. Let's talk about auditing and vulnerability assessment. Under the cat, we consider the issues that need to be addressed as part of the audit, and a set of tools from Quest Software to identify, prevent and investigate information security incidents based on machine learning (Change Auditor Threat Detection), collect logs from infrastructure objects (InTrust), audit configuration (Enterprise Reporter) and the output of audit data on all listed systems in one interface (IT Security Search).
An IT security audit determines whether the information system and its support are in line with customer expectations and company standards. From our point of view, the audit system should have the following capabilities:
- identify and detect normal and atypical activity;
- construct queries and filter data in an array of events to get the necessary information;
- escalate events to a group of responsible;
- have preconfigured reports that can be used to detect atypical activity.
The peculiarity of working with infosers, which we often see, is the performance of an audit on the residual basis. That is, the change audit is performed by the department, which is also loaded with other tasks. This implies the first problem -
')
Using embedded audit tools
There is not enough time to search and configure others. By built-in tools we mean, for example, a Windows snap-in or special Power Shell scripts. Of course, with the help of such means, an incident can only be known after the fact.
As the organization grows, the number of users and changes grows. There are studies with specific figures on this topic, but even without this, it is clear that digital exchange changes in a big way every year. The second audit problem is
Increased number of changes due to infrastructure growth
Growth may be associated with an increase in staff or the number of customers, but regardless of this, the amount of the number of changes will increase proportionally.
Audit is seriously influenced not only by internal factors (these are the first two problems), but also external - by the requirements of state bodies or corporate policies. And we come to the third audit issue -
Lack of suitable tools to meet the requirements
In the absence of suitable tools, system administrators either do not control the required changes, or do it, but with improvised means (see problem 1).
And now we turn to a review of tools that can help with the answer to the question: “And who did this?” (In fact, they will help with the answer to a bunch of other questions).
Operational audit of information security events
When we come to some companies for installation meetings, we see Power Shell based audit systems. Scripts are usually supported by a single Windows administrator. This is not a serious problem until the employee is dismissed. After his departure, the question arises: who will continue to support and develop this. A new administrator (if he has sufficient competence) usually writes such scripts again. And these are not isolated cases.
Change Auditor is a tool for operational audit of changes in the Microsoft environment and on disk arrays, which does not require the knowledge of a single person.
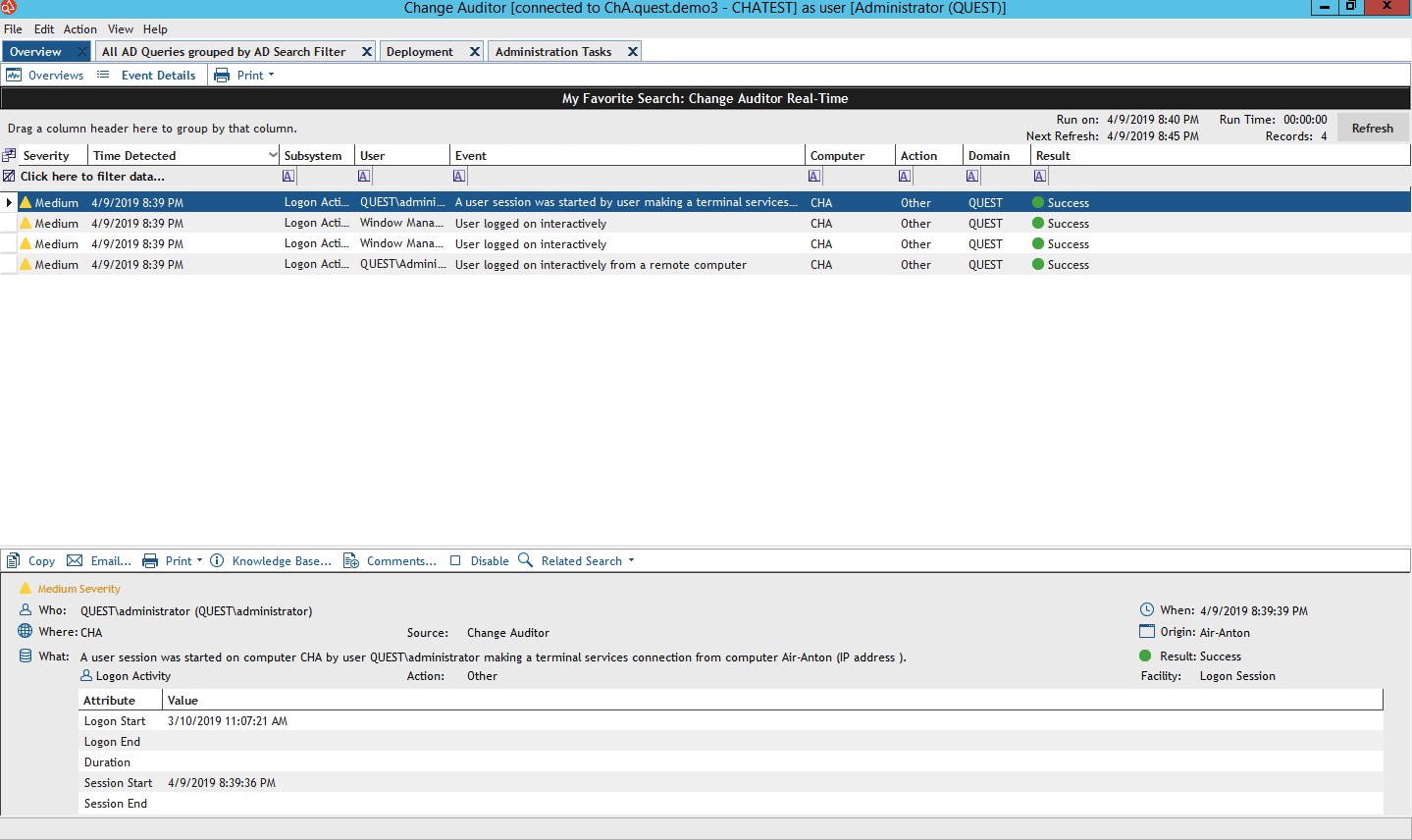
Auditing is supported: AD, Azure AD, SQL Server, Exchange, Exchange Online, Sharepoint, Sharepoint Online, Windows File Server, OneDrive for Business, Skype for Business, VMware, NetApp, EMC, FluidFS. Suitable for hybrid environments. There are predefined reports for compliance with the standards of GDPR, SOX, PCI, HIPAA, FISMA, GLBA.
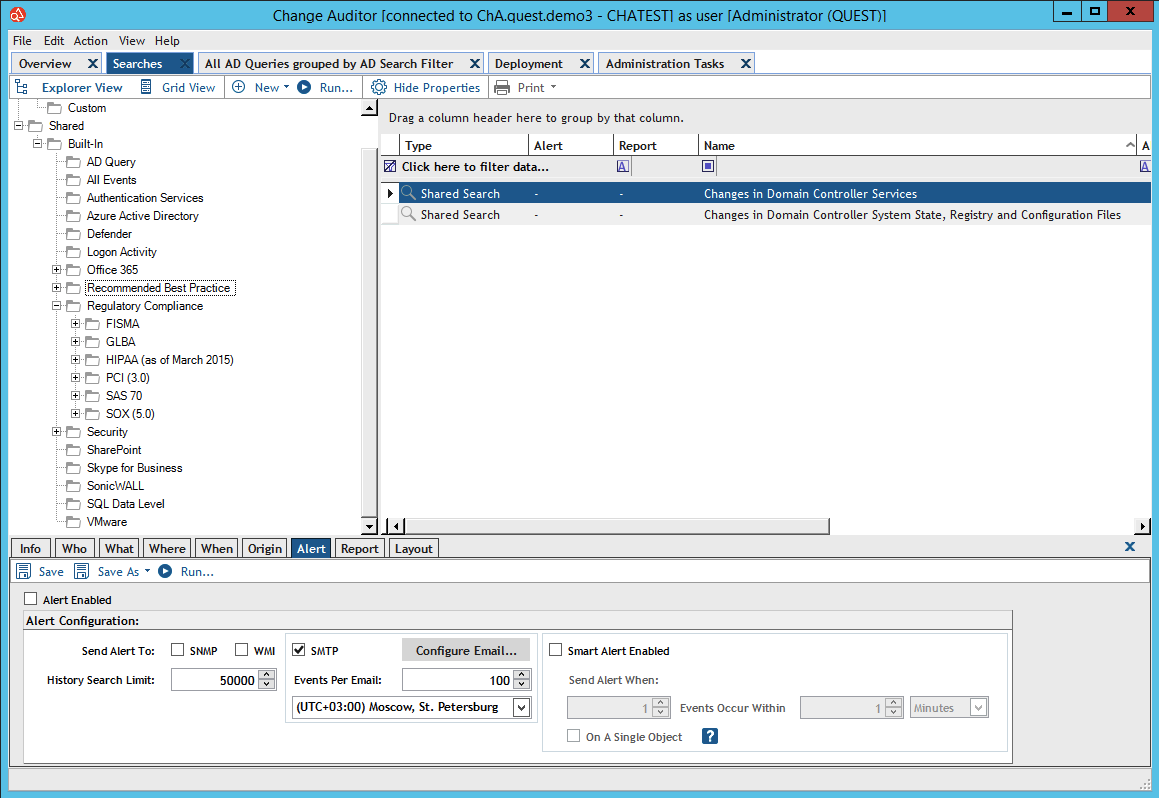
In addition to auditing, you can block changes in Change Auditor. For example, prohibit adding new users to the AD group or prohibiting a file / folder change.
Change Auditor has an additional analytics module - Threat Detection.
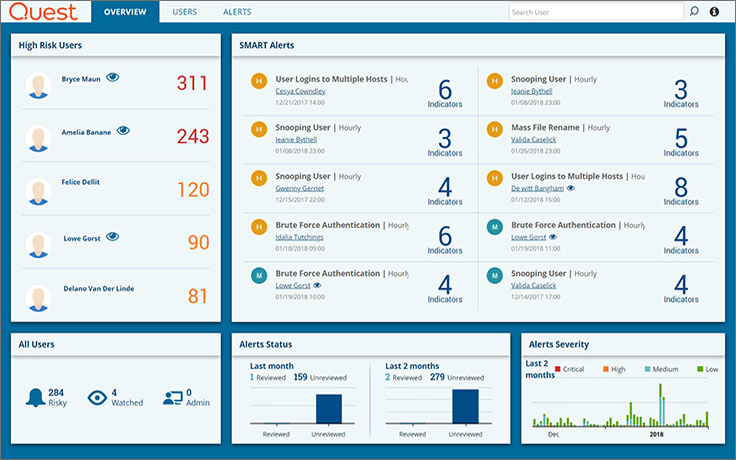
Works on the basis of machine learning (ML) and user behavior analysis (UEBA). At the entrance, it receives events from Change Auditor over the past 30 days and identifies atypical user behavior: entering from an unusual place or at an unusual time, unsuccessful password entry several times in a row on a domain controller, entering a forbidden file share, etc. The module analyzes events in several dimensions and reports anomalies.
Infrastructure Configuration Audit
For those who have long wanted to bring order to their Windows-infrastructure, but still can not reach the hands. Enterprise Reporter, a reporting tool, extracts data on objects from AD, Azure AD, SQL Server, Exchange Online, Windows Online Server, OneDrive for Business and Azure resources (virtual machines, network security groups and other objects) and builds beautiful reports.
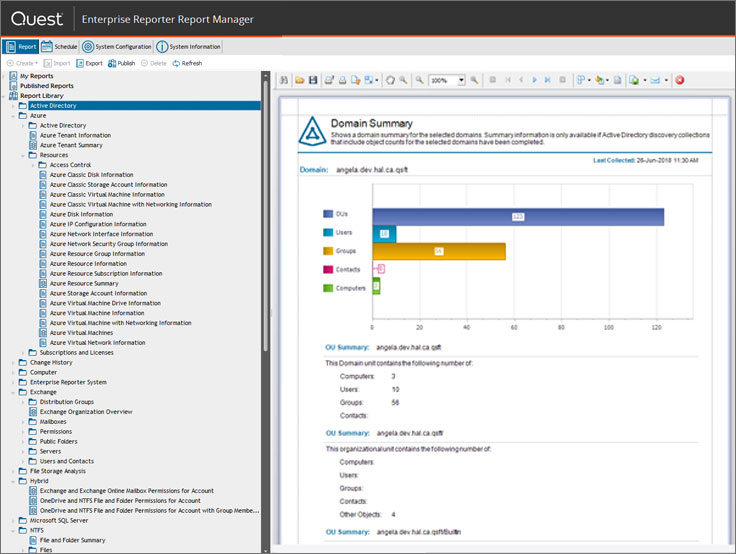
The main value of the product is an existing set of reports, which allows you to see the vulnerabilities immediately after installation. For example, at one of our customers, we found users in groups of domain administrators with the password expiration option disabled.
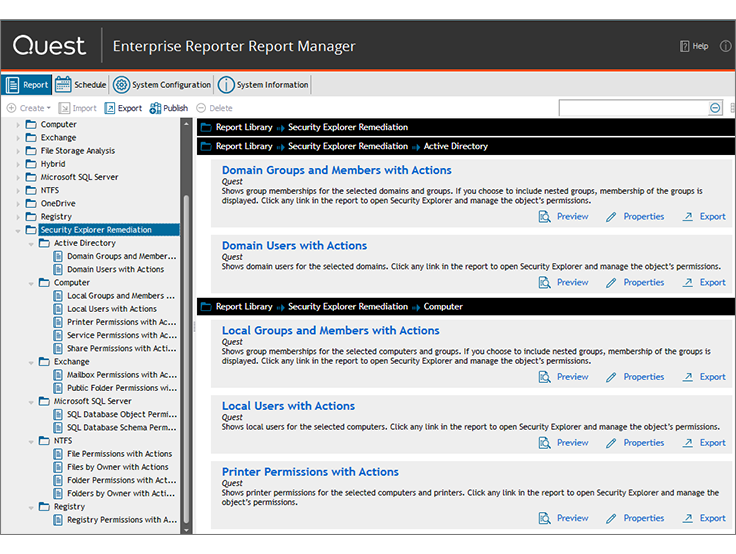
From the already prepared reports:
- users who have not logged in the past 30 days;
- expired users;
- privileged group users who have not logged in the past 30 days;
- Windows services that do not work under the local system account;
- Software installed on servers with the role of a domain controller;
- hotfixes installed on servers;
- security settings on servers;
- nested groups and users in nested groups
- Active Directory permissions;
- permissions for folders on file storage and others.
Examples of the listed reports can be viewed on the Quest website in a PDF report (the file opens immediately, registration is not needed). There are predefined reports for compliance with the standards of GDPR, SOX, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, FISMA, GLBA and others. And if in your company there are requirements for reports or you want to brand a document - there is a special designer.
Logging and analysis
Another source of information on information security events is logs. You can find in them, if not all, then almost everything. After collecting them, it would be good to normalize and structure them in order to carry out a correlation between events, for example, in AD and some text logs.
InTrust is a tool for collecting and analyzing logs from disparate sources. It can take Windows logs, text logs and syslog from network devices. After collecting all the statistics (events) is reduced to the state of the form: when it happened, what happened, where it happened, who performed the action, from where this action was performed.
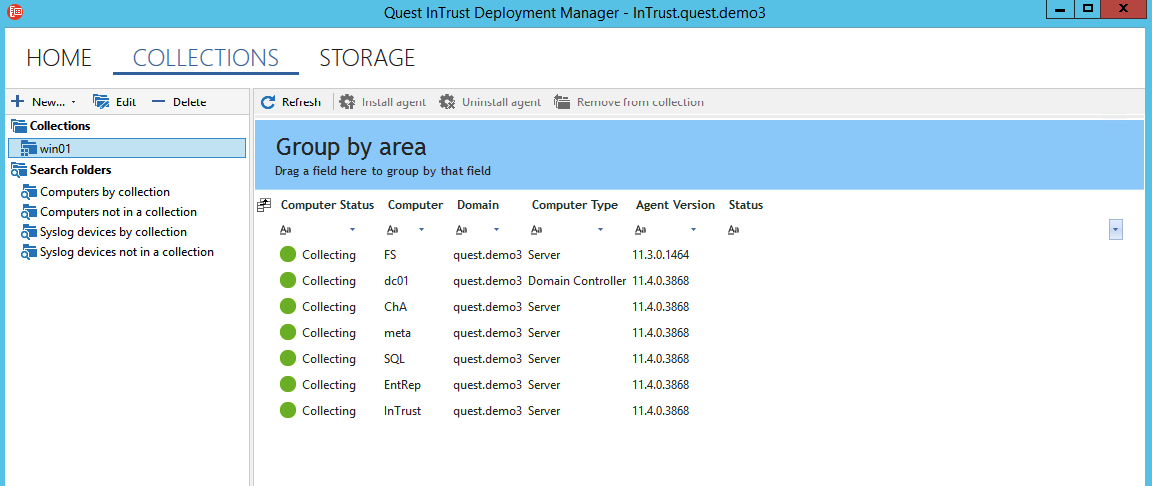
InTrust can handle up to 60,000 events per second from 10,000 sources. Often, collection agents are installed on workstations to track Windows eventlog Sysmon events (tracking changes in registry values, creating new processes with incorrect hashes, and others), PowerShell logs.
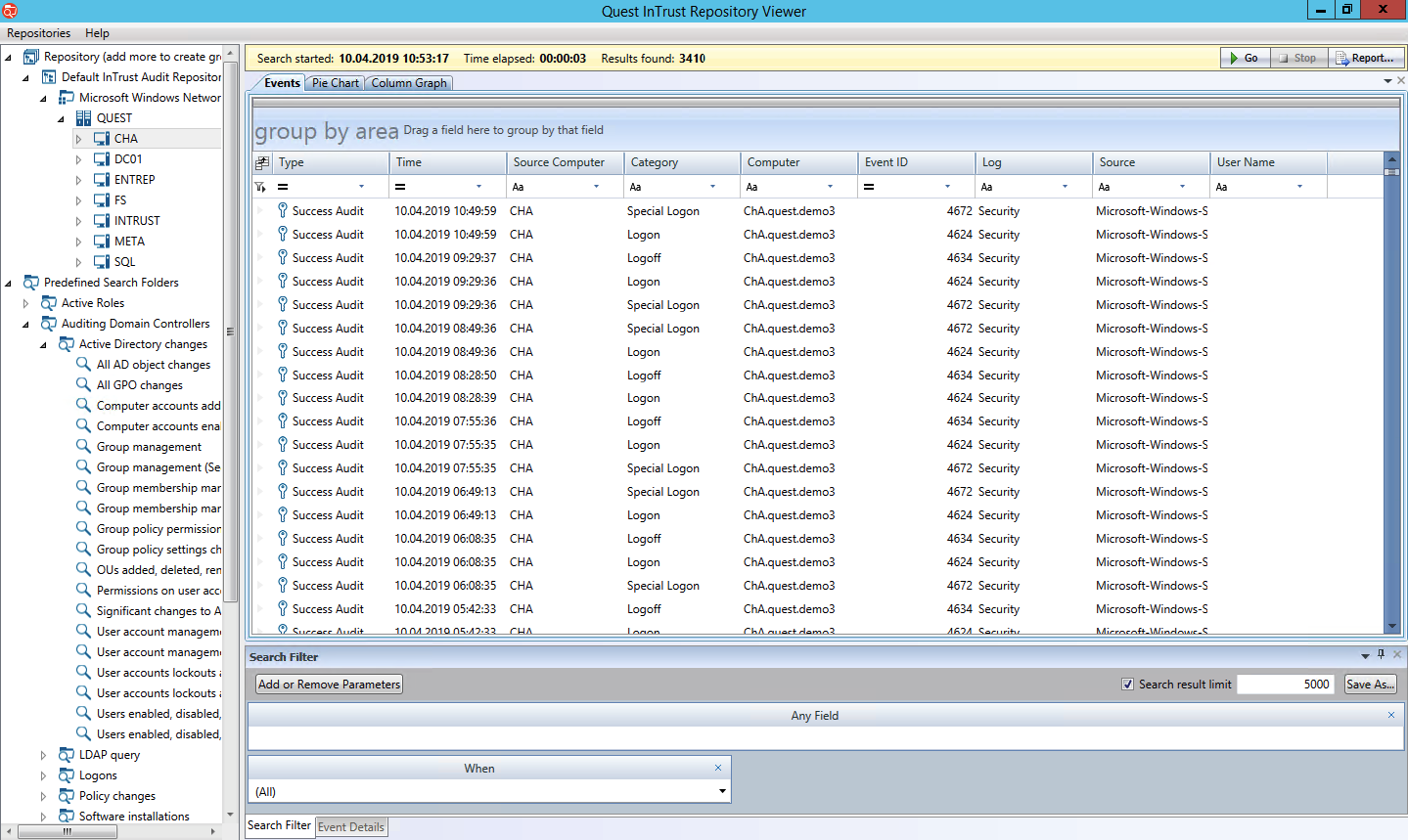
Raw data is stored in built-in storage with a compression ratio of 20: 1. There are ready-made integrations with some SIEM systems. If you use them, InTrust is a convenient way to save on licenses, since stores raw data in its storage and sends only events to SIEM.
Pool under the umbrella
To make the security concept look complete, it is advisable to combine data from all sources and observe what is happening in one window. Additionally, correlate events for lightning-fast root cause detection.
IT Security Search is a tool for global full-text search a'lya Google according to operational audit data, audit of infrastructure configuration and data from logs. All data is retrieved in real time from related systems.

You can enter a username, workstation, event type, or anything else and discover related events or configurations. When making queries, you can use logical expressions. From the results of the request, it is convenient to build reports and send them to interested parties on a schedule.
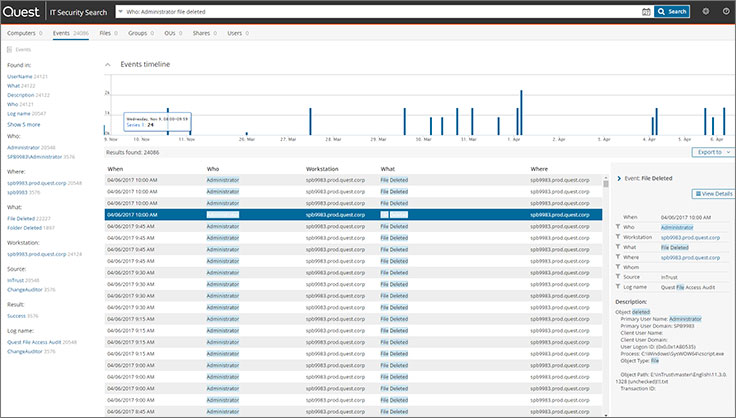
You can also roll back from changes in AD from the IT Security Search interface. That is, for example, you can restore a user deleted by mistake, with all its attributes. This is implemented through integration with another Quest product - Recovery Manager for Active Directory.
The main goal of the article is to introduce the Quest product family to audit changes. Those tools that you use now may have a different set of functions (somewhere more, somewhere less). Write in the comments what you have to deal with, what functions have proven to be useful for you and why you chose this or that solution. It is interesting to share experiences.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447512/
All Articles